19 February 2026

Insights from theoretical physics are helping scientists understand how living cells process information and use it to self-organise.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
18 February 2026

Lithuanian scientist began his three-year term chairing EMBL’s Council.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
12 February 2026

EMBL-EBI’s new Head of Infrastructure Services brings experience from the London 2012 Olympics and Paralympics and more to support the institute’s growing data needs.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2026
people-perspectivesperspectives
11 February 2026

Medaka fish help an international team of scientists study how genes and environment interact.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2026
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation
9 February 2026

In the largest study of its kind, EMBL scientists reveal that certain microbes can thrive across different ecosystems, contributing to the global spread of antimicrobial resistance.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
9 February 2026

The Nordic EMBL Partnership for Molecular Medicine has appointed Janna Saarela as its new Speaker. Saarela is the Director of the Norwegian Centre for Molecular Biosciences and Medicine (NCMBM) and succeeds Oliver Billker from the Laboratory for Molecular Infection Medicine Sweden (MIMS) in this…
CONNECTIONS
5 February 2026

Researchers at EMBL Barcelona have developed an open-source tool that makes working with complicated volumetric imaging data easier.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2 February 2026

Predoctoral Fellow Leonie Johanna Lorenz combines genomics with equations to predict how bacteria evolve and adapt to vaccines.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2026
people-perspectivesperspectives
29 January 2026
Possibly the least researched microorganism domain, archaea seem to survive anywhere. Yet it is extraordinarily challenging to study and unlock their secrets of adaptability. EMBL researchers hope to change that.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
28 January 2026

The new EMBL Grenoble group leader will explore the origin of eukaryotes and their complex cellular organisation by studying Asgard archaea and other non-model microorganisms.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
26 January 2026

LIGAND-AI set to generate open, standardised, high-quality datasets of protein–ligand interactions at an unprecedented scale.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2026
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation
23 January 2026

Virginijus Siksnys on EMBL’s interim leadership arrangements
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
22 January 2026

The EMBL community is deeply saddened by the passing of Interim Director General Professor Peer Bork, a pioneering scientist who left an indelible imprint on life science research in Europe and beyond.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
16 January 2026

EMBL and its community are deeply saddened by the death of Peer Bork, the organisation’s Interim Director General.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2026
embl-announcementsuncategorized
16 January 2026

As a core partner of the TREC expedition, EMBRC provides access to a vast network of marine stations across Europe, allowing researchers to study coastal and marine ecosystems at scale.
CONNECTIONS
15 January 2026

Alumnus Norbert Kraut reflects on how his time at EMBL led to his successes in addressing hard-to-treat lung cancer.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
13 January 2026

Building on his bioinformatics expertise, EMBL alumnus Moritz Gerstung is developing the next generation of AI tools for cancer research
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2026
people-perspectivesperspectives
5 January 2026

Now in its third year, EMBL's sabbatical fellowship programme is attracting non-traditional allied scientists. The participants see opportunities for collaboration, top-notch technology, and leapfrogging research.
CONNECTIONS
19 December 2025

An EMBO workshop explores the trends, collaborative opportunities, and progress taking place in computational structural biology.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
18 December 2025

EMBL scientists collaborate to build easy-to-use ‘Zoo’ of pre-trained AI models to help biologists and microscopists better analyse their biological images.
LAB MATTERS
18 December 2025
A new single-cell map reveals how human reproductive organs form and respond to environmental influences.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2025
research-highlightsscience-technology
8 December 2025

EMBL alumnus and Lennart Philipson Awardee Florent Cipriani reflects on his 30 years at EMBL Grenoble and his multidisciplinary career building technologies that enable new discoveries.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
4 December 2025

LimbNET is a new online platform that integrates computer modelling, experimental data, and 2D live simulations.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2 December 2025

Julio Saez-Rodriguez discusses how MCP servers are helping AI connect to life science databases, making AI a more reproducible tool for research.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivesperspectives
1 December 2025
Researchers release a comprehensive viral genome database covering diverse ecosystems to advance understanding of viral evolution and ecosystem functions.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
1 December 2025

Public lecture by the Nobel laureate and evolutionary geneticist will explore how traces of Neanderthal DNA shape human biology and health today.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
27 November 2025

EMBL Council has elected the organisation's next Director General, Anthony Hyman, who assumes the role 31 March 2026.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
27 November 2025
Researchers have visualised, in unprecedented detail, how a large RNA molecule assembles itself into a functional machine.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
26 November 2025

EMBL joined European partners at AIS25 to explore how AI can advance life-science research and support Europe’s emerging strategy for AI in science.
CONNECTIONS
25 November 2025

EMBL-EBI Team Leader Sandra Orchard reflects on a life in protein science, UniProt data curation, and championing open data standards.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivesperspectives
24 November 2025

EMBL-EBI receives UKRI Medical Research Council (MRC) and National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) funding for enhancing and translating mental-health omics data into the Open Targets Platform.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2025
announcementsembl-announcements
19 November 2025

A new genomic analysis tool developed at EMBL-EBI, is helping NHS Scotland tackle antimicrobial resistance and improve outbreak response.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2025
research-highlightsscience-technology
19 November 2025

New research suggests that inflammatory support cells play a key role in damaging bone marrow early in cancer development – potentially offering a new target for treatments that stop blood disorders before becoming cancerous.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
18 November 2025

Sixteen leading life science and IT companies, all-new livestreamed presentations, and an informative career panel: EMBL Industry Day continues to grow and evolve in its second year.
CONNECTIONS
18 November 2025

New online portal connects bacterial genomes with experimental resistance data to support antimicrobial resistance research.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2025
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation
14 November 2025

After many years abroad, Fabio Petroni has returned to Italy to establish his research group at EMBL Rome. Here, he is leading a project focused on developing AI systems to support life science research.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
10 November 2025

How EMBL-EBI is building public-private partnerships and knowledge exchange opportunities between industry and academia.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivesperspectives
6 November 2025

EMBL alumna Jona Rada reflects on her experience during the 'Summer of Science’ event organised by EMBL's Science Education and Public Engagement (SEPE) team.
LAB MATTERS
5 November 2025
A new method from EMBL-EBI and collaborators offers fast, easy-to-interpret confidence scores for phylogenetic trees for pandemic preparedness.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2025
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation
5 November 2025
EMBL scientists improve a protein analysis technique, significantly expanding its use and making it 100 times faster – a development that could accelerate drug discovery and fundamental biological research.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
3 November 2025

EMBL is leading a pilot study along the Rhine River to explore microbial biodiversity, the effects of pollutants, and the spread of antibiotic resistance. Using advanced biomolecular methods, the project aims to inform evidence-based measures to protect ecosystems and water quality.
CONNECTIONS
31 October 2025
EMBL researchers have been using a powerful technique called ultrastructure expansion microscopy to peek deeper inside living organisms and understand how they function.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
30 October 2025

Rory Bufacchi talks about the excitement of finding new understanding from existing data and developing computational models to describe living systems.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
29 October 2025

EMBL researchers have developed a new AI tool, which, through a game of molecular laser tag, is helping us better understand the origins of cancer.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
28 October 2025

Two initiatives – BRAINCITY and EMERALD – will strengthen collaboration between EMBL and the Polish scientific community. Their kick-off event on 14 October was followed by a joint NENCKI-BRAINCITY-DANDRITE Symposium in Warsaw.
CONNECTIONS
27 October 2025

EMBL researchers were awarded a BII foundation grant to support Model-MI – an in vitro model that mimics the maternal-fetal interface.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
24 October 2025
Researchers built a 3D human blood-brain barrier and discovered a key role of brain pericytes in cerebral malaria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
23 October 2025

Scientists from EMBL and CEREEP – Ecotron IleDeFrance (IDF) joined forces to advance environmental research by deploying mobile laboratories to study freshwater ecosystems and their vulnerability to human activities
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
22 October 2025

A new method for building growth charts for children with rare diseases is being integrated into DECIPHER to help clinicians and families understand child development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2025
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation
20 October 2025

EMBL Grenoble took part once again in Parvis des Sciences, highlighting EMBL efforts towards engaging more with the public and the importance of the human factor in AI development.
LAB MATTERS
17 October 2025
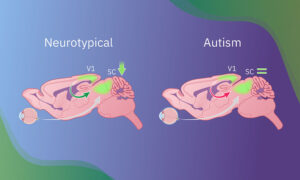
A new study from EMBL Rome scientists reveals a specific brain circuit involved in impaired sensory learning and behavioural adaptation in autism — paving the way for a deeper mechanistic understanding of the condition.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
16 October 2025

From student helper to EMBL-EBI Director, Rolf Apweiler has shaped the journey of EMBL and bioinformatics for over four decades.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivesperspectives
14 October 2025

Better than the original fairy tale, Kendrew awardee Irma Querques’s ‘Sleeping Beauty’ story offers potential for new therapeutics.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
13 October 2025

Lack of incentives and low adoption of metadata standards are limiting AI’s potential for bioimage analysis – a new paper proposes solutions.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2025
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation
10 October 2025
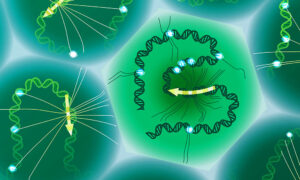
EMBL scientists have developed a more sensitive single-cell sequencing tool that links genomic variants and RNA in the same cell, helping to better uncover links to complex diseases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
7 October 2025
Deeper collaboration between EMBL-EBI and Google DeepMind brings updates to the AlphaFold Database.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2025
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation
30 September 2025

By making the world’s microbial DNA easier to explore, LexicMap helps researchers track outbreaks, study antibiotic resistance, and understand microbial diversity.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2025
research-highlightsscience-technology
30 September 2025
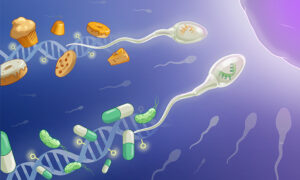
A new collaborative study from EMBL Rome scientists reveals a father’s preconception environment can leave subtle, but detectable, molecular footprints in embryos, able to shape development and long-term offspring health.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
22 September 2025

The Project Manager combines passion and scientific experience to support ocean research within BIOcean5D, a European Commission, SERI, and UKRI co-funded project of 31 partners.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
19 September 2025
A new study observed the dual roles metabolism plays in fueling growth and signalling during cell development, and looked at how this process might be controlled.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
19 September 2025
New research from the Rompani and Asari groups at EMBL Rome suggests that the pupil does more than just respond to light and internal states — it may actively shape our vision. Their findings reveal that the pupil can integrate input from both eyes, impacting the entire visual pathway.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
18 September 2025

EMBL Barcelona researchers shed light on how the blood-brain barrier is damaged during severe malaria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
17 September 2025

New AI model can estimate the long-term risk of over 1,000 diseases and forecast human health changes over a decade in advance.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2025
research-highlightsscience-technology
15 September 2025
Researchers at EMBL Barcelona have quantitatively evaluated the risk of undetected artefacts in single-cell RNA sequencing experiments.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
10 September 2025

Aybuke Kupcu Yoldas, Senior Imaging Bioinformatician at EMBL-EBI, talks about the Bioimage Archive and her journey from astrophysics to biology
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivesperspectives
9 September 2025

The Earth BioGenome Project is accelerating its efforts tenfold to sequence all life on Earth by 2035.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2025
announcementsembl-announcements
5 September 2025

An EMBL alumnus’ work with tRNA, along with support from EMBLEM, has led to a start-up, Umlaut.bio, that is positioned to aid drug development.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
3 September 2025

Jess Ewald, Research Group Leader at EMBL-EBI, uses cell profiling and AI to find and characterise chemical hazards to humans and ecosysystems.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivesperspectives
28 August 2025

A recent pan-EMBL event provided an opportunity to reflect on responsible research assessment in scientific institutions.
LAB MATTERS
27 August 2025

Aleksi Sutinen, ARISE Fellow at EMBL Hamburg, supports the users of the EMBL Hamburg beamline P12 dedicated to small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). Here, he talks about striving for the best in beamline experiments and new horizons for time-resolved SAXS at EMBL Hamburg.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
20 August 2025

Supported by funding from the Manfred Lautenschläger-Stiftung, the summer school introduces undergraduates from a range of scientific backgrounds to cutting-edge life science research.
CONNECTIONS
12 August 2025

EMBL-EBI’s newest Research Group Leader is investigating how somatic mutations reveal the hidden histories of human cells.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivesperspectives
11 August 2025

With its expeditions and mobile labs, EMBL is pioneering a new era of field-based molecular life sciences. Supported by the Klaus Tschira Stiftung and many partners, these ‘labs on wheels’ enable the study of life in context across Europe, with a view to global impact.
CONNECTIONS
8 August 2025

The Barcelona CryoZoo has received a grant from the international organisation Revive & Restore to advance research on stem cell reprogramming in wild animal species.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
5 August 2025
Scientists identified individual stem cell-like cells responsible for leukaemia relapses in kids and precisely characterised their molecular properties.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
4 August 2025

Through a week-long series of workshops and discussions, ARISE fellows learned about key aspects of research infrastructure management, scientific service provision, and entrepreneurship.
LAB MATTERS
1 August 2025

EMBL's latest Science and Society conference brought together researchers, ethicists, communicators, policy professionals, and more to discuss the thorny question of trust in science.
CONNECTIONS
31 July 2025

EMBL’s new AI strategy, backed by the German Hector Foundation, integrates AI across all areas of the life sciences to drive breakthroughs and innovation.
CONNECTIONS
30 July 2025

How a chance encounter resulted in a fruitful cross-Atlantic research collaboration
CONNECTIONS
2025
connectionstechnology-and-innovation
29 July 2025

EMBL ARISE Fellow Thomas Weber talks about his secondment at SciLifeLab in Sweden and how it helped him develop new skills in data science.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
28 July 2025

A ‘supersite’ for field research and public outreach provided optimal environment for exchange, as we find out in this interview.
CONNECTIONS
24 July 2025

A new doctoral network trains fellows as it potentially pioneers a whole new way of exploring the cellular genotype-phenotype link.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
23 July 2025

Ten years after the end of the 1000 Genomes Project, brand new insights emerge from its sample set, providing a more complete view of human genetic variation than ever before.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2025
sciencescience-technology
22 July 2025

Boehringer Ingelheim Stiftung commits €7 million to support key technology development in life sciences research.
CONNECTIONS
22 July 2025

New tool combines biological knowledge with machine learning to help researchers extract meaningful insights from complex omics data.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2025
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
17 July 2025

Australian BioCommons, Bioplatforms Australia, and EMBL have signed a formal agreement to encourage collaboration in bioinformatics and related activities.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
15 July 2025

EMBL-EBI’s new Genome Analysis Team Leader explores the potential of AI and pangenomes to enhance comparative genomics at EMBL-EBI.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivesperspectives
9 July 2025

Together with institutional partners, alumni, and collaborators who have been part of EMBL scientific journey over the years, participants engaged in insightful discussions and reflected on EMBL Grenoble's key scientific milestones.
LAB MATTERS
7 July 2025
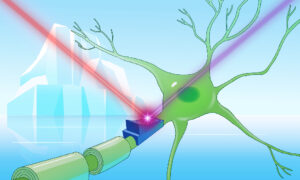
‘Cryorhodopsins’ are a group of unusual and colourful microbial molecules found exclusively in cold environments. Some of them are blue, a rare and sought-after light-absorption property. They are the first observed molecules that can act as both ‘on’ and ‘off’ switches for electrical…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2 July 2025

As EMBL’s new Chief Operating Officer, Michael Milne looks forward to building a long-term operational strategy with input from a range of EMBL stakeholders.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2 July 2025

Around 40 researchers will participate in this joint initiative, which will take place at the Toralla Marine Science Station in Vigo, Spain.
LAB MATTERS
1 July 2025

EMBL’s Interim Director General Peer Bork and Interim Executive Director Ewan Birney will jointly assume the role of EIROforum Chair.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
27 June 2025

On this Oceans Day, EMBL’s Science Education and Public Engagement (SEPE) Team joined forces with the German-American Institute (DAI) to bring the underwater world closer to families in Heidelberg.
LAB MATTERS
26 June 2025

EMBL’s 2024 annual report has been published, sharing achievements in its various missions, along with facts and figures from its 50th anniversary year.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
26 June 2025

A new EMBL spin-off leverages new insights into plant biology for more efficient crop protection
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
13 June 2025

Estonia may be one of EMBL’s newest member states, but thanks to the Tallinn University of Technology, the Traversing European Coastlines (TREC) project relished not just field sampling and outreach opportunities but also attracted the attention of one of the highest-ranking officials to visit…
CONNECTIONS
12 June 2025

Parkinson's disease, a neurodegenerative condition causing motor and non-motor symptoms like gut issues (often appearing decades early), is being investigated for its link to the gut microbiome. While previous studies have shown gut microbiome changes in Parkinson's patients, a clear consensus on…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2025
sciencescience-technology
5 June 2025
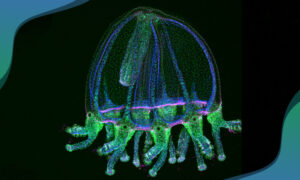
EMBL scientists are on a quest to investigate the underlying biological processes that enable regeneration in jellyfish, which could also help us understand how wounds heal.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
29 May 2025

SAVANA is a new tool designed for accurate detection of structural variations in clinical samples.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2025
research-highlightsscience-technology
28 May 2025

The 2025 edition of 'From Lab to Launch' brought together scientists and entrepreneurs at Start-up Labs Hamburg to explore funding pathways for science-based startups. Organised by EMBL, Hereon, DESY, and EMBLEM, the event featured keynote insights, a panel of experienced founders and funders, and…
CONNECTIONS
22 May 2025

Marta Cherubini, a Senior Researcher at EMBL Barcelona, is developing a new 3D in vitro model of the human placental barrier to study pregnancy complications. She enjoys crafting and repairing broken items through careful observation and problem-solving, skills that carry over from her lab…
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
19 May 2025

As Peer Bork and Ewan Birney take up interim leadership of EMBL, the organisation announces additional changes in site leadership.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
15 May 2025

Five key takeaways from an EMBL | EMBO symposium that explored the ‘wild frontiers’ of model organisms, from phytoplankton to sea anemones, waterstriders, roundworms, and more.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
14 May 2025

Edith Heard was EMBL’s fifth Director General, but is now moving on to serve as the Francis Crick Institute's Director and Chief Executive Officer. Here, she reflects on her time at EMBL and lessons learned throughout the years.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
13 May 2025

Tara Ocean Foundation’s Executive Director Romain Troublé offers his insights on the TREC project, as part of a new series spotlighting TREC partners.
CONNECTIONS
8 May 2025

EMBL’s position paper outlines its key recommendations for European Commission’s upcoming ‘Strategy for European Life Sciences’.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
6 May 2025

Mary Barlow shares her insights on change management and her new role as Head of Major Initiatives at EMBL-EBI.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivesperspectives
30 April 2025

EMBL-EBI’s new Chemical Biology Resources Team Leader aims to encourage community engagement and explore AI-driven approaches.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivesperspectives
23 April 2025

Fifth EMBL Partnership Conference brings together participants from EMBL and partner institutions to explore how AI can drive innovation in One Health. Conference participants discussed opportunities and challenges in advancing AI in life sciences and the role collaboration.
CONNECTIONS
16 April 2025
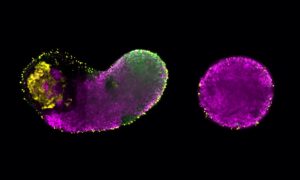
EMBL Barcelona and MPI-CBG Dresden researchers reveal how glycolysis drives early embryonic cell decisions.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
9 April 2025
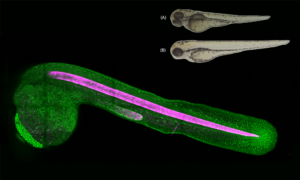
EMBL scientists investigate how zebrafish bodies change when grown at higher temperatures.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
1 April 2025

Meet Neil Humphreys, Head of the Gene Editing and Virus Facility at EMBL Rome. Neil and his team work closely with scientists to develop new models, tools, and cutting-edge technologies to support discovery and translational research.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
28 March 2025

Supported by EMBL services, students Misha Hegde & Mia Maurer have identified a previously unknown bacteriophage that targets Rhizobium rhizogenes, a pathogen harming crops. Using cutting-edge imaging and DNA sequencing at EMBL Heidelberg, they are exploring its potential as a natural alternative…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
26 March 2025

EMBL’s Advanced Mobile Laboratory (AML) is stationed at the University of Malta for one month, to provide advanced technology, expertise, and training to Malta’s scientific community. An official launch event was held at the University of Malta, with participation of local institutional…
CONNECTIONS
24 March 2025
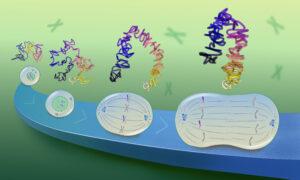
EMBL scientists have shown how overlapping loops of DNA stack upon each other in dividing cells to give rise to rod-shaped chromosomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
20 March 2025

Texas A&M University researchers work with experts from EMBL Imaging Centre to uncover how molecules navigate the nuclear pore complex.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
19 March 2025

EMBl-EBI’s new building enables the translation of the institute’s data management expertise into solutions for global challenges
LAB MATTERS
2025
announcementslab-matters
18 March 2025

EMBL’s new archivists highlight the importance of safeguarding past records to strengthen the organisation's institutional future. Together, they will focus on developing a sustainable record management framework while keeping records of valuable cultural and historical information.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
10 March 2025

EMBL Barcelona researchers developed a computational method that reconstructs embryonic development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
10 March 2025

Peer Bork and Ewan Birney take up interim leadership of EMBL as Edith Heard steps down as Director General.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
7 March 2025
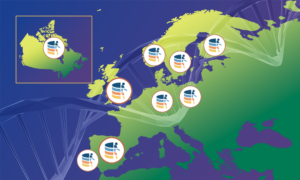
The Federated European Genome-phenome Archive (FEGA) has expanded its network and continues to evolve by embracing emerging technologies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2025
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation
6 March 2025

EMBL strengthened its ties with its newest prospect member state Bulgaria at a recent ‘information day’ designed for networking and information exchange.
CONNECTIONS
5 March 2025

New EMBL-EBI project explores the use of a concept developed in aerospace engineering to support rare disease research, diagnosis, and treatment.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivestechnology-and-innovation
25 February 2025

Nobel Laureate May-Britt Moser shares her thoughts on her science, its intrinsic rewards, and what she’ll be talking about in a few weeks at EMBL’s 2025 Kafatos Lecture.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
24 February 2025

Yehudi Bloch, ARISE Fellow at EMBL Hamburg, talks about the snow flea antifreeze protein. This is part of a series of stories about EMBL scientists and quirky, charming proteins that make them smile.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
21 February 2025

This year’s EMBL Corporate Partnership Programme annual meeting connected EMBL scientists with industry representatives to talk about AI and life sciences research.
CONNECTIONS
20 February 2025
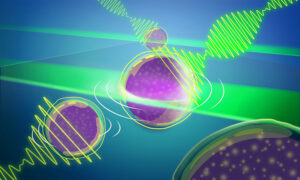
Another EMBL-engineered advance to Brillouin microscopy has significantly widened the aperture to provide quick 3D imaging in real time of light-sensitive samples.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
20 February 2025

EMBL-EBI’s new Head of IT and Technical Services (ITS) Operations will strengthen collaborative systems across EMBL and explore our use of cloud-hosting solutions.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivesperspectives
19 February 2025

African scientists awarded the 2024 EMBL-UNESCO residencies share their experience in bioinformatics and virology, emphasising the power of connections and knowledge exchange.
CONNECTIONSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
connectionspeople-perspectives
18 February 2025

Francesco talks about his work in protein science, fascination for protein design, and how he's finding the EMBL International PhD programme.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivesperspectives
17 February 2025
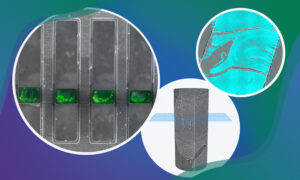
New funding from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (CZI) supports two multidisciplinary projects across EMBL’s units and sites to support the development of imaging technologies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
13 February 2025
Scientists at EMBL and DKFZ have discovered how cells in the liver maintain their identity and avoid becoming tumour cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
12 February 2025

Researchers in the Galej Group at EMBL Grenoble have provided new insights into the structure of the minor spliceosome, an essential RNA-protein complex.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
11 February 2025

Deepti Gupta, Project Manager and Database Curator at EMBL-EBI, talks about her favourite protein PIEZO1. This is part of a series of stories about EMBL scientists and quirky, charming proteins that make them smile.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivesperspectives
10 February 2025
Scientists have discovered that gut bacteria can alter molecular signatures in the brain, using a brand new method to study how carbohydrates modify proteins.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
5 February 2025

Claire O'Donovan, biocurator and Metabolomics team leader at EMBL-EBI shares lessons from her career and life.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivesperspectives
3 February 2025

Yerba mate is a popular caffeinated beverage. Scientists mapped its genome, revealing surprising facts about its biochemistry and the evolution of caffeine biosynthesis. The findings might pave the way for new varieties of yerba mate.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
31 January 2025

Nobel laureate and neuroscientist May-Britt Moser will discuss how the brain’s grid cells enable navigation and spatial memory at the 2025 Kafatos Lecture.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
30 January 2025

A new study from EMBL Barcelona researchers shows that metabolism is a selective modulator of developmental tempo, contributing to our evolutionary understanding.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
29 January 2025

Researchers from Mainz University and EMBL Hamburg have presented a new approach for assessing the form of disordered proteins by using anomalous X-ray scattering method for structural analysis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
28 January 2025
The Solve-RD project standardises genomic and clinical data across Europe to support rare disease research.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2025
announcementsembl-announcements
27 January 2025

Tim Cezard talks about the importance of genetic variation data and the move from biology to infrastructure
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivesperspectives
24 January 2025

The Paleocore project, led by the French marine institute Ifremer and part of the TREC expedition, aims to study marine sediments to understand the impact of major historical events on ecosystems.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
22 January 2025
Introducing an open-source large language model (LLM) framework designed for custom biomedical research.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2025
research-highlightsscience-technology
21 January 2025
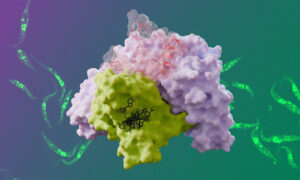
The Kowalinski group at EMBL Grenoble identified significant differences between the trypanosomal and human nuclear cap-binding complex, a key player in cellular RNA metabolism and a potential target for novel anti-parasitic drugs.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
20 January 2025

Sarah Gharbi, technician at EMBL Grenoble, talks about her favourite protein complex, which looks like a poodle. This is part of a series of stories about EMBL scientists and quirky, charming proteins that make them smile.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
14 January 2025

Study identifies a novel mechanism driving osteosarcoma and provides insights to help predict patient outcomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2025
research-highlightsscience-technology
14 January 2025

Memorandum of Understanding between EMBL and ELLIS will drive AI in European life science research, training, and technology. The strategic partnership will promote interdisciplinary training and develop innovative projects that address pressing challenges in human and planetary health.
CONNECTIONS
10 January 2025

The Arendt Group at EMBL Heidelberg focuses on mechanisms of evolution, studying Platynereis dumerilli – evolutionarily ancient marine worms found broadly along European coasts.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
10 January 2025
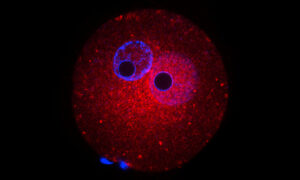
Researchers in the Boulard group at EMBL Rome demonstrated that the catalytic activity of the OGT enzyme is essential for embryonic development, and that when it’s reduced, embryo development is delayed – especially in males.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
8 January 2025

In our final 12th ‘moment of philanthropy’, we shine a light on how a donation from the Athenaeum Dietrich Götze Stiftung fuels impactful EMBL research that aims to better understand treatment-resistant childhood leukaemia.
CONNECTIONS
7 January 2025

Maria Costanzo, former predoc at EMBL Barcelona, talks about YAP, her favourite protein in the shape of a heart. This is part of a series of stories about EMBL scientists and quirky, charming proteins that make them smile.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
3 January 2025

Scientists share their experiences of creating stunning images at the EMBL Imaging Centre.
CONNECTIONS
20 December 2024

EMBL and its partners have received funding from the European Commission for two new Twinning Projects, which will build expertise and research capacity in its member states.
CONNECTIONS
19 December 2024

New Head of the Microbial Automation and Culturomics Core Facility discusses her career, her goals for the facility, and her early inspirations.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
18 December 2024
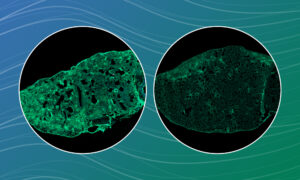
EMBL scientists discovered that dextromethorphan, an FDA-approved active ingredient in cough syrups, has potential to treat fibrotic lung disease by containing collagen and other pro-fibrotic molecules capable of forming scars inside the cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
17 December 2024

The Prevedel group at EMBL Heidelberg developed a mobile microscope: miniature in scale, fast in sample imaging, and giant in resolution.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
16 December 2024

Veijo Salo, postdoc at EMBL Heidelberg, talks about seipin, the cell’s molecular ‘bubble blower’.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
13 December 2024

EMBL announced the winners of its Unfold Your World protein art project, an initiative intended to engage young people, interweaving science with art.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
13 December 2024

Right from the early days of DNA sequencing, EMBL’s scientists have been instrumental in helping the world understand, decode, archive, and manipulate genomes at scale and across many branches of the evolutionary tree, a task they continue to excel at today.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
12 December 2024

A member of EMBL’s Responsible Research Assessment Working Group shares his thoughts on the importance of reforming strategies to assess research and researchers.
LAB MATTERS
11 December 2024

Kristaps Krims-Dāvis spent a month at EMBL Heidelberg getting a crash course in cutting-edge microscopy.
CONNECTIONS
11 December 2024

EMBL-EBI's new Functional Genomics Team Leader will develop standards for new data types and integrate AI into workflows.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
people-perspectivesperspectives
10 December 2024

The partnership will address global food security challenges through optimised agricultural research and data-driven innovation.
CONNECTIONS
10 December 2024

EMBL announces that Peer Bork and Ewan Birney will lead the organisation after the departure of Director General Edith Heard in summer 2025.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
9 December 2024

EMBL hosted a Science Day with Evonik, bringing together 16 industry experts and EMBL scientists to explore collaborative research opportunities.
CONNECTIONS
6 December 2024

Lennart Philipson Award recipient Giulio Superti-Furga discusses the scientific achievements he's most proud of, the importance of entrepreneurship, and why he had his personal genome sequenced.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
4 December 2024
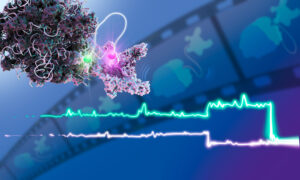
With a novel approach, EMBL scientists discovered important interactions between molecular machines, potentially offering new opportunities for drug development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
4 December 2024

Romain Linares talks about his role in managing the cryo-electron microscopy facility at EMBL Grenoble, how he sees this technique evolving in the coming years, and his passion for astronomy.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2 December 2024

Laura Marin, Head of Administration at EMBL Barcelona, talks about how finding joy at work is true success, and how she feels in her new role.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
29 November 2024
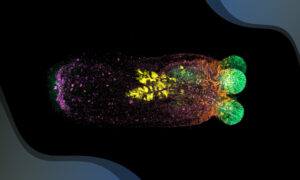
Scientists have shown how regenerating sea anemones restore their shape following a major injury, uncovering novel cellular and molecular mechanisms.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
28 November 2024

In 2023, EMBL opened its interactive World of Molecular Biology exhibition as an inspiring entree into molecular biology. This visionary project would not have been possible without an impressive array of support.
CONNECTIONS
27 November 2024

Sofia Rucli, postdoc at EMBL Rome, talks about her relationship with the protein OGT, a molecular ‘candy man’ of the cell.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
27 November 2024

EMBL and Nikon have formally broadened their partnership to accelerate development of next-generation microscopy technologies.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
26 November 2024

EMBL Grenoble took part in a series of activities during the French Science Week, highlighting EMBL’s research and the TREC scientific expedition.
LAB MATTERS
25 November 2024

The introduction of computational methods in biology opened up an entirely new world of insights and breakthroughs. Over the last several decades, EMBL has been at the forefront of discoveries and innovations that have not only propelled the field forward but also opened up access to bioinformatics…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
25 November 2024

EMBL Fellows’ Career Service launches new online resources for early- career researchers at EMBL and beyond, aimed at providing comprehensive career guidance.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
22 November 2024

The programme will advance excellence in research infrastructure management and technology development.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
22 November 2024

EMBL Rome celebrates its 25th anniversary this year – some impressions of the symposium and party organised for staff and alumni to mark this special occasion.
LAB MATTERS
21 November 2024

A recent symposium on ‘The complex life of RNA’ brought together scientists from across the world interested in exploring one of the most crucial molecules essential to life.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
20 November 2024

The findings of the study provide insights into vaccines or treatments to protect people from severe malaria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
19 November 2024

EMBL’s Head of Sustainability shares the steps the organisation has taken to make its research more sustainable.
LAB MATTERS
18 November 2024
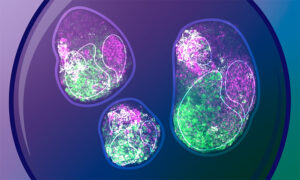
Researchers from the Trivedi Group at EMBL Barcelona unveil how cells can act autonomously during early development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
15 November 2024

EMBL Barcelona observed EMBL’s 50th anniversary with a scientific celebration that attracted alumni and other leading life scientists.
CONNECTIONS
15 November 2024

Yuvarani Masarapu, a junior bioinformatician and doctoral student at SciLifeLab in Stockholm, spent a week with EMBL collaborators, finding solutions to research challenges and expanding her scientific perspective.
CONNECTIONS
14 November 2024
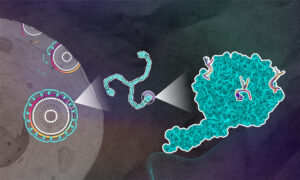
Scientists from EMBL Hamburg and CSSB have revealed key insights into the cellular process of clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
13 November 2024
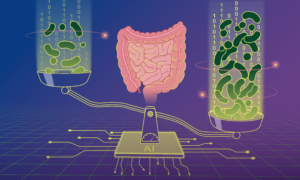
Scientists have developed a new machine-learning model to predict microbial load — the density of microbes in our guts — and used it to demonstrate how microbial load plays an important role in disease-microbiome associations.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
12 November 2024

Nicolas Foos, a postdoctoral fellow at EMBL Grenoble, talks about the implementation of a new method for in situ serial crystallography developed during his ARISE fellowship.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
11 November 2024

Jan Bláha, postdoc at EMBL Hamburg, talks about the utility of in cellulo protein crystallisation in structural biology research, his sources of inspiration, and the values of collaboration, curiosity, and resilience.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
8 November 2024

Public Engagement Officer Briony Jackson is building lasting relationships with local communities to make science accessible and engaging for all.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
people-perspectivesperspectives
6 November 2024

As we mark EMBL’s 50th anniversary, we celebrate not only the groundbreaking research and discoveries that have emerged from this prestigious institution but also the rich history and profound impact of the EMBL Course and Conference Programme.
LAB MATTERS
4 November 2024

In less than two years, the EMBL-led TREC expedition has demonstrated that large-scale international collaboration is essential for driving ground-breaking planetary and human health research with societal impact. Here, we summarise some aspects of the expedition in numbers.
CONNECTIONS
31 October 2024

Dieter Schwarz Foundation provides the ‘life’ support for innovative global research collaboration of EMBL-Stanford Life Science Alliance
CONNECTIONS
31 October 2024

Isabella Graf is EMBL’s newest group leader and the first theoretical biophysicist to join the Developmental Biology Unit.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
30 October 2024

EMBL’s Scientific Visitor Programme enables high-level scientific exchange and cross-fertilisation of ideas and technologies through sabbatical fellowships for researchers.
CONNECTIONS
28 October 2024

The ARISE summer school brought together fellows from across EMBL sites who are working on technology projects as part of EMBL’s Career Accelerator for Research Infrastructure Scientists (ARISE) programme.
CONNECTIONS
24 October 2024

Employing a library of more than 1,000 chemicals, EMBL researchers and collaborators investigated how agrochemicals affect insect populations.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
24 October 2024
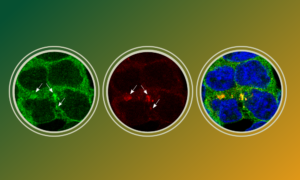
Scientists have discovered how the antiviral protein TRIM25 finds and binds viral RNA to activate an innate immune response.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
21 October 2024

EMBL’s first Industry Day offered EMBL scientists a unique opportunity to network with several leading life science companies.
CONNECTIONS
17 October 2024

Imaging lets us observe biology in action – it makes visible the hidden processes of life. From its founding, EMBL has been a centre of breakthroughs and developments in bioimaging, and it continues to play a pioneering role in this field today.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
16 October 2024

EMBL Rome volunteers participated in the European Researchers’ Night organised by the CNR in Montelibretti, attended by over 1,500 visitors. They prepared activities and games reflecting the wide variety of projects conducted at the site and across EMBL.
LAB MATTERS
15 October 2024
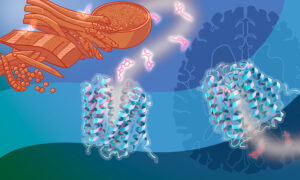
EMBL Hamburg scientists have gained molecular insights into how we absorb vitamin B1 – a mechanism with implications for disease and drug development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
15 October 2024

Daniele Ancora is an ARISE fellow in the Light Imaging Facility at EMBL Rome. With a background in theoretical physics, he develops algorithms to improve image-based omics technologies. Learn about his interdisciplinary training and his little ‘obsessions’.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
10 October 2024

A hands-on workshop offered an excellent opportunity for scientists to connect with children with whom they share a common language.
LAB MATTERS
10 October 2024
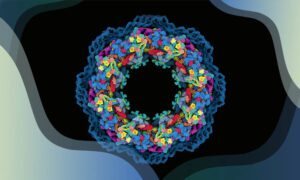
The function of biological molecules is intimately linked to their structure. In the 50 years since EMBL was established, its researchers and engineers have constantly provided leadership in structural biology research and services, resulting in many scientific breakthroughs and novel insights.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
9 October 2024
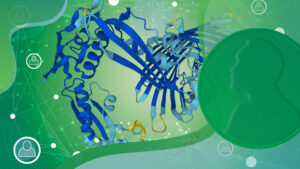
Creators of AI system AlphaFold receive 2024 Nobel Prize for Chemistry.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
sciencescience-technology
8 October 2024

The prize was awarded to John J. Hopfield, Princeton University, USA, and Geoffrey Hinton, University of Toronto, Canada, for their seminal contributions to the foundational methods that enabled the development of machine learning.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
8 October 2024
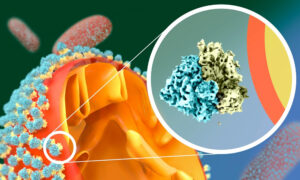
Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg and University of Virginia revealed a new cellular response to starvation: ribosomes attach to the mitochondrial outer membrane in a very unusual way, via their small subunit. The finding made in yeast might provide insights into how cancer cells survive the harsh…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
30 September 2024

The Manfred Lautenschläger Foundation helped fund EMBL’s Advanced Mobile Lab, enabling many experimental concepts.
CONNECTIONS
30 September 2024

The 13th annual meeting of the Nordic EMBL partnership for molecular medicine took place on 16–19 September 2024 in Oslo and was hosted by the Centre for Molecular Medicine Norway (NCMM).
CONNECTIONS
27 September 2024

Starting in the 1980s, EMBL’s PhD programme has played a notable role in helping train some of the brightest scientific minds in Europe, as well as in building a thriving research community focused on collaboration and innovation.
LAB MATTERS
26 September 2024

Addition of data from more diverse populations to the Polygenic Score (PGS) Catalog and a new software tool for PGS calculation could help produce more equitable disease risk predictions.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation
25 September 2024

Cell biologist Hans Clevers will discuss organoids as 'avatars' for human organs in research and medicine at the 2024 Kafatos lecture.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
24 September 2024
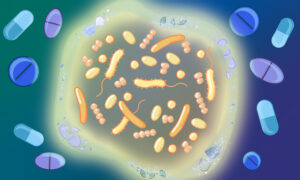
EMBL Heidelberg researchers compared the effect of drugs on isolated bacteria versus those growing in communities. This is the first study showing that bacteria are more resilient when in community due to cross-protection strategies. This could help researchers design more efficient therapies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
18 September 2024
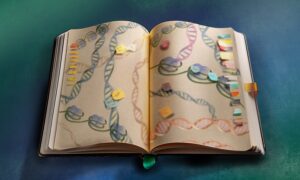
Researchers have identified key cellular control sites that regulate gene expression and prevent the activation of ancient viral sequences in the genome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
16 September 2024

EMBL-EBI Postdoctoral researcher Iguaracy Pinheiro de Sousa is using bioinformatics to support the development of better organoids.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
people-perspectivesperspectives
13 September 2024

EMBL-EBI data resources help advance biodiversity and climate change research by enabling scientists to study species interactions, evolutionary processes, ecosystem health, and more.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation
12 September 2024

A delegation from Spain’s Ministry of Science, Innovation, and Universities visited EMBL to strengthen ties and discuss future opportunities.
CONNECTIONS
11 September 2024

Julia Mahamid and Nassos Typas reflect on the direction of the Molecular Systems Biology Unit they now lead at EMBL Heidelberg.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
10 September 2024

An AI-enhanced advanced microscopy approach offers promise in better understanding glioblastomas, one of the deadliest brain cancers.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
9 September 2024

Jia Le Lim talks about contributing back to society through science, finding inspiration in the way birds fly in the sky, and winning a recent international piano competition.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
5 September 2024

PROMETHEUS is an EMBL-born grassroots initiative to promote and optimise impact-driven science.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
4 September 2024

EMBL-EBI alumnus Alvis Brazma reflects on how mathematics and mountaineering have shaped his life and why keeping things simple in bioinformatics is key.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
people-perspectivesperspectives
3 September 2024

On Friday 4 October 2024 at 18:00 CEST, the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (KNAW) in Amsterdam will host the 2024 Kafatos Lecture, delivered by renowned scientist Hans Clevers.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2 September 2024

After Suzanne Eaton’s death, family and friends raised funds for a Kinderhaus playground, providing a joyous way to remember her.
CONNECTIONS
27 August 2024
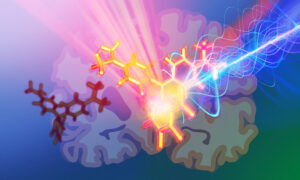
EMBL scientists applied molecular engineering to build photoacoustic probes to label and visualise neurons deep within brain tissue.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
23 August 2024

EMBL-EBI’s new Head of Applications will use his expertise in cloud infrastructure and security to support the institute’s open data resources.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
people-perspectivesperspectives
21 August 2024
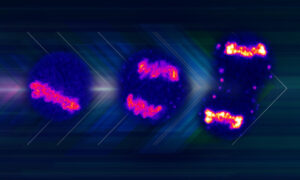
EMBL Heidelberg researchers discovered how a protein switches between repelling and gluing chromosomes during cell division. This helps the mother cell to divide the genome equally into two daughter cells and cluster chromosomes inside the daughter nuclei, ensuring a successful cell division.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
19 August 2024
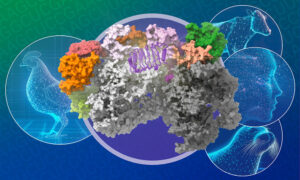
A new publication from the Cusack group sheds light on how a key avian influenza virus enzyme can mutate to allow the virus to replicate in mammals.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
16 August 2024

The TREC expedition concluded its sampling in Greece and strengthened scientific exchange and collaborative networks with their Greek partners during a political and scientific stakeholder event in Athens.
CONNECTIONS
14 August 2024

EMBL alumnus Thibaut Brunet, recipient of the 2024 John Kendrew Young Scientist Award, shares his scientific journey – from a childhood passion for nature to the discovery of a new species of choanoflagellate.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
12 August 2024
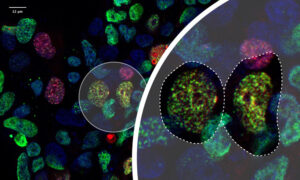
EMBL Grenoble researchers have come up with a new way to identify the targets of a crucial protein-modifying enzyme involved in diverse cellular processes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
8 August 2024

EMBL-Stanford Life Science Alliance fellow Jana Helsen shares how she balanced her life between two laboratories and countries, her latest research paper, and her passion for cover art.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
1 August 2024

Using machine learning to analyse the genetic factors behind early clinical trial termination, researchers find a link between genetic evidence and trial outcome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
research-highlightsscience-technology
31 July 2024
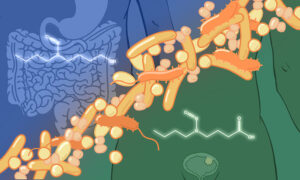
Study shows that gut bacteria can metabolise carcinogens and cause them to accumulate in distant organs, leading to tumour development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
30 July 2024

Since 2011, Roland Specker has sponsored the John Kendrew Young Scientist Award, which both supports early-career scientists while also honouring EMBL’s first director general.
CONNECTIONS
25 July 2024

A major public engagement event at EMBL Hamburg attracted thousands. A video captures the spirit of the day from participants.
LAB MATTERS
24 July 2024

EMBL's 50th anniversary symposium brought together its vibrant community, showcased its many scientific contributions, and drove discussion on the future of Europe's leading life sciences laboratory.
CONNECTIONS
18 July 2024

ARISE fellow Melanie Schneider shares how she uncovered a new interest in research infrastructures and supporting discovery.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
people-perspectivesperspectives
16 July 2024

A life-size game inspired by the Traversing European Coastlines (TREC) expedition provides the public with an inside view of the world of coastal ecology research.
LAB MATTERS
11 July 2024

Kim Gurwitz talks about her role as Scientific Training Lead at EMBL-EBI and how collaborative projects for bioinformatics training support researchers and service providers in making the most of publicly available data.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
people-perspectivesperspectives
10 July 2024

A scientific workshop on flow cytometry was organised at EMBL Rome, taking advantage of the presence of the Advanced Mobile Laboratory, the biggest unit of EMBL’s mobile lab fleet.
CONNECTIONS
10 July 2024

The dynamic world of proteomics is shaping the future of personalised medicine, but some obstacles stand in the way
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
perspectivesscience-technology
9 July 2024

Professor Edith Heard will succeed Sir Paul Nurse at the London-based institute in the summer of 2025
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
8 July 2024

EMBL’s 2023 Annual Report has been published, sharing achievements in its various missions, plus facts & figures from the year.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
4 July 2024

What makes EMBL unique? Among many things, it’s the infinite curiosity of its community.
LAB MATTERS
3 July 2024

Ewan Birney reflects on his time at EMBL and the development of the organisation through a commitment to open data and nurturing scientific talent.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
people-perspectivesperspectives
2 July 2024

Bulgaria has become the latest EMBL prospect member state, starting a three-year process toward full membership. The prospect membership opens up new opportunities for mutual exchange and collaboration. Including Bulgaria, EMBL is now supported by 29 full member states, one associate member state,…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2 July 2024
A new research paper published in Nature Communications lays the groundwork for the development of new drugs specific to genetic mutations or alterations responsible for the onset of tumours or genetic diseases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
1 July 2024

EMBL and partners announce ‘Amplifying Funds in Infection Biology’ to foster interdisciplinary and collaborative research in infection biology.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
1 July 2024

EMBL celebrates 50 years of cutting-edge European research: founded in Heidelberg by the first ten member states, Europe's pioneering Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) is now supported by 29 member states and stands for outstanding open research, scientific services for researchers, innovative…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
28 June 2024

At EMBL Rome, an immersive youth training programme is dedicated to, but also inspired by, alumnus Riccardo Cortese, thanks to private donors.
CONNECTIONS
27 June 2024
EMBL researchers and their partners have been studying microbial functions and interactions for the benefit of human and planetary health for the last two decades.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
26 June 2024

This event bridged research and entrepreneurship, fuelling innovation and discovery. Attendees immersed themselves in insightful discussions and invaluable networking opportunities, inspired to journey from lab research to entrepreneurial success.
CONNECTIONS
25 June 2024

EMBL Grenoble’s Kowalinski Group analysed the structure of an enzyme responsible for modifying tRNA molecules to fine-tune protein production. They discovered that to distinguish almost identical, yet different, tRNA molecules, the enzyme uses help from another enzyme – a type of cooperation…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
21 June 2024

The new Team Leader for Human Genomics at EMBL-EBI shares how curiosity and maths shaped her career and what it takes to be a community builder.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
people-perspectivesperspectives
19 June 2024
EMBL Hamburg scientists and collaborators discovered a new molecular mechanism in which an unstructured protein disables one of the main cancer-promoting proteins by gluing them into an elongated stack. Data from human patient samples support the role of this mechanism in prostate cancer…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
18 June 2024
A theoretical model involving tiny Minecraft-like cubes can help us understand dynamic biological processes, such as cell sorting in embryos.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
17 June 2024

EMBL´s position paper outlines the organisation’s views on the importance of science and how it could be best supported in the context of the upcoming European Framework Programme for Research and Innovation (FP10).
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
17 June 2024

For almost two months, Italy was the stage for the TREC expedition, with a rich programme of events organised across the country attended by the public, scientists, schools, and high-level political stakeholders, including Minister of University and Research Anna Maria Bernini.
CONNECTIONS
13 June 2024

Researchers explore genetic diversity found in ancient environmental DNA to help modern agricultural practices.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2024
announcementsembl-announcements
12 June 2024

A special Coffee with EMBL session celebrated EMBL’s 50th anniversary by inviting alumni to reflect on the organisation’s first two decades.
LAB MATTERS
12 June 2024

EMBL Grenoble and the ESRF hosted a workshop bringing together representatives from research and industry to discuss the ever-growing role of artificial intelligence in the field of structural biology.
CONNECTIONS
7 June 2024

EMBL-EBI data resource helps scientists upcycle animal by-products.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
perspectivesscience-technology
6 June 2024
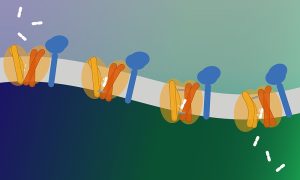
The group of Christian Löw at EMBL Hamburg and CSSB, and collaborators from the Christian-Albrechts-University Kiel and CNRS & Université Paris Cité worked together to reveal the structure and function of a previously unknown lysosome transporter, MFSD1.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
31 May 2024

Elise talks about her role in supporting EMBL Grenoble staff in daily human resources matters and the multiple events she’s been involved in to connect people, both at and outside of work.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
29 May 2024

Starting in 2014, Friends of EMBL engages a diverse range of individuals to support and connect with EMBL research. Through unique events and philanthropic contributions, members play a vital role in fostering a stronger bond between EMBL and society.
CONNECTIONS
28 May 2024
Blood stem cells from healthy people carry major chromosomal alterations, a study in Nature Genetics by researchers at the Max Delbrück Center and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) finds. The discovery suggests that we are all genetic mosaics, which may contribute to ageing-related…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
24 May 2024

Stephen Cusack, world-renowned structural biologist and former Head of EMBL Grenoble, reflects on his early influences, his achievements, and the lessons he’s learned as he embarks on his next adventure
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
23 May 2024
Large-scale study uses data from Danish health registries to predict individual risks of developing cancer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
research-highlightsscience-technology
22 May 2024

New research by EMBL scientists shows how different modes of cell division used by animals and fungi might have evolved to support diverse life cycles.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
16 May 2024

EMBL-EBI's new Head of Research shares his plans and priorities.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
people-perspectivesperspectives
14 May 2024

Toby Gibson reflects on 38 years at EMBL, the scientific tools he built along the way, and the state of science today.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
9 May 2024

A study from the Hackett group at EMBL Rome led to the development of an epigenetic editing system that allows to precisely program chromatin modifications at any specific position in the genome, to understand their causal role in transcription regulation.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
7 May 2024

María Cerezo talks about her role as Scientific Curator, how she combines it with her position as co-chair of the Staff Association, and what she believes has been EMBL's biggest achievement in its first 50 years.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
people-perspectivesperspectives
1 May 2024
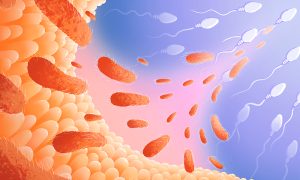
Scientists from EMBL Rome and EMBL Heidelberg found that disrupting the gut microbiome of male mice increases the risk of disease in their offspring. Their findings suggest that a father’s pre-conception environment can have lifelong effects on offspring.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
30 April 2024
A bold vision to build a centre of excellence for imaging captured the imagination and support from private and public donors to help create the EMBL Imaging Centre.
CONNECTIONS
30 April 2024

MSD joins as the latest partner in the Open Targets consortium, enhancing the initiative’s collaborative efforts in drug discovery.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2024
announcementsembl-announcements
24 April 2024

Experts in quantum computing and genomics to develop new methods and algorithms to process biological data.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
announcementsscience-technology
23 April 2024

SpatialData is a tool developed by EMBL scientists in cooperation with multiple research institutions to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies in a spatial environment, providing holistic insights into health and disease. Researchers can now freely access and use SpatialData…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
22 April 2024

BIOcean5D is an EMBL-coordinated project co-funded by the European Union that unites 31 institutes to address pressing global challenges on marine biodiversity.
LAB MATTERS
19 April 2024
New project will help inform and educate young people about the important roles proteins play in nature, health, and disease, as part of EMBL’s 50th anniversary celebrations.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
18 April 2024

The second phase of the TREC expedition focuses on the Mediterranean coast, with Barcelona, Spain, hosting the first ‘superstop’ of 2024
CONNECTIONS
10 April 2024
Data obtained through cryogenic sample electron tomography (cryo-ET) are openly available in the new Electron Microscopy Public Image Archive (EMPIAR) cryo-ET tomography browser.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2024
announcementsembl-announcements
8 April 2024

A recent EMBO | EMBL conference provided a forum for researchers to share how AI is making a difference in biology and bioinformatics.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
4 April 2024

New study from the Galej group provides deeper structural insight into the assembly of a critical molecular machine, that removes non-coding information from genes during their expression.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
3 April 2024
Diego Benusiglio, ETPOD postdoc in the Asari group at EMBL Rome, talks about his peculiar postdoctoral programme and his passion for science and Swing music
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
28 March 2024
New study uncovers the potential of immunotherapy in preventing breast cancer and creates the openly available Human Breast Cell Atlas.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
25 March 2024

The Environmental Research Initiative is a community effort of donations empowering EMBL scientists to solve global environmental challenges through molecular biology.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2024
connectionslab-matters
20 March 2024

During a visit from high-level representatives of EMBL’s member state Malta, the honourable delegation allowed a peek behind the scenes of their scientific and institutional collaborations, and shared their memories and future aspirations for the partnership.
CONNECTIONS
20 March 2024

Data standards that have been silently enabling discovery in the life sciences for decades are now making AI advances possible.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
people-perspectivesperspectivesscience
18 March 2024

The first EMBL-UNESCO infection biology research fellows share observations after residencies with EMBL researchers.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesperspectives
12 March 2024

Team Leader Sameer Velankar on why accessible training is key for AlphaFold and AI tools more generally.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
people-perspectivesperspectivesscience
11 March 2024

New research from EMBL Heidelberg shows how cells in developing embryos undergo a major shift in the way they regulate gene expression as they mature and differentiate.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
sciencescience-technology
8 March 2024

On International Women’s Day 2024, we hear from some of the women who have been working tirelessly in the field and behind the scenes as part of the Traversing European Coastlines (TREC) expedition.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
7 March 2024
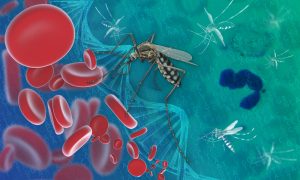
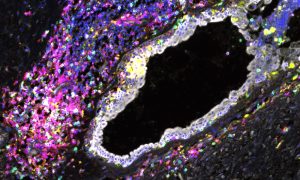
Plasmodium falciparum, a malaria parasite, uses gene conversion to produce genetic diversity in two surface protein genes targeted by the human immune system.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
announcementssciencescience-technology
6 March 2024

An international team of researchers aim to combine social determinants of health with genomics, immune profiling, and exposomics data to tackle cancer inequities at an unprecedented scale.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
announcementssciencescience-technology
6 March 2024
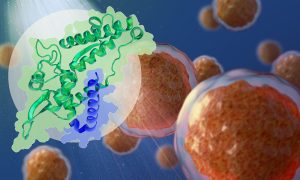
A new study from the Bhogaraju Group at EMBL Grenoble reveals how the cancer-promoting MAGE family of proteins bind to their targets, aiding the development of anti-cancer drugs that target these proteins.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
sciencescience-technology
1 March 2024

Two former EMBL scientists have been recognised for their outstanding contributions to research and leadership capabilities in the fields of evolutionary cell biology and molecular medicine.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2024
alumniembl-announcements
26 February 2024

Simone Heber talks about studying RNA transport, organising the Bike Club at EMBL, and participating in the Ironman World Championship.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
22 February 2024

The Fuchs Fund, started by Lilo and Manfred Fuchs in 2017, has become a lifeline for EMBL students facing adversity during their PhD journeys.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2024
connectionslab-matters
19 February 2024

The Traversing European Coastlines (TREC) expedition prepares to begin its next phase of sampling, with stops in Spain, Greece, Italy, and beyond.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
sciencescience-technology
12 February 2024

After 32 years at EMBL – leading a developmental biology research group and later simultaneously serving as EMBL’s Dean for its PhD programme, Anne Ephrussi has retired, ready to start her life’s next chapter.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
5 February 2024

Jacqueline shares her experience of EMBL's international PhD programme.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
1 February 2024

Renato Alves talks about his time at EMBL, the Bio-IT project, his wishes for EMBL in its anniversary year, and how a passion for night hikes and stargazing led to the creation of EMBL’s astronomy club.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
29 January 2024

Kyle Morris joins EMBL-EBI as Electron Microscopy Data Bank (EMDB) Team Leader.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
25 January 2024
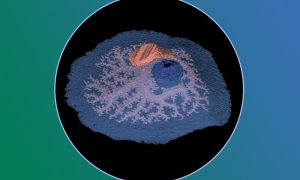
Sponges lack muscles and neurons. Yet, they make coordinated movements. Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg have discovered that sponge movement is controlled by an ancient ‘relaxant-inflammatory’ response that is also present in vertebrate blood vessels. The findings shed light on sponge physiology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
sciencescience-technology
23 January 2024

EMBL’s link to other sciences and its tradition of collaborative discovery carry on, providing the model and means to address big challenges, including climate change and biodiversity loss.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
15 January 2024

A pivotal conversation 20 years ago led to the creation of the iconic 'double-helix building' that is EMBL's Advanced Training Centre.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2024
connectionslab-matters
9 January 2024

Latvia’s life sciences sector will benefit from expanded access to the leading European research, services, and training provided by EMBL.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2024
embl-announcementslab-matters
2 January 2024

Approximately 300 scientists met up at EMBL Heidelberg to unravel the centuries-old puzzle of cancer through the modern lens of genomics.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
eventsscience-technology
21 December 2023
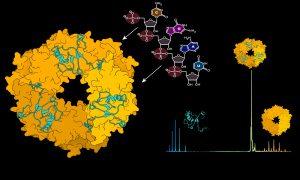
The Kosinski Group at EMBL Hamburg collaborated with other groups in Hamburg to reveal critical steps in Lassa virus ribonucleoparticle assembly and recruitment, and the crucial role played by RNA in in the Lassa virus life cycle.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
20 December 2023
Researchers reveal that healthy lung development hinges on immune-epithelial crosstalk, with implications for respiratory diseases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
research-highlightsscience-technology
20 December 2023
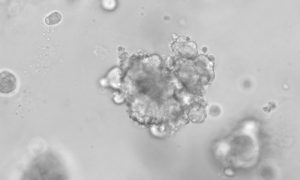
A new organoid model mimics the behaviour of neuroendocrine tumours (NETs), providing a novel and invaluable tool to study the disease in the lab.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
19 December 2023

EMBL Hamburg, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Postnova Analytics GmbH, and BioNTech SE have developed a new method to quantitatively investigate sizes of nanoparticles containing mRNA. It may become an important part of regular characterisation of mRNA nanomedicines in the future.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
18 December 2023

The two institutions celebrated the renewal of the partnership agreement initiated in 1999 for the delivery of a doctoral degree and a joint training certificate during UGA’s Welcome Day for doctoral students.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
14 December 2023

EMBL Hamburg is located at the PETRA III synchrotron, which in the future, will be upgraded to PETRA IV. Selina Storm is theEMBL@PETRA IV Programme Manager. Here, she speaks about her role and the benefits of PETRA IV for EMBL.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
14 December 2023
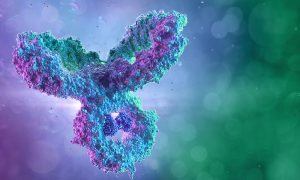
Former EMBL staff scientist founds a start-up – DenovAI – for broader, faster and cheaper antibody discovery using advanced machine learning and computational biophysics.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
13 December 2023
Victor Armijo, a mechatronics engineer at EMBL Grenoble, talks about his dream job, highlighted in EMBL’s exhibition ‘The World of Molecular Biology’.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
12 December 2023

The Barcelona Collaboratorium celebrated a milestone as it hosted the EMBO Practical Course ‘Computational modelling of multicellular systems'.
CONNECTIONS
7 December 2023

A recent success story of the Alumni Mentorship Programme is that of Luis Pedro Coelho, a Portuguese former postdoctoral fellow in the Bork Group, and his mentor Frank Gannon, former EMBO Director and EMBL Group Leader and Senior Scientist.
LAB MATTERS
29 November 2023

The new initiative brings together genomic data from various biodiversity projects to aid conservation and biodiversity efforts.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
announcementssciencescience-technology
27 November 2023

EMBL alumnus Roel Wijnaendts looks back at a long career in academic research and entrepreneurship that has left an indelible mark in the fields of instrumentation and optics.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
alumnipeople-perspectives
27 November 2023

An interdisciplinary collaboration between Hamburg scientists has yielded new insights into the structure and function of a heat-resistant enzyme from an exotic microbe. In this interview, EMBL Hamburg’s Matthias Wilmanns and TUHH’s Garo Antranikian discuss how their collaboration developed and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
24 November 2023

Representatives from politics, research and the philanthropist community joined the Minister's visit to EMBL exhibition “The World of Molecular Biology” in Heidelberg and welcomed the dialogue between science and society initiated by the exhibition.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
23 November 2023

Alba Diz-Muñoz and Arnaud Krebs from EMBL Heidelberg have received grants to work on projects that aim, respectively, to understand the cellular mechanics that control cell division and investigate the regulatory networks that govern transcription factor function.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
22 November 2023

EMBL scientist Oliver Stegle explains how AI-based tools have the potential to transform our ability to better understand the complexity of life and how these tools will shape the future of life science exploration.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
17 November 2023

The TREC expedition has come to the end of its first phase. The last superstop of 2023 was hosted by CIIMAR in Porto and, despite the adverse weather conditions, included many scientific and public engagement activities.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
16 November 2023

The newest issue of our online magazine dives deep into a critical research direction in developmental biology, structures of promiscuous proteins, EMBL’s newest service offerings in field research, and much, much more.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
16 November 2023

A new study from the Asari group at EMBL Rome shows a different retinal function in awake mice compared to isolated retinal samples. These new insights could help to develop prosthetic devices that can act as a retina in the future.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
15 November 2023

On this date (15 November), 21 years ago, the EMBL, ESRF, ILL, and IBS directors signed a memorandum of understanding to create the Partnership for Structural Biology (PSB) on the European Photon and Neutron (EPN) science campus in Grenoble.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
14 November 2023
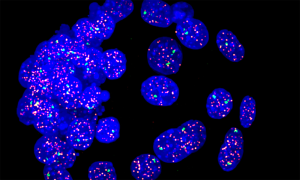
A recent EMBO | EMBL symposium brought together leading developers of imaging methods with cutting-edge applications that illustrate how imaging can answer biological questions.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
eventsscience-technology
10 November 2023

A celebratory event at the Maritime Museum Bilbao marked the partnerships that make possible the TREC expedition on land and at sea along the European coast.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
8 November 2023

Scientists from the MELIS department at UPF and EMBL Barcelona have organised a symposium to discuss the work of the visionary Catalan scientist Pere Alberch, who passed away 25 years ago.
CONNECTIONS
7 November 2023

EMBL in Spain 2023 was held in Bilbao on Friday 9 October, hosted at the Center for Cooperative Research in Biosciences (CIC bioGUNE).
CONNECTIONS
7 November 2023

EMBL Grenoble was once again present for the science outreach event ‘Parvis des Sciences’ on Saturday 14 October 2023.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
1 November 2023

In this interview, Sihyun Sung, Postdoctoral Fellow at EMBL Hamburg, talks about making molecular movies with time-resolved serial X-ray crystallography, his sources of inspiration, and the value of forging deeper connections with friends and colleagues.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
31 October 2023

Ian Smith, Chair of EMBL Australia´s Council, chats about the synergies between the organisations, opportunities for collaboration, and ideas for exciting new programmes arising out of a recent visit to EMBL Heidelberg.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
30 October 2023

EMBL participated in the recent Science and Innovation Days in Podgorica, Montenegro, sharing its passion for knowledge and curiosity.
CONNECTIONS
27 October 2023
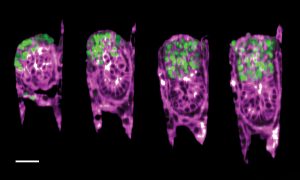
EMBL researchers have created an engineered uterus that allows a closer look at a mouse embryo’s development and its interactions with the uterine environment.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
picture-of-the-weeksciencescience-technology
26 October 2023

Jan Kosinski, Julia Mahamid, and Georg Zeller have received grants to enable ambitious projects aimed at mapping the cellular protein synthesis machinery in context and understanding complex host-microbiome interactions, respectively.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2023
embl-announcementsscience
26 October 2023
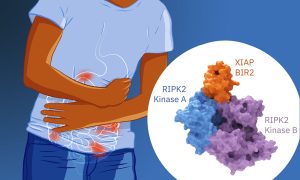
Researchers from the Cusack group at EMBL Grenoble provide structural insights on the XIAP/RIPK2 complex, a promising drug target to fight inflammatory bowel diseases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
24 October 2023

EMBL gathered together government, industry, and academic researchers to explore how to leverage the power of AI and machine learning to advance research.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
24 October 2023

EMBL stands as a leader, exemplifying how to harmoniously integrate AI in research and through its delivery of data services.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
23 October 2023

Victoria Yan, Open Science & Research Information Specialist, talks about the importance of open science, the challenges she has faced in her career, and what she enjoys about working at EMBL
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
20 October 2023

Here are six takeaways from a recent EMBO/EMBL symposium that brought together scientists to discuss the state of research involving the human microbiome and its connection to health and disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
eventsscience-technology
18 October 2023

Elena Conti will discuss how cells control the life and death of mRNA molecules at the 2023 annual Kafatos Lecture on 20 October in Munich.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2023
alumniembl-announcements
17 October 2023
In an extensive investigation, EMBL researchers have tested over 10,000 drug combinations against some of the leading pathogenic bacteria carrying antimicrobial resistance and causing mortality.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
16 October 2023

Gerald Pfister, Head of the Flow Cytometry Facility at EMBL Rome, talks about his private and professional passions and a return to his roots as part of the TREC project.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
13 October 2023

A two-week practical course introduced participants to the intricacies of studying the dynamic interplay between organisms and their changing environment and how it impacts development and evolution.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
lab-mattersscience-technology
9 October 2023

EMBL Rome celebrated the European Researchers’ Night by participating in an event organised at the CNR Campus in Montelibretti.
LAB MATTERS
6 October 2023

Zuzana Koskova is a PhD student from Slovakia who, at the age of 19, left her country to pursue her career in biological sciences in Germany. In this interview, she talks about her interests, career aspirations, and recent participation at the Info Day held in Bratislava, where she had the…
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
5 October 2023
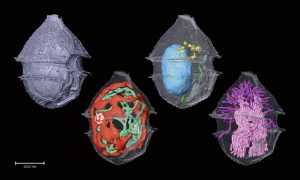
A new method developed by EMBL scientists can help us identify and investigate plankton species in field samples with greater speed, accuracy, and resolution than ever possible before.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
2 October 2023

Pioneers of the mRNA nanomedicines technology receive 2023 Nobel Prize in Physiology or medicine. EMBL is pleased to have supported the development of the application of the mRNA nanomedicine technology through our long-standing collaboration with BioNTech, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
28 September 2023

EMBL receives the German AI prize awarded for outstanding services to the research and development as well as application and commercialisation of artificial intelligence (AI) in life science research.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2023
embl-announcementsscience
27 September 2023

Structural biologist Shlomo Trachtenberg has made research trips to EMBL from Israel since the late 1970s and reflects on the boost EMBL’s technology provided his research, the ingredients for an ideal research institution, and his ongoing fascination with microscopes.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
25 September 2023

PhD student Valentina Lorenzi is using single-cell sequencing data to create a map of the developing human reproductive system.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesperspectives
21 September 2023
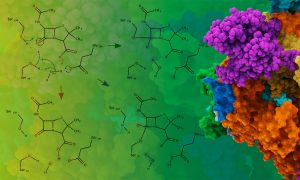
Enzymes constitute a large fraction of genomes – 20% in humans – which makes them a very important part of life. Despite decades of studies and a rich literature dedicated to understanding the reaction mechanisms of enzymes, the rules of enzyme catalysis are still not fully clear. A new…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation
21 September 2023

The 12th annual meeting of the Nordic EMBL Partnership for Molecular Medicine took place in Espoo, Finland, between 11-14 September 2023.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
21 September 2023

David Hulcoop discusses how his experience bridging organisational cultures will help address critical challenges in drug discovery and target selection at Open Targets.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
announcementslab-matterspeople-perspectives
20 September 2023

Thomas Haize talks about his passion for the ocean, what TREC means to him, a day in the field, and the captivating beauty of underwater photography.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
19 September 2023

Ensembl Variant Effect Predictor integrates Google DeepMind’s new AlphaMissense Database for better predictions of genetic variant pathogenicity.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation
18 September 2023
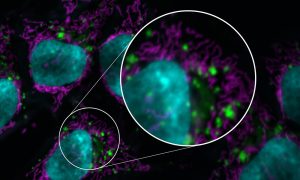
A working group of researchers from the QUAREP-LiMi initiative has developed global guidelines to improve the quality of microscopy data and images published in scientific publications.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
15 September 2023

Researchers from across the globe have gathered in Grenoble to celebrate the remarkable lifelong scientific achievements of Stephen Cusack, the former head of EMBL Grenoble.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
eventspeople-perspectives
15 September 2023

EMBL Grenoble and University of Geneva researchers shed light on the molecular activation of the MAP kinase p38α, the final ‘switch’ triggering the inflammatory response.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
14 September 2023
New research improves understanding of the molecular mechanisms behind why some cancers respond to immunotherapy and others don't.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
13 September 2023
Researchers use the AlphaFold database and Foldseek Cluster algorithm to analyse millions of predicted protein structures and offer new insights into protein evolution.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
13 September 2023
EMBL researchers have identified a novel mechanism that allows cells to sense obstacles in their path and avoid them while navigating complex environments.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
13 September 2023

Learn more about the game-based workshop that lets participants experience what it feels like to be a researcher on the TREC expedition.
LAB MATTERS
8 September 2023

As part of the EMBL-led Traversing European Ecosystems (TREC) expedition, scientists are studying plankton to understand biodiversity, health, and our planet’s future.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
lab-mattersscience-technology
8 September 2023

Sabrina Krueger, scientist-turned-training officer, shares her approach to this role and the need to be ‘true to yourself’.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
7 September 2023

EMBL Director General and Deputy Director General respond to the announcement by the European Commission and UK Government
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
announcementsembl-announcementslab-matters
6 September 2023
Learn how scientists use bio-SAXS, an experimental X-ray technique, to study the shape and dynamics of proteins and other biomolecules. SAXS can be even used to analyse the structure of mineral particles in the swordfish sword bone, which can help scientists better understand bone ageing.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
5 September 2023

Jordi van Gestel and Maria Zimmermann-Kogadeeva each receive 1.5 million EUR funding for research projects on microbial predators and the gut microbiome respectively
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
31 August 2023
For a fruit fly embryo to develop correctly, key factors need to get to the right place at the right time – a journey that starts in the developing egg, as seen in this image from the Ephrussi Group at EMBL Heidelberg
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
picture-of-the-weeksciencescience-technology
29 August 2023

Therese Welander talks about her inspiration, and supporting science by solving problems and overcoming challenges.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
24 August 2023

Elena Conti will discuss how cells control the life and death of mRNA molecules at the next annual Kafatos Lecture on 20 October in Munich.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
alumniscience-technology
22 August 2023

Ukrainian scientist Sergiy Avilov uses the microscopy skills and scientific network he built at EMBL in his current role heading the Imaging Facility at the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
alumnipeople-perspectives
21 August 2023

Experience in data management and coordination has enabled EMBL alumna Laura Clarke to pursue a career in AI development.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
people-perspectivesperspectivesscience
18 August 2023

An upcoming EMBL-led infrastructure management training will help formalise information exchange in the Rhine-Neckar region to widen access to technology and scientific services for members of the Health + Life Science Alliance.
CONNECTIONS
16 August 2023

Emerald Perlas, Head of the Histology Facility, talks about his experience in supporting multidisciplinary research at EMBL Rome and keeping up with technological advances.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
14 August 2023

EMBL-EBI Senior Scientist Rob Finn explains why data coordination and sharing are fundamental for a sustainable blue economy.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
people-perspectivesperspectivesscience
10 August 2023
SComatic enables researchers to link genotype to phenotype using only single-cell profiling data
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
8 August 2023

Clément Blanchet has been appointed to lead the team working on small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) at EMBL Hamburg. In this interview, he talks his ambitions for the future work of the SAXS Team, his passion for science, and a memorable ‘aha’ moment he had in his early career.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
3 August 2023

EMBL’s newly deployed Advanced Mobile Laboratory (AML) is bringing cutting-edge technologies to the European coast to help researchers study ‘life in context’.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
lab-mattersscience-technology
1 August 2023

By upskilling researchers on bioinformatics skills and tools, EMBL alumna Emily Perry is helping to make genomic medicine more accessible.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesperspectives
28 July 2023

EMBL organised a five-day summer school to help PhD students and postdocs learn more about research and development (R&D) related industry career roles.
LAB MATTERS
26 July 2023

The first EMBO Practical Course on imaging-based spatial-omics was organised at EMBL Rome to explore the latest techniques to visualise RNA transcripts and proteins in their native tissues.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
lab-mattersscience-technology
24 July 2023
EMBL researchers have made new strides into understanding and reversing genetic defects that underlie familial heart disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
21 July 2023
Research from the Eustermann group at EMBL Heidelberg reveals how the packaging of DNA into hexasomes impacts the function of enzymes involved in gene regulation.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
17 July 2023

Rutuja Yelmar, predoctoral Fellow at EMBL Grenoble in the Kowalinski group, talks about her passion for research, daily inspiration, and the importance of collaboration in achieving her goals.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
14 July 2023

EMBL researchers use a new cell sorting technology to gain new insights into cellular function in health and disease, as well as for other innovative applications.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
12 July 2023

Construction begins on EMBL-EBI's new building named after Janet Thornton.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
announcementsembl-announcementslab-matters
10 July 2023
This single-celled organism the size of a dust particle is capable of causing deadly tropical diseases in both humans and livestock –Trypanosoma brucei, in an image by Luciano Dolce from EMBL.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
lab-matterspicture-of-the-weekscience-technology
7 July 2023
A collaboration between EMBL Grenoble and EBRIS scientists led to the characterisation of a new compound with promising activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
6 July 2023

Through the collaborative framework agreement, EMBL and ZEISS aim to accelerate the development of imaging technology to advance life science research.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
6 July 2023
Closer collaborations with EMBL-EBI data resources set to further develop and grow this unique rare disease platform.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2023
announcementsembl-announcementsscience
5 July 2023

Enabling researchers worldwide to share and analyse pathogen data generated across the world
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation
5 July 2023

Coming from a pharmaceutical industry background, David Hulcoop is set to take over as Executive Director of the public-private partnership Open Targets.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2023
announcementsembl-announcements
5 July 2023

EMBL’s 2022 Annual Report is now available online, including a downloadable ‘Year in Review’.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
4 July 2023

Three EMBL group leaders and six EMBL alumni were recognised for their contributions to the life sciences.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
4 July 2023

EMBL will celebrate its 50th anniversary in 2024 with a dynamic scientific symposium. The event will share fundamental research that continues to open the way to scientific discoveries.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2023
embl-announcementsevents
3 July 2023

A third of all known proteins are either completely or partially unstructured. EMBL scientists contributed to a new set of guidelines – Minimum Information About a Disorder Experiment (MIADE) – that will help researchers share data on unstructured proteins in a more useful way and will enable…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
29 June 2023

Wolfgang Huber discusses why research assessment needs reform and how this could make science more diverse, more inclusive, and better
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
28 June 2023

Starts three-year process toward full membership, opening up new opportunities for mutual exchange and collaboration.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
28 June 2023

EMBL Rome alumna Urtė Neniškytė returned to her native Lithuania, helping establish the Vilnius University-EMBL Partnership Institute and advance genome-editing technologies there.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
alumnipeople-perspectives
27 June 2023

HoloFood, the first consistent collection of multiomic data about chicken and salmon gut microbiomes, set to enable the development of better animal feeds.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation
26 June 2023

The TREC expedition stop in Sopot offered an opportunity to create connections with Polish scientists and citizens around the topics of planetary biology and ocean science.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
22 June 2023

Sihem Bennour, new head of HR, foresees a deeper culture of information sharing, listening, and problem solving with EMBL staff.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
20 June 2023
Researchers from the Ebisuya Group at EMBL Barcelona have used an unprecedented stem cell zoo to compare six different mammalian species and their developmental time.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
14 June 2023

Jürgen Bauer talks about translating science into applications with societal benefit, his journey from the lab bench to business development, and technology transfer at EMBL.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
13 June 2023

A recent EMBL conference brought together scientists from various disciplines to conjoin scientific pursuits studying ‘life in context’.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
eventsscience-technology
13 June 2023

Adriana Castillo Caballero talks about her curiosity-driven career, the importance of the people in her life, and her dreams for the future
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
9 June 2023

TREC scientists, outreach specialists, and a crucial support team have been on the road, exploring life at European coasts.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
8 June 2023

EMBL-EBI data resources are being used to deliver thousands of genetic diagnostics to patients every month.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
perspectivessciencescience-technology
7 June 2023

In recognition of Janet Thornton’s retirement, we look back at some of her biggest accomplishments shaping the field of bioinformatics.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
announcementslab-matterspeople-perspectives
2 June 2023

During a visit to the Heidelberg EMBL campus, Minister Petra Olschowski learned about EMBL´s current research programme, its scientific operations and local collaborations, and explored its Imaging Centre and World of Molecular Biology exhibition.
CONNECTIONS
2 June 2023

A new tool for the interpretation of missense variation in humans – ProtVar – will help enable drug discovery.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation
31 May 2023
EMBL researchers and collaborators have begun an impactful innovation-development journey, thanks to a European Commission ‘IMAGINE’ grant.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
30 May 2023

The annual meeting organised by Italian EMBL alumni was held in Turin on 18-19 May, hosted by the University of Turin and the University of Piemonte Orientale (UPO)
CONNECTIONS
29 May 2023

The third meeting between EMBL and SciLifeLab communities took place in Uppsala and focused on data science, aiming at further expanding the collaboration
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
26 May 2023

European Commission and EMBL renew commitment, agree on new areas of cooperation, in new EC DG’s first infrastructure visit since appointment.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
26 May 2023
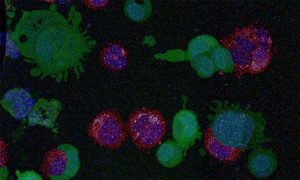
The PLAST-CELL project aims to understanding cancer progression by quantifying a cancer cell’s ability to respond to environmental stress that threatens its survival
CONNECTIONS
2023
connectionstechnology-and-innovation
25 May 2023

From biking together while at EMBL to assistant professorships at Heidelberg University, two academics soon formed a union that took them to the United States., into various industry positions, and now to a life with two young children.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
alumnipeople-perspectives
23 May 2023

Martin Pelosse, Scientific Expert at EMBL Grenoble Eukaryotic Expression Facility, explains the platform’s role in supporting the site’s cutting-edge research activities and its future applications.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
22 May 2023

Postdoctoral researcher Carolin Sauer is leveraging long-read sequencing to develop new detection methods for various cancers.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesresearch-highlights
16 May 2023

Timothy Shayers talks about his role in overseeing the renovation works at EMBL Rome, his past experiences around the world, and his personal passions.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
15 May 2023
First published in 1999 as a black-and-white printed newsletter for EMBL staff and alumni, EMBLetc. has undergone many transformations in its 24 years of existence.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
11 May 2023
EMBL´s new permanent exhibition ‘The World of Molecular Biology’ in Heidelberg is now open for registration. The exhibition takes the visitor on a journey of scales, from genomes to ecosystems, and introduces key imaging technologies.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
11 May 2023
Understanding chromothripsis offers insights into how cancer develops.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
research-highlightsscience-technology
10 May 2023

The human pangenome – one of the most complete collections of genome sequences released so far – captures rich human diversity.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
announcementssciencescience-technology
10 May 2023

EMBL Hamburg scientists have contributed to the development of the Spitrobot, a ground-breaking experimental setup that will simplify creating molecular movies. The Spitrobot automates the sample preparation for time-resolved crystallography, which is used to create 3D snapshots of protein…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
5 May 2023

Dey Group holds second annual ‘labbatical’ to step outside daily research tasks with the help of single-celled model organisms.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
lab-mattersscience-technology
4 May 2023

Vizgen, the life science company dedicated to improving human health by visualising single-cell spatial genomics information, has joined EMBL’s Corporate Partnership Programme.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
3 May 2023

EMBL-EBI is making a key contribution to a historic effort to understand the function of every human gene
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
announcementslab-mattersscience-technology
2 May 2023

The Nordic EMBL Partnership for Molecular Medicine celebrates the signing of its renewed ten years agreement between EMBL and the Universities of Aarhus, Oslo, Umeå, and Helsinki.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
28 April 2023

Croatian scientists and students from the Ruđer Bošković Institute and University of Zagreb visited EMBL to exchange ideas with researchers and public outreach experts on ways to increase interest, awareness, and involvement in science.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
28 April 2023

On Friday 21 April 2023, EMBL held a graduation ceremony to celebrate its newest group of PhDs who graduated during the last 12 months. The graduating class comprised 43 fellows representing 17 nationalities and all six EMBL sites.
LAB MATTERS
25 April 2023

On the 20th anniversary of the Human Genome Project, we look back at its history, wonder and potential.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesperspectives
20 April 2023

EMBL Hamburg partners with the Hanseatic Life Science Research Infrastructure Consortium (HALRIC) to enhance life sciences research in Scandinavia and northern Germany. The consortium builds on the HALOS project to foster collaborations between industry, hospitals, and universities, leveraging…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
20 April 2023

Angelika Thomasson, administrative assistant at EMBL Grenoble, talks about her role in supporting her colleagues in organising events and travels, what she enjoys about EMBL, and which famous female scientist she would like to have coffee with.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
19 April 2023

As a postdoc Alex Almeida used bioinformatics to push the boundaries of what we know about the gut microbiome. Here, Almeida explains how his time at EMBL-EBI generated new research avenues, and how the skills and connections from his postdoc prepared him for leading his own research group at the…
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
people-perspectivesperspectives
18 April 2023

WormBase ParaSite release 18 adds largest number of new genomes and annotations since launch, as well as full integration with AlphaFold.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
science-technologyupdates-from-data-resources
18 April 2023

Nikon Europe has intensified its engagement with EMBL's Corporate Partnership Programme to support young scientists.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
17 April 2023

Alumnus Thomas Graf reflects on his time at EMBL, offering an update on his whereabouts and advice for young scientists.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
alumnipeople-perspectives
12 April 2023

Eduard Avetisyan leads the EMBL Hamburg IT team. He joined EMBL after transitioning from particle physics research to IT. Besides providing standard IT user support, his team also enables smooth processing and computational analysis of structural biology data. Here, he talks about the joys and…
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
11 April 2023

Scientists have the technology to edit the human genome. But when should they, and who contributes to these decisions?
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesperspectives
11 April 2023

EMBL-EBI researchers have developed a new tool capable of performing state-of-the-art phylogenetic inference on larger datasets than previously thought possible.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
11 April 2023

Europe’s life sciences laboratory EMBL on 5 April welcomed Council delegates Ivana Lagator and Lidija Vukcevic from the Montenegrin Ministry of Science and Technological Development, and University of Montenegro representative Professor Danilo Mrdak, to discuss expanding research and training…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionsembl-member-stateslab-matters
6 April 2023

Darwin Tree of Life project improves bioinformatics tools for biodiversity data analysis
CONNECTIONS
2023
connectionstechnology-and-innovation
4 April 2023

EMBL’s planetary biology flagship TREC expedition has officially started. The new project applies EMBL's expertise and technologies in molecular and cellular biology to current environmental challenges, and connects with a wide range of research disciplines.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2023
embl-announcementseventsscience
4 April 2023

Upcoming EMBO/EMBL symposium provides a forum to explore how organisms function together, and how they react or adapt to changes at different molecular levels.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
eventsscience-technology
3 April 2023

Home to some of Europe’s most cutting-edge tools in molecular biology, EMBL has long shared its expertise and access to these tools through an extensive repertoire of courses, conferences, seminars, and other training. And now included in this mix is a job shadowing programme at EMBL Imaging…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
lab-mattersscience-technology
30 March 2023
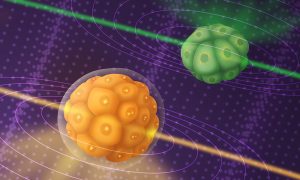
A new microscope built by EMBL researchers, based on Brillouin scattering principles, allows scientists to observe the dynamics of mechanical properties inside developing embryos in real time.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
lab-matterssciencescience-technology
30 March 2023

Interim head of EMBL Rome Cornelius Gross has been awarded an Advanced grant from the European Research Council (ERC) for his project TERRITORY, aimed at investigating the neural basis of territorial aggression and fear.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
27 March 2023

Audrey Spielmann, Lab Support Manager, talks about her role in supporting the research done at EMBL Grenoble.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
23 March 2023

The new group leader is setting up the first purely theory-focused research group at EMBL Barcelona. He aims to understand fundamental biological principles using mathematical models and computer simulations, in close collaboration with experimental researchers across EMBL.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
23 March 2023

Scientists from EMBL and its French academic partners gathered at EMBL Rome for a workshop to foster collaboration and advance research in neuroscience.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
21 March 2023

New group leader Thomas Quail studies the fundamental processes that determine how proteins organise the genome inside a cell.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
20 March 2023

Together with his team, Gergely Papp pushes the frontiers of technology development in the field of structural biology.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
17 March 2023

Biological X-ray imaging is an emerging technology that uses X-rays to image tissues or even entire organisms. It will play an important role in EMBL Hamburg’s future service portfolio, and will allow studying life on multiple scales. Team Leader Liz Duke discusses her plans to establish X-ray…
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
15 March 2023

EMBL’s site by the sea completed its fifth year of operations. We look back at some key milestones and achievements since 2017.
LAB MATTERS
13 March 2023

An annual Corporate Partnership Programme meeting provided a forum for EMBL researchers and industry representatives to discuss mobile labs, planetary biology, and other areas of common interest.
CONNECTIONS
8 March 2023

EMBL is leading the TREC project: the first pan-European and cross-disciplinary effort to examine life in its natural context.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
7 March 2023

On the occasion of International Women’s Day 2023, EMBL archivist Maria Papanikolaou discusses the traces left by the women in science who have passed through EMBL, irrevocably changing the organisation in small and big ways.
LAB MATTERS
3 March 2023

EMBL’s French site was highlighted in a short film presenting its expertise in structural biology research and services.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
1 March 2023

Physicists, engineers and robotics experts work together in EMBL Hamburg’s Instrumentation Team to design instruments that support structural biology research. The team has finished a transfer robot that facilitates automated handling of protein crystals with care and precision. This will help…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
lab-mattersscience-technology
23 February 2023
Researchers in the Prevedel Group use photoacoustic spectroscopy setup to test and optimise probes before their usage in mouse neuroscience.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
lab-matterspicture-of-the-weekscience-technology
22 February 2023

Jo McEntyre talks about data services, open data and a new era for research assessment.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesperspectives
20 February 2023

The Baltic nation of Estonia has become a full member of EMBL, joining the organisation as its 28th member state.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
16 February 2023

EMBL is one of the partners of this project that aims to accelerate drug discovery and development, bringing in expertise from EMBL Grenoble and EMBL-EBI.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
lab-mattersscience-technology
15 February 2023

EMBL Hamburg’s Sample Preparation and Characterisation (SPC) Facility offers scientists access to almost all available biophysics technologies. The facility’s staff provides advice and support with experiments and data analysis. The facility is conveniently located just next to the EMBL…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
lab-mattersscience-technology
13 February 2023

Group Leader Hanh Vu studies ‘immortal’ flatworms that can grow and de-grow to understand better factors that determine organisms’ sizes.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
11 February 2023

A recent student visitor shares her impressions from visiting EMBL’s Vincent group as we recognise International Day of Women and Girls in Science.
LAB MATTERS
7 February 2023

One of EMBL’s core missions is the development and transfer of scientific know-how and technologies to academia, industry, and commercial entities to facilitate further research, innovations, and commercialisation for the benefit of society at large. Working across Europe, EMBL has partnerships…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
7 February 2023
EMBL Grenoble scientists provide new insights into the function of an essential RNA editing enzyme.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
31 January 2023

EMBL Rome group leader Jamie Hackett receives EUR 2 million for the ModLogic project, aimed at understanding how chromatin modifications impact gene activity.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
27 January 2023

New agreement with UN organisation will enable cooperation in the fields of open science, capacity building, and talent development
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
26 January 2023

Open Targets is using artificial intelligence and machine learning to identify and prioritise drug targets.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation
25 January 2023

EMBL hosts inaugural meeting for major interdisciplinary project designed to boost understanding of ocean life
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2023
connectionslab-matters
23 January 2023

The group leader, together with three other principal investigators, has been awarded the ERC Synergy Grant, one of the most prestigious public grants in Europe.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
20 January 2023

Tasmanian flatworms add to an EMBL researcher’s collection as she studies principles that control animal body size.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
lab-matterspicture-of-the-weekscience-technology
19 January 2023
Mucus present in the mouse colon can be visualised using Alcian blue staining, as imaged here by EMBL predoctoral fellow Linda Decker.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
lab-matterspicture-of-the-weekscience-technology
16 January 2023

We look back through some of the 2022 highlights from the Darwin Tree of Life project.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
perspectivessciencescience-technology
11 January 2023

Rob Finn, one of the co-chairs of the Microbial Ecosystems theme, discusses his work, the challenges of multidisciplinary research, and how the theme is already helping to promote the exchange of scientific ideas.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
9 January 2023
EMBL Grenoble researchers have investigated the interaction between THC and some proteins it might bind to. In a recent study, they showed in vitro that THC inhibits an important human enzyme called autotaxin.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
4 January 2023
EMBL Heidelberg researchers and their collaborators reveal how the nuclear pore complex, one of the biggest molecular machines in eukaryotic cells, is assembled one protein at a time.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
3 January 2023
A new method developed by EMBL-EBI researchers helps to streamline nanopore sequencing in real-time.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
23 December 2022

Zebrafish embryos during gastrulation, a very early stage of development, to study the effect of temperature on vertebrate embryo development.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
lab-matterspicture-of-the-weekscience-technology
21 December 2022

To identify which drugs disrupt bacterial envelope integrity, the Typas group uses a molecule called chlorophenyl red-β-D-galactopyranoside.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
lab-matterspicture-of-the-weekscience-technology
20 December 2022

Europe-wide project studies coastal and marine biodiversity from viruses to whales
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2022
connectionslab-matters
19 December 2022

The Director General of EMBL was elected by her peers to become a member of one of France’s oldest national science academies.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
12 December 2022

In October 2022, EMBL Grenoble participated in the annual science outreach event Parvis des Sciences, organised by the GIANT campus under the umbrella of the French science week – La Fête de la science.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2022
connectionslab-matters
8 December 2022

EMBL alumnus and eminent molecular biologist Peter B. Becker has been named the next chair of EMBL’s Council as of January 2023.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
7 December 2022

EMBL’s EIPOD-Learning in Context programme focuses on interdisciplinary research that explores ‘life in context’ and adds a new collaborative dimension with member state organisations.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
1 December 2022
Recent studies supported by EMBL Grenoble’s expertise in structural biology research and scientific services have identified Altiratinib as a potential drug to stop toxoplasmosis infection and opened up treatment options against malaria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
30 November 2022

The new group leader in Barcelona aims to understand how cells behave in health and in disease, and approaches her favourite hobby, cooking, very similarly to her work in the lab.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
28 November 2022

A recent EMBO|EMBL symposium provided a forum for discussing recent research on a range of issues for organisms as they cope with changing environments.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
eventsscience-technology
22 November 2022

Three EMBL scientists received this year’s ERC Starting Grants, and will be awarded €1.5 million over five years to carry out research projects.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
21 November 2022

Looking to understand microbial predator-prey relationships, EMBL’s newest group leader tackles a molecular ‘arms race’ in his lab.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
18 November 2022

The biannual magazine that highlights EMBL’s research, people, and projects now has a new online home.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
18 November 2022

DANEMO is a communication platform and research support initiative launched by DANDRITE at Aarhus University. It aims to encourage scientists in Denmark to engage with EMBL and EMBO. The DANEMO symposium from 3-4 November in Aarhus focused on raising awareness of the new EMBL programme ‘Molecules…
CONNECTIONS
17 November 2022

EMBL deepens scientific collaboration, opening the door for greater engagement and opportunities for Malta’s life science community
CONNECTIONS
3 November 2022

Researchers and engineers have integrated a CrystalDirect harvester into the fully automated beamline MASSIF-1, a unique combination of structural biology technologies that is now open to external academic users.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
lab-mattersscience-technology
27 October 2022

Newly appointed member of the ASAPbio Board of Directors, EMBL Group Leader Gautam Dey speaks about preprints, data management, and open science.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
21 October 2022

After a postdoc at Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel, Flora Vincent has joined EMBL’s Developmental Biology unit to further explore the world of phytoplankton.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
20 October 2022

The recent construction of the new ID29 beamline in Grenoble is pioneering a new way of doing experiments in time-resolved crystallography and opening up technology transfer possibilities
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
lab-mattersscience-technology
13 October 2022

The Royal Microscopical Society awarded Ardan Patwardhan and Wim Hagen with Scientific Achievement Award
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
12 October 2022

Visit of delegation from the Ruđer Bošković Institute to EMBL Heidelberg marks a new chapter in scientific and institutional cooperation
CONNECTIONS
11 October 2022

The final pilot project in Iceland marked the countdown to the ‘Traversing European Coastlines’ (TREC) expedition to study coastal ecosystems and their response to changes in the environment.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
lab-mattersscience-technology
7 October 2022

Leading scientific research facilities launch the Health + Life Science Alliance Heidelberg Mannheim. The research alliance aims to build the Rhine-Neckar region into an internationally leading biomedical-technological cluster focusing on life sciences, the health economy, and medical technology.
CONNECTIONS
7 October 2022

EMBL's Partnership Conference highlights the value of its networks, bringing researchers together to build new scientific connections.
CONNECTIONS
6 October 2022

The institutes have launched a joint new initiative which aims to make biology as engineerable as an aeroplane or a bridge.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2022
connectionslab-matters
29 September 2022

EMBL reminds teachers of freely available educational resources and workshops just in time for school.
LAB MATTERS
28 September 2022
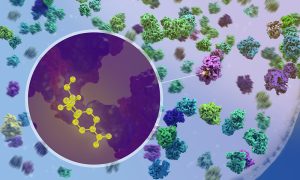
New research by EMBL scientists shows at atomic detail how antibiotics affect the process of protein production inside bacteria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
26 September 2022

Researchers have come up with a way to test the efficacy of hundreds of anticancer drug combinations – simultaneously, rapidly, and accurately.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
23 September 2022

Cell biologist Anthony Hyman and DeepMind’s Demis Hassabis and John Jumper were announced among 25 Breakthrough Prize recipients
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
21 September 2022
The Federated EGA is set to improve access to sensitive human data in a safe and secure way.
CONNECTIONS
2022
announcementsconnectionsscience
21 September 2022

EMBL joined a kick-off event focusing on the developments related to the upgrade of the PETRA III synchrotron storage ring to PETRA IV at the DESY campus, where EMBL Hamburg is located. PETRA IV could open new possibilities at EMBL Hamburg, contributing to the goals of the EMBL Programme…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
lab-mattersscience-technology
20 September 2022

Dieter Schwarz Foundation renews 3-year funding to EMBL for the EMBL | Stanford Life Science Alliance, a unique international collaboration bringing together researchers from the two leading institutions to develop transformative technologies and accelerate biomedical research.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2022
connectionslab-matters
16 September 2022
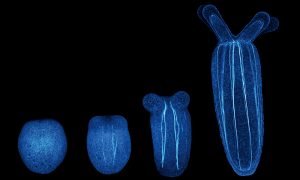
The latest research from EMBL’s Ikmi group employs interdisciplinary approaches to show how sea anemone ‘exercise’ changes their developing size and shape, uncovering an intimate relationship between behaviour and body development
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
15 September 2022

EMBL researchers used data from over 300 human faecal microbiota transplants to gain an ecological understanding of what happens when two gut microbiomes clash.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
12 September 2022

20 secondary school students from all over Italy participated in the fourth edition of Summer in Science at EMBL Rome.
LAB MATTERS
9 September 2022

As the career landscape continues to change for PhDs and postdocs, the EMBL Fellows’ Career Service offers webinars that present professional options in and beyond academia.
LAB MATTERS
7 September 2022

The Scientific Visitor Programme shares EMBL tools and talent with outside researchers in collaborative, multidisciplinary environments.
LAB MATTERS
6 September 2022

A new grant will provide a way for fundamental metabolomic research to realise its commercial potential and promise in aiding drug development and precision medicine.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
lab-mattersscience-technology
1 September 2022
EMBL researchers use a “fearless” computer reconstruction and a two-centuries-old mathematical approach to study limb bud growth.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
31 August 2022
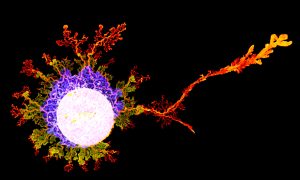
Physarum polycephalum, a single, giant cell containing tens of thousands of nuclei is large enough to be photographed with a phone.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
26 August 2022

EMBL delegation including the Director General visits Iceland marking another stage in this deepening scientific collaboration
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2022
connectionslab-matters
24 August 2022

EMBL’s imaging centre makes advanced microscopy technologies accessible to the international scientific community.
LAB MATTERS
2022
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
22 August 2022

Ewan Birney, Deputy Director General of EMBL and Director of EMBL-EBI, reveals the key factors that enabled AlphaFold to change the world of biology.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
people-perspectivesperspectivesscience
16 August 2022

Virginie Uhlmann, Research Group Leader at EMBL-EBI and one of the co-chairs of the Theory@EMBL transversal theme, chats about how this theme will open up new research avenues.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
12 August 2022
A new method for the robust analysis of copy number variation and used UK Biobank data to identify links between genome and disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
11 August 2022
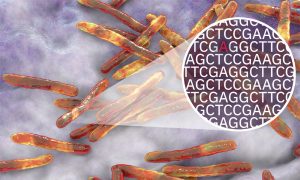
International consortium analyses the genetic sequences and antibiotic susceptibility of 10,000 global Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
9 August 2022

The EMBL Lautenschläger summer school, held 4–15 Jul 2022, introduced students from a range of scientific backgrounds to interdisciplinary life science research.
LAB MATTERS
5 August 2022
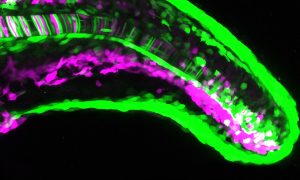
How do gene expression patterns result in the generation of different cell types? Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg used the zebrafish notochord to find out.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
4 August 2022
EMBL and UW researchers plus additional collaborators have constructed a complete map of fruit fly embryonic development using machine learning. This research is foundational to better understanding overall embryo development in other species, including humans.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
1 August 2022
Machine learning has helped researchers uncover new insights into how bacteria infect host cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
28 July 2022

AlphaFold database offers a look at 3D protein universe.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation
27 July 2022

The first meeting of the Latvian Bioinformatics Forum points towards an even brighter future for the country’s role in European life sciences
CONNECTIONS
26 July 2022

EMBL’s site by the sea hosted a trio of conferences this summer, covering topics ranging from vascular biology to engineered living systems to evolution.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2022
connectionslab-matters
22 July 2022

Jan Kosinski, Group Leader at EMBL Hamburg and one of the co-chairs of the Infection Biology theme in EMBL’s new programme, chats about how this theme will support his work and help establish new collaborations.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
20 July 2022

EMBL’s new archive and records manager, Maria Papanikolaou, explains the dual role she and an additional colleague will have in the Office of Science Information Management.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
18 July 2022

EMBL researchers now understand the function of an elusive small DNA in bacteria and have developed a tool that can be used to better understand what might ‘switch on’ bacterial immune defences.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
15 July 2022

The GEEF facility at EMBL Rome supports scientists worldwide with scientific expertise and state-of-the-art gene editing technologies.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
lab-mattersscience-technology
14 July 2022

Microbial communities play essential roles in ocean ecology and planetary health. A recent publication highlights priorities for understanding and protecting ocean microbiomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
13 July 2022

Scientists identify previously unexplored gene segments to be added to human genome databases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
6 July 2022

Cornelius Gross, Miki Ebisuya and Nassos Typas join EMBO, the prestigious organisation for the life sciences.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
5 July 2022

Creating a cutting-edge facility for the global life science community doesn't happen overnight. We spoke to some of those who worked to turn this dream into a reality.
CONNECTIONS
1 July 2022

Representatives from politics, industry and academia attended the inauguration ceremony at EMBL Heidelberg
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2022
embl-announcementsevents
30 June 2022

Participating researchers will lead projects to develop novel technologies for better science.
LAB MATTERS
29 June 2022

EMBL’s 2021 Annual Report is now available, sharing mission highlights from the year in a new digital-first, sustainable format.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
23 June 2022

Former chair of EMBL Council to take office as the next President of the Max Planck Society in June 2023.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2022
alumniembl-announcements
22 June 2022

EMBL Director General Edith Heard joined other L’Oreal-UNESCO Laureates in Paris for a series of events celebrating these outstanding researchers and their contributions.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
21 June 2022

Researchers from EMBL and CSIC came together to discuss microbial communities, diversity, and behaviour, in the context of One Health.
CONNECTIONS
15 June 2022
EMBL research with Enolase 1 (ENO1) points to a possible new way to understand RNA’s leading role in how cells develop.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
10 June 2022

Two days of events with institutes in the country add a new chapter to successful scientific collaboration
CONNECTIONS
10 June 2022
Scientists have solved several mysteries around the structure and function of a true molecular giant: the human nuclear pore complex. They created the most complete model of the complex thanks to combining the program AlphaFold2 with cryo-electron tomography, integrative modelling, molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
8 June 2022

Two former EMBL staff members have been recognised for their outstanding contributions to research in the fields of brain evolution and cancer.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2022
alumniembl-announcements
8 June 2022

The African BioGenome Project and EMBL have signed a Memorandum of Understanding to support each other in building genomics and bioinformatics capacity across Africa
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2022
announcementsconnectionslab-matters
8 June 2022

EMBL and IIT scientists met in person at EMBL Rome to strengthen their collaboration and explore new opportunities for scientific exchange
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2022
connectionslab-matters
7 June 2022

Pascale Cossart, one of the world’s foremost authorities on the biology of Listeria, brings four decades of expertise in intracellular bacterial parasitism to EMBL as a visiting scientist.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
3 June 2022
Researchers have discovered the mechanism by which a family of DNA motor proteins packages loosely arranged strands of DNA into compact individual chromosomes during cell division.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
2 June 2022

A new formal collaboration agreement enables will help smooth the transition from fundamental science to innovation.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2022
connectionslab-matters
1 June 2022
Researchers discover how DNA mutations change blood cell production and how this relates to ageing and cancer development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
1 June 2022

The GSK Vaccines site in Siena hosted the annual EMBL in Italy event. The hybrid meeting brought together industry leaders, representatives from biotech start-ups, data scientists, and researchers from academia.
CONNECTIONS
31 May 2022
Researchers in the Ensembl team are making the most of machine learning methods to speed up genome annotation pipelines
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation
23 May 2022

Fergal Martin discusses the importance of open access data and his work in different biodiversity initiatives
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
21 May 2022

EMBL Director General Edith Heard has been elected as a foreign member of The Royal Danish Academy of Sciences and Letters in recognition of her academic excellence. Heard is among 15 new members of the Academy, which has been advancing basic research and interdisciplinarity for nearly 280 years.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
19 May 2022

Joint workshop brings researchers together on site and virtually to discuss broad range of planetary biology topics.
CONNECTIONS
18 May 2022

Students from the Business Academy Aarhus visit EMBL Hamburg annually. Many of them return later as trainees to gain experience as lab technicians. EMBL Hamburg offers great opportunities to learn diverse techniques and work with various equipment. This experience helps them in their future jobs in…
LAB MATTERS
17 May 2022

Janet Thornton, the inaugural winner of the FEBS Journal Open Science Award, explains the importance and impact of open science.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesperspectives
12 May 2022

How text mining collaborations benefit our research, data resources, and the wider scientific community.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation
11 May 2022

Peter Harrison discusses the importance of data accessibility and his passion for biodiversity and agricultural genomics.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
10 May 2022

EMBL’s Head of Genome Biology announced as Fellow of the Royal Society for her exceptional contributions to science.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
6 May 2022
Researchers at EMBL Heidelberg found that inversions in the human genome are more common than previously thought, which impacts our understanding of certain genetic diseases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
6 May 2022
EMBL researchers revise the old problem of sintering droplets to understand the mechanical properties of tissues.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
5 May 2022

EMBL’s first Imaging Centre Symposium will occur onsite at EMBL and include tours of the new Imaging Centre on 31 May, introducing participants to the facility and its staff and featuring talks on the rapid developments in imaging technologies that have led to notable biological and medical…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2022
embl-announcementsevents
5 May 2022
Virginie Uhlmann shares her tips for using deep learning for bioimage analysis in the life sciences.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
perspectivessciencescience-technology
4 May 2022

The honour recognises distinguished and continuing achievements in original research.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
28 April 2022
Scientists at EMBL Barcelona have created for the first time a 3D in vitro model that recapitulates the periodic formation of human somites – structures that give rise to the spinal column.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
27 April 2022

Professor Kristina Djinović-Carugo has been appointed as the next head of EMBL Grenoble. She will join EMBL in July from the Max Perutz Laboratories at the University of Vienna, where she is currently Head of the Department of Structural and Computational Biology and full Professor of Structural…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
27 April 2022

Slovenian structural biologist Kristina Djinović-Carugo will join EMBL in July as the new Head of EMBL Grenoble. We spoke to her about her background, research interests, and plans for EMBL Grenoble.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
25 April 2022

Ewan Birney discusses the input of both genetics and our environment in making us who we are
LAB MATTERS
2022
lab-mattersperspectives
22 April 2022

EMBO Director Fiona Watt discusses preprints, data sharing, and evaluation in light of EMBL’s new Open Science policy
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
12 April 2022

EMBL and the Sapienza University of Rome confirm their reciprocal interest in intensifying collaborations and launch new opportunities for exchange of expertise
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2022
connectionslab-matters
8 April 2022

Recent studies from the Hackett group at EMBL Rome have revealed new insights on the mechanism regulating transmission of non-genetic information during embryonic development, and inspired a scientific illustration
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
6 April 2022

Researchers from the MANE collaboration bring you the most comprehensive human genome annotation dataset to date.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
6 April 2022

EMBL Heidelberg’s Matthias Hentze receives the Biochemical Society’s Centenary Award for his discoveries in RNA biology.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
30 March 2022

John Lees joins EMBL-EBI as a Group Leader in Pathogen informatics and modelling.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
25 March 2022

After a two-year break, the summer school organised by Adamas Scienza and EMBL in collaboration with CNR is back. It will take place at the International Research Campus of Monterotondo (Rome) from 13 to 24 June 2022.
LAB MATTERS
24 March 2022

Researchers lay out a set of principles for open genomic data sharing or pathogens
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
perspectivesscience-technology
23 March 2022

Condensates are membraneless organelles that control specific functions within a cell. Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg have shown how the physical state of condensates can influence biological function.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
23 March 2022

Zamin Iqbal and his team are working with researchers all over the globe to help put a stop to Tuberculosis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
perspectivessciencescience-technology
21 March 2022

Our researchers highlight their contributions to the Darwin Tree of Life project and how new genome annotations helps to further biodiversity research
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
announcementssciencescience-technology
20 March 2022

Judith Zaugg, Group Leader at EMBL Heidelberg, has been awarded an ERC Consolidator Grant of €2 million funded under the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme. Over the next five years, the grant will enable her group to study cellular interactions in the human bone…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
17 March 2022

EMBL condemns in the strongest terms the unjustified military invasion of Ukraine by the Russian Federation, with the support of Belarus, and the resulting loss of life and human suffering. We express our deepest sympathy to the Ukrainian people and to all the victims of this war. As an…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
17 March 2022

The African BioGenome Project aims to safeguard biodiversity and build bioinformatics capacity across Africa
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
perspectivessciencescience-technology
16 March 2022
EMBL’s imaging technology helps researchers gain insights in the fungus’ journey from the lung to the brain.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
9 March 2022
A molecular signature of 27 microorganisms in stool defines the high-risk population for the most common pancreatic cancer and could be used for early detection of the disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
4 March 2022

EMBL hosted a futuristic infection biology conference, but it offered even more: an opportunity for postdocs to share their work and network towards future research homes.
LAB MATTERS
4 March 2022
Deep learning models can improve protein annotations and has helped expand the Pfam database.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
perspectivessciencescience-technology
4 March 2022

Genomes are made up of thousands of individual pieces – genes – which are expressed at different levels. Researchers at EMBL have shed light on how the placement of a gene affects its expression, as well as that of its neighbours.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
4 March 2022
A recent study by EMBL researchers proposes a new method to grow early embryos in the laboratory. With a 3D culture set-up, scientists can closely monitor the changes embryos undergo around the time of implantation.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
3 March 2022

An exploration of what gender bias looks like in science and how organisations and individuals can address it
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesperspectives
2 March 2022

New study: EMBL PhDs and postdocs develop skills that make them highly employable in roles that drive research and innovation in academia, industry, and other sectors.
LAB MATTERS
2 March 2022

The new permanent ‘The World of Molecular Biology’ exhibition will open in mid-2023 at EMBL’s headquarters in Heidelberg. It will encourage people to actively engage with science and its relevance for everyday life.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
25 February 2022
Researchers from the Furlong group at EMBL have come up with a way to observe the development of fruit-fly embryos simultaneously at the genetic and cellular levels, generating a high-resolution and integrated view of how different cell lineages form.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
23 February 2022

The 11th annual Nordic EMBL Partnership for Molecular Medicine meeting was hosted in virtual format by DANDRITE, the Danish node of the Partnership, from 31 January–2 February 2022. The programme included updates from all partnership nodes, discussions about opportunities for new collaborations,…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2022
connectionslab-matters
23 February 2022

Scientists urge the adoption of a sensible international policy for digital sequence information.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
announcementssciencescience-technology
23 February 2022

Michael Dorrity, one of EMBL’s newest group leaders, is studying how the environment influences early life stages in zebrafish.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
10 February 2022

Open Targets, a consortium focused on drug target identification, prioritisation, and validation, announced today that Pfizer has joined as a partner.
CONNECTIONS
2022
announcementsconnectionsscience
9 February 2022

Agreement signed with Latvia’s Biomedical Research and Study Centre will boost academic exchange and collaboration on some of the largest challenges facing human and planetary health.
CONNECTIONS
8 February 2022
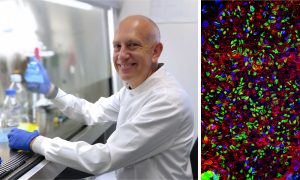
Experiences at EMBL Rome led former group leader to establish his start-up in Italy, developing a new generation of gene therapies.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
alumnilab-mattersscience-technologytechnology-and-innovation
7 February 2022

DeepMind visits EMBL Heidelberg to discuss current and future implications of Artificial Intelligence for life science research.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
1 February 2022

EMBL Hamburg’s Grzegorz Chojnowski from the Wilmanns Group developed software called findMySequence, which identifies proteins’ amino-acid sequences based on electron cryo-microscopy and X-ray crystallography data. It’s useful for identifying unknown proteins in samples from natural sources.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
27 January 2022

Ahead of the annual meeting of the Nordic EMBL Partnership for Molecular Medicine, we spoke with its new Speaker, Mark Daly. Mark Daly, FIMM Director, recently accepted the post of Speaker of the Nordic EMBL Partnership. He explains his vision of the future cooperation between EMBL and the Nordics.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2022
connectionseventslab-matters
24 January 2022
An exploration of where in the world genomics methods are applied and where the data are used.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
perspectivessciencescience-technology
24 January 2022

The new EMBL Imaging Centre held its first on-site training workshop, introducing undergraduate students to the basics of volume electron microscopy. This marks the first of many opportunities to aid capacity-building in imaging techniques in Europe.
LAB MATTERS
21 January 2022
EMBL researchers, in collaboration with BD Biosciences, have demonstrated a new technology that allows rapid image-based sorting of cells. The new technology represents a major upgrade to flow cytometry and has applications in diverse life science fields.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
21 January 2022

On track to reach an ambitious goal of 3,000 genomes sequenced by the end of 2022, what’s next for the Earth Biogenome Project?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
announcementssciencescience-technology
19 January 2022

EMBL announces details about its next programme, ‘Molecules to Ecosystems’. It will guide studying life across scales and in context with changing environments.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
announcementsembl-announcementslab-matters
18 January 2022

The Galej group at EMBL Grenoble has recently obtained high resolution snapshots of a crucial step in RNA splicing involving the U2 snRNP complex, a crucial component of the human spliceosome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
14 January 2022

Melissa Harrison joins EMBL-EBI as the new Team Leader of Literature Services. We found out more about her plans for open access publishing and Europe PMC.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
12 January 2022

A delegation from EMBL has participated in inauguration of a new facility — Incubator House — located in Szeged, Hungary.
CONNECTIONS
10 January 2022

Kristina Haase, Group Leader at EMBL Barcelona, will receive €1.5 million over the next five years to develop her project on 3D vascularised in vitro cardiac tissues.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
4 January 2022
Researchers have identified hundreds of new bacterial species and viruses in the human skin microbiome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
3 January 2022

This year marks the beginning of EMBL’s next programme ‘Molecules to Ecosystems’ to advance the understanding of life across scales and in the context of changing environments.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
22 December 2021

The memorandum of understanding (MoU) signed between EMBL and the Institute for Advanced Biosciences (IAB) a year ago has already catalysed new grants for joint research projects related to cancer and infection biology, thereby deepening collaborative activities.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
21 December 2021
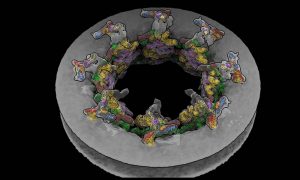
EMBL Hamburg’s Kosinski Group, the Beck Laboratory at the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics, and colleagues at EMBL Heidelberg recorded the nuclear pore complex contracting in living cells. They visualised the movement with an unprecedented level of detail with help of new software called…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
20 December 2021

The agreement focuses on reinforcing the collaboration between scientists to strengthen our understanding of the organism in its environment.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
20 December 2021

Showing a continued commitment to providing a diverse and inclusive organisation for conducting leading molecular biology research, EMBL has launched an Equality, Diversity, and Inclusion (EDI) strategy.
LAB MATTERS
20 December 2021
Using cryo-EM and structural biology techniques, EMBL researchers have shown how two proteins of Legionella pneumophila interact. This finding sheds light on a mechanism critical to the infection process and could lead to the development of new drugs to treat pneumonia.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
17 December 2021

A look back at some of the 2021 highlights from the Darwin Tree of Life partner institutes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
17 December 2021

The systematic application of AI in life sciences as in the AlphaFold algorithm for predicting protein structures has been named '2021 Breakthrough of the Year' by Science magazine.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
16 December 2021

EMBL alumnus Denis Duboule has been selected as the speaker for the inaugural Kafatos Lecture to take place in October 2022.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2021
alumniembl-announcements
16 December 2021

EMBL announces the release of its new Open Science Policy, contributing to positive culture change across the life sciences.
LAB MATTERS
15 December 2021

Bork Group at EMBL Heidelberg analysed a new global gene database to study how genes emerge and spread across various habitats on our planet. In the future, the group will expand the database and use it for studying microbial gene evolution and dispersal at a finer-grained scale.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
9 December 2021
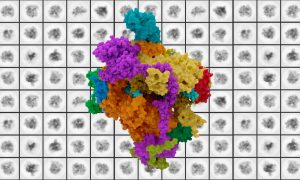
New structural biology research provides fundamental information critical to understanding enzyme mutations connected to rare diseases and cancers.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
9 December 2021

EMBL Senior Scientist and Head of the Genome Biology Unit is among the researchers honoured for outstanding work by the German Research Foundation (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, DFG).
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
9 December 2021

EMBL and the French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) signed a memorandum of understanding.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
8 December 2021
Researchers studying a massive cohort of European patients have found that commonly prescribed drugs for cardiometabolic disorders can have long-term effects on the gut microbiome. Such effects can complicate the understanding of how disease affects the microbiome and must be taken into…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
7 December 2021
RNA vaccines, such as the ones for COVID-19, represent a new approach in vaccine technology. Cy Jeffries, faculty staff scientist at EMBL Hamburg, explains the clever technology behind RNA vaccines, and how structural biology contributes to its development. EMBL Hamburg collaborated on several…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
3 December 2021

The new EMBL Imaging Centre has announced its first open user call, and new project evaluation process and training opportunities.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
2 December 2021
EMBL structural biology is part of an international collaboration addressing zoonotic disease caused by Lassa virus.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
29 November 2021

Using gene editing and three types of microscopy, one of EMBL’s newest group leaders is deciphering the functions of one of the smallest molecules involved in cell division, motility, and signalling, known as a centriole.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
26 November 2021

EMBL has taken another step towards strengthening its scientific relationship with Lithuania.
CONNECTIONS
25 November 2021

Maria Zimmermann-Kogadeeva is one of EMBL’s newest group leaders and a computational biologist whose research group applies computational modelling to better understand the metabolism of gut bacteria and their potential to have far-reaching impacts on other organs.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
24 November 2021

Tudor Groza joins EMBL-EBI as our new Phenomics Team Lead. We found out from Tudor exactly what this new role will entail
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
18 November 2021

The upcoming 22nd EMBL Science & Society Conference will explore the One Health approach, which advocates for greater cross-sectoral collaboration and communication across the human-animal-environment interface.
CONNECTIONS
16 November 2021

How genomics, open data, and multidisciplinary science can improve food security.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
15 November 2021

An alumnus reflects on the reptile database he started in 1996 while at EMBL. The database helps understand biodiversity issues.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
alumniscience-technology
15 November 2021

A new model could serve as a platform to investigate critical placenta barrier phenomena, including defence against bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
lab-mattersscience-technology
14 November 2021

A new life sciences lecture series commemorates the legacy of former EMBL Director General Fotis Kafatos for people around the world.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2021
alumniembl-announcements
13 November 2021

EMBL alum Lara Urban has developed mobile DNA approaches to monitor impacts upon biodiversity in remote areas of New Zealand and elsewhere.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
alumniscience-technology
12 November 2021

Correlative microscopy service enables PhD student from Switzerland to study structure and location of proteins cells use to communicate.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
lab-mattersscience-technology
10 November 2021

The GA4GH Data Use Ontology (DUO) supports a data authorisation and access framework to streamline consent to use biomedical data
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
10 November 2021

Independent impact review finds EMBL experimental services are ‘critical’ for research and endorses EMBL as a world-class service provider for academia and industry.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
lab-mattersscience-technology
10 November 2021
A vast, curated collection of bacterial genomes is now organised, searchable and open to the community.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
9 November 2021

EMBL's PhD and postdoc programmes evolve to the more multidisciplinary way of doing great molecular biology research.
LAB MATTERS
8 November 2021

Each year, EMBL Hamburg’s Svergun Group offers practical EMBO courses and lecture courses on biological small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). The courses provide young scientists an opportunity to gain hands-on experience by measuring their own samples, and by exploring different aspects of SAXS…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
lab-mattersscience-technology
5 November 2021

Ken Holmes, outstanding pioneer of structural biology and founder of EMBL´s Hamburg site, died on 2 November 2021 at the age of 87.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
alumnipeople-perspectives
5 November 2021

What can sponges tell us about the evolution of the brain? Sponges have the genes involved in neuronal function in higher animals. But if sponges don’t have brains, what is the role of these? EMBL scientists imaged the sponge digestive chamber to find out.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
3 November 2021
Scientists at EMBL Hamburg determined the molecular structure of Peptide Transporters 1 and 2. The findings will enable developing drugs that more efficiently pass from the gut to target tissues.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
28 October 2021

Svetlana Dodonova is one of EMBL's newest group leaders, leading a team of researchers who will study how genetic material is organised inside cells using structural biology approaches.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
27 October 2021

Independent study reveals that EMBL-EBI open data resources are critical for the life sciences.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
lab-mattersscience-technology
26 October 2021

The engagement of US and European Big Science facilities
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
26 October 2021

The Darwin Tree of Life project is an unprecedented initiative sequencing 70,000 species
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
26 October 2021

International project uses biomolecular data to improve animal feed and make meat production more sustainable
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
26 October 2021
Using metagenomic data to find novel enzymes for plastic degradation and beyond
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
25 October 2021

EMBL attends COP26 to argue for strategy to involve molecular biology in the Green Recovery
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
25 October 2021

EMBL Hamburg’s Sample Preparation and Characterisation (SPC) Facility has released eSPC, an online platform for analysing data from biophysical experiments. The platform enables the scientific community to analyse data from different experiments without the need to travel.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
22 October 2021
A technology around since the ‘60s, flow cytometry has increasing applications. New leadership at EMBL’s flow cytometry facilities is looking to ease use, expand training, and encourage more collaboration.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
lab-mattersscience-technology
21 October 2021

EMBL has held a joint workshop with the Belgian Science Policy Office, BELSPO, underlining their long-standing collaboration and commitment to future cooperation.
CONNECTIONS
21 October 2021

The BY-COVID project aims to make infectious disease data, including COVID-19, openly available to everyone.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
19 October 2021

Profiling M. tuberculosis strains from 27 countries to reveal causes of drug resistance.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
19 October 2021

Ian Dunham walks us through his career so far including working on the human genome project, seeing his work on the cover of Nature and his current role as Director of Open Targets.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
18 October 2021
Researchers develop a new high-throughput approach to assess the functional significance of protein phosphosites.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
18 October 2021

Professor Edith Heard is among new members elected to US National Academy of Medicine
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
15 October 2021
The Graham and Crump groups at the University of Cambridge and the Svergun Group at EMBL Hamburg have discovered a mechanism by which the herpes simplex virus takes control of the molecular machinery of human cells. Their work reveals how a dedicated viral protein hijacks key host proteins, forcing…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
14 October 2021

Largest in-depth analysis of genomic data tracks the spread of SARS-CoV-2 lineages in England.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
13 October 2021
Researchers from EMBL’s Typas group and collaborators have analysed the effects of 144 antibiotics on the wellbeing of gut microbes. The study improves our understanding of antibiotics’ side effects and suggests a new approach to mitigating the adverse effects of antibiotics therapy on gut…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
12 October 2021

If researchers can identify specifically when good cells go bad, they can potentially understand disease better.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
8 October 2021

The two organisations have signed a memorandum of understanding to support scientific cooperation in the exploration of coastal and oceanic ecosystems.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
7 October 2021

This autumn, students begin their PhD in research groups across EMBL’s six sites.
LAB MATTERS
7 October 2021

EMBL will host a conference to look at the state of the pandemic, lessons learned, and ways to improve pandemic preparedness. Here’s a sneak peek into what promises to be another interesting and informative EMBL conference.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
eventsscience-technology
6 October 2021
Structural biology provides insights into the diverse functions of fibrous protein in humans, amphibians, and bacteria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
5 October 2021

EMBL scientists and colleagues have developed an interactive atlas of the entire marine worm Platynereis dumerilii in its larval stage. The PlatyBrowser resource combines high-resolution gene expression data with volume electron microscopy images.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
4 October 2021

A memorandum of understanding (MoU) has been signed between EMBL and the University of Tartu, a leading centre of research and training. The MoU aims to strengthen cooperation between EMBL and the life science research community in Estonia.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
30 September 2021

Scientists in EMBL’s Prevedel Group have developed a pioneering microscopy technique that allows researchers to observe cells hidden within opaque tissues, such as live neurons embedded deep in the brain.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
29 September 2021

In the lab, Diënty Hazenbrink works with microbes that live in our guts. In her free time, she enjoys wildlife photography. A shared set of skills facilitates both activities.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
28 September 2021

EMBL and Hungarian research institutes will collaborate to address urgent biological and environmental challenges.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
27 September 2021

Hundreds of school children explore the beauty of proteins through art
LAB MATTERS
23 September 2021
Some of the most amazing creatures live in the deep blue sea. The Mesoscopic Imaging Facility (MIF) at EMBL Barcelona was recently involved in studying one unique feature of the octopus: the ephemeral structures on the surface of their skin called Kölliker’s organs.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
22 September 2021

EMBL and Helmholtz Association have signed a memorandum of understanding. The expanded collaboration of both institutions will focus on research related to health.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
20 September 2021

MOrgAna is an open source, user-friendly, modular software that is able to analyse organoids with machine learning.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
17 September 2021
EMBL scientists have found evidence of an unexpected role for retinal cells in pre-processing visual information; their results provide potential opportunity for future prosthetic visual aids.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
16 September 2021
3D-Beacons Network acts as a one-stop shop for protein structures by combining and standardising data from several providers.
CONNECTIONS
15 September 2021

A research collaboration used machine learning to map tumour molecular make-up, potentially paving way to more customised cancer treatment.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
10 September 2021
Packaged for simple installation and free use, the novel method DECODE enables researchers to reduce imaging times and increase localisation density in single-molecule localisation microscopy (SMLM).
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
9 September 2021

Former EMBL Director General Professor Iain Mattaj was awarded the German Cross of Merit (‘Verdienstkreuz 1. Klasse des Verdienstordens der Bundesrepublik Deutschland’) at a ceremony held at EMBL Heidelberg on 9 September 2021.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2021
alumniembl-announcements
9 September 2021

EMBL's science education department makes the latest scientific research more accessible for teachers and students.
LAB MATTERS
8 September 2021
A new collaborative study led by EMBL group leaders Kiran Patil, Nassos Typas, and Peer Bork has found that common medications accumulate in human gut bacteria. This process reduces drug effectiveness and affects the metabolism of common gut microbes, thereby altering the gut microbiome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
7 September 2021

In the Mesoscopic Imaging Facility (MIF) at EMBL Barcelona, researchers study the details of biological systems in the context of organs, body parts, or entire organisms. This image shows OPTiSPIM1, one of the custom light-sheet microscope setups available at the facility.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
6 September 2021
Researchers have combined spatial gene expression information with single-cell genomics data to create a high-resolution atlas of mouse organogenesis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
30 August 2021

Giulia Zanetti from the Institute of Structural and Molecular Biology (ISMB) in London explains how the collaboration with the Cryo-Electron Microscopy Service Platform enabled her group to reveal the structure of protein transport complexes.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
lab-mattersscience-technology
20 August 2021

The new team leader at EMBL Hamburg talks about her plans to establish biological X-ray imaging and high-throughput tomography.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
17 August 2021

EMBL launches new mentoring opportunity, linking Master’s students with postdoctoral researchers.
LAB MATTERS
12 August 2021

EMBL Director General Edith Heard has been elected a member of the German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina. Her admission to the ‘Human Genetics and Molecular Medicine’ section recognises her outstanding professional contributions to science.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
10 August 2021

MASSIF-1, run jointly by EMBL Grenoble and the ESRF, is a beamline for macromolecular crystallography. It is used by the research community to study the 3D structure of proteins, which is important for drug development.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
lab-mattersscience-technology
4 August 2021

EMBL alumnus Angus Lamond reflects on the process of translating the importance of fundamental research – to EMBL and wider society.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
alumnipeople-perspectives
3 August 2021

A community of scientists is looking at the estimated three billion heart muscle cells in a human heart to better understand heart disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
alumniscience-technology
30 July 2021

Distinctions recognise Peer’s development and sharing of bioinformatics tools as well as his significant contributions to bioinformatics research, education, and services.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
29 July 2021
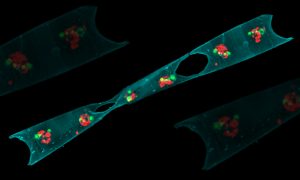
Analysis of more than 2 million images has boosted understanding of ocean microbes, shedding light on the distribution of nitrogen-fixers at a global level
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
27 July 2021
A collaboration led by EMBL Hamburg’s Svergun Group used small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) at the European XFEL to obtain data on samples containing coronavirus spike proteins and antibodies that bind them.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
22 July 2021
Partners use AlphaFold, the AI system recognised last year as a solution to the protein structure prediction problem, to release more than 350,000 protein structure predictions including the entire human proteome to the scientific community.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
22 July 2021
DeepMind and EMBL-EBI to make millions of protein structure predictions freely available to the scientific community.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
22 July 2021
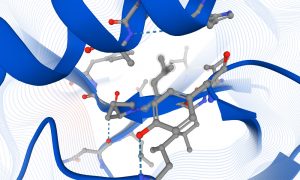
A discussion of the applications that AlphaFold DB may enable and the possible impact of the resource on science and society.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
21 July 2021
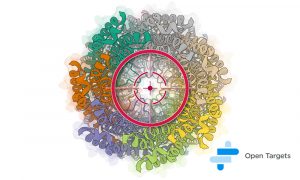
Researchers establish a framework for identifying new drugs capable of exploiting a cell’s own machinery.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
20 July 2021

Mehdi Khadraoui, a former member of the EMBL Communications team, took this close-up of a black redstart.
LAB MATTERS
13 July 2021

EMBL Director General Edith Heard has warmly welcomed Fiona Watt, who will become the new director of EMBO.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
13 July 2021

EMBL alumni Ilaria Piazza and Ken Holmes have been recognised for their outstanding contributions, and will receive their awards as part of the celebrations for EMBL World Alumni Day.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
alumnipeople-perspectives
12 July 2021
EMBL scientists generate a high-resolution crystal structure of the Kinesin-1/aTm1 transport complex in the fruit fly.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
9 July 2021

EMBL’s Melissa Graewert and colleagues are taking a structural biologist’s approach to better understanding nanoplastic particles.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
8 July 2021

We all like a story about rediscovering treasures, right? Well, that’s just what happened recently at EMBL Grenoble!
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
alumnipeople-perspectives
7 July 2021
Research in the Typas group uncovers new details of the strategies Salmonella uses to survive in infected cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
6 July 2021

The EMBL Imaging Centre is preparing for external user access, after an on-time and on-budget build and handover to the science team.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
5 July 2021

EMBL welcomes Sarah Dyer, the new Non-Vertebrate Genomics Team Leader at EMBL-EBI.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
2 July 2021

Dr Alexander Aulehla has been appointed the new Head of EMBL’s Developmental Biology Unit, and will take up the role starting in July 2021.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
30 June 2021

EMBL Director General Edith Heard has warmly welcomed the appointment of Professor Maria Leptin as the next President of the European Research Council (ERC)
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
29 June 2021
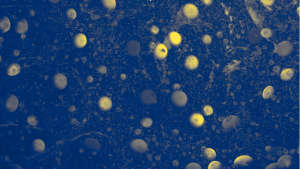
As evocative as a constellation of planets, these egg cells within a mouse ovary are at different stages of maturity.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weeksciencescience-technology
25 June 2021
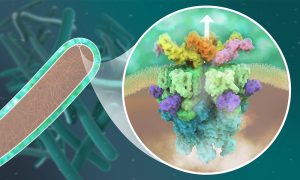
EMBL Hamburg’s Wilmanns and Kosinski groups have determined the detailed structure of a bacterial protein complex critical for tuberculosis infection.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
23 June 2021
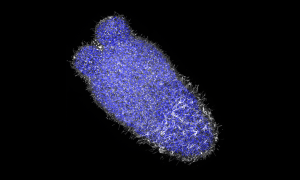
EMBL PhD student Anniek Stokkermans captured this side view of a Nematostella vectensis larva during this transition, using instrumentation in the Advanced Light Microscopy Facility at EMBL Heidelberg.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
22 June 2021

Anna Erzberger, one of EMBL’s newest group leaders, will provide unique perspective as a theoretical biological physicist.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
21 June 2021

At an EMBL Science & Society lecture, science journalist Kai Kupferschmidt advocated for accurate, clear and contextual science communication.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
eventspeople-perspectives
18 June 2021

After work in antimicrobial resistance, EMBL postdoc Laura Carroll is using machine learning for next-gen antibiotic development.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
people-perspectivesscience
17 June 2021

EMBL group leaders Julia Mahamid, Anna Kreshuk & Jonas Ries awarded Chan Zuckerberg Initiative grant to advance what we see inside cells.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
16 June 2021

Researchers investigate how external factors can influence the persistence of microbe species in the human gut
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
15 June 2021

As perfect as a summer night sky, these nuclear pores help calibrate a customised super-resolution microscope in EMBL’s Ries group.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
9 June 2021

New software enables scientists to visualise RNA secondary structures using the world’s largest RNA structure dataset.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
8 June 2021

John Marioni, Alex Bateman, and Takashi Hiiragi have been elected to EMBO Membership.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
8 June 2021

EMBL is conducting an Impact Assessment of our experimental services to understand the value these services have for our external user community. If you have accessed EMBL experimental services at one or more of our facilities to support the conduct of your research, we would like to hear from you.
LAB MATTERS
8 June 2021
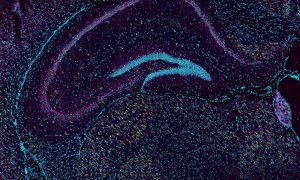
At EMBL, we have many dream teams – groups of individuals who support each other, innovate, and work together. One of those dream teams bridges two core facilities at EMBL Rome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
5 June 2021

EMBL’s EU Green Week event showcased various ways molecular biology research can help solve environmental challenges.
LAB MATTERS
4 June 2021

EMBL Director Matthias Hentze describes the Environmental Research Initiative: a community effort to solve global environmental challenges.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
3 June 2021

Under the innovative Planetary Biology research theme, EMBL scientists aim to understand life in the context of its environment.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
1 June 2021

EMBL and the Swedish Science for Life Laboratory sign agreement to advance science together.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
1 June 2021
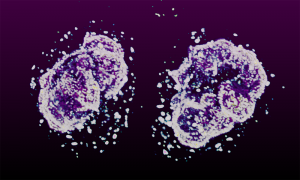
Captured by EMBL postdoc Arina Rybina, these ‘nuclear twins’ are two daughter nuclei straight after division of a HeLa cell.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
31 May 2021

The largest in-depth analysis of genomic surveillance data mapping out the dynamics of 62 lineages of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
25 May 2021
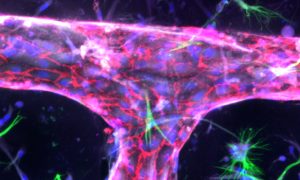
The Bernabeu Group aims to increase our knowledge of cerebral malaria, using in vitro engineered networks of human blood vessels and brain cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
21 May 2021

EMBL scientists support research on malaria by providing freely available data resources and using innovative experimental approaches. Our Course and Conference Office facilitates the exchange of knowledge in the field by hosting the annual BioMalPar conference.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
20 May 2021

EMBL’s most recent Science and Society seminar explored how best to harness big data to address multi-faceted issues of a pandemic.
CONNECTIONS
20 May 2021

The Gesellschaft für Biochemie und Molekularbiologie has awarded a FEBS Anniversary Prize to Michael Zimmermann for his gut microbiome research.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
18 May 2021
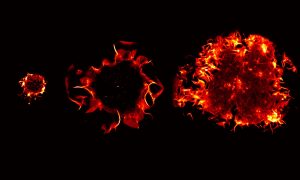
The EMBL Picture of the Week features a series of Jurkat T cells during different stages of the activation process.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
17 May 2021
Leading international experts gathered to showcase progress in the fight against COVID-19 and share lessons for the future.
CONNECTIONS
17 May 2021

Researchers at EMBL Hamburg reveal how peg-like proteins clasp and reshape the cell membrane
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
12 May 2021

A workshop run by EMBL Hamburg explored opportunities for structural biology at the future, upgraded PETRA IV synchrotron.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
eventsscience-technology
10 May 2021

A memorandum of understanding has been signed between EMBL and Inserm to strengthen their scientific cooperation.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
7 May 2021

EMBL scientists have combined artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms with two cutting-edge microscopy techniques.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
5 May 2021

Zehra Sayers explains what makes the SESAME synchrotron special, why we should not fear failure, and why curiosity is her biggest driver.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
alumnipeople-perspectives
30 April 2021

The EMBL-Tara Ocean Foundation collaboration will expand opportunities to jointly explore molecular connections between ocean and humankind.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
29 April 2021

EMBL Hamburg’s integrated structural biology facility has contributed to the success of a large-scale SARS-CoV-2 study
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
28 April 2021

Researchers reveal the best technology for assembling reference genomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
28 April 2021

The European Molecular Biology Laboratory and the Italian Institute of Technology have signed an agreement to expand the scope of their collaboration to include areas of mutual interest and in the context of EMBL’s 2022-2026 Programme “Molecules to Ecosystems”.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
27 April 2021

EMBL Director General Edith Heard has been elected into the US National Academy of Sciences, recognising her contributions to research.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
27 April 2021
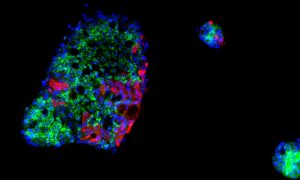
EMBL scientists, together with collaborators from Heidelberg University, have provided further evidence of the gut’s role in COVID-19.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
27 April 2021
A page from a biologist’s colouring book? EMBL’s new interior wall design? Not quite – a bunch of liver cells, grown in the lab so that scientists can learn about fatty liver disease, or steatosis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
26 April 2021

Edith Heard has been appointed to a new World Health Organization advisory council.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
26 April 2021

A memorandum of understanding has been signed between EMBL, Collège de France, and the Institute of Biology of the Ecole Normale Supérieure (IBENS).
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
22 April 2021
Researchers identify differences in immune response in asymptomatic COVID-19 cases compared to those with severe symptoms
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
21 April 2021

In a talk on 29 April, Professor Jeanette Woolard will share her experience of creating a more positive research culture
LAB MATTERS
20 April 2021

EMBL and Portugal are bringing together leading scientists to highlight the role of fundamental research in tackling infectious diseases.
CONNECTIONS
20 April 2021
What does coronavirus’s spike protein look like in 3D? EMBL scientists and colleagues used cryo-electron tomography and molecular dynamics simulations to find out.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
16 April 2021

Researchers have used a metagenomics approach to piece together the genomes of yeasts found in wild lichens.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
15 April 2021

Scientists from the CABANA project explore how open data is benefiting global research efforts.
CONNECTIONS
13 April 2021

Florent Cipriani, who recently retired as Head of the Instrumentation Team after a long career at EMBL Grenoble, is one of the pioneers of instrumentation development in this field.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
lab-mattersscience-technology
13 April 2021

Throwback to June 2014: While EMBL Heidelberg’s main entrance is still in the dark, the well-known EMBL logo is already lit by the morning sun.
LAB MATTERS
2021
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
9 April 2021

Researchers use large-scale human genetic studies to identify drug targets important for managing COVID-19 in its early stages
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
9 April 2021
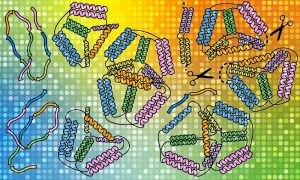
Using EMBL Hamburg’s world-class structural biology infrastructure, researchers advance the folding of protein ‘origami’ designed in the lab.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
8 April 2021

Researchers have used human medical and genetic data from UK Biobank to investigate the genetics of age-related diseases
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
7 April 2021

The challenges and opportunities when setting up a global archive for bioimages
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
6 April 2021

This MoU formalises a 15-year collaboration between the two institutes and strengthens Grenoble as a European research centre in the life sciences.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
6 April 2021
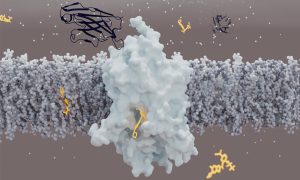
Scientists have determined the structure of Glycine Transporter 1. The finding could open new avenues for developing therapeutics for psychiatric disorders
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
6 April 2021
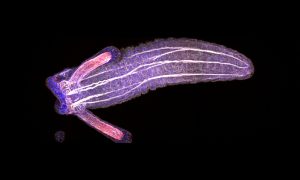
This image of a young Nematostella vectensis polyp shows two of the characteristic tentacles as well as the gaping mouth of the animal.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
30 March 2021

The new group leader at EMBL Rome will study how embryos can inherit non-genetic information from their parents that causes stable and heritable effects
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
30 March 2021

Scientists at EMBL Hamburg use droplets of protein solution to grow protein crystals. By exposing the crystals to X-rays, they are able to determine the protein’s molecular structure.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
23 March 2021

The cafeteria at EMBL Heidelberg now offers espresso and cappuccino with a more intense flavour and which are produced in a ‘green’ way.
LAB MATTERS
2021
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
22 March 2021

EMBL alumnus Kai Simons did early work with Semliki Forest virus membranes, which is now central to a COVID-19 vaccine.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
alumniscience-technology
16 March 2021

EMBL’s site in Monterotondo has recently been blessed with blue skies and sunshine, leading to trees blooming early on campus.
LAB MATTERS
2021
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
15 March 2021

Nassos Typas has received the German VAAM Research Award.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
11 March 2021

EMBL alumnus Pawel Masiewicz has transferred skills and experience gained at EMBL to oversee starting materials for mRNA vaccine development.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
alumnipeople-perspectives
9 March 2021

The contribution of EMBL Group Leader and Senior Scientist Wolfgang Huber has been recognised by the International Society for Computational Biology
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
9 March 2021

This photo shows the European Photon and Neutron (EPN) science campus where EMBL Grenoble is located. A delightful spring breeze in the air melts the last remaining patches of snow in the mountains.
LAB MATTERS
2021
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
8 March 2021

Tracey Brown from Sense about Science shares her thoughts on the need to empower women to share and access scientific information.
LAB MATTERS
8 March 2021

Members of EMBL’s Equality, Diversity and Inclusion Committee explain how EMBL is choosing to challenge through its LEAP mentoring programme.
LAB MATTERS
4 March 2021
Scientists in the Stegle group and colleagues have studied induced pluripotent stem cells from around 1,000 donors to identify correlations between individual genetic variants and altered gene expression. They linked more than 4,000 of the genetic variants responsible for altered expression…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
3 March 2021
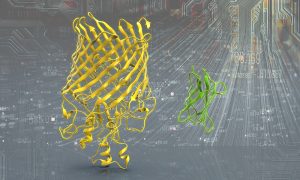
Thousands of new protein structure models, prected using deep learning, now available to explore
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
3 March 2021

EMBL invites Simon Gallow, an advocate at UN Women UK, to give a talk marking International Women’s Day.
LAB MATTERS
2 March 2021
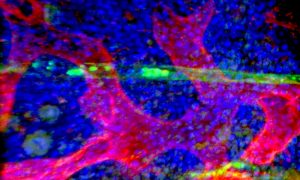
A new method has the potential to boost international research efforts to find drugs that eradicate cancer at its source.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
2 March 2021
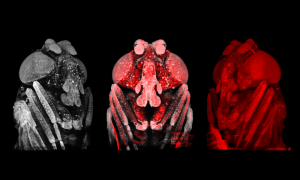
Like caterpillars turning into beautiful butterflies, fruit fly larvae have to go through metamorphosis to finish their development. However, despite the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster being one of the best studied model organisms in biology, comparatively little attention has been given to this…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
1 March 2021

Applications are now open for the Life Science Alliance’s Bridging Excellence Fellowships, enabling postdocs to carry out collaborative projects at EMBL and Stanford University.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
26 February 2021

EMBL's Environmental Officer Brendan Rouse explains more about his role as a European Climate Pact Ambassador.
LAB MATTERS
26 February 2021

As one of EMBL’s newest group leaders, Sinem Saka will combine multiple technologies, such as microscopy and single-cell omics, to solve biological puzzles.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
25 February 2021
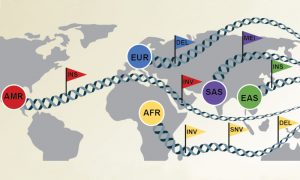
A collaboration including EMBL scientists has created the most diverse set of reference human genomes ever assembled.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
23 February 2021

Being a woman in science takes allies, not just great science. Here, EMBL’s L’Oréal–UNESCO Fellows talk about support networks.
LAB MATTERS
23 February 2021
Liang Xue used cryo-electron tomography to capture this detailed image of a Mycoplasma pneumoniae cell.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
22 February 2021

Anne Ephrussi has been awarded the German Feldberg Prize 2022 in recognition of her outstanding research.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
22 February 2021

The Sample Preparation and Characterisation (SPC) Facility at EMBL Hamburg is one of the founding members of the Molecular-Scale Biophysics Research Infrastructure (MOSBRI). Within this new European initiative, the SPC Facility will offer services related to membrane proteins, protein complexes,…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
19 February 2021

Gautam Dey is fascinated by the evolutionary origins of the nucleus, and is looking forward to making the most of EMBL's infrastructure.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
18 February 2021
Scientists identify more than 140 000 virus species in the human gut; more than half have never been seen before
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
18 February 2021

Professor Dame Janet Thornton discusses work–life balance, the support she has received during her career, and how organisations can help staff during the COVID-19 pandemic
LAB MATTERS
17 February 2021

Researchers from EMBL and Heidelberg University Hospital combine high-resolution imaging to observe the infection process in cell nuclei, opening the door for new therapeutics.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
16 February 2021
A team of EMBL scientists and colleagues have analysed how the novel coronavirus affects proteins in human cells. They identified several human proteins as potential drug targets to prevent viral replication.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
16 February 2021
This week's Picture of the Week, which could also be a masterpiece of modern art, shows the enzyme RNA polymerase III, an assembly of 17 individual proteins combined into this complex structure.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
11 February 2021

EMBL and EMBRC have signed a memorandum of understanding for increased scientific collaboration.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
11 February 2021

EMBL Teen Maria-Theresa Licka shares how female scientists guided & inspired her to develop an app to ID vine disease.
LAB MATTERS
9 February 2021

Researchers at EMBL Heidelberg have identified sequences in human proteins that might be used by SARS-CoV-2 to infect cells. They have discovered that the virus might hijack certain cellular processes, and they discuss potentially relevant drugs for treating COVID-19.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
9 February 2021

Roshni Mooneeram discusses what Equality, Diversity and Inclusion (EDI) is to her, and what the meaning of allyship is.
LAB MATTERS
9 February 2021

The regular structures of crystals are a source of inspiration and fascination to us humans. While the crystals in this picture were not grown in nature, but instead by Petra Drncova from EMBL Grenoble, they share the same attributes as those found in nature.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
8 February 2021
New EMBL research shows where & to what degree a component of cellular machinery known as RNA Pol III is mutated and becomes problematic.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
5 February 2021
A new paper from the Galej group at EMBL Grenoble describes the structure of key parts of the Integrator complex, involved in gene expression.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
4 February 2021

Open letter galvanises life science community in support of open COVID-19 data
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
3 February 2021

A new lineage of coronavirus was first identified in the UK, but why is it spreading much more rapidly within the population?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
2 February 2021
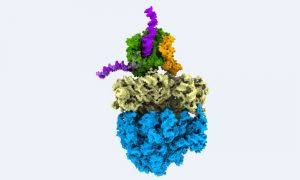
This colourful image shows biological information flow in action: It’s a supramolecular assembly of DNA, RNA and proteins, observed directly inside a bacterial cell while turning genetic information into protein.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
29 January 2021

EMBL and CNR have signed a memorandum of understanding to strengthen scientific cooperation. The agreement will foster collaborative projects and integrate them within the European and global scientific landscape.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
28 January 2021

The latest issue of Science in School highlights the eight members of EIROforum.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
27 January 2021

New group leader Nicoletta Petridou explains her fascination with the complexity of early embryo development, and how the interdisciplinary nature of EMBL will aid her research.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
26 January 2021

Engineers at EMBL Hamburg installed specially designed mirrors to reflect and focus X-ray beams onto tiny crystals made of proteins or other biological molecules.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
20 January 2021

A note on the coronavirus variant B.1.1.7, which has first been described in the U.K. and has spread to 57 countries. The note summarises epidemiological information about the spread of B.1.1.7 in the U.K. collated and in part conducted by researchers from EMBL-EBI.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
20 January 2021

EMBL and the German Cancer Research Center in Heidelberg are increasing their already existing collaborations with a Memorandum of Understanding between the two institutions.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
19 January 2021

Freshwater sports can cause waterborne infections, but real-time DNA sequencing could help.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
19 January 2021
It’s almost a year since the coronavirus outbreak was declared a pandemic, affecting all our lives. While the virus continues its grip on the world, scientists are understanding it better and better, increasing our knowledge about it and opening up new ways to fight it.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
18 January 2021

EMBL has a packed schedule of courses and conferences for 2021, ready to go ahead virtually, regardless of limitations on physical gatherings
LAB MATTERS
18 January 2021

The EMBL Imaging Centre is scheduled to open in 2021 with Timo Zimmermann as Team Leader for advanced light microscopy technology development and service provision.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
15 January 2021

One of EMBL’s newest group leaders, Olivier Duss, will explore how RNA folds into functional structures and how it works with proteins to control a diverse range of activities in the cell.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
14 January 2021
Researchers at the Technion – Israel Institute of Technology and EMBL Hamburg, in collaboration with scientists in Israel and Spain, have discovered remarkable molecular properties of an antimicrobial peptide from the skin of the Australian toadlet. The discovery could inspire the development of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
12 January 2021

EMBL’s sites in Grenoble, Hamburg, and Heidelberg form the newest Instruct Centre. The new centre offers users access to a broad range of state-of-the-art facilities.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2021
connectionslab-matters
12 January 2021

Structural biologists want to study proteins at the atomic level. The device shown in this Picture of the Week is essential for this.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
5 January 2021

Understanding why disagreement is good for COVID science. EMBL Deputy Director General Ewan Birney offers tips for sorting through the discourse.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
people-perspectivesscience
5 January 2021
Fluorescent dyes light up a cellular community of neurons and brain immune cells (microglia), which were derived from stem cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
4 January 2021
Researchers discovered the dominant species of bacteria in kefir grains cannot endure without other species that help the 'team' survive.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
23 December 2020

Schoolchildren create exquisite protein-inspired artworks
LAB MATTERS
22 December 2020

Despite restrictions, 2020 has been a busy year for the Darwin Tree of Life Project. We take a look at some of this year’s achievements and highlights.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
22 December 2020
It is that time of year to get into the holiday spirit, prepare for some time at home and relax after a strange and stressful year. Even the cells in our Picture of the Week are getting into the holiday spirit, forming this colourful Christmas tree.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
21 December 2020

The story of a life-long friendship and a professional partnership that sowed the seeds for a ground-breaking vaccine technology.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
alumniscience-technology
18 December 2020
Gene activation requires the cooperative activity of multiple transcription factors. Until now, the mechanism used by these factors to coordinate their actions has been poorly understood. EMBL’s Krebs group presents a DNA footprinting method that makes it possible to determine whether…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
17 December 2020

December has seen the start of a new chapter in the collaboration that has for years marked the relationship between the European Commission (EC) and EMBL.
CONNECTIONS
15 December 2020

The first snowflakes have fallen on the Vercors Mountains, right behind the EMBL Grenoble building, and an almost full moon is showing up during a sunny morning.
LAB MATTERS
2020
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
11 December 2020

Facilitated by EMBL’s Scientific Visitor Programme in 2019, Silvia Dias Almeida spent a year in the Diz-Muñoz group, helping solidify her career plans and set her up for a competitive PhD programme in biomedical imaging.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
9 December 2020
A new paper from EMBL’s Savitski team and Typas group describes their work on E. coli and how it brings a greater understanding of the way genes function and interact.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
9 December 2020

Funding by the European Research Council (ERC) will support research on the timing of developmental processes in mammals
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
8 December 2020

With the external scaffolding removed, another step in the construction of the EMBL Imaging Centre is complete. Now we get a first glimpse of the final look of this stunning building.
LAB MATTERS
2020
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
7 December 2020

While cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) was first envisioned in 1968, the advances the Mahamid group are bringing to this 3D method for studying molecules directly inside cells are new, and are likely to greatly expand its use.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
4 December 2020

How artificial intelligence can help us solve the mysteries of the protein universe
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
2 December 2020
The Chan Zuckerberg Initiative has recognised four EMBL researchers with their most recent awards, showing how tech trailblazers are integral to advancing science and medicine.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
2 December 2020
Scientists in the Diz-Muñoz group at EMBL Heidelberg are working to build understanding of the role that mechanical properties play in affecting cell behaviour – a young and rapidly developing field of study. They have developed and successfully used a highly specialised technique to manipulate…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
2 December 2020
Members of the EMBL community are working to improve our understanding of the parasites that cause malaria and sleeping sickness
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
1 December 2020

Biotechnology company BioNTech and Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz conduct collaborative research with EMBL scientists at the beamline P12 in Hamburg
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
1 December 2020

Hamburg hosts one of EMBL’s six sites. The city is notorious for its windy and rainy weather. Lots of rain also means a high chance of beautiful rainbows!
LAB MATTERS
2020
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
30 November 2020

Bioinformaticians at EMBL-EBI and beyond are adapting computational tools to investigate coronavirus genomes and proteins.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
25 November 2020

At EMBL’s Science and Society conference, Ugandan campaigner Vanessa Nakate spoke about the need to take action on climate change.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
eventspeople-perspectives
24 November 2020
Studying cancers means also knowing what healthy cells look like. In this case, mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) from healthy bone marrow are a bit ‘loopy’.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
23 November 2020
Microbiomes, plastics, and connectivity – AtlantECO aims to understand the fabric of the Atlantic Ocean.
CONNECTIONS
23 November 2020
Researchers have studied SARS-CoV-2 replication in cells and obtained detailed insights into the alterations induced in infected cells. This information is essential to guide the development of urgently needed therapeutic strategies for suppressing viral replication and induced pathology.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
23 November 2020

EMBL’s Eileen Furlong, Chair of the Equality and Diversity Committee and Head of the Genome Biology Unit, responds to the recent Nature Comms paper on the potential effects of mentor–mentee relationships.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
20 November 2020

EMBL Director General Edith Heard introduced EMBL’s future plans during a parliamentary event at the Paul-Löbe-Haus of the German Bundestag in Berlin. She shared examples of EMBL’s research and outlined how EMBL’s activities will develop.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2020
connectionslab-matters
17 November 2020
Ever-evolving technology and related budgetary, regulatory, and management challenges prompted EMBL to establish its new ARISE fellowship programme, which begins accepting applicants in December.
LAB MATTERS
17 November 2020

Despite the cold autumn weather, workers are busy on the rooftop of the parking garage at EMBL Heidelberg. The 2176 m² rooftop is getting transformed into a combination of a green roof and a photovoltaic plant. The planted green roof will retain rainwater, while the solar panels – installed in…
LAB MATTERS
2020
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
10 November 2020
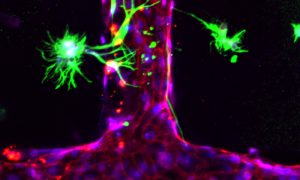
To help understand cerebral malaria the Bernabeu group has created in vitro engineered networks of human blood vessels.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
4 November 2020
By screening hundreds of sybodies (synthetic mini-antibodies), scientists have identified one that might stop SARS-CoV-2 from infecting human cells. This work, which holds promise for treating COVID-19, was conducted by EMBL Hamburg and collaborators from the Centre for Structural Systems Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
3 November 2020

On autumn days without Heidelberg’s characteristic fog, the woods present themself in beautiful colours. You may even capture a rainbow.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
28 October 2020

Researchers in the Gross group at EMBL Rome have investigated the mechanism behind defensive behaviour in mice. They have identified a specific area of the brain that encodes both spatial and threat cues to drive location-specific defensive responses.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
27 October 2020
The nucleus of this cell fluoresces in bright green thanks to GFP-labelled nucleoporin proteins. EMBL scientists use engineered nucleoporins as 3D reference standards to improve super-resolution microscopy.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
23 October 2020

Why should researchers make artificial intelligence more transparent and how can they do it?
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
lab-mattersscience-technology
22 October 2020

EMBL’s Rupert Lück is engaged in developing the European Open Science Cloud (EOSC): the infrastructure that will support the future of data sharing and analysis in Europe.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2020
connectionslab-matters
20 October 2020

Open access data benefits millions of scientists around the world and is essential for a rapid response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
20 October 2020

In 2012, EMBL used ecological lawn mowers to keep the grass short around the Advanced Training Centre at EMBL Heidelberg.
LAB MATTERS
2020
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
19 October 2020

EMBL and CIML have signed a memorandum of understanding that will open up new scientific opportunities.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2020
connectionslab-matters
16 October 2020
A three-day virtual conference, ‘Gender Roles and their Impact in Academia’, explored how biology, social structures, and unconscious bias shape gender roles, and discussed ways to achieve equal opportunities for men and women in academia.
LAB MATTERS
16 October 2020

New associate group leader at EMBL Hamburg investigates the structure of functional amyloids in bacteria and in human disease
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
15 October 2020
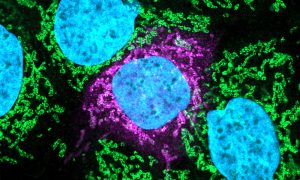
Scientists from the Beltrao Group at EMBL-EBI and collaborators identified drug targets common to SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV-1, and MERS-CoV, three pathogenic coronaviruses. They also found potential drugs that could be repurposed as COVID-19 treatments, and against emerging coronavirus strains in the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
15 October 2020

Maria Arruda is on a mission to make scientists think more about the role they play in society. After a career in academia and the life sciences, she is trying to help others see the bigger picture when it comes to the responsibility of the scientist.
LAB MATTERS
14 October 2020
Researchers from EMBL Heidelberg have established an automated pipeline to create mutations in genomic enhancers, letting them watch evolution unfold before their eyes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
13 October 2020
A group of scientists led by EMBL Hamburg’s Christian Löw provide insights into the molecular structure of proteins involved in the gliding movements through which the parasites causing malaria and toxoplasmosis invade human cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
13 October 2020

On 9 October, EMBL and the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) signed a Memorandum of Understanding that paves the way for stronger collaboration between these two leading research institutions.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2020
connectionslab-matters
13 October 2020
Sea anemones are amazing creatures. Despite their plant-like appearance and their tendency to remain fixed in one spot, they are actually animals.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
8 October 2020

Research facilities play a crucial role in the advancement of science by supporting scientists with specialised expertise and state-of-the-art equipment. The Microscopy Facility at EMBL Rome exemplifies this role by making a wide variety of light microscopy technologies available to its researchers…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
lab-mattersscience-technology
7 October 2020
The genome editing tool CRISPR–Cas9 – which plays a critical role in EMBL’s research – was recognised by the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
6 October 2020
Members of an EMBL-led research group with collaborators in Estonia and Russia have built and trained a deep learning model to better understand how cells grow and divide.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
6 October 2020
We’ve all had wounds at certain times in our lives. But they heal due to the self-repairing mechanisms in the body.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
5 October 2020

On 8 September, EMBL and Vilnius University Life Sciences Center signed a framework agreement for the establishment of the VU LSC–EMBL Partnership for Genome Editing Technologies.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2020
connectionslab-matters
1 October 2020

EMBL’s network of alumni plays a vital role in advancing the life sciences globally. EMBL provides research, services, and infrastructure that help former staff to do this effectively. For several years EMBL has been discovering more avenues to help the life sciences across Europe. A key part of…
CONNECTIONS
29 September 2020

The partnership between EMBL and four Nordic research institutions aims to stimulate scientific exchange and inspire scientific collaborations. This year’s conference of the Nordic EMBL Partnership for Molecular Medicine included many talks by EMBL researchers and a presentation by EMBL’s…
CONNECTIONS
29 September 2020

To study the effect of commonly used drugs on bacterial envelopes, EMBL scientists applied a biochemical assay using a colour reaction. The deeper the red, the stronger the disruptive effect of the drug.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
24 September 2020

EMBL’s 21st Science and Society Conference will address scientific and societal responses to mass extinctions. Ahead of his keynote speech, renowned palaeontologist Mike Benton explains how looking into the deep past can give us vital insights into the future of life on Earth.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
eventsscience-technology
22 September 2020

How does your crystal garden grow? EMBL's Electron Microscopy Core Facility was able to capture this garden of blooming crystals as they studied mosquito reproductive cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
18 September 2020
The internal clock that governs the development of embryos ticks slower for humans than for mice. Differences in the speed of biochemical reactions underlie the differences between species in the tempo of development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
17 September 2020

The EMBL conference that explored direct and indirect impacts from the current pandemic on women in science allowed for information and story sharing both in the form of lectures but also via online platforms like Slack and social media that included Twitter.
LAB MATTERS
15 September 2020
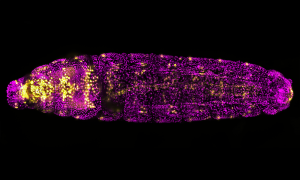
Not just another pretty fruit fly. This magenta and golden drosophila larva is lit up with a fluorescent molecule to help researchers study heart formation.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
10 September 2020

ARISE fellowships to offer first-ever comprehensive training for bioscience infrastructure operations
LAB MATTERS
8 September 2020
Researchers have found the cause of dilated cardiomyopathy – a leading cause of heart failure – and identified a potential treatment for it: a drug already used to treat acne.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
8 September 2020
A decadal roadmap points the way to cell-based medicine for Europe
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
lab-mattersscience-technology
8 September 2020
While this may seem like a nebula made up of interstellar clouds of dust and ionised gases, this image isn’t of a galaxy beyond the Milky Way.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
7 September 2020
The Gerstung Group at EMBL-EBI and collaborators have developed a statistical model that analyses genomic data to predict whether a patient has a high or low risk of developing oesophageal cancer.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
7 September 2020

Two EMBL speakers gave presentations that looked toward the future and at ways to trailblaze on the endless frontier of science.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2020
connectionslab-matters
4 September 2020

Erin Tranfield recently joined the EMBL Alumni Association Board as one of 15 newly elected members. Here, she talks about her new role on the board and reflects on how a life-changing event made her refocus her perspective on work and life.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
alumnipeople-perspectives
3 September 2020

Maria Bernabeu and Wojciech Galej have each been awarded €1.5 million to research malaria and pre-mRNA splicing, respectively.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
3 September 2020
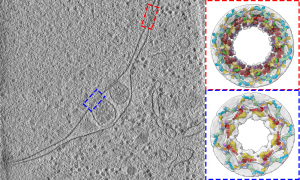
Scientists from the Beck group have studied the 3D structure of nuclear pores in budding yeast. They show how the architecture of the nuclear pore complex differs inside cells compared to its form observed in vitro studies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
2 September 2020
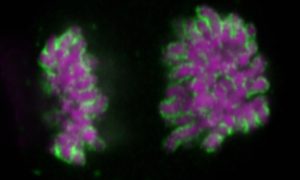
Researchers have uncovered how cells remove unwanted components from the nucleus following mitosis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
2 September 2020
EMBL-EBI is one of the eight European institutes involved in the Humanoid Cell Atlas initiative, a new open-access platform that combines single-cell profiling and organoid technology
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
2 September 2020
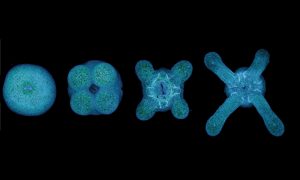
An international group of researchers, led by scientists from EMBL Heidelberg, have discovered that the number of tentacle arms a sea anemone grows depends on the amount of food it eats.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
1 September 2020

As the EMBL Fellows' Career Service program reaches a milestone, it reflects on its first year and looks forward to ways to improve its offerings to EMBL postdocs and predocs.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
1 September 2020
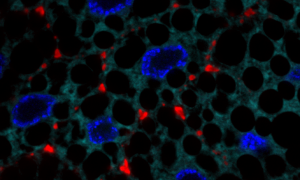
Those heart-shaped cells aren't just for show. They help tell the story of two proteins working together
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
31 August 2020
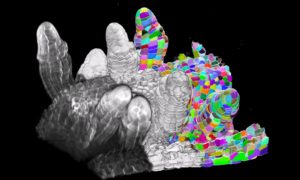
Starting with computer code and moving on to a more user-friendly graphical interface called PlantSeg, the Kreshuk Group at EMBL and collaborators built a simple open-access method to provide the most accurate and versatile analysis of plant tissue development to date.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
27 August 2020

The Head of the Electron Microscopy Core Facility at EMBL Heidelberg receives Mid-Career Scientific Achievement Award 2020
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
26 August 2020

More than 500 people have registered for an EMBL conference, "The impact of the COVID-19 crisis on women in science: Challenges and solutions." Scheduled for 9 September, the conference is free and open to all. Pre-registration is still available and required to attend.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
eventsscience-technology
25 August 2020

The EMBL International PhD Programme is one of EMBL’s flagship training programmes. It forms part of our efforts to train and inspire talented scientists to become skilled and creative future leaders. Submission of applications for the current PhD student recruitment round is now possible.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
25 August 2020

The beamlines run jointly by EMBL Grenoble and the ESRF reopen today, unveiling significant upgrades that exploit the brand new fourth generation ESRF synchrotron source.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2020
embl-announcementsscience
25 August 2020
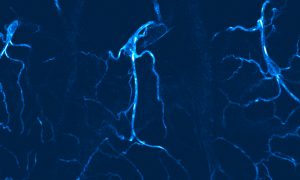
Beautiful flashes of blue colour help light the way for researchers to study cells in fruit fly larva that provide oxygen to tissues.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
24 August 2020

The new team leader offering services in electron microscopy discusses his hopes and plans for the forthcoming EMBL Imaging Centre
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
20 August 2020

The Web Development team provides a central source of web design and development for EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI). In July, Geetika Malhotra joined the team as their new Head.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
19 August 2020
An international team of scientists involving Ewan Birney's group has investigated the function of a complex mesh of muscle fibres that line the inner surface of the heart.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
19 August 2020
Discoveries at EMBL will help researchers to interpret one of the most common types of experiments in genomics and medical studies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
18 August 2020
Researchers studied the spike protein on the surface of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. With its spikes, the virus binds to human cells and infects them. The study gave surprising insights into the spike protein, including an unexpected freedom of movement and a protective coat to hide it from antibodies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
18 August 2020
Despite their ghostly appearance, these are very real cell nuclei infected with Influenza A virus – the only influenza virus known to cause pandemics.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
11 August 2020
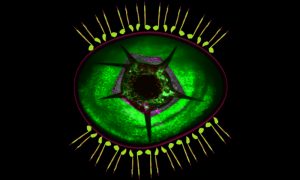
This image is a composite of lateral pentascolopidial organs, a wing imaginal disc pouch, and an epithelial wound in a Drosophila larva. The organs are arranged here like eyelashes. Cells surrounding an epidermal wound appear as the iris and pupil of this artistic eye.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
7 August 2020

As he enters retirement, Head of EMBL Rome Phil Avner reflects on his scientific career and memories from his time as Head of EMBL’s site in Italy
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
6 August 2020

Researchers from all life science disciplines – from fundamental biological research to medical applications – generate immense datasets. Analysing these datasets and gaining new knowledge from them is a growing challenge for scientists. The fields of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
lab-mattersscience-technology
5 August 2020

A global team of researchers including the Flicek Team at EMBL-EBI has partnered up with the Māori tribe Ngātiwai to sequence the genome of the tuatara, a rare reptile endemic to New Zealand.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
4 August 2020
This group of cells represents an interesting example of organ formation where cells simultaneously move and change their shapes in a highly coordinated manner.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
3 August 2020

The human genome harbours about 19 000 protein-coding genes, many of which still have no known function. As scientists unveil the secrets of our DNA, they come across novel genes that they need to refer to using a unique name. The Human Genome Organisation’s Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) at…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
31 July 2020
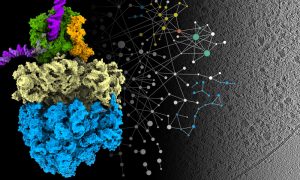
A new approach that allows researchers to see molecular machinery at work inside cells has offered a deeper understanding of how bacteria produce proteins and a unique glimpse into how they respond to antibiotics.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
30 July 2020

Europe PMC has begun indexing full-text COVID-19 preprints along with the associated data. The project aims to accelerate research to fight the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
29 July 2020
The Svergun group at EMBL Hamburg has released the course ‘Solution Scattering from Biological Macromolecules’ in an online format for the first time. The course explores different aspects of small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) for studying the structure of macromolecules.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2020
embl-announcementsevents
28 July 2020
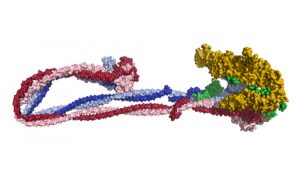
EMBL scientists and collaborators help reveal the process by which enormous quantities of DNA are folded into cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
28 July 2020
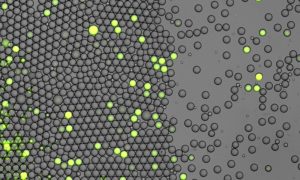
Bacterial cells are embedded in microfluidic droplets in oil. The fluorescence indicates the presence of the targeted DNA strain with the help of a characteristic DNA sequence.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
27 July 2020
Researchers have developed an artificial intelligence algorithm that uses computer vision to analyse tissue samples from cancer patients. The algorithm can distinguish between healthy and cancerous tissues, and can also identify patterns DNA and RNA changes in tumours.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
21 July 2020

The image shows one of the four rows of roof lights above the atrium, which is the main public space of the Imaging Centre.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
21 July 2020
EMBL scientists have created a new, realistic 3D testbed that could help achieve the goal of stopping cancers before they start by studying cancer cells as they first form.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
20 July 2020
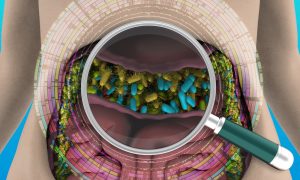
An international team of scientists has collated all known bacterial genomes from the human gut microbiome into a single large database. Their work will allow researchers to explore the links between bacterial genes and proteins, and their effects on human health.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
17 July 2020

EMBL Director General Edith Heard and EMBO Director Maria Leptin respond to the current proposal on the Multiannual Financial Framework.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
17 July 2020

European collaboration receives funding to explore risks and impact of future infectious disease outbreaks.
LAB MATTERS
16 July 2020

Three changes in senior staff positions have been confirmed at EMBL today. Jessica Vamathevan becomes Head of Strategy, Jan Korbel becomes Head of Data Science for EMBL Heidelberg, and Nassos Typas becomes Senior Scientist.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
14 July 2020
The image shows a larva of Platynereis dumerilii, a marine worm. The image here was produced by Constantin Pape, a visiting predoctoral fellow in the Kreshuk group at EMBL Heidelberg.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
13 July 2020

The European Learning Laboratory for the Life Sciences (ELLS), EMBL’s education facility, invites secondary school science teachers to participate in a virtual training course this autumn entitled ‘Introducing your microbiome’.
LAB MATTERS
8 July 2020

Latvia has joined EMBL as a prospect member, starting a three-year process toward full membership.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
8 July 2020

This year, EMBO elected 63 new members, including Alexander Aulehla, Group Leader and Senior Scientist at EMBL Heidelberg, and Paul Flicek, Associate Director of EMBL-EBI Services, Senior Scientist, Group and Team Leader at EMBL-EBI.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
8 July 2020

The CrystalDirect® technology, combined with the web-based CRIMS software enable a fully automated, remote-controlled protein-to-structure pipeline.
LAB MATTERS
8 July 2020
The virtual EMBL Conference ‘SARS-CoV-2: Towards a New Era in Infection Research’ explored the importance of fundamental research, collaboration, and data science in containing the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, and discussed opportunities to improve our response to pandemics in the future.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
eventsscience-technology
7 July 2020

EMBL brings together more than 1700 people from all over the world, from a variety of academic and cultural backgrounds. This creates an environment in which there is constant exchange of both scientific knowledge and cultural heritage. While it seems obvious that EMBL, as an international…
LAB MATTERS
2020
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
6 July 2020

EMBL Director General Edith Heard has been elected a senator of the Max Planck Society, one of Germany’s leading scientific research organisations. She joins the Senate along with Nobel Laureates and EMBL alumni Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard and Stefan W. Hell, as well as nine additional new…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
3 July 2020
Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg have investigated stem cells and how they differentiate to become neurons. Their approach included an assessment of the complex interplay of molecules during the differentiation process and generated fundamental new insights into the role of a protein called Sox2 in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
2 July 2020

The governing Council of EMBL has approved Director General Edith Heard’s restructure of senior management with effect from 1 July 2020.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
2 July 2020
A study conducted by the Hackett group at EMBL Rome has identified key factors controlling the complex system of gene regulation during early embryo development, shedding new light on the mechanisms behind these events and on their evolutionary implications. Their findings are published in Nature…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
1 July 2020

Open Targets welcomes new Informatics Science Director
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
30 June 2020
A national consortium including EMBL and the DKFZ is set to launch the German Human Genome–Phenome Archive, creating an invaluable bridge between fundamental biomedical research and applied healthcare.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2020
connectionslab-matters
30 June 2020

Local beekeeper Jörg Staffel has set up three bee colonies on the grass slope in front of the ATC building.
LAB MATTERS
2020
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
29 June 2020

To study how SARS-CoV-2 infects cells, the Gene Editing and Embryology Facility (GEEF) at EMBL Rome will generate mice that express a human version of a protein called ACE2. The mouse line will be shared with preclinical research collaborators carrying out vaccine and antibody trials, and with the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
29 June 2020
Researchers evaluate how the new coronavirus rewires human proteins for its own replication, and identify several antiviral drugs ready for clinical trials
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
26 June 2020
Today we celebrate the 20th anniversary of the first draft of the entire human genome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
26 June 2020

EMBL is joining the virtual seminar series ‘Life Science Across the Globe’ – a timely initiative to foster international scientific exchange across countries and continents, starting on 1 July.
LAB MATTERS
25 June 2020

EMBL scientists develop a new molecular tool to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice. This tool is able to cause targeted epigenetic modifications of specific genes in specific cell populations. They will use it in mice to target airway cells that express the ACE2 protein – the receptor that…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
24 June 2020

DNA damage caused by chemical mutagens is not repaired immediately and can create more genetic diversity in tumours.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
23 June 2020

EMBL is striving to make its labs and offices a welcoming and inclusive environment for all. To achieve this goal, EMBL's Equality and Diversity Officers, Luisa Vieites Rodrigues and Zac O'Sullivan, are working closely with leadership and the EMBL community. In this interview, they share their…
LAB MATTERS
23 June 2020

Elisa Kreibich from EMBL’s Krebs group baked an EMBL cake for the farewell of Alexandra Martitz, the first master student in their lab.
LAB MATTERS
2020
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
22 June 2020
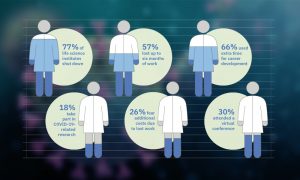
Jan Korbel and Oliver Stegle have performed a survey of fellow life scientists to learn how the current crisis, with partial or complete institutional shutdowns, is affecting their work.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
lab-mattersscience-technology
18 June 2020
To explore the origins of gender imbalances in academia and possible ways of overcoming them, international experts will meet for the virtual EMBL | EMBO | HHMI conference ‘Gender Roles and their Impact in Academia’ from 13–15 Oct 2020. The conference’s outcomes will be integrated into a…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2020
embl-announcementsevents
17 June 2020

While global research on coronaviruses has shed light on the function of many SARS-CoV-2 proteins, the role of some crucial components remains unknown. Researchers at EMBL Grenoble will use a range of structural biology methods to try to solve some of the puzzles of the molecular mechanics of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
16 June 2020

Scientists at EMBL and Heidelberg University Hospital are studying how the novel coronavirus behaves in the gut to try to better understand its epidemiology and prevent its spread. To do this, they are combining advanced imaging and sequencing technologies to study coronavirus in human intestinal…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
16 June 2020

In this composite image, visual artist Mona Kakanj assembled three different biological structures in fly larvae into a flower. The original images were taken as part of a research project by Parisa Kakanj in Maria Leptin’s group.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
15 June 2020

The European Molecular Biology Laboratory has secured 6.8 million Euros funding from the European Commission to launch a unique training programme. The ARISE Programme will train and develop Europe’s next generation leadership for research infrastructures in the life sciences.
LAB MATTERS
15 June 2020
The emergence of previously unknown pathogens, such as the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, raises many questions. To explore these questions in an international scientific forum, EMBL will host the virtual conference ‘SARS-CoV-2: Towards a New Era in Infection Research’ on 3 July. Invited…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2020
embl-announcementsevents
12 June 2020
Scientists discovered that antihypertensive agent alters the tissue characteristics of colon cancer metastases. This "stiffness" of metastases has an effect on the therapeutic success.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
11 June 2020

Scientists at EMBL Rome unveil the mechanism behind the most studied epigenetic modification.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
9 June 2020
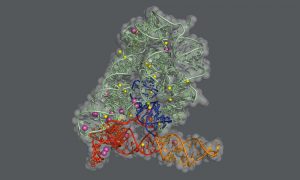
Researchers in the Marcia group at EMBL Grenoble and the De Vivo lab at the Italian Institute of Technology in Genoa have obtained some of the most detailed ever snapshots of the splicing process in systems known as group II self-splicing introns. The new insights will help scientists to develop…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
9 June 2020

EMBL researchers are studying COVID-19-related molecules by exposing them to high-brilliance X-ray beams. The Svergun group at EMBL Hamburg is using biological small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) as part of a global effort by scientists to elucidate the structural organisation of SARS-CoV-2…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
9 June 2020
This image shows mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), their cell skeletons (green) and nuclei (blue) under a confocal microscope, photographed by Julia Hansen in the lab of Matthieu Boulard at EMBL Rome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
8 June 2020
Scientists including members of EMBL’s Typas group have investigated how immune cells called macrophages respond to infection by the intracellular pathogen Salmonella enterica. They discovered that Salmonella causes newly produced cathepsins to accumulate in the nuclei of infected cells to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
2 June 2020
This image is a 3D-rendering of the automatic segmentation of a HeLa cell, made by Julian Hennies from the Schwab team at EMBL Heidelberg.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
1 June 2020
Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg have developed a new method, called Targeted Perturb-seq (TAP-seq), which increases the scale and precision of functional genomics CRISPR–Cas9 screens by orders of magnitude. Their method overcomes limitations in previous applications of single-cell RNA sequencing,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
27 May 2020
Researchers from EMBL Grenoble have developed a way to visualise large RNAs in 3D using biochemical and structural biology techniques.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
27 May 2020

EMBL and the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) restart the activities of the Joint Structural Biology Group in Grenoble to support coronavirus-related projects. A new initiative will allow users to be granted access to the High-Throughput Crystallisation (HTX) lab at EMBL and to a…
CONNECTIONS
26 May 2020

EMBL scientists have performed a large-scale analysis of over 4700 SARS-CoV-2 genome sequences. They found that many of the most interesting changes in the SARS-CoV-2 genome that have been reported so far are likely to be technical artefacts, rather than biological mutations.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
26 May 2020
In the Leptin Group, Eva Hasel investigates the innate immune system in Japanese rice fish.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
22 May 2020
Scientists hope that a legacy of the novel coronavirus in recovered COVID-19 patients – antibodies in their blood – could lead to drugs to treat others. The Merten group at EMBL Heidelberg has pivoted its microfluidics platform to support the search for neutralising antibodies that could…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
22 May 2020

Researchers in EMBL’s Zaugg group have studied the causes of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), a rare disease that causes high blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs. The study, carried out in collaboration with Stanford University School of Medicine, compared lung cells of patients…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
19 May 2020

The nervous system has fascinated Georgia Rapti ever since her first introduction to biology. Her research group in the Developmental Biology unit will focus on understanding the early biological events involved in the nervous system’s formation.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
19 May 2020
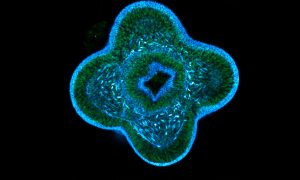
The image shown here, taken by Anniek Stokkermans from EMBL’s Ikmi Group, shows a larva of Nematostella vectensis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
15 May 2020
Researchers from the Sharpe group at EMBL Barcelona have published a method to track the developmental history of a cell using the gene editing tool CRISPR–Cas9, but without the need to create transgenic organisms.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
14 May 2020

EMBL welcomes NetApp, a leader in cloud data services empowering global organisations to change their world with data, as member of the Corporate Partnership Programme of the EMBL Advanced Training Centre.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2020
connectionslab-matters
13 May 2020

EMBL scientists will contribute to the new German COVID-19 OMICS Initiative to study the biological mechanisms contributing to coronavirus infections. EMBL group leaders Jan Korbel and Oliver Stegle, who is also affiliated with the DKFZ Heidelberg, will coordinate the set-up of IT infrastructures…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
12 May 2020
This image of the starlet sea anemone was taken by Petrus Steenbergen using a stereoscope.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
11 May 2020

The Sample Preparation and Characterisation Facility (SPC) at EMBL Hamburg reopens to support scientists working on Covid-19 research. The SPC Facility is one of the best equipped facilities in Europe is therefore in high demand from external users. Re-opening the facility also allows experts at…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
6 May 2020

DNA mutations are caused by a combination of DNA damage and repair, shows study by EMBL-EBI and collaborators.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
6 May 2020
The image shown here, taken by Daniel Rios-Barrera from the Leptin Group shows the cells of the early wing tissue of the fly during larval development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
5 May 2020

By re-opening the High-Throughput Crystallisation (HTX) lab at EMBL Grenoble, EMBL is supporting structural biology projects to respond to the health threats posed by coronaviruses.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
4 May 2020

The Nordic EMBL Partnership for Molecular Medicine has been awarded 210,000 euros. The funds will be used to train the next generation of specialists and research leaders in molecular medicine in the Nordic countries.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2020
connectionslab-matters
30 April 2020

The Marquez Team has restarted operations at the High-Throughput Crystallisation (HTX) lab at EMBL Grenoble. The team has developed a fully automated protein-to-structure pipeline, which can be operated remotely and provides virtual access to the facilities.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
30 April 2020

EMBL electron microscopy specialists collaborate with researchers from Heidelberg University Hospital to understand the changes occurring in cell structures upon SARS-CoV-2 infection.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
29 April 2020
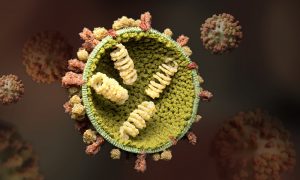
The infectious disease commonly known as flu is caused by the influenza virus. It spreads around the world in seasonal outbreaks, causing millions of infections and hundreds of thousands of deaths each year. Stephen Cusack, Head of EMBL Grenoble, has been studying different aspects of the influenza…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
28 April 2020
In human cells, the genetic material is packaged into 23 different DNA molecules, the chromosomes. Each chromosome is present in two copies, one inherited from the paternal sperm, and the other from the maternal egg. During most of the cell’s life, chromosomes take the shape of long,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
28 April 2020

Scientists at EMBL Hamburg and Karolinska Institutet Stockholm aim to find synthetic antibodies – known as nanobodies – that bind a surface protein of the novel SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. Nanobodies could prevent the virus from entering human cells and causing COVID-19.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
27 April 2020

EMBL scientists working in the groups of Matthias Hentze and Wolfgang Huber have created RBPbase – a database of RNA-binding proteins – to assist the identification of proteins that interact with the SARS-CoV-2 RNA genome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
24 April 2020

In March 2020, planes were grounded, streets went quiet, and our lives changed forever. But while the world came to a halt, many scientists were ramping up their efforts to understand the new virus.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
23 April 2020

The virtual EMBO | EMBL symposium ‘The Four-Dimensional Genome’ brought together 470 participants. Here, Jürgen Deka, Head of External Scientific Training, discusses how he and his team overcame the organisational challenges.
LAB MATTERS
22 April 2020

To address global challenges, we need to better understand life in the context of environmental change, says EMBL Director General Edith Heard
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
22 April 2020

Brendan Rouse came to Heidelberg in March as EMBL’s Environmental Officer, tasked with monitoring the organisation’s environmental impact and promoting sustainable practices. Here, he discusses his plans for the new role.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
21 April 2020
This Picture of the Week shows a stained cryosection of a retina – the light-sensitive part of the eye – of an ancient fish, the lamprey.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
20 April 2020

Researchers from EMBL Heidelberg have created a complete description of early embryo development, accounting for every single cell in the embryo.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
20 April 2020

The new collaborative space will help scientists, public health and healthcare professionals around the world to fight the coronavirus pandemic.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
17 April 2020

EMBL Heidelberg reopens the Cryo-Electron Microscopy Service Platform to support coronavirus structural biology research.
CONNECTIONS
16 April 2020

Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg are contributing their expertise in a community effort to develop large-scale testing methods for coronavirus. Their goal is to increase the capacity and speed of testing, which is crucial for containing the pandemic.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
15 April 2020

EMBL researchers are studying how drugs that have shown good results against COVID-19 work in living cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
15 April 2020

The Protein Expression and Purification Core Facility at EMBL Heidelberg will produce proteins for several coronavirus-related research projects, to assist the development of new strategies to fight the virus.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
14 April 2020
What may look like a branch of a tree with the first flower buds emerging after winter are, in fact, tracheal cells of a fruit fly larva and their nuclei.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
9 April 2020
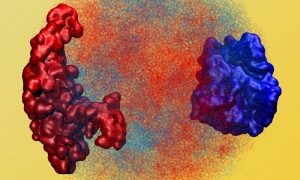
EMBL researchers in the Heard group at EMBL Heidelberg explore the interaction between DNA organisation and gene expression in the early embryo
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
9 April 2020

EMBL Director General Edith Heard responds to the resignation of the President of the European Research Council (ERC)
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
7 April 2020

EMBL is all about exciting science, through which we aim to achieve a fundamental understanding of biological processes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
3 April 2020
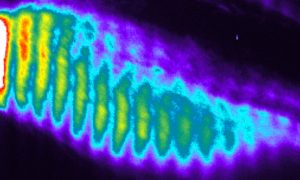
EMBL scientists examine the molecular causes of a rare hereditary disease of the spine and ribs
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
2 April 2020
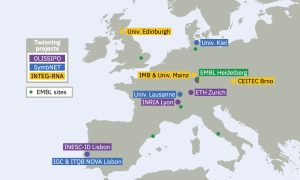
Three international teams involving EMBL Heidelberg have been granted funding from the European Commission for three Twinning projects with institutes in Portugal and the Czech Republic.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2020
connectionslab-matters
1 April 2020

The causes of 40 percent of all cases of certain medulloblastoma – dangerous brain tumours affecting children – are hereditary. These are the findings of a recent genetic analysis carried out by scientists from EMBL and numerous colleagues around the world.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
31 March 2020

Bastian Drees is a biophysicist turned librarian, who joined EMBL in January as the new Head of Library. Here, he discusses the changing role of libraries and how they can help scientists organise and share their results.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
31 March 2020

Paola Bertucci, from the Arendt Group at EMBL Heidelberg, studies the evolution of Platynereis dumerilii – a species of annelid polychaete worm.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
27 March 2020

EMBL-EBI set to launch European COVID-19 Data Platform to help store, share, and analyse research data linked to the COVID-19 pandemic.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
25 March 2020

EMBL is committed to providing a safe and healthy working environment for our staff and visitors.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
24 March 2020

The iconic ATC – celebrating its 10 year anniversary this year – reflects the blue sky, the clouds and the rays of the Sun.
LAB MATTERS
2020
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
20 March 2020

Stories from EMBL’s past are captured via the EMBL Archive’s Oral Histories programme
LAB MATTERS
17 March 2020

Committee recognises outstanding contributions of EMBL alumni to science journalism and genome editing
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2020
alumniembl-announcements
17 March 2020
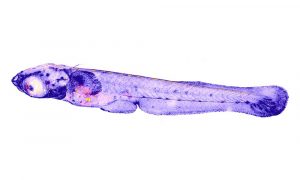
The medaka shown in this Picture of the Week was captured by Eva Hasel, a postdoc in the Leptin group at EMBL Heidelberg.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
11 March 2020
The Heidelberg-based LeukoSyStem consortium investigates leukaemia stem cells in acute myeloid leukaemia. The German Federal Ministry of Education and Research financially supports this collaboration between Heidelberg University Hospital, HI-STEM gGmbH, the German Cancer Research Center and EMBL.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2020
embl-announcementsscience
11 March 2020

How Joana Moscoso bridges the gap between science and society
LAB MATTERS
10 March 2020

This image, taken by Raphaël Cohen-Aberdam from the Cipriani team, shows that the weather for the Grenoble Lab Ski Day 2020 was just perfect!
LAB MATTERS
2020
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
5 March 2020
EMBL researchers investigate the role of a histone protein in regulating gene expression
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
3 March 2020

Colder winter weather has finally arrived EMBL-EBI. It’s the first time the site has seen snow this winter.
LAB MATTERS
2020
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
28 February 2020
EMBL researchers combine multiple datasets to develop expandable atlas of an entire animal
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
26 February 2020

Theresia Bauer and EMBL discuss organisational developments and future strategies
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2020
connectionslab-matters
25 February 2020

Annual Reception celebrates EMBL’s achievements in 2019 and explores its way ahead
LAB MATTERS
25 February 2020
In the Trivedi Group at EMBL Barcelona, Krisztina Arató and Jia Le Lim study the early development of zebrafish embryos.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
20 February 2020

EMBL’s new Science and Society Manager shares her plans for fostering multidisciplinary dialogue
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
19 February 2020

New group leader at EMBL Heidelberg employs synthetic chemistry to develop novel tools for biology
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
people-perspectivesscience
18 February 2020

2020 call now open for FNR funding of bilateral projects between EMBL and Luxembourg
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2020
connectionslab-matters
18 February 2020
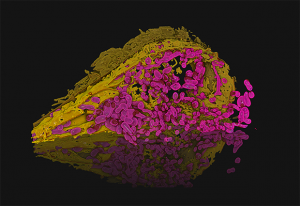
In this image, Julian Hennies from the Schwab Team has reconstructed the 3D structure of a human cell's organelles.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
13 February 2020

EMBL Director General recognised alongside four other exceptional women in the life sciences
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
11 February 2020
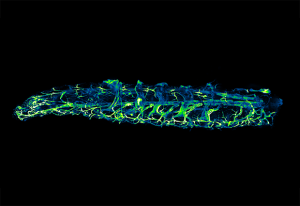
This image shows the tracheal system of a live fruit fly larva. Daniel Rios from the Leptin Group and Dimitri Kromm from the Hufnagel Group used this advanced microscope to investigate the dynamics of tracheal cells during development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
10 February 2020
This technique provides a simple but effective way to study the functions of organs in living animals
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
10 February 2020

How EMBL’s ‘Microscope in Action’ introduces teenagers to the basics of fluorescence microscopy
LAB MATTERS
6 February 2020
Scientists provide important new insights into the molecular basis of X-inactivation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
5 February 2020

EMBL co-leads most comprehensive study of genetic causes of cancer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
5 February 2020

Cloud computing offers unprecedented opportunities for global-scale research collaborations. It also presents a unique set of challenges in terms of data protection and the ethics of data sharing.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
5 February 2020
The largest and most comprehensive catalogue of cancer-specific RNA alterations reveals new insights into the cancer genome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
5 February 2020

Researchers at EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) and the Francis Crick Institute have analysed the whole genomes of over 2600 tumours from 38 different cancer types to determine the chronology of genomic changes during cancer development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
5 February 2020

Scientists from EMBL present a tool for large-scale analysis of genomic data with cloud computing. Main advantages of the new tool, called Butler, are continuous system monitoring and its ability to self-heal in case of failure, allowing for 43% more efficient data processing than previous…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
5 February 2020
Using the dataset from the Pan-Cancer project, scientists has developed methods to group, classify, and describe large rearrangements of the genome that are a key driver of cancer.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
5 February 2020

Analysis of whole cancer genomes gives key insights into the role of the non-coding genome in cancer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
5 February 2020
Researchers at Harvard Medical School and EMBL-EBI have carried out the largest analysis across cancer types of the newly discovered mutational phenomenon chromothripsis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
5 February 2020

Using the data from the Pan-Cancer project EMBL scientists describe how our genetic background influences cancer development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
4 February 2020
New resource that categorises genes essential for supporting life could be used to identify rare disease mutations
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
4 February 2020
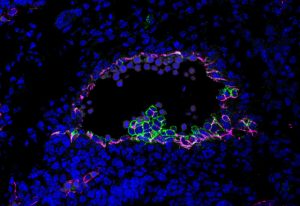
Morgan Oatley and her colleagues in Christophe Lancrin’s group investigated how haematopoietic stem cells emerge from the endothelium in developing mouse embryos.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
31 January 2020

Today marks the next chapter in the UK’s relationship with Europe. While we wait to see what a future relationship brings, researchers will continue to work across borders to tackle society’s most pressing problems, such as climate change, ageing, and disease.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
29 January 2020
New grant will increase collaboration between imaging centres and fuel scientific discovery
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
28 January 2020

Strengthening ties between EMBL and Israel through the Scientific Visitor Programme
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
people-perspectivesscience
28 January 2020
Muzamil Majid Khan, a postdoc in the Pepperkok team at EMBL Heidelberg, studied the piece of tissue visible in this image.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
27 January 2020

New group leader at EMBL Barcelona is investigating how malaria affects the human circulatory system
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
people-perspectivesscience
24 January 2020

László Palkovics, Hungarian Minister for Innovation and Technology, visited EMBL Heidelberg
CONNECTIONS
24 January 2020
EMBL researchers have developed a method to observe interactions between transcription factors
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
23 January 2020

EMBL Director honoured by the international RNA Society
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2020
embl-announcementsevents
22 January 2020

The new EMBL spinoff company Araxa Biosciences GmbH aims to set new standards for the development of antibody-based therapeutics and diagnostics
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
lab-mattersscience-technology
21 January 2020

Dame Janet Thornton presents the 2019 EMBL Insight Lecture: Ageing and disease – what is the link?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
eventsscience-technology
21 January 2020

Kristina Haase brings an engineer’s perspective to vascular disease and regenerative medicine
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
people-perspectivesscience
21 January 2020

Judith Reichmann will receive this year’s Paul Ehrlich and Ludwig Darmstaedter Prize for Young Researchers
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
21 January 2020
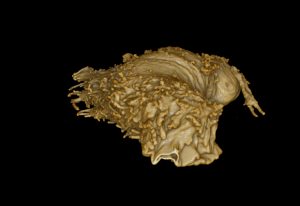
The image shown here is a 3D-rendering created by Julian Hennies from the Schwab team.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
20 January 2020
EMBL scientists identify drug targets in blood and organs
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
20 January 2020

The latest issue of the free magazine, Science in School, is now available for teachers worldwide.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
15 January 2020

The call for applications for Bridging Excellence Fellowships is now open
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
14 January 2020

The club provides a social outlet for EMBLers with a social conscience
LAB MATTERS
14 January 2020

This image has been composed from thousands of individual super-resolution microscopy images. It was created by Markus Mund in the Ries Group.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
7 January 2020
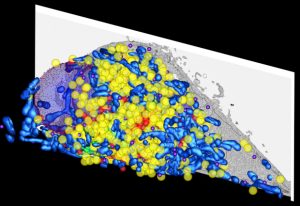
What might also be an artistic representation of a scattered bowl of Skittles is actually a 3D reconstruction of a high-pressure frozen HeLa cell.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
31 December 2019
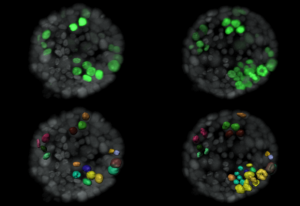
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women. It is so deadly because tumours often return after successful cancer treatment. This recurrence is caused by individual dormant cancer cells remaining inside the breast. These cells can develop into active cancer cells…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
24 December 2019
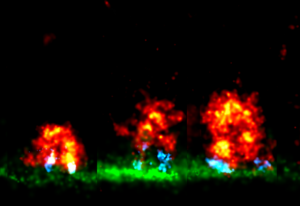
What looks like a photo-series of an explosive eruption are actually uptaking proteins, captured by Markus Mund from the Ries Group at EMBL Heidelberg. The images were made in an attempt to learn how the different proteins that take up molecules into the cells via endocytosis – the cellular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
23 December 2019

Researchers have developed a cheaper and faster method to check for genetic differences in individual cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
23 December 2019
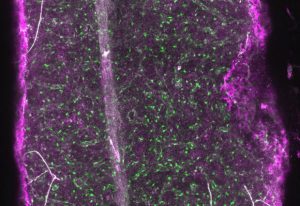
Researchers have developed new methods to reveal the 3D-organisation of bone marrow at a single cell level
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
20 December 2019
The software diffTF quantifies activity of transcription factors and predicts their mode of action
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
19 December 2019

EU funding for iNEXT-Discovery consortium unlocks key technologies for structural biology
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2019
embl-announcementslab-matters
18 December 2019

Celebrating the construction progress with a traditional German ceremony
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
17 December 2019

EMBL’s Jan Ellenberg reflects on the process of forming a European research infrastructure
LAB MATTERS
17 December 2019
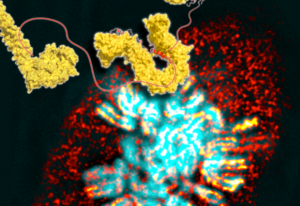
DNA is present in each cell of our body. If all the DNA from one human cell was removed and aligned in a single strand, it would in theory add up to a total length of about two metres. In order to fit into the nucleus of a cell, DNA has to be compressed by […]
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
13 December 2019

Forty-seven PhD students from all of EMBL’s six sites were celebrated during EMBL’s 2019 Graduation Ceremony on Friday 13 December
LAB MATTERS
13 December 2019

Resource has implications for disease research
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
13 December 2019

EMBL is now a member of the Instruct-ERIC organisation
LAB MATTERS
2019
announcementslab-matters
10 December 2019
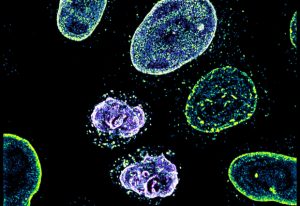
This picture of the week, taken by Arina Rybina in the Ellenberg group at EMBL Heidelberg, shows a high-resolution 3D microscopy image of living human cells: HeLa cells. In this fascinating fluorescing microspace, two newly formed daughter nuclei are captured to study the assembly of nuclear pore…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
9 December 2019

Professor Eiríkur Steingrímsson will commence his initial one-year term as Chair of EMBL Council on 1 January 2020.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2019
embl-announcementslab-matters
6 December 2019
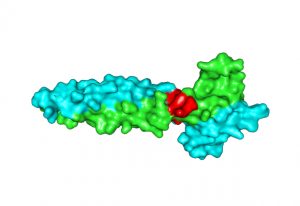
A new paper describes a unique mechanism of partner selectivity in transcription factors.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
3 December 2019
This beautiful mosaic of mostly hexagonal cells is the outer skin layer of a zebrafish larva as seen under a microscope. Each skin cell exhibits a unique pattern of actin ridges. Actin is a family of globular multifunctional proteins found in almost all eukaryotic cells. Actin forms microfilaments,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
2 December 2019

Unique long-term collaboration agreement to provide new imaging technologies
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
29 November 2019

Exploring the diverse routes by which EMBL scientists are driving forward neurobiology
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
26 November 2019
The hormone insulin helps to remove sugar from the blood after a meal. This is important, as in the long term high blood sugar levels damage our bodies. Diabetes of type 1 or type 2 is a direct consequence of a failure to produce sufficient insulin or to release it from the cells in which […]
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
25 November 2019
For many students in the life sciences, finishing a PhD marks a professional crossroads
LAB MATTERS
22 November 2019

Crick and EMBL PhDs talk science over coffee
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
people-perspectivesscience
21 November 2019
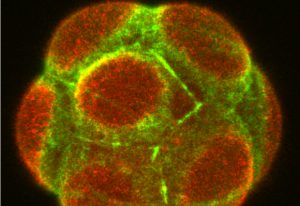
Shedding light on the mechanisms that control the fate of embryonic cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
20 November 2019

The Szilárd Library celebrates its 40th anniversary on 20 November 2019.
LAB MATTERS
19 November 2019
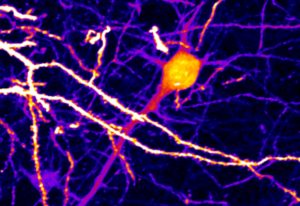
The brain is the most complex organ in the human body. Yet despite it being the organ that makes us conscious beings – and despite the fact that researchers have been studying it for generations – it’s still a constant source of surprise. To help lift the veil on some of its mystery, Lina…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
18 November 2019
A new technique in cryo-EM
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
18 November 2019

Two recent events have expanded EMBL’s collaboration with one of its newest member states
CONNECTIONS
15 November 2019
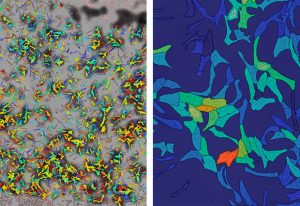
EMBL is a collaborator in four of the projects funded in the first phase of ATTRACT.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2019
embl-announcementslab-matters
14 November 2019
EMBL researchers have published two new studies involving the nuclear pore complex
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
12 November 2019

Children's rights stored in synthetic DNA
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsscience
8 November 2019

On microbiomes, public engagement and not being boring
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
eventspeople-perspectives
7 November 2019
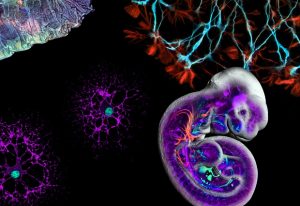
Euro-BioImaging now established as a European Research Infrastructure Consortium
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2019
connectionslab-matters
6 November 2019

Teresa Rodó shares insights from her career in the pharmaceutical industry
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
eventspeople-perspectives
5 November 2019

Edith Heard is inaugurated as EMBL Director General
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
5 November 2019
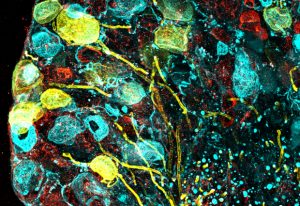
Traditionally, we talk about having five senses: sight, hearing, taste, smell and touch. In reality, our bodies are capable of much more. Sitting right under our skin are a variety of sensory neurons, which are specialised in detecting light touch, pain, temperature, itch or the body’s position.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
4 November 2019

New possibilities for gene therapies
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
30 October 2019

Nadia Rosenthal describes how she built EMBL Rome’s mouse house
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
alumnipeople-perspectives
29 October 2019

EMBL career advisors discuss the new portfolio of activities
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2019
embl-announcementslab-matters
29 October 2019

The three bluish blobs shown in the top right corner of this image may not resemble the sphere of noodles that is the human brain, but they are still essential – at least for the fruit fly. This Picture of the Week shows the brain lobes of Drosophila. It’s an insect so tiny and so […]
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
28 October 2019

Highlights from the Tara stopovers in Rome, Marseille, and Barcelona
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
23 October 2019
EMBL’s Genomics Core Facility supports students participating in the annual iGEM competition.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
22 October 2019
Is it a fungus or a strange plant? Actually it’s the larval form of Platynereis – a group of marine ringed worms. Scientists have been using them in their studies for the past 70 years, and they are among the preferred lab organisms. They are easy to keep in the lab, and under temperature and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
18 October 2019
Funding awarded to EMBL-EBI for tuberculosis monitoring tool
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
15 October 2019

EMBL not only produces excellent science and innovative technologies; it also shares its knowledge and experience with partners from around the world – and with the public. As well as offering teacher training in the European Learning Laboratory for the Life Sciences, science movie nights, and…
LAB MATTERS
2019
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
11 October 2019

EMBL at the first annual European Research and Innovation Days
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
10 October 2019

Scientists will discuss the challenges ahead for international science at the EMBL in the USA event.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
alumnipeople-perspectives
9 October 2019

During the Nacht der Forschung 2019, everyone was able to become a scientist for a day at EMBL
LAB MATTERS
8 October 2019
Despite missing the characteristic stripes one would expect from a zebra – or a zebrafish – the fractals in this Picture of the Week show a zebrafish; or at least some cells in a zebrafish embryo, a few hours after fertilisation. Zebrafish are not only popular aquarium fish, they are also an…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
3 October 2019
EMBL joins Tara in Barcelona to promote science and interdisciplinarity
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
1 October 2019
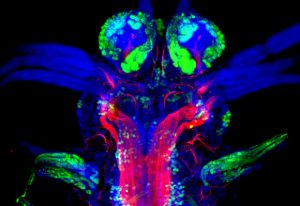
Model organisms are species that are studied extensively to understand particular biological phenomena and processes, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. The small marine ringed worm Platynereis dumerilii gained…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
30 September 2019

EMBL Barcelona will host the 2019 EMBL in Spain event
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
alumnipeople-perspectives
26 September 2019

From 27–30 September, Tara will be docked in the port of Marseille, France’s second largest city.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
25 September 2019

Fruit flies have something that we don’t have: they produce a protein called dumpy. This protein is the largest created by insects, and is comparable in size to the largest human protein – titin. While titin is vital for our muscle function, dumpy connects the soft cells of the insect’s…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
20 September 2019

When: Friday, 4 October at 16:30 – 18:00. Where: The press conference will be held on the Tara schooner at the Port Olímpic in Barcelona. What: A press conference on the new Tara mission on microplastics and Tara’s cooperation with EMBL.…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
17 September 2019
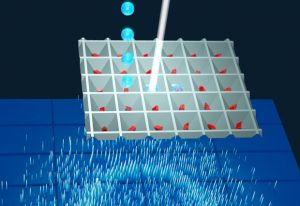
Researchers from Hamburg simplify time-resolved X-ray crystallography
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
17 September 2019

It’s evening and the Sun is setting over the mountains surrounding the city of Grenoble – home to one of EMBL’s six sites – bathing the mountaintops in fiery red light. The Picture of the Week, taken by Zuzanna Kaczmarska shows the lab she worked in after a long and busy day. Bottles…
LAB MATTERS
2019
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
16 September 2019
What: A press conference on the new Tara mission on microplastics and the Tara Ocean Foundation’s cooperation with EMBL. The press briefing will be followed by a visit to the schooner.When: Friday 27 September at 13:00 CEST.Where: The press conference will be held on the Tara…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
12 September 2019
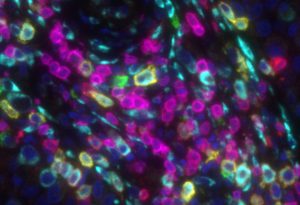
Immunotherapy: the role of B cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
12 September 2019

The next stop on Tara’s journey will be at the mouth of the Tiber
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
10 September 2019
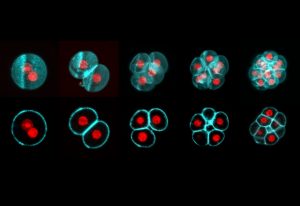
All mammalian life starts with the fusion of egg and sperm, resulting in the creation of a single cell called a zygote. This develops into an embryo through a series of cell divisions, in which the number of cells doubles at each step. Todays’ Picture of the Week was taken by Manuel Eguren of the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
6 September 2019
EMBL-EBI celebrated its 25 anniversary on 1 September 2019
LAB MATTERS
5 September 2019

September’s alumni event in Marseille will coincide with a Tara stopover
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
alumnipeople-perspectives
4 September 2019
When: Friday 13 September at 14:30.Where: The press conference will be held on the Tara schooner at the Porto Turistico di Roma (Lungomare Duca degli Abruzzi, 84, 00121 Roma RM, Italy).What: A press conference on the new Tara mission on microplastics and the Tara Ocean Foundation’s…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
3 September 2019

This gorgeous image of a stained adult marine worm was created by former EMBL postdoc Hernando Martinez using structured microscopy. The worm itself was captured during plankton extraction off the coast of Sweden. There are over 10 000 species of these swimming worms, and they have adapted to every…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
29 August 2019

The inaugural EMBL Lautenschläger Summer School ran from 15–26 July at EMBL Heidelberg.
LAB MATTERS
28 August 2019

Exploring the cancer genomics labyrinth
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
people-perspectivesscience
27 August 2019

The most basic building blocks of life are the biological molecules in our cells. While these molecules are too small to see with most microscopes, they have incredibly complex and beautiful structures. Therefore, the Protein Data Bank in Europe (PDBe), The Art Society CANTAB and The Art Society…
LAB MATTERS
2019
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
26 August 2019

Klaus Rajewsky recalls the pioneering spirit of EMBL Rome’s first years
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
alumnipeople-perspectives
20 August 2019

MEG3 adopts a complex three-dimensional structure to fulfil its tumour suppressor function.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
20 August 2019
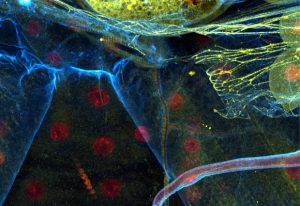
Today’s picture of the week is not only a colourful one, it is also a snapshot of the vast number of shapes that the cells inside an animal body can adopt. How this variety comes about is investigated in the Leptin group at EMBL Heidelberg. To understand the shapes of the cells in fruit fly…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
15 August 2019
Understanding how ageing works at a molecular level
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
13 August 2019

Working in a lab very often requires some kind of protection: gloves, safety goggles, lab coat, hearing protection. Sandra – now at BASF in Ludwigshafen – had fun getting ready for her work in the medicinal chemistry lab at EMBL! Here, she is about to grind potassium permanganate and copper…
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
people-perspectivespicture-of-the-week
12 August 2019

Bernd-Uwe Jahn, former EMBL Administrative Director, Ministerialrat and Jurist has passed away
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
alumniembl-announcements
9 August 2019

Native Scientist’ organises multilingual science workshops for children of migrant communities.
LAB MATTERS
8 August 2019

Images by EMBL researchers are included in an art–science exhibition in a Barcelona Metro station.
LAB MATTERS
6 August 2019

Schoolchildren get creative with 3D protein structures
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsscience
6 August 2019
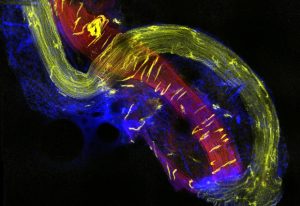
Low blood pressure (hypotension) or high blood pressure (hypertension) are risk factors for many diseases and affect more than 20% of the global population. How blood pressure is regulated is part of the research done in the Heppenstall group at EMBL Rome. In today’s Picture of the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
5 August 2019

Frank Gannon discusses the strong links between Australia and EMBL.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
alumnipeople-perspectives
2 August 2019

Eric Karsenti's combined loves of biology and sailing set in motion the Tara Oceans expedition
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
people-perspectivesscience
31 July 2019

Interview with Janka Motešická: a EUCYS 2018 prize winner
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
30 July 2019

The 1700 people working at EMBL’s six sites come from more than 80 different countries. Many of them haven’t come straight from their home country to one of the EMBL sites but have also lived in other countries in between. While all of them are proud to work at EMBL they are also proud of…
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
people-perspectivespicture-of-the-week
29 July 2019

Dr Cristian D. Magnus discusses LGBTQ+ issues and diversity in science
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
alumnipeople-perspectives
26 July 2019

EMBL Lab Day 2019 filled the ATC with art and games
LAB MATTERS
25 July 2019

Indrek Reimand discusses the life sciences in Estonia, a prospect member of EMBL.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2019
embl-announcementslab-matters
24 July 2019
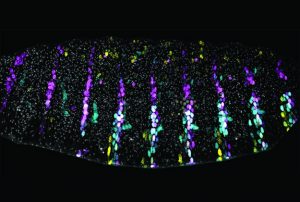
Enhancers in Drosophila embryos gather together to preserve phenotypes under stressful conditions
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
23 July 2019

Promotions for Anne Ephrussi, Rainer Pepperkok, Paul Flicek and Jo McEntyre
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2019
embl-announcementslab-matters
23 July 2019

The main funder of the EMBL Lautenschläger Summer School reflects on codes of conduct around giving
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
eventspeople-perspectives
23 July 2019
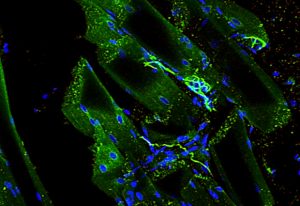
Every single moment of our life we use our muscles – most of the time without even thinking about it. Some muscles, like our heart, we cannot even control at all. How our brain communicates with our muscles is still not fully understood. The communication between our brain and our skeletal…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
22 July 2019
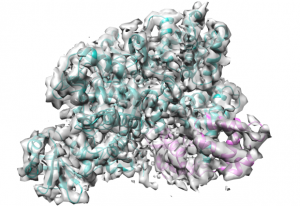
SidJ enforces a unique modification on human proteins and helps legionella grow.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
22 July 2019

Michael Zimmermann's group will investigate how gut microbes affect the body’s response to drugs.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
people-perspectivesscience
19 July 2019

Programme for Heidelberg | Mannheim
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
18 July 2019

EMBL scientists collaborate to develop new protocol for screening membrane protein stability
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
17 July 2019

Tomasz Smolarek and Natalia Kret in conversation.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
16 July 2019

Funding for EMBL | Stanford Life Science Alliance.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
16 July 2019
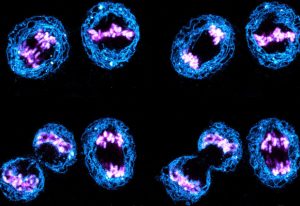
This colourful picture, taken by EMBL postdoc Arina Rybina using a confocal fluorescence microscope, shows human cells in the process of cell division. Eventually, each mother cell brings into existence two identical daughter cells. To visualise the process by light microscopy, different cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
15 July 2019

Does rearranging chromosomes affect their function? EMBL scientists reveal uncoupling of 3D chromatin organisation and gene expression.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
12 July 2019

The life science community is deeply saddened by the death of Suzanne Eaton
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
alumniembl-announcements
11 July 2019
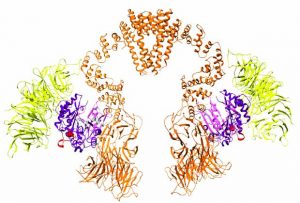
Using cryo-EM, scientists have determined the structure of a large protein complex called Elongator.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
10 July 2019

How computer processing of human language is harnessed by EMBL scientists
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
9 July 2019
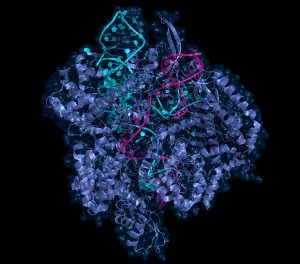
What CRISPR may bring for the future of biology, and how it is used at EMBL
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
9 July 2019

EMBL has six sites in Europe and the newest is EMBL Barcelona. It opened in October 2017 and is still growing. Eventually, it will be home to eight research groups, all of them working to discover how tissues and organs function and develop. EMBL Barcelona is located in the Barcelona Biomedical…
LAB MATTERS
2019
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
8 July 2019

Reflecting on 20 years of EMBLEM
LAB MATTERS
5 July 2019

EMBL alumna Jennifer Deegan built a prize-winning system for photographing ferns
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
alumniembl-announcements
5 July 2019

The naked mole-rat as a model organism in ageing research
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
alumnipeople-perspectives
4 July 2019

Setting up a kids coding club - where to start
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
3 July 2019
New insights into mechanisms behind embryonic development
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
2 July 2019

The BioImage Archive - EMBL-EBI's first dedicated imaging data resource
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
2 July 2019
What looks like a pair of scary alien eyes is actually the final stage in the duplication of a cell. Cell duplication is preceded by a process called mitosis, in which the replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Mitosis is the prerequisite for a cell to divide into two identical…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
1 July 2019
A conversation about art-science collaborations and the importance of drawing in biology.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
people-perspectivesscience
28 June 2019

EIPOD4 will prepare researchers for the increasing interdisciplinarity of scientific career paths
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2019
embl-announcementslab-matters
28 June 2019

The increasing importance of code in the biological sciences
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
27 June 2019

Nobel prize laureate Susumu Tonegawa describes his work in memory research over the past decade
LAB MATTERS
27 June 2019

The programme promotes education, collaboration and cutting-edge research
LAB MATTERS
26 June 2019

Joining forces to support early-career scientists
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2019
connectionslab-matters
26 June 2019

Using genomics to help endangered species
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
25 June 2019

EMBL is an intergovernmental organisation, currently supported by 26 member states, one prospect and two associate member states. There are more than 1700 people working at EMBL, who come from more than 80 countries, creating a multicultural environment. EMBL also operates from six sites in Europe:…
LAB MATTERS
2019
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
21 June 2019

Tara schooner welcomes on board journalists, policymakers, funders and scientists
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
20 June 2019
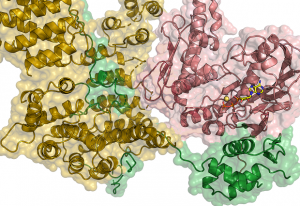
The mystery of how condensin maintains the integrity of the genome during cell division.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
19 June 2019

The team at ELLS use Lego to teach children the fundamentals of DNA.
LAB MATTERS
18 June 2019
Have you ever wondered what reflex testing is about? Why does your doctor tap the space below your knee with a hammer to see if your leg kicks forward? At the centre of this involuntary reaction is the muscle spindle, of which you can see a close-up in today’s Picture of the Week. Muscle spindles…
LAB MATTERS
2019
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
17 June 2019

EMBL Hamburg and Tara raise awareness of the risks of microplastic pollution and global infection
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
13 June 2019

The head of EMBL’s Barcelona site joins a prestigious group of more than 1800 scientists worldwide
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
12 June 2019
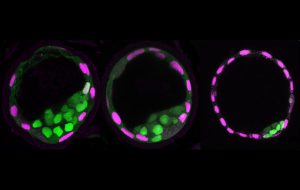
Uncovering new role of fluid pressure in controlling embryo size and cell fate
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
11 June 2019

Lithuania becomes EMBL’s 27th member state
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2019
embl-announcementslab-matters
11 June 2019

Laboratories all over the world are often chaotic, a bit messy and look grey and unwelcoming. Not so in this lab, pictured by EMBL staff member Emily Savage. The differently coloured fluids, arranged in a row, bring vivid colours into the more subdued environment of the lab. The picture was taken…
LAB MATTERS
2019
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
7 June 2019

Overwhelmed as a biologist getting to grips with computer programming? EMBLers are here to help!
LAB MATTERS
6 June 2019

Professor Tim Lewens challenges the human genome’s unique place in bioethics
LAB MATTERS
4 June 2019
When: Monday 17 June at 10:30Where: The press conference will be held on the Tara schooner at the Sandtorhafen in the Hamburg harbourWhat: A press conference on the new Tara mission on microplastics and Tara’s cooperation with EMBL. A tour of the schooner will be organised with the…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
4 June 2019
Most of us love brewer’s yeast, or at least the food that it’s helped us to produce since ancient times. Without Saccharomyces cerevisiae (its Latin name) we couldn’t enjoy wine, beer or most types of bread. Besides its role in food production, S. cerevisiae is also an important model…
LAB MATTERS
2019
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
3 June 2019
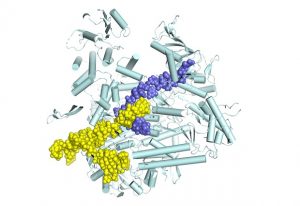
Snapshots of the flu virus replication machine in action
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
31 May 2019

EMBL got together with the global science festival Pint of Science to explain and celebrate science.
LAB MATTERS
28 May 2019

EMBL’s sites provide spectacular views, such as this fiery sunset at the Wellcome Genome Campus in Hinxton. The campus, in the heart of the Cambridgeshire countryside, is home to several institutes and organisations working on genomics and computational biology. Among them is EMBL’s European…
LAB MATTERS
2019
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
21 May 2019
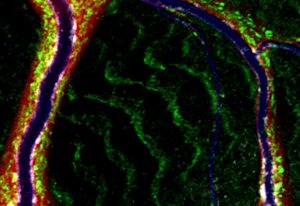
This image – resembling a network of rivers and canals – actually shows the tracheal tip cell of a fruit fly. Fruit flies are heavily used in research and they are a common model organism in developmental biology. Researchers at EMBL use the larvae of fruit flies to study tracheal cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
16 May 2019
Tara Ocean Foundation launches the exploration of 10 European rivers
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
15 May 2019
Scientists develop software tools for automated acquisition of electron microscopy data
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
14 May 2019

EMBL is a world-leading organisation for life science research. Its scientists work in diverse research fields spanning the whole of molecular biology. While the molecules the researchers are working on are often microscopic and impossible to see with the naked eye, one research topic clearly…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
9 May 2019

Edith Heard and Jean-Eric Paquet discuss the future of European science
LAB MATTERS
7 May 2019

The hexagons visible in this Picture of the Week are the eyes of an ordinary housefly, visualised with a scanning electron microscope. Former staff member Anna Steyer, who captured this brilliant image, has coloured seven of the receptor areas of the eye to create a stylised version…
LAB MATTERS
2019
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
2 May 2019

EMBL success in attracting EU funding
LAB MATTERS
29 April 2019

A newly developed 3D microscope visualises fast biological processes better than ever.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
26 April 2019

Results from the Tara Oceans expedition reveal the Arctic Ocean as a cradle of viral biodiversity
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
25 April 2019

EMBL scientists have discovered that the proteome is substantially affected by both sex and diet
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
18 April 2019

The current and previous Directors General discuss what it means to lead an organisation like EMBL
LAB MATTERS
16 April 2019
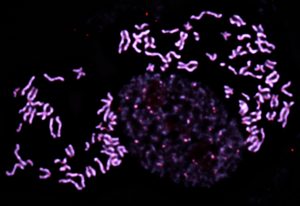
Thorough characterisation of structural variants in human genomes
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
12 April 2019

Building bonds between academia and industry
LAB MATTERS
11 April 2019

The Nordic EMBL Partnership directors discuss the value of collaborating across borders
LAB MATTERS
10 April 2019
Large CRISPR screen prioritises hundreds of promising genes for personalised cancer treatment
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
8 April 2019

New head of ORD will build and expand the partnerships that help EMBL achieve its ambitions
LAB MATTERS
5 April 2019
The Francis Crick Institute and EMBL have agreed to work together to strengthen European science
LAB MATTERS
2 April 2019
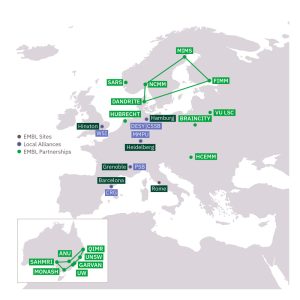
EMBL’s Plamena Markova reflects on the EMBL Partnership Programme
LAB MATTERS
1 April 2019

Foundation stone ceremony for world-class high-resolution microscopy centre in Heidelberg
LAB MATTERS
1 April 2019

Colorectal cancer characterised by consistent changes in gut bacteria across continents, cultures and diets
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
28 March 2019
EMBL scientists create membraneless organelle to build proteins in living cell
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
26 March 2019

EMBL begins partnership with Polish centre of excellence for neural plasticity and brain disorders
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2019
connectionslab-matters
21 March 2019

PDBe-KB - new data resource for protein structure and function launches
LAB MATTERS
18 March 2019

New EMBL group leader explores what neurobiology can teach us about what it means to be human
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
people-perspectivesscience
14 March 2019

On 20 February, over 250 local supporters and friends met Edith Heard to celebrate a successful year
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
eventspeople-perspectives
11 March 2019

Scientists develop technology to measure how ATP concentration affects protein solubility in cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
8 March 2019

New group leader at EMBL Grenoble is investigating the cellular role of melanoma antigens
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
26 February 2019
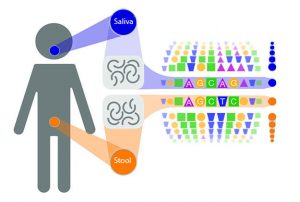
Many microbes traverse the oral-gut barrier
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
21 February 2019

Scientists honoured for contributions in cancer immunotherapy and structural biology
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
alumnipeople-perspectives
20 February 2019

How organs form in a mouse embryo
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
18 February 2019
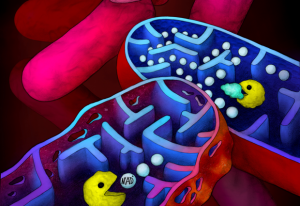
Suicide system in tuberculosis bacteria might hold key to treatment
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
14 February 2019

EMBL scientists identify RNA regulating protein behaviour in switch of normal roles
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
11 February 2019
Researchers identify novel gut bacteria species and call for more data from beyond Europe and North America
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
6 February 2019

On 5 February 2019, EMBL welcomed Poland as its 26th member state
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2019
connectionslab-matters
4 February 2019

A new database of bacteria in the human microbiome is the most comprehensive to date.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
4 February 2019
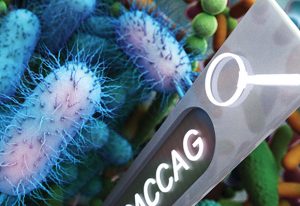
New search engine allows researchers to identify antibiotic resistance genes or mutations in real time
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
4 February 2019
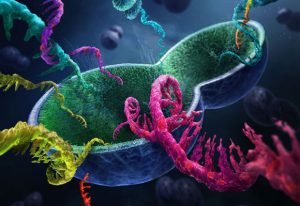
Scientists develop high-throughput yeast single-cell RNA sequencing method
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
1 February 2019
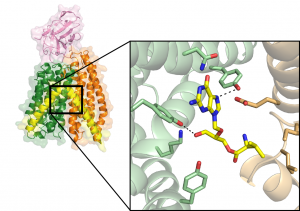
Scientists develop structural model that could help in the development of drugs with increased absorption rates
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
31 January 2019

Enhancing the world's bioinformatics infrastructure
LAB MATTERS
31 January 2019

A collection of the most read articles from the EMBL news website in 2018
LAB MATTERS
24 January 2019

Federated data sharing will now be possible on an unprecedented scale
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
23 January 2019

New director drives drug discovery partnership forward
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
17 January 2019

Joining forces to advance training in biomedical research and therapy
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2019
connectionslab-matters
2 January 2019

On January 1 2019, Edith Heard takes up the position of EMBL’s Director General
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
19 December 2018

Scientists build self-organising features into robot swarms to study shape formation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
18 December 2018

EMBL’s Design Team Lead on translating scientific discoveries into visual designs
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
17 December 2018
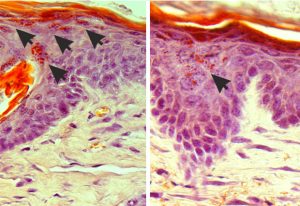
EMBL researchers have found a way to stop itch with light in mice
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
17 December 2018

What genetics can tell us about the structure of ancient human populations
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
eventspeople-perspectives
10 December 2018

Cancer researchers have developed a computer model to predict the course of disease for prostate cancer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
7 December 2018

EMBL’s GeneCore steps up to discover the facts and settle disputes
LAB MATTERS
6 December 2018
Researchers develop new method to analyse the entire protein-RNA network of the cell
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
5 December 2018

EMBL partners with the Hungarian Centre of Excellence for Molecular Medicine
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2018
connectionslab-matters
3 December 2018

EMBL-EBI industry case study: Biocatalysts
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
30 November 2018
What does it take to create a vaccine or improve cancer therapies?
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
lab-mattersscience-technology
28 November 2018

EMBL postdocs discover industry-led research opportunities at the Corporate Summer School
LAB MATTERS
27 November 2018

The EMBL Teens reporters discover the European Researchers’ Night
LAB MATTERS
26 November 2018

New algorithm will enhance understanding of relationship between genotype and environmental factors
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
26 November 2018

Building bridges between scientists and software developers
LAB MATTERS
22 November 2018

Nina Kathe, Winner of the EU Contest for Young Scientists visits EMBL
LAB MATTERS
21 November 2018

The EMBL Archive is open for business!
LAB MATTERS
19 November 2018

Scientists uncover effects of mutation that can cause autism and intellectual disability
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
16 November 2018

How EMBL scientists are using machine learning to advance biology
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
lab-mattersscience-technology
15 November 2018
The De Renzis group investigated invagination, the first step of organ development in embryos.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
9 November 2018

Translating 2D hospital scans into 3D prints is informing patients and aiding surgeons
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
alumniscience-technology
8 November 2018

Genomes of 66,000 UK species to be sequenced in global effort to sequence all known eukaryotic species
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
7 November 2018
EMBL scientists investigate the structure of a key protein involved in blood clotting
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
2 November 2018
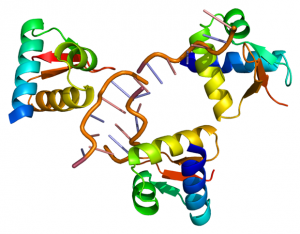
The Hentze Lab enhanced a RNA-interactome capture technique to pave the way towards medical progress
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
31 October 2018

Speeding up time-resolved X-ray crystallography with EMBL beamline P14
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
31 October 2018
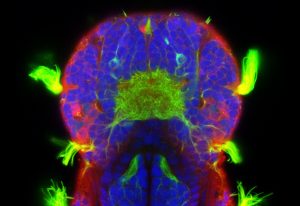
EMBL researchers discover that four organs in a marine worm’s head can sense different chemicals
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
30 October 2018

Pharmaceutical company Sanofi strengthens drug targets discovery collaboration Open Targets
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2018
connectionslab-matters
29 October 2018
EMBL Barcelona invites locals to celebrate its Inauguration Symposium
CONNECTIONS
26 October 2018

Ioanna Ydraiou and Bernd Pulverer spoke about their view of challenges and opportunities of OA.
LAB MATTERS
24 October 2018
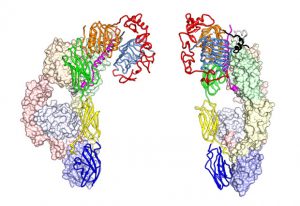
New study reveals how to make therapeutic insulins more effective than they currently are
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
23 October 2018
ERC grantees Wolfgang Huber and Oliver Stegle share their vision for the next 10 years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
22 October 2018
Researchers at EMBL Hamburg have released the next generation of their ARP/wARP software
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
lab-mattersscience-technology
19 October 2018

17 young scientists experienced hands-on training at EMBL Hamburg.
CONNECTIONS
16 October 2018
How embryonic stem cells develop into the germ line
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
15 October 2018
EMBL scientists gain mechanistic insights into how cellular signalling controls gene regulation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
9 October 2018

Meet Wendy Bickmore, Director of the MRC Human Genetics Unit, who spoke at the EMBL in the UK event
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
alumnipeople-perspectives
8 October 2018

EMBL alumni Gareth Griffiths and Rein Aasland receive the 2018 “Volunteer of the Year” award
CONNECTIONS
5 October 2018

Scientists in Finland met to share ideas and discover research opportunities
CONNECTIONS
4 October 2018

EMBL alumni and researchers working throughout Spain met in Madrid
CONNECTIONS
1 October 2018

Researchers from EMBL and Heidelberg University unveil the molecular mechanisms of ageing
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
27 September 2018

Meet the organisers of EMBO’s first course on molecular geobiology
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
eventsscience-technology
20 September 2018

EMBL and Promega collaborate to train young scientists
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2018
connectionslab-matters
17 September 2018
Retromer’s 3D structure improves understanding of cellular sorting and packaging
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
13 September 2018

X-ray experiments show that scaffolding protein PDZK1 has a L-shaped conformation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
10 September 2018
Real-time tracking of proteins during mitosis is now possible using a 4D computer model
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
5 September 2018

ATTRACT initiative will fund 170 breakthrough detection and imaging ideas with market potential
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2018
connectionslab-matters
30 August 2018

Complex metabolomics analyses in the cloud
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
29 August 2018
EMBL scientists discover how a component of the cohesin ring binds DNA
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
27 August 2018

Theoretical physicist Robbert Dijkgraaf discusses the importance of curiosity-based research
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
eventspeople-perspectives
23 August 2018
Large-scale systematic analysis explores how inherited genome affects drug response of cancer cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
22 August 2018

New head of the Mesoscopic Imaging Facility at EMBL Barcelona will help scientists visualise nature
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
people-perspectivesscience
16 August 2018

The ATTRACT initiative, of which EMBL is a partner, has launched an open call for seed funding
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2018
embl-announcementslab-matters
14 August 2018

The EMBL community, past and present, gather for special events around Lab Day 2018
LAB MATTERS
7 August 2018

EMBL Rome opens its labs for students to get their first real taste of science
LAB MATTERS
3 August 2018
An engineer’s approach to understanding morphogenesis
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
people-perspectivesscience
2 August 2018

Discover how EMBLers across all sites share their passion for science
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
1 August 2018
First global survey of soil genomics reveals a war between fungi and bacteria
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
26 July 2018
EMBL researchers visualise the proteins needed to capture molecules and bring them into a cell
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
26 July 2018

The Protein Data Bank in Europe celebrates its schools art project with its largest exhibition yet
LAB MATTERS
17 July 2018
Europe PMC adds preprints to its search
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
12 July 2018
Mammalian life begins differently than we thought
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
11 July 2018

Scientists show how bacteria and other microorganisms are passed on from mother to child
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
10 July 2018
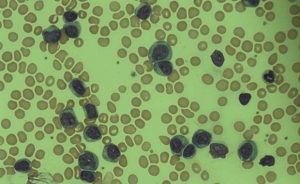
Acute myloid leukaemia risk could be detected years before diagnosis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
9 July 2018

New group leader at EMBL Barcelona creates artificial biological systems to study animal development
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
people-perspectivesscience
6 July 2018

EMBL scientists investigate how bacteria melt to study their reaction to drugs
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
4 July 2018
Combining antibiotics with each other, non-antibiotic drugs or food additives can alter their effectiveness
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
29 June 2018
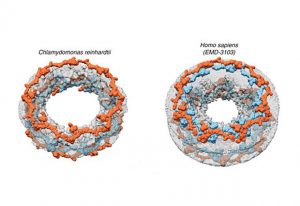
EMBL scientists reveal NPC architecture of algae
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
27 June 2018

Alumni share how joining EMBL’s IT team was a career upgrade
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
alumnipeople-perspectives
26 June 2018
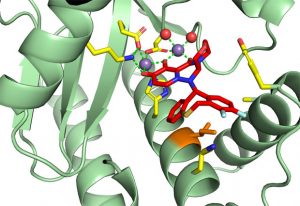
EMBL scientists investigate how influenza virus responds to new drug treatment
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
25 June 2018

EMBL researchers develop method that simplifies the isolation of DNA- and RNA- protein complexes
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
22 June 2018

Combinations of cancer drugs can be quickly and cheaply tested using a novel microfluidic device
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
21 June 2018

The programme promotes education, collaboration and cutting-edge research
LAB MATTERS
20 June 2018
EMBL scientists extend Turing’s theory to help understand how biological patterns are created
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
20 June 2018
New computational method uses multi-omics analysis for personalised medicine
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
19 June 2018

More than 80 attendees gathered at the EMBL in Italy event at the FIRC Institute of Molecular Oncology (IFOM) in Milan
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
alumnipeople-perspectives
18 June 2018
EMBL researchers guide the shape of cells and tissues with optogenetics
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
11 June 2018

Roche and EMBL join forces
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2018
connectionslab-matters
8 June 2018

A history of EMBL in six objects from the EMBL Archive
LAB MATTERS
4 June 2018

Which of our genes will be passed on to our children? Simone Köhler wants to find out
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
people-perspectivesscience
1 June 2018

EMBL and Pint of Science join forces to entertain and educate
LAB MATTERS
31 May 2018
Of mice and gorillas: using mouse data for conservation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
30 May 2018

Montenegro becomes EMBL’s 25th member state
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2018
connectionslab-matters
29 May 2018
Scientists at EMBL Hamburg determine shapes of intermediate states in dynamic biological systems
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
28 May 2018
EMBL’s next Director General reflects on the questions that drive her research
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
people-perspectivesscience
25 May 2018

EMBL alumna Melina Schuh recognised for excellence in science
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
alumnipeople-perspectives
24 May 2018

EMBL-EBI PhD student launches start-up focusing on epigenetics and wellbeing
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
23 May 2018
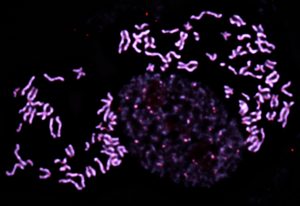
EMBL group leader Jan Korbel reflects on his scientific origins and current research
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
14 May 2018

Elisa Izaurralde, EMBL alumna, has passed away
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
alumnipeople-perspectives
11 May 2018

EMBL’s Director General has been elected to the National Academy of Sciences of the United States
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2018
embl-announcementslab-matters
10 May 2018
Researchers identify genes that can cause brain tumours in children and other cancers later in life
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
9 May 2018

EMBL alumna, Èlia Benito-Gutiérrez, on how her research and career evolved after searching the seas
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
8 May 2018

Mark Green, EMBL-EBI’s Head of Administration reflects on his time at the institute
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
alumnipeople-perspectives
7 May 2018

New platform transforms CRISPR gene editor into precision tool
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
4 May 2018

New partner strengthens drug discovery collaboration
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2018
connectionslab-matters
3 May 2018

What worms can tell us about cancer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
2 May 2018

On April 12, EMBL hosted 200 attendees at its Annual Reception in Heidelberg and highlighted its role as a training hub.
LAB MATTERS
26 April 2018
EMBL scientists uncover large solubility and thermal stability changes of proteins during the cell cycle
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
25 April 2018
Discover how EMBL scientists are using GPU computing to push biology forward
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
24 April 2018
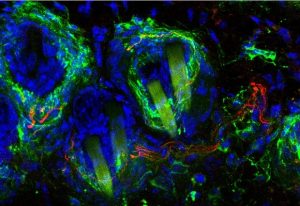
Scientists at EMBL Rome develop new method that uses light to manage neuropathic pain in mice
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
23 April 2018

Montenegro’s Minister of Science discusses the importance of international collaboration in research
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2018
connectionslab-matters
20 April 2018

New Heidelberg group leader creates tools to help biologists work faster and better
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
people-perspectivesscience
19 April 2018

Dog and human gut microbiomes have more similar genes and responses to diet than previously thought
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
people-perspectivesscience
18 April 2018

Markus Ralser, upcoming EMBO workshop speaker, on how metabolism brought chemistry to life
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
eventspeople-perspectives
9 April 2018

Open-source software allows standard microscopes to accurately image 3D structures
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
9 April 2018
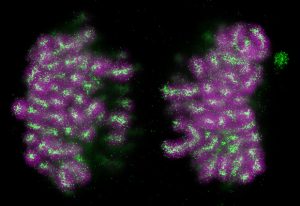
EMBL scientists count and locate chromosomal proteins during cell duplication
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
5 April 2018
Launch of the first free global online catalogue of PDX models
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
28 March 2018

New EMBL-EBI Group Leader will make sense of bioimaging data
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
people-perspectivesscience
26 March 2018
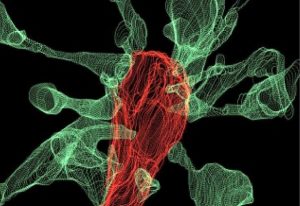
For the first time, EMBL Rome researchers have captured microglia nibbling on brain synapses on film.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
22 March 2018
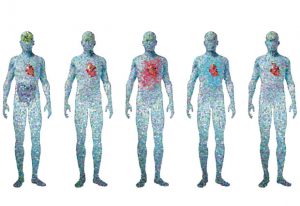
Following the completion of the Human Genome Project in 2001, scientists and the media described the genome as “the book of life”, holding the answers to the way genes are linked to disease. Yet, seventeen years later, we are still deciphering how cells interpret this book. Since…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2018
connectionslab-matters
22 March 2018
What does a cell's location tell us?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
21 March 2018

The new head of facility at EMBL Hamburg will help users solve protein puzzles
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
people-perspectivesscience
21 March 2018

EMBL Group Leader creates Ben Barres Prize to support talented young neuroscientists
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2018
embl-announcementslab-matters
20 March 2018
EMBL scientists discover how blood vessel cells become blood stem cells during embryonic development
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
19 March 2018
One in four drugs with human targets inhibit the growth of bacteria in the human gut, and may promote antibiotic resistance, EMBL researchers report in Nature
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
19 March 2018

EMBL scientists show how to grow a wide range of gut bacteria in the lab
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
15 March 2018

EMBL scientists unravel the molecular basis of a major antibiotic resistance transfer mechanism
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
15 March 2018
Scientists at EMBL and Cellzome develop technology to monitor the effects of drug treatments on protein degradation and synthesis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
14 March 2018
EMBL scientists show how chromatin usage in individual cells reveals developmental trajectories
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
14 March 2018
Thanos Halazonetis discusses the EMBO/EMBL Symposium: DNA Replication: From Basic Biology to Disease
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
eventsscience-technology
13 March 2018

For Vasiliki Karyoti, troubleshooting and problem-solving take on a greater meaning at EMBL
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
12 March 2018

School students build fluorescence microscopes designed by members of the Prevedel group and ELLS
LAB MATTERS
8 March 2018
EMBL scientists discover how two guidance cues work together when neurons project axons across the midline
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
7 March 2018

New EMBL spinoff company Velabs Therapeutics aims to speed up discovery of therapeutic antibodies
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
lab-mattersscience-technology
6 March 2018
Is depression in your genes?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
5 March 2018

Maria Leptin reflects on how to create a research environment that serves the needs of the community
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
5 March 2018

EMBL and EMBO hosted the ERC's Scientific Council in Heidelberg 28 February to 2 March
CONNECTIONS
2 March 2018
EMBL recognises the outstanding work of alumni with the John Kendrew and Lennart Philipson Awards
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2018
alumniembl-announcements
28 February 2018

Join us in our new editorial theme as we ask how everything began
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
28 February 2018
New technique offers insight into early cell life
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
23 February 2018

Discover the past lives and journeys that brought people to EMBL
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
23 February 2018

Access to state-of-the-art microscopes and outstanding expertise
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
22 February 2018
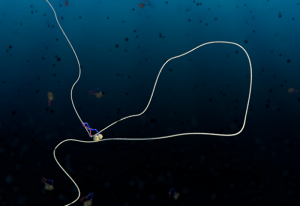
Researchers from Delft University and EMBL crack the mystery of condensin’s neat DNA loop extrusion
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
22 February 2018

EMBL scientists show that the rhythm between Wnt and Notch waves enables patterning in embryos.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
21 February 2018
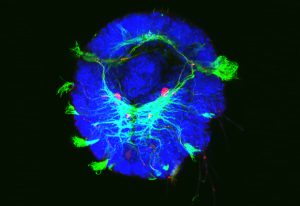
EMBL scientists discover how a molecule’s role changes from simple metabolite to instructive signal
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
21 February 2018

Joining forces for single-cell research
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2018
connectionslab-matters
20 February 2018

“In testimony of my great thankfulness”
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
alumnipeople-perspectives
16 February 2018

New EMBL group leader explores biophysical properties of chromosomes and other cellular assemblies
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
people-perspectivesscience
15 February 2018

EMBL Barcelona organises first school activity to coincide with the International Day of Women in Science
LAB MATTERS
15 February 2018
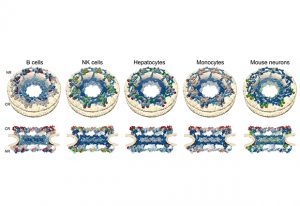
EMBL scientists create a turnover catalogue of almost 10.000 proteins from primary cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
13 February 2018

EMBL experts outline the trends shaping scientific training in the coming years
LAB MATTERS
12 February 2018
Network of genes linked to development of diabetes
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
12 February 2018

How Darwin’s work revealed the intimate relationship between orchids and insects
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
9 February 2018

EMBL’s new group leader studies how gene expression is controlled
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
people-perspectivesscience
8 February 2018

EMBL’s training programme launches its first e-learning courses: introductions to optogenetics and CLEM
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2018
embl-announcementsevents
31 January 2018

EMBL welcomes Slovakia as its 24th member state
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2018
connectionslab-matters
31 January 2018
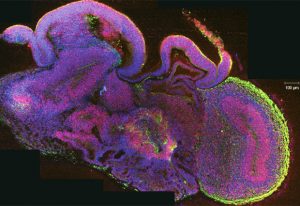
What opportunities can organoids bring to further the understanding of the human brain?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
eventsscience-technology
30 January 2018

Among refurbished labs, alumni relive memories and find traces of their time at EMBL
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
alumnipeople-perspectives
30 January 2018
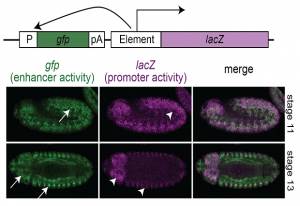
EMBL scientists show that some promoters can act as enhancers and vice versa
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
29 January 2018
EMBL instrumentation teams adapting tech to run biological experiments on the synchrotron after its upgrade
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
lab-mattersscience-technology
22 January 2018

Nick Goldman of EMBL-EBI issued a challenge in 2015. In 2018, a winner emerged just in time.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
17 January 2018
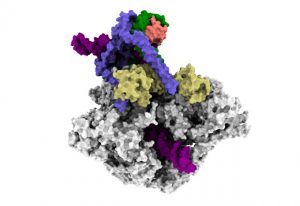
EMBL researchers uncover how a key enzyme that helps cells make new proteins starts its work
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
15 January 2018
New EMBL group leader investigates the mystery of heritable gene silencing
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
people-perspectivesscience
8 January 2018

New group leader studies sea anemones to investigate why some animals regenerate better than others
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
people-perspectivesscience
4 January 2018
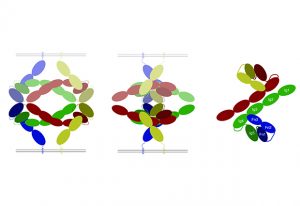
EMBL researchers solve a decades-long debate on a key process for brain and embryo-development
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
28 December 2017

EMBL scientists unveil how 3D chromatin structure affects RNA splicing
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
22 December 2017

Historian Soraya de Chadarevian explores how EMBL’s first Director General shaped molecular biology
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
21 December 2017

Molecule mapping method raises interest in forensics, agriculture and microbiome studies
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
21 December 2017

A look back at some of the most read stories on EMBL’s news website this year
LAB MATTERS
20 December 2017

What are the strangest genomes in EMBL-EBI's Ensembl?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
20 December 2017
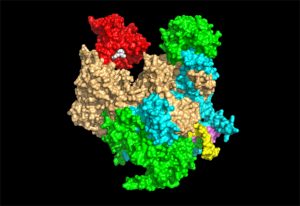
ERC grantee Stephen Cusack shares his vision for the next ten years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
14 December 2017
EMBL experts outline the trends shaping scientific training in the coming years
LAB MATTERS
14 December 2017
EMBL physicist-turned-biologist alumni win 2017 Kendrew and Phillipson awards
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
alumnipeople-perspectives
13 December 2017
New research reveals that two different mechanisms are responsible for chromosome folding
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
8 December 2017

How a research technician with a master’s degree contributed to Nobel Prize-winning work
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
alumnipeople-perspectives
7 December 2017
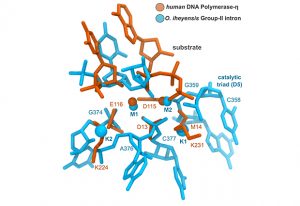
EMBL scientists superimpose structures of two-metal-ion enzymes and reveal new potential drug targets
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
7 December 2017

New research shows how pores form in the membrane that surrounds a cell’s nucleus
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
6 December 2017

High resolution 3D protein structures in a giffy with PDBe
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
5 December 2017

Curious about what goes on in EMBL’s Fly Room? Prepare to be a fly on the wall
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
4 December 2017

Takeda joins pioneering public-private drug discover collaboration Open Targets
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
4 December 2017

New group leader based in Grenoble aims to unveil the mechanisms of RNA editing
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
people-perspectivesscience
1 December 2017

New BioModels infrastructure supports significantly more model formats and offers improved search
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
30 November 2017

James Sharpe, Head of EMBL Barcelona, co-chairs the morphogenetic engineering-themed conference
CONNECTIONS
30 November 2017
New method for 3D imaging microorganisms lends insight into the creatures that inhabit our oceans
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
30 November 2017

EMBL Director General elect, Edith Heard, awarded 2017’s Grand Prix Inserm for her work in epigenetics
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2017
embl-announcementslab-matters
29 November 2017

EMBLers across all sites share how their curiosity about the world shapes their everyday life
LAB MATTERS
28 November 2017

Interview with EMBL’s Joint Heads of Government and EU Relations
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
27 November 2017

Takashi Hiiragi and Lars Steinmetz received Advanced Grants from the European Research Council (ERC)
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2017
embl-announcementslab-matters
24 November 2017
The Mahamid group studies meso-scale molecular assemblies in intact cells and model organisms at molecular resolution
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
people-perspectivesscience
24 November 2017
EMBL releases recommendations for the 9th EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
23 November 2017

EMBL alumna Sigrid Reinsch trained as a cell biologist – now she helps run experiments in space
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
alumnipeople-perspectives
22 November 2017
Insights into the reproduction of Plasmodium parasites in mosquitoes reveal rapid and broad activity
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
22 November 2017

20,000 visitors get sneak peek at giant particle accelerators at DESY DAY in Hamburg
LAB MATTERS
21 November 2017

Former EMBL Director General Fotis Kafatos passes away
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
alumnipeople-perspectives
20 November 2017

Six curious questions and the EMBL community's answers. Check back each week for the next question
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
20 November 2017

EMBL and HeidelbergCement sign Memorandum of Understanding
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
16 November 2017

Jacques Dubochet, Nobel laureate and former EMBL group leader, reflects on a key aha moment
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
alumnipeople-perspectives
14 November 2017
EMBL researchers create highest resolution 3D model of important structure within Ebola virus
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
14 November 2017

Inside the Centre for Structural Systems Biology
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
13 November 2017
A summary of recent research highlights from EMBL
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
10 November 2017

EMBL and the European synchrotron ESRF extend their Joint Structural Biology Group
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2017
connectionslab-matters
10 November 2017

As a new cryo-EM facility is inaugurated, EMBL’s Michael Hons describes his role in the project
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
7 November 2017

How open data is changing our pursuit of discovery
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
6 November 2017

Aid for Labs is an EMBL-based charity aiming to provide scientific equipment to researchers in need
LAB MATTERS
3 November 2017

A talent for organisation has taken EMBL’s Steffi Kandels-Lewis across the globe
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
2 November 2017

Five things researchers have learned from bizarre fruit flies
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
25 October 2017

Find out how curiosity is driving some of the work we do here at EMBL
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
25 October 2017

Meet Ig Nobel emcee Marc Abrahams, an EMBL Science and Society speaker in December
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
eventsscience-technology
25 October 2017

Interview with Rolf-Dieter Heuer, guest speaker at EMBL's 2017 Annual Reception
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
eventspeople-perspectives
25 October 2017

Working on scientific instruments has taken EMBL alumnus Simon Sheldon to the ends of the Earth
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
alumnipeople-perspectives
23 October 2017

Alumnus Michael Parker talks about his career, research highlights and how EMBL has played a role
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
alumnipeople-perspectives
19 October 2017

Women from academia, industry and politics met at EMBL to fuel career growth and opportunities
LAB MATTERS
5 October 2017
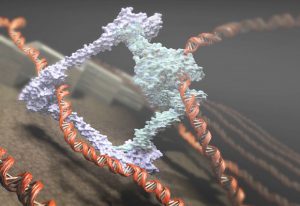
EMBL researchers and collaborators unravel how chromosomes form
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
4 October 2017

EMBL alumnus recognised for cryo-electron microscopy work
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2017
embl-announcementsscience
4 October 2017

How Australia’s associate membership of EMBL empowers scientists and drives collaboration
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2017
connectionslab-matters
4 October 2017

Bernt Eric Uhlin, Director of MIMS, will replace Kjetil Taskén, Director of NCMM
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2017
connectionslab-matters
3 October 2017
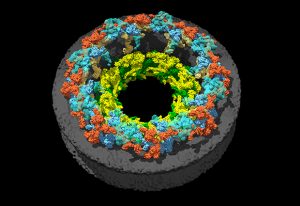
EMBL’s new group leader based in Hamburg aims to create models of infection cycles
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
people-perspectivesscience
2 October 2017

EMBL’s annual reception took place on 18 September, with more than 150 attendees
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2017
connectionslab-matters
29 September 2017

EMBL-EBI and collaborators engage schools in a large-scale genome decoding project
LAB MATTERS
29 September 2017

Q&A with EMBL-EBI's Head of Chemical Biology data services
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
people-perspectivesscience
27 September 2017

How microbes can create niches for each other
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
22 September 2017

International experts gather at EMBL-EBI to reflect on the future of bioinformatics training
LAB MATTERS
21 September 2017
New study by Paola Kuri and Maria Leptin shows how inflammation happens in zebrafish in real time
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
18 September 2017

How the work of the Courses and Conferences team has changed over the years
LAB MATTERS
7 September 2017

EMBL researchers separated facts from fiction at a Friends of EMBL Science Movie Night
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVESSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesscience-technology
1 September 2017

Newly opened European X-Ray Free-Electron Laser celebrates start of user operations
CONNECTIONS
31 August 2017

German state and federal governments agree funding for microscopy centre at EMBL Heidelberg
LAB MATTERS
29 August 2017
How patient-derived computational models can help researchers understand cancer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
28 August 2017

Lars Steinmetz. Director of the Life Science Alliance, reflects on the EMBL|Stanford initiative
CONNECTIONS
25 August 2017
Biologists Sydney Brenner and Richard J. Roberts addressed the importance of scientific archives
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
11 August 2017

Meet Justin Crocker, EMBL’s new group leader in gene regulation during evolution and development
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
people-perspectivesscience
9 August 2017

A new group at EMBL-EBI aims to decipher cell signalling networks
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
people-perspectivesscience
1 August 2017

The Iqbal research group hopes to build a 'Google of bacteria' to help better interpret the genome
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
people-perspectivesscience
26 July 2017

School student Andrea Totaro and EMBL group leader Christophe Lancrin reflect
LAB MATTERS
25 July 2017

NEB joins EMBL’s corporate partnership programme
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2017
connectionslab-matters
24 July 2017

EMBL-EBI supports bioinformatics training and capacity in Latin America
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2017
connectionslab-matters
20 July 2017
Genetic data from a major cohort now distributed via EMBL-EBI
CONNECTIONS
11 July 2017

EMBL’s cycling team complete epic journey to raise money for Heidelberg’s children’s hospital
LAB MATTERS
11 July 2017

EMBL’s unit in Italy changes name to better reflect new research focuses and highlight its location
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2017
embl-announcementslab-matters
7 July 2017

EMBL’s Iain Mattaj, the new Chair of EIROforum, on EIROforum’s role
CONNECTIONS
6 July 2017

On 29 June, at a ceremony in front of 700 guests, the Centre for Structural Systems Biology (CSSB) in Hamburg, was officially opened. At the event on the Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (DESY) Campus in Hamburg, Helmut Dosch, Chairman of the DESY Board of Directors, presented Head of EMBL Hamburg…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2017
connectionslab-matters
29 June 2017
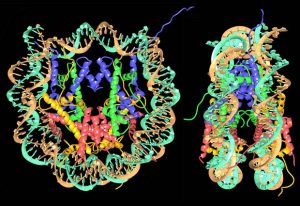
Tim Richmond looks back on the work that revealed the high-resolution structure of the nucleosome
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
eventsscience-technology
28 June 2017

Celebrating 40 years since the first EMBO electron microscopy training course
LAB MATTERS
28 June 2017

The 2018 EMBL course and conference sneak preview is now available!
LAB MATTERS
28 June 2017

Edith Heard’s mandate scheduled to begin 1 January 2019
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2017
embl-announcementslab-matters
27 June 2017
Science and Society event answers controversial questions about gut microbes
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
eventsscience-technology
26 June 2017

IMPC explains how much the sex of animals is misdirecting research results
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
26 June 2017

EMBL-EBI and IMPC characterised over 3000 mouse genes, revealing new gene associations with disease
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
15 June 2017

Exploring the potential of user experience for life sciences through industry workshops
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
eventsscience-technology
14 June 2017
The Image Data Resource - prototype of the first open repository linking imaging and molecular data
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
13 June 2017
EMBL’s Cornelius Gross wants to understand fear responses and the brain circuitry that governs them
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
9 June 2017
EMBL researchers complete a molecular atlas showing gene expression in all cells in an entire animal
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
6 June 2017
Two EMBL researchers are exploring new ways to filter out noise and get to the data they need
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
1 June 2017

EMBL-EBI, the Broad and UCSC Genomics Institute to build Data Coordination Platform with CZI support
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
lab-mattersscience-technology
31 May 2017

EMBL’s Hiroki Asari investigates how our internal state can change the way our eyes work
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
29 May 2017

Meet the head of EMBL's new Barcelona site, James Sharpe
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
people-perspectivesscience
29 May 2017

Inventor of OPT will be the first Head of EMBL’s new Barcelona site
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2017
embl-announcementslab-matters
25 May 2017

An EMBL collaboration devises a new method that could speed up vaccine development for HIV
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
24 May 2017

People across EMBL’s sites reflect on the ways they perceive their world
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
15 May 2017
Hallmarks of residual breat cancer cells suggest new approaches for preventing relapse
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
11 May 2017
Introducing one of the largest collections of high-quality human induced pluripotent stem cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
8 May 2017

The life science community is deeply saddened by the loss of EMBL alumnus Riccardo Cortese
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
alumnipeople-perspectives
8 May 2017

Accelerating researchers’ access to next-generation light-sheet microscopy
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2017
connectionslab-matters
5 May 2017

Meet Monterotondo’s new group leader for epigenetic reprogramming and inheritance, Jamie Hackett
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
people-perspectivesscience
3 May 2017
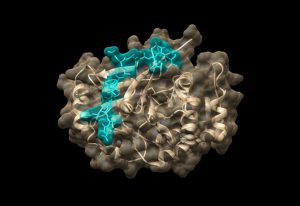
ERC grantee Maja Köhn shares her vision for the next ten years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
2 May 2017

EMBL welcomes its 23rd member state, with a promising collaboration already in place
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2017
embl-announcementslab-matters
27 April 2017
EMBL researchers develop an optical method for measuring the release of insulin from single cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
25 April 2017
EMBL scientists detect important function of genetic sequence our ancestors assimilated from a virus
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
13 April 2017
EMBL-EBI researchers identify mouse epigenetic clock that could help scientists understand ageing
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
12 April 2017

EMBL alumnus Konrad Müller has sadly passed away
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
11 April 2017

Call for applications for school students to join ‘Summer in Science’ in Monterotondo
LAB MATTERS
11 April 2017
EMBL scientists add crucial knowledge to understanding of the bacterium that causes tuberculosis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
10 April 2017
Spanish government and EMBL sign agreement for new site
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2017
embl-announcementslab-matters
10 April 2017

EMBL Director-General, Iain Mattaj, reflects on the work done to establish a new site in Barcelona
LAB MATTERS
7 April 2017

EMBL’s Monterotondo site strengthens links with the Italian scientific community
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2017
connectionslab-matters
6 April 2017
Study by EMBL and DKFZ researchers means origins of myeloid leukaemias may need rethinking
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
6 April 2017

Silke Schumacher explains how the new EMBL site in Barcelona came into being
LAB MATTERS
5 April 2017
New Master's programme for research infrastructure managers – set to launch autumn 2017
LAB MATTERS
31 March 2017

Researchers use single-cell sequencing to understand how cells age
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
29 March 2017

Anna Tramontano, bioinformatics pioneer and EMBL alumna, has passed away
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
29 March 2017

Janet Thornton reflects on the contributions of EMBL alumna Anna Tramontano
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
29 March 2017

The research community mourns the passing of Anna Tramontano
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
alumnipeople-perspectives
29 March 2017
Diversity, internationality and collaboration works, writes EMBL Director-General Iain Mattaj
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
24 March 2017

“Without John Kendrew there would have been no EMBL,” wrote Ken Holmes
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
24 March 2017
ERC grantee Edward Lemke shares his vision for the next ten years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
21 March 2017

EMBL’s new Academic Coordinator and Dean of Graduate Studies Monika Lachner leads programmes that help young scientists to flourish
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
13 March 2017
ERC grantee Detlev Arendt shares his vision for the next ten years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
13 March 2017
ERC grantee Eileen Furlong shares her vision for the next ten years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
9 March 2017
Keeping bacterial chromosomes tangled could lead to new approaches to treatment
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
8 March 2017

Ottoline Leyser on the fallacy of failure and the road to self-determination
LAB MATTERS
6 March 2017

Reconstructing T-cell development in high resolution
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
6 March 2017
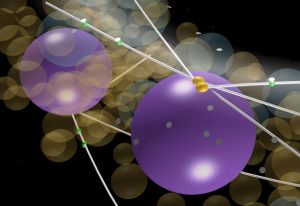
EMBL researchers develop a computer model to explore the movement of nuclei in a multinuclear cell
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
6 March 2017

EMBL alumnus Joep Muijrers talks about making the transition from science into business
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
alumnipeople-perspectives
2 March 2017
Differentiated and undifferentiated cells get energy in different ways, sensor made at EMBL shows
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
28 February 2017

EMBL alumna Zehra Sayers key driver of the Middle East’s first synchrotron project
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
alumnipeople-perspectives
24 February 2017

EMBL alumna Nicola Mulder reflects on her pan-African bioinformatics project and its impact
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
alumnipeople-perspectives
23 February 2017

Flies can do a lot for science, inside and outside the lab. EMBL alumna Isabel Palacios explains how
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
alumnipeople-perspectives
16 February 2017

Sartorius and EMBL join forces to support advanced training and science education
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2017
connectionslab-matters
16 February 2017

GSK and EMBL have signed an agreement to enhance understanding of disease and drug mechanisms
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2017
connectionslab-matters
16 February 2017

Beamline BM14 in Grenoble shuts down, continues collaboration with India
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
lab-mattersscience-technology
14 February 2017
A new technique developed at EMBL reveals the way fats interact with other molecules in cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
13 February 2017

EMBL scientists discovered that common mutations can change the shape of gene promoters
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
31 January 2017

In this interview from the EMBL Archive, Sir John Kendrew reflects on his time leading 'the Lab'.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
26 January 2017

Helke Hillebrand on leaving EMBL after 9 years as Academic Coordinator and Dean of Graduate Studies
LAB MATTERS
26 January 2017

Healing and anxiety are influenced by the genetics of one’s social partners
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
25 January 2017

New group leader Wojciech Galej investigates RNA-protein complexes involved in gene expression
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
people-perspectivesscience
12 January 2017

New mechanism revealed
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
9 January 2017
EMBL scientists find out how the prefrontal cortex puts a break on instinctive behaviours
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
21 December 2016
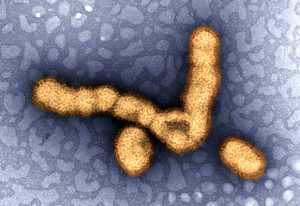
Understanding how the flu virus steals host RNA offers hope of new drugs
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
21 December 2016
Inducible mechanism found by EMBL scientists links receptor degradation and replenishment
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
20 December 2016

Ewan Birney's nine "Structures of Christmas" celebrate 20 years of PDBe
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
lab-mattersscience-technology
20 December 2016

Iain Mattaj on failure, adventure, determination and the Scientific Method
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
19 December 2016

For the past two months EMBL Heidelberg has hosted around 60 first year PhD students from EMBL’s International PhD Programme (EIPP). From thousands of applicants, the students were selected from over 40 countries to work on their PhD research at one of EMBL’s five sites – Grenoble, Hamburg,…
LAB MATTERS
15 December 2016
EMBL scientists use new techniques to describe the architecture of conical HIV capsids
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
14 December 2016

A new crystallography platform in Grenoble opens the door to new technological developments
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2016
embl-announcementslab-matters
13 December 2016
Research on the effect of nerve cell stiffness on sensitivity to touch could lead to new painkillers
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
8 December 2016

The PEPC course celebrated its 10th anniversary in Hamburg from the 12 – 20 September this year
CONNECTIONS
7 December 2016

Paul Nurse’s failed experiment inspired a career that would uncover key mechanisms of cell division
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
5 December 2016
New method combines signalling pathway data resources to improve systems biology research
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
2 December 2016

How Christian Löw’s failed experiment led to an unexpected scientific journey
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
1 December 2016

EMBL’s Petra Riedinger retires after 40 years producing posters, graphics, artwork and more
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
29 November 2016

How a team of scientists and artists at EMBL transformed microscopy data into stunning 3D images
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
lab-mattersscience-technology
24 November 2016
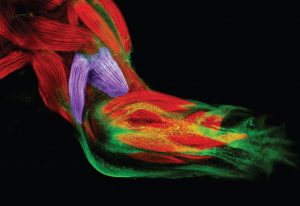
Exploring what it would take to regrow a lost limb, and what we might learn along the way
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
24 November 2016
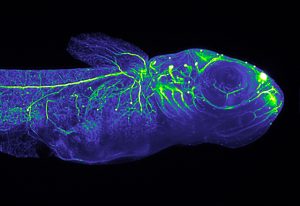
Ernst Stelzer earns 2016 Lennart Philipson award for advances in light sheet microscopy
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
alumnipeople-perspectives
24 November 2016

EMBL alumnus Jop Kind reflects on the questions that led him to this year’s John Kendrew Award
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
alumnipeople-perspectives
23 November 2016
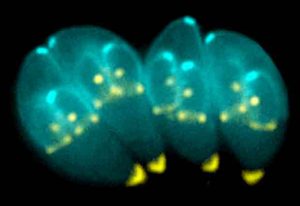
Parasite’s method of rewiring our immune response leads to novel tool for drug tests
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
22 November 2016

EMBL study finds that rearranging how DNA packs the nucleus can activate cancer genes
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
lab-mattersscience-technology
18 November 2016
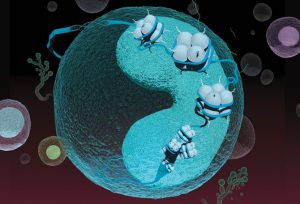
BLUEPRINT: EMBL-EBI and the push to decipher the blood epigenome
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
17 November 2016

Check out the newly revealed programme for 2017
LAB MATTERS
17 November 2016
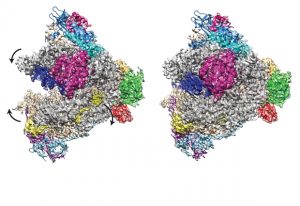
Cryo EM reconstruction of RNA Polymerase I reveals details of how molecule binds and transcribes DNA
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
15 November 2016

Open source bioinformatics method for finding metabolites makes experiments comparable across labs
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
11 November 2016

Upgraded server room is ready to take the heat at EMBL Grenoble
LAB MATTERS
10 November 2016

Hope Jahren’s autobiography educates and delights
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
4 November 2016
Where design meets bioinformatics, new scientific perspectives abound.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
3 November 2016
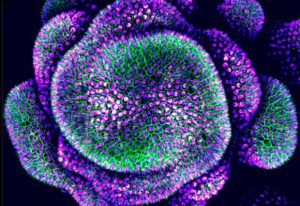
What happens when plant's leaf-placing feedback loop isn't quite right
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
27 October 2016

Robert Prevedel develops deep-tissue microscopy for scientists to peer deep inside living organisms
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
people-perspectivesscience
20 October 2016

Participants learn about EMBL’s ocean biodiversity research at the Fall Gala
CONNECTIONS
19 October 2016
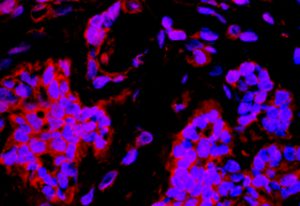
New platform useful for studies of protein binding, human tissue and more
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
17 October 2016

We catch up with neuroscientist Craig Stark, speaker at the EMBL/EMBO Science and Society Conference
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
14 October 2016

Global Alliance for Genomics and Health chose Birney to lead efforts to bring genomics to the clinic
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2016
embl-announcementslab-matters
14 October 2016
A rapid, versatile mechanism that modifies proteins is revealed to be crucial for the evolutionary process
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
6 October 2016

Rosemary Wilson talks about imposter syndrome and how to handle it
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
4 October 2016

EMBL scientists investigate how leaves grow flat to efficiently capture sunlight
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
30 September 2016

CamNTF hosts meetings around Cambridge, open to all scientists interested in new therapeutics
CONNECTIONS
30 September 2016
IMPC study identifies 410 genes essential to life in the mouse, providing a window on human disease
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
29 September 2016

EMBL recently attended the Naturejobs Career Expo, advising scientists about their career options
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2016
connectionslab-matters
28 September 2016

Eberhard Bengsch explains why EMBL’s events programme attracts him time and again
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
eventspeople-perspectives
27 September 2016

CORBEL Open Call launches October 2016, for access to 15 facilities and 8 research infrastructures
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
lab-mattersscience-technology
27 September 2016

Take part in an EMBL conference or symposium for free as an EMBL events reporter
LAB MATTERS
26 September 2016
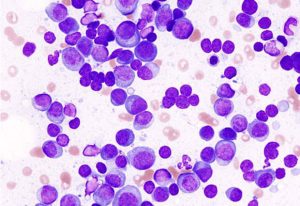
Side-effects of leukaemia drug explained, reveal possibility of repurposing to treat other diseases
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
26 September 2016

New head of Proteomics Core Facility also runs stability proteomics lab
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
people-perspectivesscience
23 September 2016
Puzzle of nuclear pore formation in growing nuclei solved
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
21 September 2016

EMBL alumnus Angus Lamond is driving forward new ways to explore the proteome
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
alumnipeople-perspectives
20 September 2016

Past meets present as Library head Ioanna Ydraiou interviews EMBL’s first librarian
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
alumnipeople-perspectives
13 September 2016
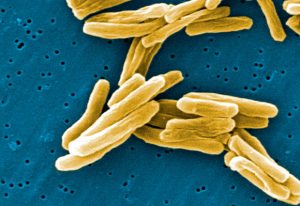
EMBL researchers help to design a lead compound active against four different pathogens
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
13 September 2016

Stephen Cusack looks back on the early days of his collaboration with Anacor developing anti-infectives
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
13 September 2016

Andrés Palencia on the design of compounds that may help fight drug-resistant TB and more
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
13 September 2016

A new repository helps identify emerging trends in data-driven science.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
lab-mattersscience-technology
12 September 2016

EMBL and the Hubrecht Institute signed a 5-year partnership agreement
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2016
connectionslab-matters
30 August 2016

Collaborating to take crystallography into a new time dimension
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
30 August 2016
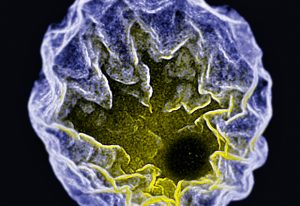
3D printing, gaming, virtual reality and lenticular posters bring new perspectives to research
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
30 August 2016

Turning the spotlight on the diverse universe of EMBL’s 200-strong postdoc community
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
30 August 2016

Celebrating the rich history of scientific contributions in Malta, EMBL's newest member state
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2016
connectionslab-matters
30 August 2016

Emmanuelle Charpentier sheds light on how CRISPR–Cas9 went from side project to global revolution
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
30 August 2016

Unexpected adventures at EMBL LearningLAB focused on biodiversity
LAB MATTERS
30 August 2016

"If I have an aim, I’ll find a solution" – meet EMBL alumnus Jochen Wittbrodt
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
alumnipeople-perspectives
30 August 2016

Integration, collaboration and openness on agenda for Carlos Moedas, European Commissioner for Research
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
30 August 2016

EMBL and ESRF scientists and mechanics work together on upgrade for one of Europe’s big X-ray sources
CONNECTIONS
30 August 2016

Alumnus and entrepreneur Marc Zabeau speaks at inaugural Life Science Funders and Foundations event
CONNECTIONS
30 August 2016
'The PDB plays a crucial role in structural biology research and development'
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
30 August 2016

Bruce Alberts on fixing the broken academic career pipeline
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
30 August 2016

Scientific community manager, alumnus Aidan Budd, connects people with shared interests, values, goals
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
alumnipeople-perspectives
29 August 2016

EMBL scientists regularly receive prestigious awards – meet the latest honourees.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2016
embl-announcementslab-matters
26 August 2016

Team leader investigates how the gut microbiome could relate to human diseases
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
10 August 2016

Storage of pre-made nuclear pores allows for rapid cell division in fruit fly embryos
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
8 August 2016
Detailed structure paves the way for more effective cancer therapies
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
4 August 2016

German students visit EMBL-EBI on a tour to explore a new culture and different career paths
LAB MATTERS
3 August 2016
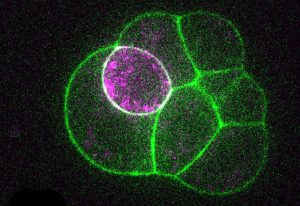
Strength of contraction determines whether cells become embryo or placenta
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
1 August 2016
Molecular messengers synthesised to help study how cells respond to outside stimuli
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
28 July 2016

New technique reveals uncharted docking sites in RNA-binding proteins
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
22 July 2016

EMBL Alumni Association Board review progress and discuss new initiatives
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2016
alumniembl-announcements
14 July 2016
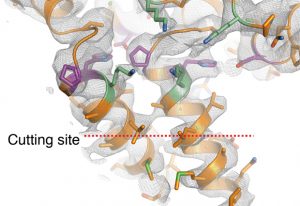
Study provides insights into workings of new HIV drugs and how virus becomes resistant
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
12 July 2016

Core Technologies in Life Sciences (CTLS) association will be key resource for facility professionals
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
7 July 2016
“Like getting hold of a microscope for the first time”
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
30 June 2016

Collaborations shorten distance between EMBL Heidelberg, Germany, and CEITEC in Brno, Czech Republic
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
30 June 2016

In a time of great uncertainty, key facts about EMBL's status, collaborations, funding and recruitment
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
29 June 2016

New group leader combines physics and biology to answer the 'hows' of cell movement
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
people-perspectivesscience
24 June 2016

27 former Bork lab members joined Peer for a full-day get-together this summer
LAB MATTERS
24 June 2016

The UK’s decision to leave the EU has no direct consequences for the UK’s membership of EMBL
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2016
embl-announcementslab-matters
16 June 2016

Studying at EMBL in Grenoble helps Japanese postdoc see her native country through different eyes
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
14 June 2016
How cells eliminate protein deposits that can lead to neurodegenerative disorders
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
13 June 2016

Establishing a programme of research, development and user services for time-resolved crystallography
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
9 June 2016

Meet the secret timekeepers of EMBL events: AV technicians Sean Nightingale and Jan Abda
LAB MATTERS
7 June 2016

Grenoble-based Partnership for Structural Biology (PSB) renewed for five more years
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2016
connectionslab-matters
27 May 2016

Marco Tripoldi and Valeria Carola join colleagues and peers at gathering of Italy-based alumni
CONNECTIONS
23 May 2016

Abel Ureta-Vidal and Louise Modis join colleagues and peers at gathering of UK-based alumni
CONNECTIONS
22 May 2016

What's a microbiome? How on Earth do they work?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
20 May 2016

Dozens of postdocs boosted their careers with a voyage aboard the Tara Oceans research schooner
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
people-perspectivesscience
20 May 2016

New method enables scientists to use light to direct where cancer cells go
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
17 May 2016

From shared interests at a conference to a surprising discovery
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
17 May 2016
Upgrading your conference experience with the new EMBL Events app
LAB MATTERS
10 May 2016
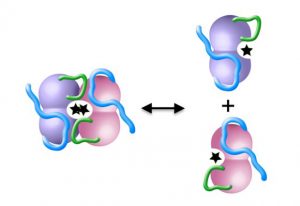
Unexpected results: structure of DAPK enzyme reveals dual-purpose loop
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
9 May 2016

A perfect match: behaviourist Takefumi Kikusui visits the Gross group to explore animal attraction
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
3 May 2016
Largest-ever study of breast cancer genomes reveals new genes and mutations
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
28 April 2016
Stool transplants: finding the right match important, EMBL study shows
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
21 April 2016

How EMBL scientists are discovering and understanding the waves and rhythms inside us
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
21 April 2016

Florent Cipriani talks about his passion for developing beamline instrumentation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
21 April 2016

EMBL PhD project puts development in a new light
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
21 April 2016

Neuroscientist and comedian Sophie Scott explains the complexity and social importance of laughter
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
eventspeople-perspectives
21 April 2016

Review of 'Life’s Blueprint: The Science and Art of Embryo Creation' by Benny Shilo
LAB MATTERS
21 April 2016

EMBL's ninth administrative director Keith Williamson looks back at 14 years at the Laboratory
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
alumnipeople-perspectives
21 April 2016

Illustrator Edmond Baudoin donates an original artwork to the EMBL Archive
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
21 April 2016

EMBL rewards the special work of alumni through the John Kendrew and Lennart Philipson awards.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2016
alumniembl-announcements
21 April 2016

EMBL scientists regularly receive prestigious awards – meet the latest honourees.
LAB MATTERS
21 April 2016

Meet a driving force behind collaborations with the Slovak Republic, alumnus Jozef Ševčik
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
alumnipeople-perspectives
21 April 2016

Gareth Griffiths, new Chair of the Alumni Association, reveals his many perspectives of EMBL
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
alumnipeople-perspectives
21 April 2016
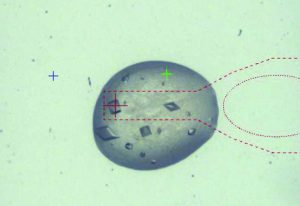
CrystalDirect, developed at EMBL, automates crystal preparation for X-ray analysis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
14 April 2016
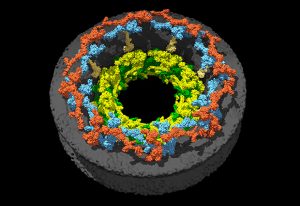
First detailed structural description of all the rings of nuclear pores
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
14 April 2016

Alumna Angela Relogio tells us about her passion for science, communication and mentoring
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
alumnipeople-perspectives
7 April 2016

Why does a cookie look different depending on how hungry you are? Neuroscientist Asari wants to find out
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
people-perspectivesscience
31 March 2016
Information on structure of molecule used for genome engineering yields increased efficiency
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
24 March 2016
Subtle genetic differences destine cells to placenta or animal, very early in embryo development
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
24 March 2016
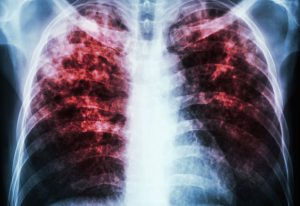
How an EMBL team is making and sharing tools to explore tuberculosis protein structures
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
21 March 2016

Commentary in Nature Methods introduces the EMPIAR resource and gives glimpse of future developments
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
21 March 2016
1st real-time video of starfish egg cell eliminating crucial structures, to ensure embryo viability
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
21 March 2016
New technique uses X-rays to find landmarks when combining fluorescence and electron microscopy
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
18 March 2016
Neural mechanisms in mouse brains indicate that we actively forget as we learn
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
8 March 2016
![A new tool for single-cell genomics helps us better understand differences between T cell populations. [Illustration: Spencer Phillips, EMBL-EBI]](https://www.embl.org/news/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/TCell_news_EMBL-e1457443531496-300x205.jpg)
TraCeR: new method for studying T cells opens up opportunities to explore immune responses
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
8 March 2016

Award acknowledges leadership in gender equality on the Wellcome Genome Campus
LAB MATTERS
7 March 2016
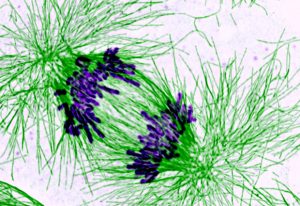
Structural insights into how cohesin keeps DNA together during the cell cycle
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
3 March 2016
First detailed atlas of start points for genes expression in malaria-causing parasite
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
29 February 2016

Iain Mattaj talks about the search for his successor
LAB MATTERS
25 February 2016

“It’s a bit like drawing a picture of an intricate object just by looking at its shadow on the wall."
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
16 February 2016
How stem cells resist change
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
12 February 2016
What do cells in an embryo have in common with schools of fish, swarms of fireflies, and applauding audiences?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
11 February 2016
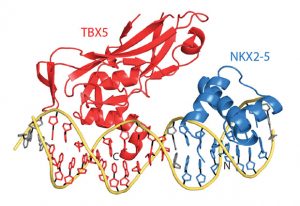
How transcription factors interact to create a heart
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
11 February 2016

Independent analysis of EMBL-EBI underscores the value and impact of open data in the life sciences
LAB MATTERS
10 February 2016

Plankton network linked to ocean's biological carbon pump revealed
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
8 February 2016

Pioneering target validation collaboration expands to accelerate drug discovery research.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2016
connectionslab-matters
4 February 2016

Protein screens developed at EMBL Hamburg now commercially available
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
28 January 2016

Former Head of EMBL Grenoble passed away on 21 January 2016 at the age of 89
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
alumnipeople-perspectives
25 January 2016

"We’re open! We’re open to working with everybody, we’re open to new things."
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
18 January 2016
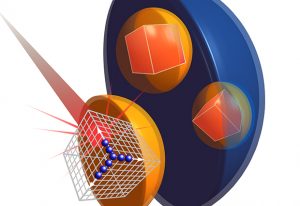
Hamburg collaborators analyse protein crystals inside the cells that made them.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
15 January 2016
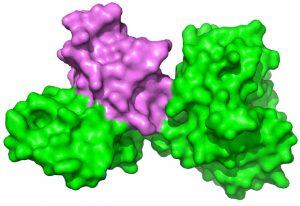
Further insights into how viral enzymes degrade the cell walls of Clostridia bacteria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
13 January 2016

Scientist and showman: PhD student Vasily Sysoev shares his passion for outreach.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
eventspeople-perspectives
11 January 2016
New method is first to enable parallel profiling of the transcriptome and epigenome of a single cell.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
17 December 2015

From initial development to a start-up company: Selective Plane Illumination Microscopy (SPIM) at EMBL.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
17 December 2015

With 28 conferences and 57 courses, 2016 will be EMBL’s most eventful year to date.
CONNECTIONS
17 December 2015

Find out what’s in store at the 2016 Core Technologies for the Life Sciences meeting.
CONNECTIONS
17 December 2015

GOBLET initiative supports pan-African bioinformatics trainers in Cape Town.
CONNECTIONS
16 December 2015

Designer Aditya Kusuma Jati reveals what makes a good event poster.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
eventspeople-perspectives
14 December 2015
New microscope can record the first days of a mouse embryo’s life
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
11 December 2015
Making it easier to visualise, understand and predict how proteins combine to drive biological processes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
9 December 2015

Two PhD students sink their teeth into the science and speculations of Jurassic Park.
LAB MATTERS
8 December 2015
Identifying evidence-based relationships between drug targets and diseases.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2015
connectionslab-matters
2 December 2015
Commonly used diabetes drug metformin impacts gut bacteria more than disease itself
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
30 November 2015
The new Toolkit for Trainers, an online resource hosted at EMBL-EBI, helps biomedical science trainers create and explore new ways of teaching.
LAB MATTERS
30 November 2015

"There’s nothing nicer than seeing a user leave the facility happy"
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
27 November 2015

Connecting entrepreneurs and world leaders in genomics to address opportunities and challenges.
CONNECTIONS
25 November 2015
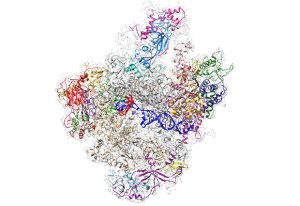
CryoEM solves 3D atomic structure of largest and most elusive RNA polymerase.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
25 November 2015

Compelling short stories that shine light on the life and work of EMBL staff.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
25 November 2015

Roland Block, EMBL's Head of HR, on emphasising the ‘human’ in human resources.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
25 November 2015

From jumping genes to organ transplants, the non-human features that make us human.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
25 November 2015
What really sets humans apart? Forming societies, teaching and compassion, says Agustin Fuentes.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVESSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
people-perspectivesscience-technology
25 November 2015

Ewan Birney on the risks, rewards and realities of studying humans as a model species.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
25 November 2015

Halldór Stefánsson on the long history of complex interactions between humans and animals.
LAB MATTERS
25 November 2015

Giuseppe Testa reflects on the myriad intersections of our digital and biological lives.
LAB MATTERS
25 November 2015

Highlights from the 'What makes us human?' symposium at EMBL Heidelberg.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
eventspeople-perspectives
25 November 2015

Postdoc Thibaut Brunet reviews two popular science books that explore the rise of Homo sapiens.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
25 November 2015

What does a physicist do in a biology lab?
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
24 November 2015

EMBL scientists regularly receive prestigious awards – meet the latest honourees.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2015
embl-announcementslab-matters
24 November 2015

Sybrand van der Zwaag gives his five top tips for young researchers thinking about their next move.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
24 November 2015

A snapshot of the many activities and events that took place in the world of EMBL this Autumn.
LAB MATTERS
23 November 2015

Energy, enthusiasm and endurance on tap as thousands attend 12-hour Hamburg Night of Science.
LAB MATTERS
19 November 2015
Using lasers to shed light on how tissues get into shape
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
12 November 2015

From paper microscopes to zebrafish embryos, EMBL Science Days stand had something for everyone.
LAB MATTERS
11 November 2015

Annual EMBL-EBI Open Day showcases bioinformatics services, training and career opportunities.
LAB MATTERS
9 November 2015
Embryology, genomics and bioinformatics combine to identify factors regulating mammalian pluripotency.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
6 November 2015

Behind the scenes of the EMBL alumni chapter meeting in Zürich, Switzerland.
CONNECTIONS
4 November 2015

Science met business and strangers became friends at the first Friends of EMBL Ladies Night.
LAB MATTERS
30 October 2015

Fibres that pull membrane to form a vesicle exert a force that’s 2500 times a yeast cell’s own weight
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
30 October 2015
Findings help demonstrate the evolutionary basis for allergy.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
29 October 2015
Enzyme Portal makes it easier to explore all enzyme-related data in EMBL-EBI’s public resources.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
26 October 2015

Hamburg researchers have a ball creating game to explain transporter protein mechanism.
LAB MATTERS
23 October 2015

Behind the scenes of the EMBL-VIB alumni Benelux meeting.
CONNECTIONS
15 October 2015

Evaluation of MinION™ sequencer finds performance and reliability consistently good.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
14 October 2015

Study of mouse embryonic stem cells reveals new genes involved in the stem-cell regulatory network.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
14 October 2015
A microscopy technique is poised to shine new light on biological questions: as sheets of light can scan everything from developing embryos to single cells or functioning brains, a technique called light-sheet microscopy is gaining traction. It enables scientists to observe living cells in three…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
lab-mattersscience-technology
9 October 2015
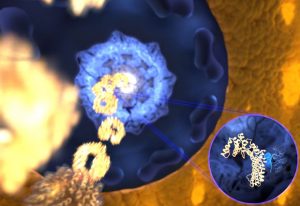
Spaghetti-like proteins are surprisingly effective 'keys'
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
5 October 2015

Amidst the excitement of Nobel Week, behind the scenes of the annual Lindau Nobel Laureate Meetings.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2015
connectionslab-matters
2 October 2015

1000 Genomes Project pushed technologies and knowledge forward to understand what is 'normal' human genetic variation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
1 October 2015
From the role of diatoms to how life evolved - scientists' pressing questions about life in the sea.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
1 October 2015

Long-time events pro Antje Seeck gives us her take on how to organise a successful conference.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
eventspeople-perspectives
30 September 2015

Missing a gene may not be a big deal – a conclusion from global catalogue of genetic changes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
29 September 2015

Sveiki Lietuva! Lithuania becomes EMBL’s fourth prospect member state.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2015
embl-announcementslab-matters
29 September 2015

EMBL-Wellcome Genome Campus events collaboration showcases open, application-based science.
CONNECTIONS
29 September 2015

Gold medal celebrates Eric Karsenti’s exceptional career and outstanding contributions to biology.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2015
embl-announcementslab-matters
29 September 2015

Renewals and reunions: EMBL’s Nordic partners look to the future.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2015
connectionslab-matters
28 September 2015

Insights from organisers of upcoming EMBO|EMBL Aquatic Microeukaryotes symposium.
CONNECTIONS
28 September 2015

Highlights from EMBL-EBI’s Training Programme: Open Day, revamped webpages, free webinar series.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2015
embl-announcementsevents
23 September 2015

A nuclear pore riddle: how can you use the same number of pieces to form two rings that fit inside each other?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
22 September 2015

MASSIF-1 processes its 10,000th crystal, less than one year after the beamline became operational.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
17 September 2015

Multifaceted approach reveals how brain and liver age, helps explain why ageing brain loses plasticity.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
14 September 2015

Introducing the Small Angle Scattering Biological Data Bank, developed at EMBL Hamburg.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
lab-mattersscience-technology
14 September 2015
![Tara expeditions docks in London, September 2015, on its way to the UN Climate Change Conference in Paris. [PHOTO: Robert Slowley]](https://www.embl.org/news/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/1509-tara-london-ib-300x206.jpg)
Tara Oceans research vessel welcomes aboard scientists, policymakers and funders.
CONNECTIONS
13 September 2015

Ephrussi group alumni reunite in Heidelberg for a surprise birthday celebration.
LAB MATTERS
11 September 2015

Alumni Rune Linding and Guillermo Montoya join colleagues and peers at the first Danish chapter meeting.
CONNECTIONS
10 September 2015

New computational method to study biological signalling networks in healthy and cancer cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
9 September 2015

Insights from the evangelical Vint Cerf, a “founding father of the Internet”, during a visit to EMBL.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
eventspeople-perspectives
7 September 2015

“A structure alone is not so interesting, you need the biology too,” says new NMR-focused group leader
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
7 September 2015

Genevieve Almouzni and Nicolas Le Novère share their insights at alumni chapter meeting hosted in the UK.
CONNECTIONS
3 September 2015

New group explores why patients with same cancer exhibit unique constellations of genetic mutations.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
26 August 2015

"It's like living a review!" Participants of recent super-resolution microscopy course share their highlights
CONNECTIONS
25 August 2015

Maja Köhn’s lab is ideal to learn what life is like working at the interface of disciplines.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
24 August 2015

EMBL rewards the special work of alumni through the John Kendrew and Lennart Philipson awards.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
alumnipeople-perspectives
24 August 2015

Andrew Miller, first head of EMBL Grenoble, reflects on four decades at the Outstation.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
alumnipeople-perspectives
24 August 2015

Janet Thornton reflects on her time as Director of one of Europe’s fastest growing research institutes.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
24 August 2015

EMBL Alumni Association board meets for the last time in their current constellation.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2015
alumniembl-announcements
24 August 2015

Results are in for the EMBL Alumni Association board election – the board takes up office in 2016.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2015
alumniembl-announcements
24 August 2015

Theodore Alexandrov is using mathematics to analyse the countless molecules produced by our cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
24 August 2015

Alumnus Thomas Vaccari reflects on the first joint symposium with EMBL Monterotondo, in Milan.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
eventspeople-perspectives
24 August 2015

EMBL scientists regularly receive prestigious awards – meet the latest honourees.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2015
embl-announcementslab-matters
24 August 2015

Behind the scenes of start-up Miroculus, developing a non-invasive test for early-stage disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
alumniscience-technology
24 August 2015

A journalist who spent six weeks aboard Tara reflects on the expedition’s extraordinary outcomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
24 August 2015

What’s on your Summer reading list? Here are some favourites of staff in the Lab.
LAB MATTERS
24 August 2015

Alumnus Luis Bejarano asked Spanish students to stick out their tongues to analyse their microbiome.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
alumnipeople-perspectives
24 August 2015

A contagious cancer threatens the Tasmanian devil – extract from Science in School journal.
LAB MATTERS
24 August 2015

Alumni Reuben Leberman, Jeremy Smith, Elena Seiradake, and Winfried Weissenhorn share their stories.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
alumnipeople-perspectives
24 August 2015

Maria Kamber, who heads the mouse facility, ensures “dignity, compassion and respect” for her charges.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2015
connectionslab-matters
20 August 2015
EMBL scientists map ‘switches’ for distant control of gene expression.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
20 August 2015
Collaboration between scientists reveals collaboration between lipids.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
20 August 2015

EMBL Core Facilities collaborate with French research programme Signalife to revive training visit.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2015
connectionslab-matters
12 August 2015

Leading scientists will gather in Heidelberg this November to discuss the potential of personalised health.
CONNECTIONS
10 August 2015

Crowd sourcing initiative to predict effects of toxic compounds: results of 2013 DREAM Challenge.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
6 August 2015

A mathematician who got ‘sucked in’ to biological problems, meet new team leader Theodore Alexandrov.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
people-perspectivesscience
4 August 2015
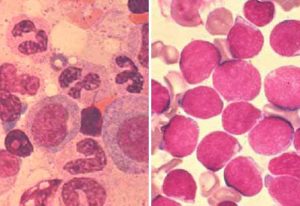
Multidisciplinary research provides clues to new treatments for deadly form of leukaemia in children
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
3 August 2015
How T-cells are trained on what not to kill
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
28 July 2015

Molecular Medicine Partnership Unit (MMPU) with the University of Heidelberg, renewed until 2025.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2015
connectionslab-matters
28 July 2015

Alumnus Damian Brunner revisits EMBL in a very special capacity, as Swiss delegate on EMBL’s Council.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
17 July 2015

Web of lies? Science Movie Night reveals science behind the most famous spider bite in film history.
LAB MATTERS
16 July 2015
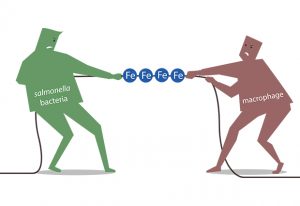
Iron regulatory proteins play important role in combatting infection, protecting against Salmonella.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
16 July 2015
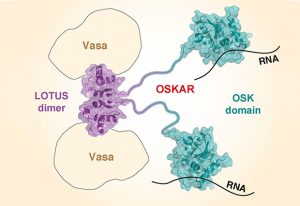
3D structure of Oskar protein gives first molecular insight into how it functions.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
13 July 2015

EI3POD: flagship interdisciplinary postdoc programme opens its doors to academia and industry.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2015
embl-announcementslab-matters
10 July 2015
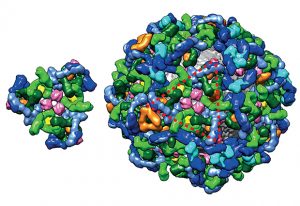
3D imaging unravels COPI coat of cells' transport vesicles.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
9 July 2015

Jan Korbel and colleagues publish commentary on risks and rewards of genome cloud computing.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
9 July 2015
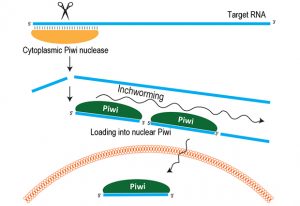
European team identify mechanism for producing piRNAs that silence jumping genes in germline cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
9 July 2015

“Interactions: that’s what I like the most in biology” – meet Lukáš Janošík, EUCYS 2014 prize winner.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
9 July 2015

Database administrator's photo essay reflects internationality and personality of the Genome Campus.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
3 July 2015

Academic community clouds take cancer research towards a brighter future.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
lab-mattersscience-technology
2 July 2015

Industrial partners and BioStruct-X facility members gather for Workshop at EMBL Hamburg.
CONNECTIONS
30 June 2015

Staff gather to celebrate Janet Thorton's 14 years as Director of EMBL-EBI.
LAB MATTERS
22 June 2015

EMBL-EBI organises an evening of talks and discussion about the global spread of infectious disease.
CONNECTIONS
18 June 2015
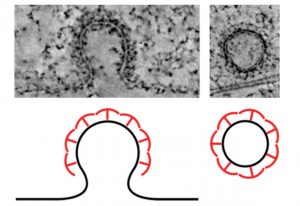
Behaviour of clathrin proteins, crucial for endocytosis, is clarified using new imaging techniques.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
18 June 2015

Sarah Teichmann recognised for her contributions to science with the EMBO Gold Award 2015.
LAB MATTERS
18 June 2015

A puzzling peculiarity resolved by Hamburg’s Sample Preparation and Characterisation facility.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
18 June 2015

Staff, alumni, partners and more meet at EMBL Grenoble to celebrate Outstation's 40th anniversary.
LAB MATTERS
16 June 2015

Researchers at EMBL-EBI speed up complex GWAS analyses with new method and algorithm.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
15 June 2015

EMBL’s new open access policy aims to make EMBL research widely and freely accessible.
LAB MATTERS
15 June 2015
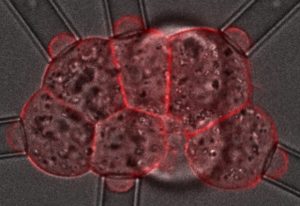
Cells 'dance' as they draw together during early embryo development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
10 June 2015

CERN openlab enters a new phase, expanding to include EMBL-EBI and other public research organisations.
LAB MATTERS
4 June 2015
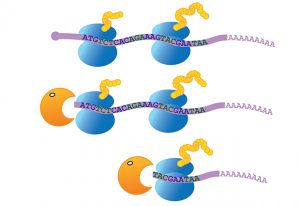
Decaying RNA molecules tell a story that could add more chapters to the study of ribosomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
3 June 2015
Jenny Cham blogs about how ORCID helps distinguish her from all the other Jenny Chams in the world.
LAB MATTERS
2 June 2015

HMMER – a fast, sensitive search tool – helps find sequence relationships deep in evolutionary time.
LAB MATTERS
27 May 2015

ELIXIR receives major Horizon 2020 funding to ‘EXCELERATE' activities over the next four years.
LAB MATTERS
21 May 2015

Tara Oceans results reveal climate change insights, and a treasure trove of novel species and genes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
21 May 2015
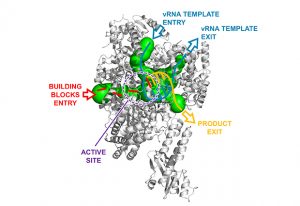
Detailed structural study shows distantly related viruses share a common machinery for replication.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
21 May 2015
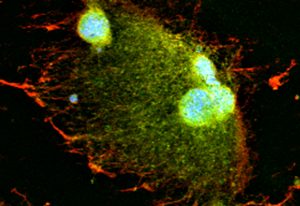
EMBL scientists demonstrate that spatial constraints are a key factor in determining nucleus size.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
18 May 2015
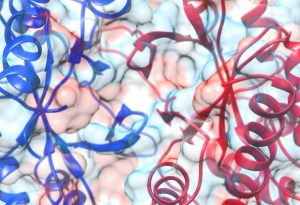
New research shows that some proteins domains can function even with big parts missing.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
12 May 2015
Not all embryonic macrophages are the same, and only some are destined to become microglia.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
7 May 2015
Unveiling the shape of... the 'molecular bin man' – cryoEM helps reveals p62 polymer in 3D.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
5 May 2015

Stanford University biophysicist KC Huang on his collaboration with the Typas group in Heidelberg.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
5 May 2015

Stephen Cusack, head of EMBL Grenoble, among 47 new Royal Society fellows.
LAB MATTERS
5 May 2015

In their quest to make structural biology more accessible, PDBe launches a new website.
LAB MATTERS
5 May 2015

Cooperate or compete? Microbes show us that getting along is the better choice for communities.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
30 April 2015

Get ready to vote for your EMBL Alumni Association board.
LAB MATTERS
29 April 2015

EMBL’s new Archivist will help chronicle the twists and turns, ups and downs of life at the Lab.
LAB MATTERS
29 April 2015

Career insights from Riccardo Cortese, whose start-up is developing an Ebola vaccine candidate.
LAB MATTERS
29 April 2015
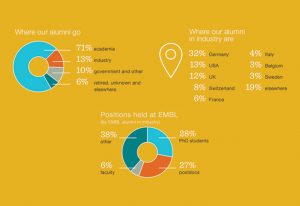
Alumni in senior positions in industry share career challenges, highlights and EMBL’s continuing role.
LAB MATTERS
29 April 2015

Q&A: Which analogy best describes your research?
LAB MATTERS
29 April 2015

Ben Lillie takes us on a journey through the art and craft of personal narrative.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2015
eventspeople-perspectives
29 April 2015

Karin Sasaki is helping bridge the gap between quantitative and life science at EMBL.
LAB MATTERS
29 April 2015

Radiocarbon studies are helping researchers shine light on how neurons stay stable yet adaptable.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
20 April 2015
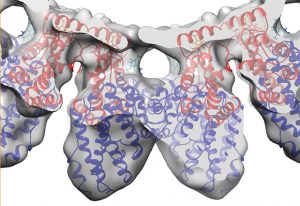
Ground-breaking microscopy technique gives unprecedented insight into endocytosis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
15 April 2015

Exploring the science and magic of Lil Bub – alumna launches project to sequence the ‘Lilbubome’.
LAB MATTERS
14 April 2015
New single-cell genomics techniques bring ‘omics to evolution and development research.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
9 April 2015

Major EU funding for CORBEL, facilitating access to data and biological imaging facilities.
LAB MATTERS
7 April 2015

GWAS Catalog, originally developed by the NHGRI in the US, moves to EMBL-EBI.
LAB MATTERS
6 April 2015
Coin toss inspires CorMap: a new statistical test that sidesteps need for error estimation.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
2 April 2015
Go Team Genome! New method reveals genetic teamwork in drosophila genome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
1 April 2015

Klaus Tschira, a tireless supporter of science, education and talent, died 31 March 2015.
LAB MATTERS
25 March 2015

EMBL’s corporate partners zoom in on big data and bioimaging.
CONNECTIONS
16 March 2015
New fully automated technique enables scientists to chart complex protein networks in living cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
11 March 2015

Rolf Apweiler and Ewan Birney appointed Joint Directors of EMBL-EBI, as Janet Thornton steps down.
LAB MATTERS
10 March 2015

A quick round-up of the latest EMBL-EBI service releases.
LAB MATTERS
8 March 2015

Wellcome Genome Campus gives first Best Practice Award for Supporting Women in Science.
LAB MATTERS
6 March 2015

EMBL Grenoble celebrates 40 years with a symposium for staff, alumni and facility users on 4–5 June.
LAB MATTERS
4 March 2015
Combining three different kinds of microscopy to determine how molecules move during endocytosis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
2 March 2015
Building and visualising protein-interaction networks is easier and more accurate thanks to IntAct.
LAB MATTERS
27 February 2015

Jeffrey Barrett appointed Director of CTTV, the GSK, EMBL-EBI and Sanger Institute partnership.
LAB MATTERS
25 February 2015
How strong does a spindle need to be? Videos put cell’s chromosome-separating machinery to the test
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
20 February 2015
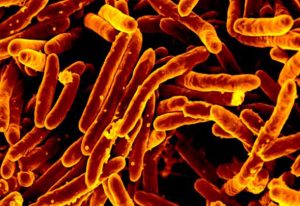
Hamburg-led tuberculosis study demonstrates the power of collaboration.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
19 February 2015

First LearningLAB of 2015 makes science of protein structure crystal clear for 22 teachers.
LAB MATTERS
16 February 2015

EMBL Insight Lecture – Why do we do what we do? – now available to view online.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
eventsscience-technology
6 February 2015

Tried and tested do's and don'ts of crowdsource writing.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
6 February 2015
New way mice starve pathogens raises alternative approach to treatments for anaemia of chronic disease
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
4 February 2015
New microscopy-based method goes beyond gene sequencing, pinpointing the cause of disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
28 January 2015

How repurposing non-coding elements in the genome gave rise to the great ‘mammalian radiation’.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
28 January 2015

A blog extract by Ewan Birney reflects on the challenges of moving a massive data-centre.
LAB MATTERS
28 January 2015

New Bar-ChIP method makes it easier to search for epigenetic marks in many samples at once
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
27 January 2015
First experimental proof that a key cellular machine forms by uniting pre-assembled modules.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
26 January 2015
Find answers to 40 of your questions about life, the Lab and everything!
LAB MATTERS
26 January 2015
Films by alumnus’ lab shortlisted for 2014 Visualisation Challenge, 'The Vizzies'.
LAB MATTERS
26 January 2015

How the Rosetta Mission’s comet landing led to unexpected destinations for alumna Karin Ranero,
LAB MATTERS
26 January 2015
A brief history of microscopes, from van Leeuwenhoek to Betzig, Hell and Moerner.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
26 January 2015

EMBL scientists regularly receive prestigious awards – meet the latest honourees.
LAB MATTERS
26 January 2015

As EMBL Hamburg celebrates 40 years, we explore the past, present and future of crystallography.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
26 January 2015

Which tales have illuminated something important to you? Staff from the Lab provide their favourite.
LAB MATTERS
26 January 2015

Meet Dean of Graduate Studies, Helke Hillebrand.
LAB MATTERS
26 January 2015

From using light to control brain activity to illuminating fruit fly development and mice’s sense of touch
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
26 January 2015

Ken Holmes, one of the visionaries behind EMBL and EMBL Hamburg, looks back to where it all began.
LAB MATTERS
23 January 2015

PhD student Silvia Rohr on studying eyes – and talking about it for a general audience.
LAB MATTERS
23 January 2015

Alumnus Stefan Hell on his 2014 Nobel Prize for Chemistry
LAB MATTERS
20 January 2015

New project aims to speed up detection and response to disease outbreaks using genome technology.
LAB MATTERS
20 January 2015

New statistical method for RNA-seq analysis creates order out of seeming chaos.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
16 January 2015

New Christian Boulin Fellowship: 15 awards of up to €1500 for visitors to EMBL’s Core Facilities.
LAB MATTERS
9 January 2015

New group leader Marco Marcia aims to broaden horizons while mapping molecules.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
8 January 2015

EMBL-EBI supports relaunch of yourgenome.org, to bring genetics advances to a wider audience.
LAB MATTERS
7 January 2015
Research led by Teichmann group identifies fundamental mechanism for controlling protein function.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
19 December 2014

Showcasing EMBL at the Congress of the Hellenic Society of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
LAB MATTERS
18 December 2014

How do E.coli and similar bacteria grow safely? By using barrel-plugs as sensors.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
18 December 2014

Announcing winners of the John Kendrew Young Scientist Award, and inaugural Lennart Philipson Award.
LAB MATTERS
18 December 2014

Compound that can restore the function of poorly working mitochondria, with therapeutic potential.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
15 December 2014

Third round of calls for joint research projects between EMBL and Luxembourg in 2015
LAB MATTERS
11 December 2014

EMBL Hamburg celebrates four decades of vision, pioneering research and beamline services.
CONNECTIONS
11 December 2014

The day EMBL Hamburg predocs and postdocs invited Nobel Prize Winner Ada Yonath to dinner.
LAB MATTERS
9 December 2014
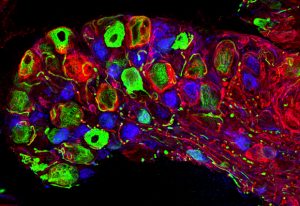
Unprecedented detail in images of mouse neurons thanks to new SNAP-tagging microscopy technique.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
5 December 2014

Employee number 47 retires, leaving behind a legacy that intricately linked her life with EMBL.
LAB MATTERS
1 December 2014

Genome-based insights into evolution of malaria-carrying Anopheles mosquitoes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
28 November 2014

In two months, 2.3 million diffraction images collected on new, fully automated ESRF/EMBL beamline.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
28 November 2014

Largest collection of helminth genomic data ever assembled, in new open-access WormBase ParaSite.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
27 November 2014

Workshops, seminars and honorary lectures – strong start for EMBL’s newest associate member state.
LAB MATTERS
24 November 2014

Life Science Nord event reveals how pharmaceutical companies use synchrotrons for their research.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
eventsscience-technology
21 November 2014

EMBL-EBI supports Big Biology Day, inspiring 500 youngsters with jelly-baby DNA and golf-tee viruses.
CONNECTIONS
19 November 2014

Get a flavour of the 15th EMBL|EMBO Science and Society Conference from alumnus Freddy Frischknecht.
LAB MATTERS
19 November 2014

First complete picture of flu virus polymerase. A story of two decades of blood, sweat and sneezes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
19 November 2014

Alumnus Jan Medenbach harnesses the shared experience of peers (and pioneers) at EMBL event.
LAB MATTERS
19 November 2014
Which courses and conferences will you attend in 2015? EMBL’s annual event calendar: out now!
LAB MATTERS
19 November 2014

Appetite to ZzZzZzZ… bite-sized highlights from this year’s Science and Society conference.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
eventsscience-technology
18 November 2014

The important thing is forming good biological questions, says new group leader in Genome Biology.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2014
people-perspectivesscience
18 November 2014

Course attendees go hunting (protein) aliens in a quest for optimal SAXS data.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
eventsscience-technology
17 November 2014

Whether it’s information or people, the art of connecting is key to new group leader Judith Zaugg
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2014
people-perspectivesscience
14 November 2014

First series of training courses jointly organised by EMBL and Illumina is a resounding success.
CONNECTIONS
11 November 2014

Alumna Anna Bartosik shares insights and hopes for EMBL's newest prospect member state, Poland.
LAB MATTERS
4 November 2014
'Big Data to Knowledge' project by UCLA, Scripps and EMBL-EBI to transform protein data to knowledge.
LAB MATTERS
4 November 2014

EMPIAR lets researchers take a closer look at the images used to build 3D molecular structures.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
4 November 2014

Open Day in Grenoble celebrates crystallography for the Fête de la Science.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
eventsscience-technology
3 November 2014

In a Statement of Intent signed this month, Poland becomes a prospect member state of EMBL, and the new partners agree to explore possibilities for long-term cooperation, with a view to the country becoming a full member state within three years. “Poland has a strong and active life science…
CONNECTIONS
3 November 2014
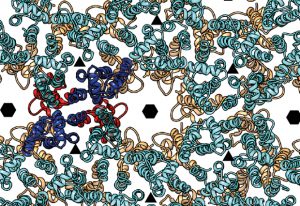
Unprecedented detail on HIV structure continues virus’ string of surprises.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
3 November 2014

How to make good quality samples for good quality structural biology experiments.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
eventsscience-technology
31 October 2014

New, open repository helps researchers share computational models of disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
29 October 2014

Kidney cancer linked to exposure to aristolochic acid, an ingredient in some herbal remedies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
27 October 2014

How the author of a prize-winning project on bee travel ended up at a stem cells and cancer conference
LAB MATTERS
23 October 2014

Like sports teams, cells can huddle to communicate in secret and organise group behaviour
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
22 October 2014
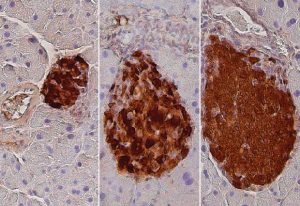
Growth factor IGF-1 boosts natural defence against type-1 diabetes and multiple sclerosis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
21 October 2014

European Variation Archive makes it easier to explore detailed information about genetic variation.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
21 October 2014
How does EMBL-EBI run millions of jobs for its users while moving its two large data centres?
LAB MATTERS
20 October 2014
How Nobel-winning work by alumnus Stefan Hell shapes and inspires current EMBL scientists' research.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
17 October 2014

Music, bubbles and DNA: a collaborative project brings artist and scientist together
LAB MATTERS
17 October 2014

From anemones to starfish, sea creatures are helping understand development, evolution and more.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
17 October 2014
Flow cytometry: finding needles in haystacks
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
17 October 2014

EMBL scientists regularly receive prestigious awards - meet the latest honourees
LAB MATTERS
17 October 2014

Drumming, drama, dancing and discovery in a diary of art and science event, Roche Continents.
LAB MATTERS
17 October 2014

It’s question time for Director General Iain Mattaj in this extract from the alumni reunion magazine.
LAB MATTERS
17 October 2014

Bibliophiles from the Lab pick out the stories that have inspired them at work and elsewhere.
LAB MATTERS
17 October 2014

Charles Spence invites you to taste the difference.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2014
eventspeople-perspectives
17 October 2014

German Science Minister and other honoured guests celebrate 40 years of ‘Learning from life’.
LAB MATTERS
17 October 2014

Alumnus Giovanni Frazzetto on what happens when art, literature, theatre, and science come together.
LAB MATTERS
17 October 2014

PhD student Charles breeze found inspiration at this year's Lindau Nobel Laureate meeting.
LAB MATTERS
17 October 2014

Alumni Association elections: board member nominations wanted!
LAB MATTERS
17 October 2014

EMBL Alumna Frieda Glöckner looks back more than four decades to where it all began.
LAB MATTERS
14 October 2014

Experts from multiple fields come together to understand how the instructions in genes are read
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
eventsscience-technology
10 October 2014

From vitamin C to safe matches, a sample of notable scientists from our newest prospect member state.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2014
people-perspectivesscience
9 October 2014

Pathfinding – poetic and practical – was a common theme in blogs from the EMBL network.
LAB MATTERS
8 October 2014

Pooling programming and problem-solving expertise in bioinformatics at EMBL-EBI.
CONNECTIONS
6 October 2014

The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) welcomes Hungary as its newest prospect member state. In a Statement of Intent signed this month, Hungary and EMBL agree to explore possibilities for long-term cooperation, with a view to the country becoming a full member state within three years.…
CONNECTIONS
25 September 2014
How plankton gets jet lagged: the same hormone governs our sleep patterns and a daily marine migration.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
16 September 2014

An interview with keynote speaker Michael Rossmann.
LAB MATTERS
15 September 2014

Stephen Fuller, from 1981–2000 an EMBL postdoc, group leader then Head of Unit, died on 25 August.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2014
alumnipeople-perspectives
15 September 2014

EMBL-EBI hosts successful first EMBO Practical Course in Genotype to Phenotype Mapping.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
eventsscience-technology
12 September 2014
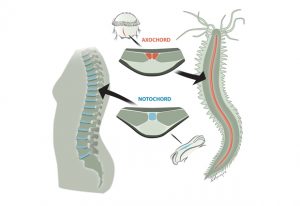
Evolutionary surprise: notochord likely evolved from muscle, earlier than assumed.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
12 September 2014
Researchers produce pristine stem cells, which can be precisely changed into clinically relevant cell types.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
11 September 2014
LAB MATTERS
10 September 2014

Gibbon genome gives insights into evolution of this singing, swinging, tree-dwelling ape.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
10 September 2014

RNAcentral is the first unified resource for all types of non-coding RNA data.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
8 September 2014

Andrew D Robertson, scientific coordinator of EICAT between 2011–12, died on 14 August 2014.
LAB MATTERS
5 September 2014

Tschira-Jugendakademie pupils get hands-on during day of DNA barcoding
LAB MATTERS
2 September 2014

Research building for interdisciplinary Centre for Structural Systems Biology (CSSB) takes shape.
CONNECTIONS
29 August 2014
Bronwen Aken discusses what research into the rabbit genome reveals about animal domestication.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
27 August 2014

Nordic partners focus on "enhancing research enterprise", says Kjetil Taskén
LAB MATTERS
21 August 2014
PhD Symposium poster reveals how a cell’s inner workings serve as both inspiration and toolkit.
LAB MATTERS
20 August 2014
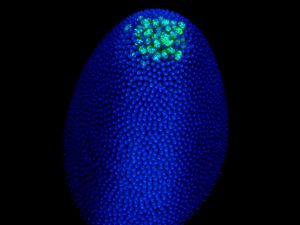
Vasa protein preserves pieces of 'enemy' DNA to help protect the genes of future generations.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
18 August 2014

Artist Stephen Wright gifts artwork inspired by DNA storage research to EMBL-EBI.
LAB MATTERS
11 August 2014

PhD students reap rewards and rave reviews as Summer School of Science organisers
CONNECTIONS
8 August 2014

A quick round-up of the latest EMBL-EBI service releases
LAB MATTERS
8 August 2014

Gyron Ltd awarded contract to supply EMBL-EBI's data centres over the next five years
LAB MATTERS
8 August 2014
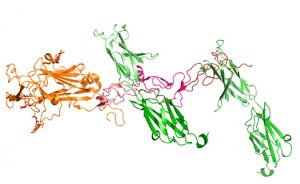
How a single molecule can attract and repel growing brain connections
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
8 August 2014

Ensembl has incorporated a vast amount of knowledge into a fully annotated reference human genome
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
6 August 2014
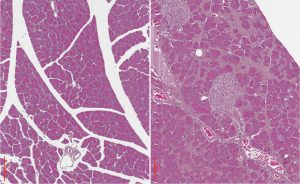
A rare form of an iron overload disorder kills pancreatic function, Heidelberg scientists find
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
6 August 2014
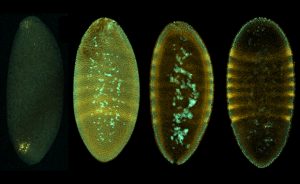
How fruit flies beat the cold, plus the value of precisely controlled experiments and detailed analysis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
4 August 2014
Edward Lemke edits special issue of ChemBioChem on boom of technology for genetic code expansion
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
1 August 2014

EMBL students successfully take science to the pub
CONNECTIONS
31 July 2014

"Thank you, EMBL, for changing my life" – reunion celebrates great science and great scientists
LAB MATTERS
31 July 2014

New genomics API allows researchers to share anonymised genetic data seamlessly across platforms.
LAB MATTERS
31 July 2014

Celebrating 50 years of EMBO, 40 years of EMBL and the success of molecular biology in Austria
LAB MATTERS
24 July 2014
Molecular switch enables viruses to destroy C.diff bacteria – potential alternative to antibiotics
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
20 July 2014

Marmoset genome provides insights into chimerism: data available in Ensembl genome explorer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
17 July 2014
Cell biologists "underestimate the complexity" of protein interactions, says Toby Gibson.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
16 July 2014

Have a pressing question? EMBL experts are standing by to answer! Submit yours today.
LAB MATTERS
15 July 2014

Czech delegate Jana Bystřická represents EMBL's 21st member state at her first Council Meeting.
LAB MATTERS
10 July 2014

Embed chemists in biology departments, asking their own biological questions, says Carsten Schultz
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
10 July 2014

Anniversary reflections on connections between scientific and political interests.
CONNECTIONS
8 July 2014

EMBL-EBI’s anniversary celebration: blue skies thinking, Robin Ince and a biology-themed cake
LAB MATTERS
8 July 2014

EMBL Monterotondo celebrates double anniversary with fun, fireworks, festa and familiar faces
LAB MATTERS
2 July 2014

Surprising finding: enhancers find their targets long before activation in Drosophila embryos
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
1 July 2014

As the Lab turns 40, staff and alumni share 40 things that make EMBL, EMBL
LAB MATTERS
1 July 2014

School ambassadors show next generation that scientists are more ‘role model’ than ‘mad professor’
LAB MATTERS
1 July 2014

EMBL scientists regularly receive prestigious awards - meet the latest honourees
LAB MATTERS
1 July 2014

Scientist-turned-writer Lucas Brouwers follows his instincts to find interesting stories
LAB MATTERS
1 July 2014
Surprising protein from a flu-like virus is 10 000th ESRF structure
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
1 July 2014

To photographer Horst Hamann, it's the people, not the science, that make EMBL unique
LAB MATTERS
1 July 2014

Film enthusiasts from the Lab review their favourite science movies, one for each EMBL decade
LAB MATTERS
1 July 2014

Focusing on basic research is crucial for the development of more advanced genetics techniques
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
1 July 2014

Christian Boulin, EMBL’s Director of Core Facilities and Services, died on 27 April 2014
LAB MATTERS
1 July 2014

What might life alien life look like? Lewis Dartnell studies extreme bacteria to find out
LAB MATTERS
1 July 2014

As the Lab turns 40, staff and alumni share 40 things that make EMBL, EMBL
LAB MATTERS
1 July 2014
Two EMBL alumni, each developing community-led tools to support life science research
LAB MATTERS
1 July 2014
New ways of handling and distributing data at PDBe to tackle ever larger and more complex proteins
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
1 July 2014

Busy times for EMBL keep Director of International Relations Silke Schumacher on the move
LAB MATTERS
1 July 2014

New EMBL Archive will serve as a record of accomplishments, past, present and future
LAB MATTERS
1 July 2014

Scientists from EMBL's five sites reflect on the opportunities and challenges that might lie ahead
LAB MATTERS
1 July 2014

Which scientific breakthroughs would EMBL scientists most like to see in the next 40 years?
LAB MATTERS
1 July 2014

Staff and alumni around the world get active in EMBL running shirts to celebrate our anniversary
LAB MATTERS
25 June 2014

A new EMBL-EBI biomedical initiative works to determine the best target proteins for new drugs.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2014
connectionslab-matters
25 June 2014
Scientists determine the structure of auxin response factors: daisy-chains that regulate gene expression
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
25 June 2014

Enabling neighbours: intact genes can cause cancer when placed near "enhancing" regions of DNA
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
21 June 2014

Data from first ever worldwide Ocean Sampling Day will be shared via EMBL-EBI resources this autumn.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
16 June 2014

Teaming up in Ireland to address big challenges in biology
CONNECTIONS
10 June 2014

Forty years after its foundation, EMBL announces its 21st member state: the Czech Republic. Building on a successful bilateral relationship, the Czech Republic’s membership grants Czech scientists access to EMBL’s state-of-the-art instruments, facilities and world-class training…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2014
embl-announcementsevents
6 June 2014
Reference sheep genome, published by International Sheep Genomics Consortium, available in Ensembl
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
5 June 2014
A kaleidoscope of molecules is needed to clean up dead brain cells, and failure can have disastrous consequences
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
25 May 2014
How a DNA stretch influences face formation and contributes to common congenital malformations
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
18 May 2014
High-resolution structure reveals crucial interactions for HIV maturation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
18 May 2014
DNA-coralling protein complex in an unexpected bind
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
9 May 2014
Genome Campus researchers discover that some immune cells turn themselves off by producing a steroid.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
8 May 2014
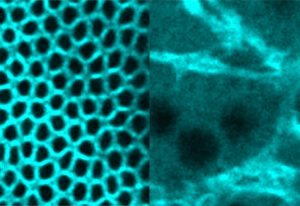
The balance behind membrane changes that turn one cell into 6000 as a fruit fly embryo develops
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
24 April 2014
Tsetse fly genome sequenced; scientists hope to find new ways to control sleeping sickness.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
22 April 2014

At a signing ceremony today, Argentina joins the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) as an associate member state. The move strengthens the ties between the European and Latin American life science communities. It grants Argentinian scientists access to EMBL’s world-class facilities and…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2014
embl-announcementsevents
27 March 2014
A pioneering public-private research initiative between GSK, the European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) and the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute is to harness the power of ‘big data’ and genome sequencing to improve the success rate for discovering new medicines. The new Centre for…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2014
connectionslab-matters
7 March 2014

The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) welcomes the Slovak Republic as the first country to join its new Prospect Member scheme. In a Statement of Intent signed last month, the Slovak Republic and EMBL agree to explore the possibilities for long-term cooperation, with a view to the…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2014
embl-announcementsevents
24 February 2014

Europe is uniting to make state-of-the-art imaging technologies accessible to biomedical researchers throughout the continent in a concerted manner. The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and seven countries (Belgium, Finland, Italy, Poland, Slovakia, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom)…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2014
connectionslab-matters
2 February 2014
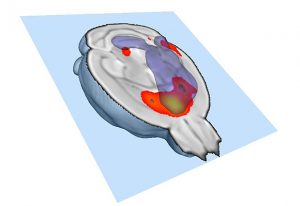
In many people with autism and other neurodevelopmental disorders, different parts of the brain don’t talk to each other very well. Scientists have now identified, for the first time, a way in which this decreased functional connectivity can come about. In a study published online today…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
10 November 2013
What do bullies and sex have in common? Based on work by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Monterotondo, Italy, it seems that the same part of the brain reacts to both. In a study published today in Nature Neuroscience, the researchers found that – at least in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
23 October 2013
The molecular machine that makes essential components of ribosomes – the cell’s protein factories – is like a Swiss-army knife, researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and the Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas in Madrid, Spain, have found.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
13 October 2013
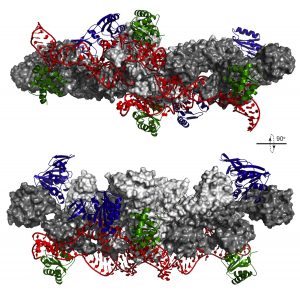
An important step in building ribosomes – the cell’s protein factories – is like a strictly choreographed dance, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have discovered. To build these factories, other ‘machines’ inside the cell have to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
25 September 2013
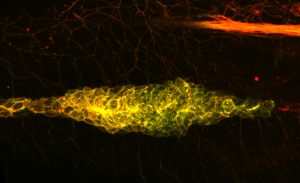
Migrating cells, it seems, cover their tracks not for fear of being followed, but to keep moving forward. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have now shown that cells in a zebrafish embryo determine which direction they move in by effectively…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
12 September 2013
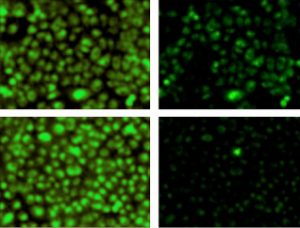
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg and Regensburg University, both in Germany, and the University of Lisboa, in Portugal, have discovered a promising potential drug target for cystic fibrosis. Their work, published online today in Cell, also uncovers a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
11 August 2013
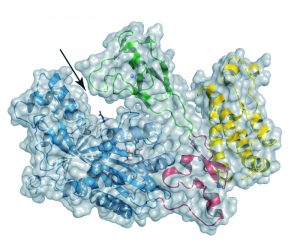
Like a fireman who becomes an arsonist, a protein that prevents cells becoming cancerous can also cause tumours, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Grenoble, France, have discovered. The finding, published today in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, stems…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
11 August 2013
How our body processes cholesterol has a well-known impact on our health, but it turns out that another ‘fat molecule’ – or lipid – may be at the heart of some diseases which were thought to involve cholesterol. A group of proteins linked to conditions such as metabolic syndrome and some…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
7 August 2013
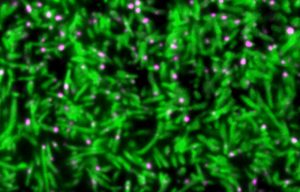
The process cells use to ‘swallow’ up nutrients, hormones and other signals from their environment – called endocytosis – can play a crucial role in shaping the cells themselves, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have found. The study,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
11 July 2013
It’s a parent’s nightmare: opening a Lego set and being faced with 500 pieces, but no instructions on how to assemble them into the majestic castle shown on the box. Thanks to a new approach by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
14 May 2013
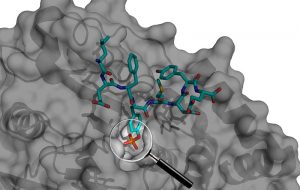
Although we know the tool’s general purpose, it can sometimes be difficult to tell if a specific pair of precision tweezers belongs to a surgeon or a master jeweller. It is now easier to solve similar conundrums about a type of protein that allows cells to react to their environment, thanks to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
24 April 2013
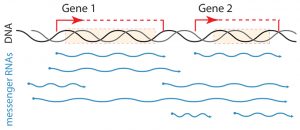
Like musicians in an orchestra who have the same musical score but start and finish playing at different intervals, cells with the same genes start and finish transcribing them at different points in the genome. For the first time, researchers at EMBL have described the striking diversity of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
27 March 2013
Euro-BioImaging, the pan-European open access research infrastructure for biological and medical imaging technologies, invites leading European imaging facilities to submit proposals to participate. Applications to become a Euro-BioImaging node will be reviewed by a board of independent…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2013
connectionslab-matters
11 March 2013
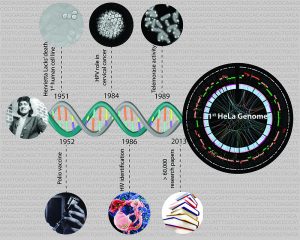
HeLa cells are the world’s most commonly used human cell lines, and have served as a standard for understanding many fundamental biological processes. In a study published today in G3: Genes, Genomes and Genetics online, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
5 March 2013

Today, the Nordic EMBL Partnership for Molecular Medicine celebrates two important milestones: the renewal of the partnership agreement for an extended period of 10 years, and the expansion of the Nordic EMBL network with the official opening of the Danish Research Institute of Translational…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2013
connectionslab-matters
28 February 2013
During embryo development, genes are dynamically, and very precisely, switched on and off to confer different properties to different cells and build a well-proportioned and healthy animal. Fgf8 is one of the key genes in this process, controlling in particular the growth of the limbs and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
28 February 2013
Studies screening the genome of hundreds of thousands of individuals (known as Genome-wide association studies or GWAS) have linked more than 100 regions in the genome to the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
11 February 2013
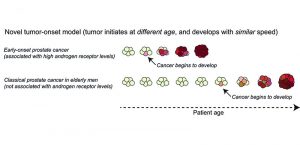
While prostate cancer is the most common cancer in elderly Western men it also, but more rarely, strikes patients aged between 35 and 50. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, in collaboration with several other research teams in Germany*, have…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
4 February 2013
Mature cells can be reprogrammed to pluripotency and thus regain the ability to divide and differentiate into specialized cell types. Although these so-called induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) represent a milestone in stem cell research, many of the biochemical processes that underlie…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
31 January 2013
Scientists at the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) and the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology in the UK have discovered how our genome keeps the effects of mutations in check. The discovery, published in the journal Cell, will help in the study of diseases such as cancer and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
23 January 2013
Researchers at the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) have created a way to store data in the form of DNA – a material that lasts for tens of thousands of years. The new method, published today in the journal Nature, makes it possible to store at least 100 million hours of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
17 January 2013
This may look like yet another video of a dividing cell, but there’s a catch. You are looking at chromosomes (red) being pulled apart by the mitotic spindle (green), but it’s not a cell, because there’s no cell membrane. Like a child sucking an egg out of its shell, Ivo Telley from the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
6 January 2013
A research team of scientists from EMBL Grenoble and the IGBMC in Strasbourg, France, have, for the first time, described in molecular detail the architecture of the central scaffold of TFIID: the human protein complex essential for transcription from DNA to mRNA. The study, published today…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
19 December 2012
Gene expression wave in the lower part of the future vertebrae column of a mammalian embryo. As the wave goes forward, new pre-vertebrae are formed and the future vertebrae column elongates. (Image and video credit: Nature) In a nutshell: The size of pre-vertebrae in a mammalian embryo is…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
5 December 2012
In a nutshell : The gut metagenome is the collection of all the genomes of all the microbes in the human intestinal tract : it is specific to each human, like a second genetic signature At least in healthy humans, this personal metagenome is stable over time The gut metagenome is…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
31 October 2012
In a nutshell: 1st map combining human genetic variation at different scales – from single letters to large chunks Based on genomes of 1092 healthy people from Europe, the Americas and East Asia Could help identify genetic causes of disease, rather than just links Data made freely available in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
27 September 2012
In a nutshell: Looping and unlooping DNA adjusts readout from gene and spread of regulation throughout the genome When a gene forms a loop, its output increases, as the transcription machinery that reads it is trapped into moving only along that gene When the gene loop is undone, transcription…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
23 September 2012
In a nutshell: New method allows precise analysis of proteins released by cells over time (distinguishes them from proteins in the cells’ culture serum) Advantages: cells don’t have to be starved: avoids bias and allows more cell types to be studied; can follow fast reactions like immune…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
5 September 2012
Today, an international team of researchers reveal that much of what has been called ‘junk DNA’ in the human genome is actually a massive control panel with millions of switches regulating the activity of our genes. Without these switches, genes would not work – and mutations in these regions…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
2 August 2012
Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Grenoble, France, have determined the detailed 3-dimensional structure of part of the flu virus’ RNA polymerase, an enzyme that is crucial for influenza virus replication. This important finding is published today in PLoS…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
19 July 2012

What do you get when you dissect 10 000 fruit-fly larvae? A team of researchers led by the EMBL- European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) in the UK and the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics (MPI) in Germany has discovered a way in which cells can adjust the activity of many…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
12 July 2012
Italy has pledged to participate in ELIXIR, a major undertaking to safeguard the results of life science research in Europe. With one of Europe’s larger economies now demonstrating its commitment to ELIXIR, this burgeoning research infrastructure is well placed to continue its excellent progress.…
CONNECTIONS
5 July 2012
A traffic policeman standing at a busy intersection directing the flow of vehicles may be a rare sight these days, but a similar scene appears to still frequently play out in our cells. A protein called Lem4 directs a crucial step of cell division by preventing the progress of one molecule while…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
21 June 2012
Savira pharmaceuticals GmbH, a spin-off of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) based in Vienna, Austria, has signed a collaboration and license agreement with Roche, thus further strengthening the links between fundamental research and major pharmaceutical development companies. This…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
3 June 2012
As a retrovirus matures, the two parts of its shell protein (red and blue or yellow and blue) dramatically rearrange themselves, twisting and moving away from each other. (Credit: EMBL/T.Bharat) Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have for the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
3 June 2012
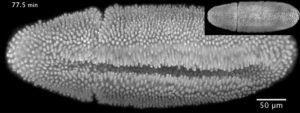
“This video shows a fruit fly embryo from when it was about two-and-a-half hours old until it walked away from the microscope as a larva, 20 hours later,” says Lars Hufnagel, from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany. “It shows all the hallmarks of fruit fly…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
3 June 2012
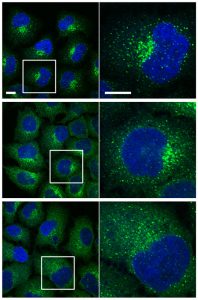
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have conducted the first comprehensive census of human cells’ export workers. In a study published online today in Nature Cell Biology, they found an unexpected variety of genes involved in transporting…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
31 May 2012

In one of the most famous faux pas of exploration, Columbus set sail for India and instead ‘discovered’ America. Similarly, when scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, set out to find enzymes – the proteins that carry out chemical…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
24 May 2012
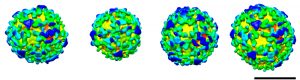
These spheres may look almost identical, but subtle differences between them revealed a molecular version of the robots from Transformers. Each sphere is a vesicle, a pod that cells use to transport materials between different compartments. The images, produced by Marco Faini from John…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
24 May 2012
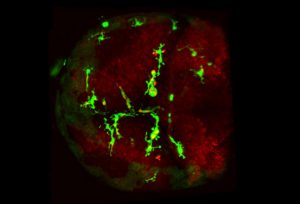
Like emergency workers rushing to a disaster scene, cells called microglia speed to places where the brain has been injured, to contain the damage by ‘eating up’ any cellular debris and dead or dying neurons. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
22 April 2012

Just as banks store away only the most valuable possessions in the most secure safes, cells prioritise which genes they guard most closely, researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) have found. The study, published online today…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
20 March 2012

As spring arrives, flowers seem to bloom everywhere – even under the microscopes at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany. But the ‘flowers’ in this picture actually help an animal, not a plant, to pass on its genes. The image, which has been false-coloured…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
18 March 2012
Like any law-abiding train passenger, a molecule called oskar RNA carries a stamped ticket detailing its destination and form of transport, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have found. They show that for this molecule, moving in the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
1 March 2012
Today a consortium of leading IT providers and three of Europe’s biggest research centres (CERN, EMBL and ESA) announced a partnership to launch a European cloud computing platform. ‘Helix Nebula ‐ the Science Cloud’, will support the massive IT requirements of European…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
28 February 2012
The bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae, which causes atypical pneumonia, is helping scientists uncover how cells make the most of limited resources. By measuring all the proteins this bacterium produces, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
23 February 2012
Breakthroughs in biomedical science are a step closer today, with the launch of a new distributed research infrastructure for the science of structural biology: Instruct. The launch of Instruct will give academic and commercial scientists across Europe access to a full portfolio of integrated…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
19 February 2012
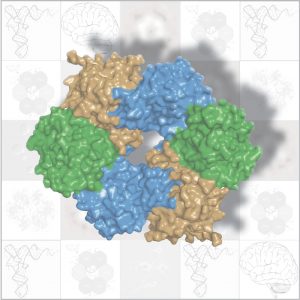
In fairy tales, magic rings endow their owners with special abilities: the ring makes the wearer invisible, fulfils his wishes, or otherwise helps the hero on the path to his destiny. Similarly, a ring-like structure found in a protein complex called ‘Elongator’ has led researchers at the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
14 February 2012
Myomesin stretching to 2.5 times its length. Credit: EMBL/Wilmanns. In this video, a protein called myomesin does its impression of Mr. Fantastic, the leader of the Fantastic Four of comic book fame, who performed incredible feats by stretching his body. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
2 February 2012
If you wanted to draw your family tree, you could start by searching for people who share your surname. Cells, of course, don’t have surnames, but scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have found that genetic switches called enhancers, and the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
19 January 2012
An inherited mutation in a gene known as the guardian of the genome is likely the link between exploding chromosomes and some particularly aggressive types of cancer, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), the German Cancer Research Centre (DKFZ) and the University…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
12 January 2012
A team of geneticists and computational biologists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute and Cancer Research UK reveal how an ancient mechanism is involved in gene control and continues to drive genome…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
8 January 2012
As an embryo develops, different genes are turned on in different cells, to form muscles, neurons and other bodily parts. Inside each cell’s nucleus, genetic sequences known as enhancers act like remote controls, switching genes on and off. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
5 December 2011
The European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) and the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) warmly welcome today’s announcement from the UK Government of a £75 million commitment from the Department for Business, Innovation…
LAB MATTERS
13 October 2011
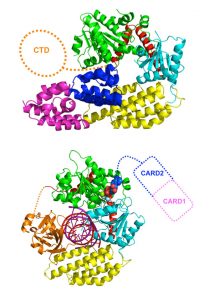
When a thief breaks into a bank vault, sensors are activated and the alarm is raised. Cells have their own early-warning system for intruders, and scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Grenoble, France, have discovered how a particular protein sounds that alarm when it…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
14 September 2011
Today marks an important step for ELIXIR, Europe’s emerging research infrastructure for life-science information, as five countries plus the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding to catalyse the implementation and construction of ELIXIR. The…
LAB MATTERS
18 August 2011
When an egg cell is being formed, the cellular machinery which separates chromosomes is extremely imprecise at fishing them out of the cell’s interior, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have discovered. The unexpected degree of trial-and-error…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
7 August 2011

Researchers can now watch molecules move in living cells, literally millisecond by millisecond, thanks to a new microscope developed by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany. Published online today in Nature Biotechnology, the new technique provides…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
21 July 2011
Gardeners know that some trees require regular pruning: some of their branches have to be cut so that others can grow stronger. The same is true of the developing brain: cells called microglia prune the connections between neurons, shaping how the brain is wired, scientists at the European…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
21 July 2011
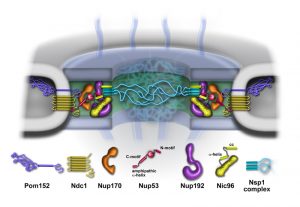
A fungus that lives at extremely high temperatures could help understand structures within our own cells. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and Heidelberg University, both in Heidelberg, Germany, were the first to sequence and analyse the genome of a heat-loving fungus,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
5 July 2011

Lennart Philipson, who served as EMBL’s second Director General, has passed away. Lennart headed EMBL for over a decade between 1982-93, a crucial time for molecular biology when different scientific disciplines in the life sciences were becoming increasingly interlinked. He reorganised the…
LAB MATTERS
17 June 2011
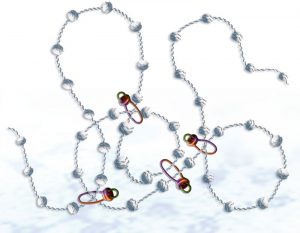
As any rock-climber knows, trailing a long length of rope behind you is not easy. A dangling length of rope is unwieldy and hard to manoeuvre, and can get tangled up or stuck on an outcropping. Cells face the same problem when dragging chromosomes apart during cell division. The chromosomes are…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
20 April 2011
In the future, when you walk into a doctor’s surgery or hospital, you could be asked not just about your allergies and blood group, but also about your gut type. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and collaborators in the international MetaHIT…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
20 March 2011
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have developed a new method for studying gene regulation, by employing a jumping gene as an informant. Published online today in Nature Genetics, the new method is called GROMIT. It enables researchers to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
11 March 2011
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have developed a new method which enables researchers to label any protein of their choice with any of a wide variety of previously available compounds, in living cells, by introducing a single reactive…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
6 March 2011
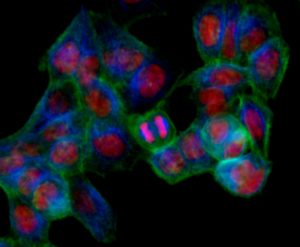
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the German Cancer Research Centre (DKFZ), both in Heidelberg, Germany, have developed a new method that uncovers the combined effects of genes. Published online today in Nature Methods, it helps understand how different genes can…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
4 March 2011

In a Memorandum of Understanding signed today, the European Commission (EC) and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) formalise their desire to maintain and further develop their cooperation. “I am delighted to sign the renewed and strengthened Memorandum of Understanding between the…
LAB MATTERS
14 February 2011
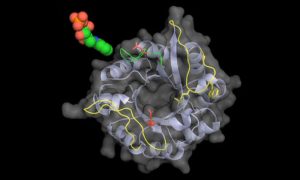
In a paper published online today in PNAS, scientists from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Hamburg, Germany, reveal new insights into the workings of enzymes from a group of bacteria including Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium that causes tuberculosis. The new findings…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
9 February 2011
The Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) welcome news that funding has been earmarked from the UK’s Large Facilities Capital Fund for ELIXIR – the European Life-science…
LAB MATTERS
3 February 2011
In our not-so-distant evolutionary past, stress often meant imminent danger, and the risk of blood loss, so part of our body’s stress response is to stock-pile blood-clotting factors. Scientists in the Molecular Medicine Partnership Unit (MMPU), a collaboration between the European Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
2 February 2011
A detailed analysis of data from 185 human genomes sequenced in the course of the 1000 Genomes Project, by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, in collaboration with researchers at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute in Cambridge, UK, as well as the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
23 January 2011
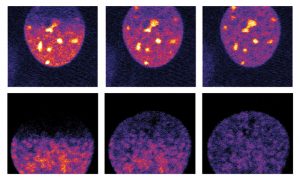
The sight of a researcher sitting at a microscope for hours, painstakingly searching for the right cells, may soon be a thing of the past, thanks to new software created by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany. Presented today in Nature Methods, the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
12 December 2010
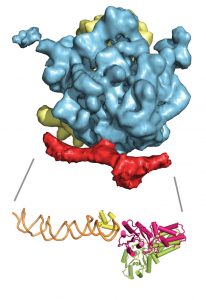
Like an overprotective parent on the first day of school, a targeting factor sometimes needs a little push to let go of its cargo. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Grenoble, France, have visualised one such hand-over. They were the first to determine the structure…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
2 December 2010
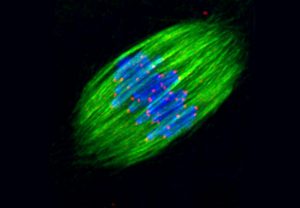
From microscopy to computer tomography (CT) scans, imaging plays an important role in biological and biomedical research, but obtaining high-quality images often requires advanced technology and expertise, and can be costly. Euro-BioImaging, a project which launches its preparatory phase today,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
16 November 2010
The cells in the different parts of this video are always the same (grey), but, like actors using make-up to highlight different facial features, they have fluorescent labels that mark different cellular components in different colours: blue shows the nucleus, yellow shows tubulin (a component of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
8 November 2010

At the Autumn 2010Council meeting of the EIROforum, a partnership of seven European intergovernmental research organisations with large research infrastructures, the Directors General unanimously accepted the European X-Ray Free-Electron Laser Facility (European XFEL), based in Hamburg, Germany, to…
LAB MATTERS
27 October 2010
The 1000 Genomes Project, a major international collaboration to build a detailed map of human genetic variation, has completed its pilot phase. The results are now published in the journal Nature and freely available through the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
2 September 2010
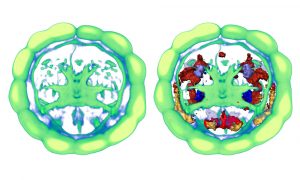
Our cerebral cortex, or pallium, is a big part of what makes us human: art, literature and science would not exist had this most fascinating part of our brain not emerged in some less intelligent ancestor in prehistoric times. But when did this occur and what were these ancestors? Unexpectedly,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
25 August 2010
Fear can make you run, it can make you fight, and it can glue you to the spot. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Monterotondo, Italy and GlaxoSmithKline in Verona, Italy, have identified not only the part of the brain but the specific type of neurons that determine…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
5 August 2010
During cell division, microtubules emanating from each of the spindle poles meet and overlap in the spindle’s midzone. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have uncovered the molecular mechanism that determines the extent of this overlap. In a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
3 August 2010
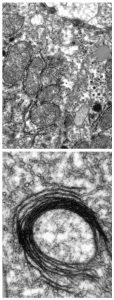
Most organisms need iron to survive, but too much iron is toxic, and can cause fatal organ failure. The same is true inside cells, where iron balance must also be maintained. In a study published today in Cell Metabolism, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
4 July 2010
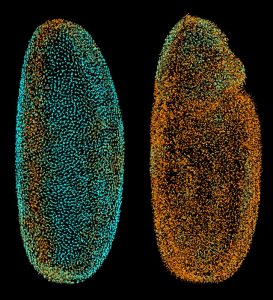
The scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, who ‘fathered’ the Digital Embryo have now given it wings, creating the Fly Digital Embryo. In work published today in Nature Methods, they were able to capture fruit fly development on film, and were the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
24 June 2010
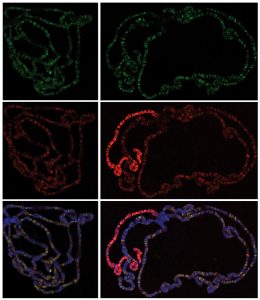
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and the Max-Planck Institute of Immunobiology Freiburg have identified a novel protein complex that regulates around 4000 genes in the fruit fly Drosophila and likely plays an important role in mammals, too.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
31 May 2010
Red blood cells, the delivery men that take oxygen to cells all around the body, have short lives. To keep enough of them in circulation, the human body produces around 2 million of these cells every second – even more in response to challenges like severe blood loss. In a study published today…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
2 May 2010
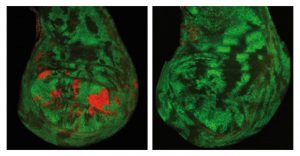
During embryonic development, proteins called Polycomb group complexes turn genes off when and where their activity must not be present, preventing specialised tissues and organs from forming in the wrong places. They also play an important role in processes like stem cell differentiation and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
8 April 2010
Just like members of an orchestra are active at different times although playing the same piece of music, every cell in our body contains the same genetic sequence but expresses this differently to give rise to cells and tissues with specialised properties. By integrating gene expression data from…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
1 April 2010
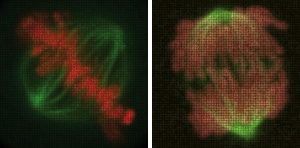
Name a human gene, and you’ll find a movie online showing you what happens to cells when it is switched off. This is the resource that researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and their collaborators in the Mitocheck consortium are making freely…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
18 March 2010
Once the human genome was sequenced in 2001, the hunt was on for the genes that make each of us unique. But scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and Yale and Stanford Universities in the USA, have found that we differ from each other mainly because…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
16 March 2010

Today, the Nordic EMBL Partnership for Molecular Medicine officially inaugurates the Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland (FIMM) in Helsinki. Together with the Centre for Molecular Medicine Norway (NCMM, University of Oslo) and the Laboratory for Molecular Infection Medicine Sweden (MIMS, Umeå…
LAB MATTERS
9 March 2010

Today, the German Minister for Education and Research, Annette Schavan, officially opens the new training and conference centre for the life sciences on the campus of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg. “This new centre in Heidelberg will form a central European…
LAB MATTERS
4 March 2010
The thousands of bacteria, fungi and other microbes that live in our gut are essential contributors to our good health. They break down toxins, manufacture some vitamins and essential amino acids, and form a barrier against invaders. A study published today in Nature shows that, at 3.3 million,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
31 January 2010
The last ancestor we shared with worms, which roamed the seas around 600 million years ago, may already have had a sophisticated brain that released hormones into the blood and was connected to various sensory organs. The evidence comes not from a newly found fossil but from the study of microRNAs…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
26 January 2010
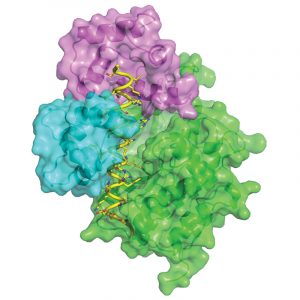
Cells rely on a range of signalling systems to communicate with each other and to control their own internal workings. Scientists from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Hamburg, Germany, have now found a way to hack into a vital communications system, raising the possibility of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
19 January 2010
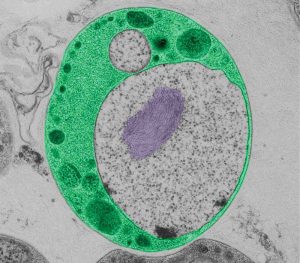
Although they are present almost everywhere, on land and sea, a group of related bacteria in the superphylum Planctomycetes-Verrucomicrobia-Chlamydiae, or PVC, have remained in relative obscurity ever since they were first described about a decade ago. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
18 January 2010
ChEMBLdb, a vast online database of information on the properties and activities of drugs and drug-like small molecules and their targets, launches today with information on over half a million compounds. The data lie at the heart of translating information from the human genome into successful new…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
10 December 2009
Is it a boy or a girl? Expecting parents may be accustomed to this question, but contrary to what they may think, the answer doesn’t depend solely on their child’s sex chromosomes. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany and the Medical Research…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
10 December 2009
Almost a century after it was discovered in fruit flies with notches in their wings, the Notch signalling pathway may come to play an important role in the recovery from heart attacks. In a study published today in Circulation Research, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL)…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
26 November 2009
What are the bare essentials of life, the indispensable ingredients required to produce a cell that can survive on its own? Can we describe the molecular anatomy of a cell, and understand how an entire organism functions as a system? These are just some of the questions that scientists in a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
8 November 2009
Much as adrenaline coursing through our veins drives our body’s reactions to stress, the plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) is behind plants’ responses to stressful situations such as drought, but how it does so has been a mystery for years. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
4 November 2009
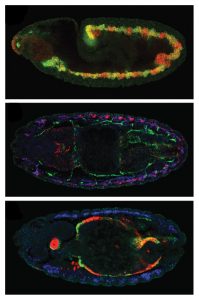
Embryonic development is like a well-organised building project, with the embryo’s DNA serving as the blueprint from which all construction details are derived. Cells carry out different functions according to a developmental plan, by expressing, i.e. turning on, different combinations of genes.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
1 October 2009
For many years, the mosquitoes that transmit malaria to humans were seen as public enemies, and campaigns to eradicate the disease focused on eliminating the mosquitoes. But, as a study published today in Science shows, the mosquitoes can also be our allies in the fight against this common foe,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
30 September 2009
In the quest for speed, olympic swimmers shave themselves or squeeze into high-tech super-suits. In the body, sperm are the only cells that swim and, as speed is crucial to fertility, have developed their own ways to become exceptionally streamlined. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
21 September 2009
For scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Monterotondo, Italy, what seemed like a disappointing result turned out to be an important discovery. Their findings, published online this week in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), provide…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
13 September 2009
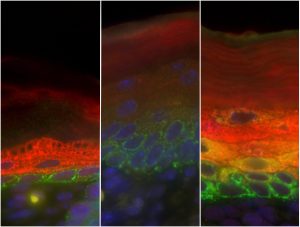
Stem cells have a unique ability: when they divide, they can either give rise to more stem cells, or to a variety of specialised cell types. In both mice and humans, a layer of cells at the base of the skin contains stem cells that can develop into the specialised cells in the layers above.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
25 August 2009
BBSRC has awarded funding to the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), based at Hinxton near Cambridge, to permit a dramatic increase in the institute’s data storage and handling capacity. The funding is the first step in developing the existing…
LAB MATTERS
13 August 2009
Our genome is constantly under attack from things like UV light and toxins, which can damage or even break DNA strands and ultimately lead to cancer and other diseases. Scientists have known for a long time that when DNA is damaged, a key enzyme sets off a cellular ‘alarm bell’ to alert the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
2 August 2009
Chronic inflammatory lung diseases like chronic bronchitis and emphysema are a major global health problem, and the fourth leading cause of death and disability in developed countries, with smoking accounting for 90% of the risk for developing them. Work by scientists at the European Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
7 July 2009
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the University of Heidelberg, Germany, have come a step closer to understanding how cholesterol levels are regulated. In a study published today in the journal Cell Metabolism, the researchers identified 20 genes that are involved…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
26 June 2009

On June 26 2009 the joint international Unit for Virus and Host Cell Interactions (Unité Mixte Internationale) was formally established in Grenoble. The unit is run jointly by CNRS, the Grenoble outstation of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the Grenoble University Joseph…
LAB MATTERS
25 June 2009
Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, came a step closer to understanding how cells close gaps not only during embryonic development but also during wound healing. Their study, published this week in the journal Cell, uncovers a fundamental…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
23 June 2009
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the University Clinic Heidelberg, Germany, have produced a three-dimensional reconstruction of HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus), which shows the structure of the immature form of the virus at unprecedented detail. Immature HIV is…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
22 June 2009

Mice are one of biology’s most important model organisms, because 98% of their genes and many of their traits and diseases are similar to ours. Researchers at the Mouse Biology Unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) take advantage of these similarities and use mice to study…
LAB MATTERS
9 June 2009
The life sciences are scaling up and produce huge amounts of data and new literature at an amazing pace. The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) now offers a new free service to help researchers, teachers and students keep up-to-date with scientific literature on the web, especially when…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
28 May 2009
Proteins are the executive agents that carry out all processes in a cell. Their activity is controlled and modified with the help of small chemical tags that can be dynamically added to and removed from the protein. 25 years after its first discovery, researchers at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
4 May 2009
Most cellular processes are carried out by molecular machines that consist of many interacting proteins. These protein complexes lie at the heart of life science research, but they are notoriously hard to study. Their abundance is often too low to extract them directly from cells and generating…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
30 April 2009
Recycling is important not only on a global scale, but also at the cellular level, since key molecules tend to be available in limited numbers. This means a cell needs to have efficient recycling mechanisms. Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and Heidelberg University,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
23 April 2009
It can be found in all life forms, and serves a multitude of purposes, from energy storage to stress response to bone calcification. This molecular jack-of-all trades is polyphosphate, a long chain of phosphate molecules. Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
24 February 2009
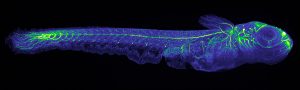
‘Useless fish with big eyes’. This is what Medaka, the name of the Japanese killifish in the pictures, means in Japan where it originally comes from. While its eyes are undeniably big, the fish has proven remarkably useful for scientists. It is a simple model organism, amenable to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
4 February 2009
Influenza is and remains a disease to reckon with. Seasonal epidemics around the world kill several hundred thousand people every year. In the light of looming pandemics if bird flu strains develop the ability to infect humans easily, new drugs and vaccines are desperately sought. Researchers at…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
25 January 2009
Genes that contain instructions for making proteins make up less than 2% of the human genome. Yet, for unknown reasons, most of our genome is transcribed into RNA. The same is true for many other organisms that are easier to study than humans. Researchers in the groups of Lars Steinmetz at the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
12 December 2008
Microscope designer Leica Microsystems and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) signed a corporate partnership agreement today whereby Leica Microsystems becomes a founder partner of the EMBL Advanced Training Centre scheduled to be completed in September 2009. Besides its financial…
LAB MATTERS
3 December 2008
Cell division is one of the most fundamental processes of life. It explains how one cell can give rise to an organism of several million cells, it determines the shape of different life forms and it underpins our body’s capacity to heal when injured. Often we only notice how important cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
24 November 2008
The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and PerkinElmer Life and Analytical Sciences, a global leader in life science research, drug discovery and cellular science, today announced that they have entered into a corporate partnership in support of EMBL’s Advanced Training Centre in…
LAB MATTERS
20 November 2008

The best-selling novel The swarm captured the imagination of countless readers with the fascination of marine life. But it also showed how little we understand life in the depth of the ocean. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the Max Planck Institute (MPI)…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
22 October 2008
What at the first sight could be pictures of planets or other cosmic structures are actually microscope images of balls (cysts) of human kidney cells. They were taken by Emmanuel Reynaud, in the group of Ernst Stelzer at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), with a widefield microscope.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
16 October 2008
Today at a meeting organised by the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, scientists from around the globe announced the formation of the International Human Microbiome Consortium (IHMC), an effort that will enable researchers to characterise the relationship of the…
LAB MATTERS
9 October 2008
Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) have generated a digital zebrafish embryo – the first complete developmental blueprint of a vertebrate. With a newly developed microscope scientists could for the first time track all cells for the first 24 hours in the life of a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
23 July 2008
The Wellcome Trust has awarded £4.7 million (€5.8 million) to EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) to support the transfer of a large collection of information on the properties and activities of drugs and a large set of drug-like small molecules from the publicly listed…
LAB MATTERS
20 July 2008
Mouse mothers-to-be have a remarkable way to protect their unborn pups. Because the smell of a strange male’s urine can cause miscarriage and reactivate the ovulatory cycle, pregnant mice prevent the action of such olfactory stimuli by blocking their smell. Researchers from the European…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
11 July 2008
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) discovered a new way to make use of drugs’ unwanted side effects. They developed a computational method that compares how similar the side effects of different drugs are and predicts how likely the drugs act on the same target…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
9 July 2008
Genetic recombination, the process by which sexually reproducing organisms shuffle their genetic material when producing germ cells, leads to offspring with a new genetic make-up and influences the course of evolution. In the current issue of Nature, researchers at the European Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
4 July 2008
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) is a condition that unexpectedly and unexplainably takes the lives of seemingly healthy babies aged between a month and a year. Now researchers of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory in Monterotondo, Italy, have developed a mouse model of the so-called crib…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
20 June 2008
What makes a human different from a chimp? Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) have come one important step closer to answering such evolutionary questions correctly. In the current issue of Science they uncover…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
30 May 2008
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) in Hinxton, UK, have revealed new insights into how sex chromosomes are regulated. A chromatin modifying enzyme helps compensate for the fact that…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
28 May 2008
In a contract signed today, the European Commission has awarded €4.5 million to a pan-European consortium to decide upon the best way to unite Europe’s biological data resources into a sustainable, integrative bioinformatics network for the life sciences. The European Life-science…
LAB MATTERS
7 May 2008
UK-based researchers at the Medical Research Council Functional Genomics Unit in Oxford and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute in Cambridge have revealed the genetic makeup of the one of the world’s strangest mammals. They have analysed the DNA…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
4 May 2008
Influenza is currently a grave concern for governments and health organisations around the world. Now one of the tactics used by influenza virus to take over the machinery of infected cells has been laid bare by structural biologists at the EMBL, the joint Unit of Virus Host-Cell Interaction of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
8 April 2008
Leukaemia – cancer of blood or bone marrow – is caused by mutations that allow defective blood cells to accumulate and displace healthy blood. To devise effective therapies it is crucial to know which mutations cause leukaemia and which cell type gives rise to leukaemic cells. Researchers from…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
6 March 2008
Epigenetic regulation – modifications to the structure of chromatin that influence which genes are expressed in a cell – is a key player in embryonic development and cancer formation. Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg now gained new insight…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
5 February 2008
Much less widely known than the dangerous consequences of iron deficiencies is the fact that too much iron can also cause problems. The exact origin of the genetic iron overload disorder hereditary hemochromatosis [HH] has remained elusive. In a joint effort, researchers from the European Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
22 January 2008
Drawing on the expertise of multi-disciplinary research teams, the map developed by the 1000 Genomes Project will provide a view of biomedically relevant DNA variations at a resolution unmatched by current resources. The European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), working with long-term collaborator…
LAB MATTERS
8 January 2008
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) have discovered that proteins that regulate the body’s iron household play a vital role in making sure enough nutrients and water are absorbed in the intestine. Mice lacking these proteins suffer from weight loss and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
17 December 2007
It does not take much to injure a muscle. Sometimes one sudden, inconsiderate movement does the job. Unfortunately, damaged muscles are not as efficient at repair as other tissues such as bone. Researchers of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s Mouse Biology Unit (EMBL), Italy, and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
11 December 2007
ArrayExpress, the publicly available database of transcriptomics data at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), has doubled in size in 2007, reaching the 100,000-hybridisation milestone. The database now holds snapshots of gene expression…
LAB MATTERS
5 December 2007
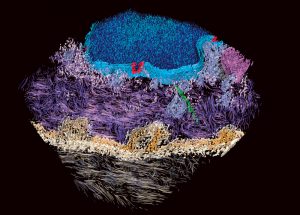
Seeing proteins in their natural environment and interactions inside cells has been a longstanding goal. Using an advanced microscopy technique called cryo-electron tomography, researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) have visualised proteins responsible for cell-cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
2 December 2007
Cells in our body come in various shapes and sizes. Each cell is shaped in such a way as to optimise it for a specific function. When things go wrong and a cell does not adopt its dedicated shape, its function can be impaired and the cell can cause problems in the body. Researchers at […]
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
12 November 2007

Today, the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) announces Luxembourg as the new member of its international community. Accepted by EMBL’s council and ratified by the parliament of Luxembourg, the Grand-Duchy has officially joined the institute as the 20th member state. “EMBL is…
LAB MATTERS
23 October 2007
The European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) officially opens its new East Wing today with a reception for prominent guests. The East Wing will be jointly opened by Ian Pearson, Minister of State for Science and Innovation, UK, and Robert-Jan Smits,…
LAB MATTERS
21 October 2007
New insights into the cellular signal chain through which pheromones stimulate mating in yeast have been gained by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory [EMBL]. Similar signal chains are found in humans, where they are involved in many important processes such as the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
3 October 2007
Today the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), the University of Helsinki, Finland, the University of Oslo, Norway, and Umeå University, Sweden, officially launch their new Nordic EMBL Partnership for Molecular Medicine. The agreement will encourage scientific exchange and collaborations…
LAB MATTERS
15 September 2007
Many neuronal disorders, including epilepsy, schizophrenia and lissencephaly ─ a form of mental retardation ─ result from abnormal migration of nerve cells during the development of the brain. Researchers from the Mouse Biology Unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Italy,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
10 September 2007
Scientists from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) have developed a new method to prepare and image biological samples in three dimensions with laser light-sheet based fluorescence microscopy. The technological advance, which is published in the current online issue of Nature…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
28 August 2007
Three papers published by EMBL scientists and their collaborators will make it much easier to share and compare information from large-scale proteomics data. The papers are published in Nature Biotechnology on 8 and 26 August. As the quantity of available biological information and the use of…
LAB MATTERS
9 August 2007
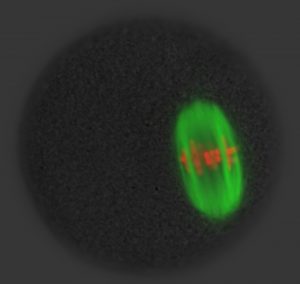
Which genes are passed on from mother to child is decided very early on during the maturation of the egg cell in the ovary. In a cell division process that is unique to egg cells, half of the chromosomes are eliminated from the egg before it is fertilised. Using a powerful microscope, researchers…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
30 July 2007
The UniProt Consortium, which includes the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), has added a new database repository for metagenomic and environmental data to its family of protein sequence databases. Metagenomics is the large-scale genomic…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
11 July 2007
Today, delegates representing the 19 member states of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) offered Australia associate membership in EMBL’s international community. The membership is planned to start officially in January 2008 and will initially last for seven years. “EMBL…
LAB MATTERS
9 July 2007
To protect us from disease our immune system employs macrophages, cells that roam our body in search of disease-causing bacteria. With the help of long tentacle-like protrusions, macrophages can catch suspicious particles, pull them towards their cell bodies, internalise and destroy them. Using a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
8 July 2007
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the University of Michigan have discovered a gene that protects us against a serious kidney disease. In the current online issue of Nature Genetics they report that mutations in the gene cause nephronopthisis (NPHP) in humans and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
29 June 2007
Hormones control growth, metabolism, reproduction and many other important biological processes. In humans, and all other vertebrates, the chemical signals are produced by specialised brain centres such as the hypothalamus and secreted into the blood stream that distributes them around the body.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
22 June 2007
A new mechanism to attack hard-to-treat fungal infections has been revealed by scientists from the biotech company Anacor Pharmaceuticals Inc., California, and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory [EMBL] outstation in Grenoble, France. In the current issue of Science they describe…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
15 June 2007
Scientists at the Samuel Lunenfeld Research Institute of Mount Sinai Hospital (Canada), the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (Germany), and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (USA) have created a new computational method called NetworKIN. This method uses biological networks to better…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
14 June 2007
The ENCyclopedia Of DNA Elements (ENCODE), an international research consortium organised by the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), today published the results of its exhaustive, four-year effort to build a “parts list” of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
10 June 2007
A human cell contains an enormous 1.8 metres of DNA partitioned into 46 chromosomes. These have to be copied and distributed equally into two daughter cells at every division. Condensation, the shortening of chromosomes, allows the cell to handle such huge amounts of genetic material during cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
5 June 2007
Why does the same diet make some of us gain more weight than others? The answer could be a molecule called Bsx, as scientists from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), the German Institute for Nutrition (DIFE), Potsdam, and the University of Cincinnati report in the current issue of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
3 June 2007
People who suffer from anxiety tend to interpret ambiguous situations, situations that could potentially be dangerous but not necessarily so, as threatening. Researchers from the Mouse Biology Unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Italy have now uncovered the neural basis for…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
22 May 2007
It was the world’s earliest public database of DNA and RNA sequences and remains Europe’s primary nucleotide sequence resource. The database is maintained by EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute in Hinxton (UK) in collaboration with its US and Japanese counterparts GenBank and…
LAB MATTERS
16 May 2007
Over 30% of our genes are under the control of small molecules called microRNAs. They prevent specific genes from being turned into protein and regulate many crucial processes like cell division and development, but how they do so has remained unclear. Now researchers from the European Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
4 May 2007
When a cell divides, normally the result is two identical daughter cells. In some cases however, cell division leads to two cells with different properties. This is called asymmetric cell division and plays an important role in embryonic development and the self-renewal of stem cells. Researchers…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
20 April 2007

The rise of the central nervous system (CNS) in animal evolution has puzzled scientists for centuries. Vertebrates, insects and worms evolved from the same ancestor, but their CNSs are different and were thought to have evolved only after their lineages had split during evolution. Researchers from…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
14 March 2007
Inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative Colitis, severely impair the lives of more than four million people worldwide. The development of effective therapies against these diseases requires an understanding of their underlying molecular mechanisms. Researchers from…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
6 March 2007
Like our body every cell has a skeleton that provides it with a shape, confers rigidity and protects its fragile inner workings. The cytoskeleton is built of long protein filaments that assemble into networks whose overall architecture and fine detail can only be revealed with high resolution…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
4 March 2007

The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) has developed a new computational tool that makes images obtained with cutting-edge microscopes even sharper. The technological advance and its applications are published in this week’s online issue of the journal Nature Methods. Since the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
25 February 2007
In 1918, 50 million people died during a worldwide influenza pandemic caused by mutation of a bird-specific strain of the influenza virus. Recently H5N1, another highly infectious avian strain has caused outbreaks of bird flu around the world. There is great concern that this virus might also…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
12 February 2007
Liver cancer is one of the deadliest cancers worldwide; every year sees more than 400,000 new cases, and most of the victims die in less than one year. Despite extensive research, the underlying molecular mechanisms of the disease are poorly understood. A new study by researchers from the Mouse…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
11 February 2007
We all know that iron deficiencies are dangerous, but also too much iron is bad for our health. Our body stores excess iron in various tissues, where it can lead to organ failure and even death if not treated before irreversible damage has occurred. Researchers from the Innsbruck Medical…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
2 February 2007
Microorganisms make up more than a third of the Earth’s biomass. They are found in water, on land and even in our bodies, recycling nutrients, influencing the planet’s climate or causing diseases. Still, we know surprisingly little about the smallest beings that colonise Earth. A new…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
1 February 2007

The German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF) has awarded 8.8 Million Euro to the Hamburg Outstation of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) for the construction of an Integrated Research Facility for Structural Biology at the new PETRA-III storage ring of the German…
LAB MATTERS
22 January 2007
The European Commission has awarded 3.7 Million Euro under the European Union Framework 6 Programme over the next four years to a new Marie Curie Research Training Network, coordinated by Dr. Andreas Ladurner at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL). The long molecules of DNA that carry…
LAB MATTERS
8 January 2007
From today scientists will be able to access a vast collection of biomedical research and to submit their own published results for inclusion in a new online resource. Based on a model currently used by the US National Institute of Health, UK PubMed Central (UKPMC) will provide free access to a…
LAB MATTERS
8 January 2007
Phone numbers, the way to work, granny’s birthday – our brain with its finite number of nerve cells can store incredible amounts of information. At the bottom of memory lies a complex network of molecules. To understand how this network brings about one of the most remarkable capacities of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
29 December 2006
A cell is a busy place. In a permanent rush hour, molecules are transported along a dynamic motorway system made up of filaments called microtubules. Microtubules constantly grow and shrink and are rapidly assembled wherever a cargo needs to go, but during this transportation process they need to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
14 December 2006

Today, Janez Potočnik, European Commissioner for Science and Research, received a statement of support for the European Charter for Researchers and the Code of Conduct for the Recruitment of Researchers from EIROforum. “The EIROforum partners warmly welcome this valuable initiative by…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2006
connectionslab-matters
11 December 2006
Today the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) launches its new, faster and easier website with an exhaustive search engine at its centre. The web interface has been streamlined on the basis of user feedback from a recent extensive…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
lab-mattersscience-technology
4 December 2006
The BioModels Database, hosted by the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) in Cambridge, UK, has entered a formal data-exchange agreement with the Database of Quantitative Chemical Signalling (DOQCS) of the National Centre for…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2006
connectionslab-matters
27 November 2006
Today the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) launches CiteXplore, a new freely accessible literature resource service. Biological researchers require two crucial sources of information: scientific literature published in peerreviewed…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
lab-mattersscience-technology
2 November 2006

Muscle wasting can occur at all ages as the result of genetic defects, heart failure, spinal injury or cancer. A therapy to cure the loss of muscle mass and strength, which has a severe impact on patients’ lives, is desperately sought. Blocking a central signal molecule, researchers from the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
6 October 2006
Today, the German Minister for Education and Research, Annette Schavan, breaks ground for the new training and conference centre for the life sciences that will be built on the EMBL campus in Heidelberg. The German Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF), the Klaus Tschira…
LAB MATTERS
27 September 2006
The life of a cell is all about growing and dividing at the right time. That is why the cell cycle is one of the most tightly regulated cellular processes. A control system with several layers adjusts when key components of the cell cycle machinery are produced, activated and degraded to make sure…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
7 September 2006
Today the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) and the Spanish Ministry for Education and Science (MEC) officially launch their new joint EMBL/CRG Research Unit in Systems Biology on the campus of the Barcelona Biomedical Research Park. The Spanish…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2006
embl-announcementslab-matters
3 September 2006

Blood cells have limited lifespans, which means that they must be continually replaced by calling up reserves and turning these into the blood cell types needed by the body. Claus Nerlov and his colleagues at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) unit in Monterotondo, Italy, in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
25 August 2006
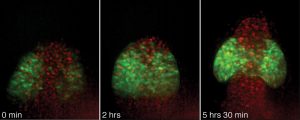
Eyes are among the earliest recognisable structures in an embryo; they start off as bulges on the sides of tube-shaped tissue that will eventually become the brain. Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg have now discovered that cells are programmed to make…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
25 August 2006
Cells in an embryo divide at an amazing rate to build a whole body, but this growth needs to be controlled. Otherwise the result may be defects in embryonic development or cancer in adults. Controlling growth requires that some cells divide while others die; their fates are determined by signals…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
9 August 2006
Today EMBL scientists, EMBL’s commercial affiliate, EMBL Enterprise Management Technology Transfer GmbH (EMBLEM) and EMBL’s venture vehicle, EMBL Ventures GmbH, announce the foundation of Elara Pharmaceuticals GmbH, a start-up company that will translate basic research findings into new…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
lab-mattersscience-technology
6 August 2006
Depression, coordination and speech problems, muscle weakness and disability are just a few of the symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Researchers from the Mouse Biology Unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Italy and the Department of Neuropathology at the Faculty of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
31 July 2006
Scientists will be able to access a vast collection of biomedical research at the touch of a button thanks to a major new initiative that aims to promote the free transfer of ideas in a bid to speed up scientific discovery. Based on a model currently used in the United States, UK PubMed Central…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2006
embl-announcementslab-matters
11 July 2006
In the early days of X-ray crystallography obtaining a three-dimensional model of a protein required wire models, screws, bolts and years of tedious calculations by hand. Today macromolecular models are built by computers – thanks to sophisticated software and in particular a package called…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
lab-mattersscience-technology
29 June 2006
Croatia has officially joined the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) as the organisation’s 19th Member State. The Croatian parliament ratified its membership after EMBL’s council had accepted the country’s application. “Joining EMBL is a very important step…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2006
embl-announcementslab-matters
16 June 2006
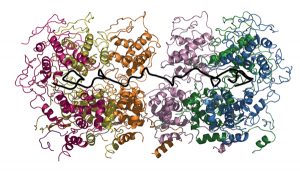
Ebola, measles and rabies are serious threats to public health in developing countries. Despite different symptoms all of the diseases are caused by the same class of viruses that unlike most other living beings carry their genetic information on a single RNA molecule instead of a double strand of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
29 May 2006
Tuberculosis remains one of the deadliest threats to public health. Every year two million people die of the disease, which is caused by the microorganism Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Roughly one third of the world’s population is infected and more and more bacterial strains have developed…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
3 May 2006
Today the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s (EMBL) European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), the Swiss Institute for Bioinformatics (SIB), the University of Cologne, Germany, and the European Patent Office launch FELICS (Free European Life-science Information and Computational Services).…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2006
connectionslab-matters
25 April 2006
EMBOSS, the European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite, has received a vital funding boost from the UK Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) that will guarantee its continued maintenance under an open source license for the next three years. This ends two years of…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2006
connectionslab-matters
10 April 2006
Today three research organisations announce the merging of their expertise to fight cardiovascular diseases, which are among the most common health problems and causes of death in the world. The Magdi Yacoub Institute (MYI) at the UK’s Harefield Heart Science Centre, Imperial College London,…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2006
connectionslab-matters
5 April 2006
Today the network of excellence for Biology and Pathology of the Malaria Parasite (BioMalPar), will bring together the world’s elite in the field of Malaria research at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg. At the second annual BioMalPar conference, organised jointly…
CONNECTIONS
28 March 2006
Science is moving more rapidly than ever; one groundbreaking discovery chases the next at an incredible speed. School teachers have trouble keeping up with the pace, and many pupils call science classes “boring”. Today, Europe’s major research organisations launch Science in…
LAB MATTERS
16 March 2006
Recent research at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) reveals new insights into how cells achieve equality between the sexes. A new link discovered between the membrane surrounding the nucleus and the male X-chromosome in fruit flies may play a crucial role in determining how active…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
2 March 2006
In 1870 the German scientist Ernst Haeckel mapped the evolutionary relationships of plants and animals in the first ‘tree of life’. Since then scientists have continuously redrawn and expanded the tree adding microorganisms and using modern molecular data, yet, many parts of the tree…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
16 February 2006
A detailed structural picture of a molecule that plays a key role in activating the Epstein Barr Virus in human cells has now been obtained by researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the Institut de Virologie Moléculaire et Structurale (IVMS), associated with the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
22 January 2006
Today researchers in Germany announce they have finished the first complete analysis of the “molecular machines” in one of biology’s most important model organisms: S. cerevisiae (baker’s yeast). The study from the biotechnology company Cellzome, in collaboration with the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
11 January 2006

Imagine grabbing two snakes by the tail so that they can’t wriggle off in opposite directions. Scientists at the Hamburg Outstation of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and collaborators from King’s College in London have now discovered that something similar happens to a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
10 January 2006

On Friday, 13 January 2006, the new Carl-Ivar Brändén Building (CIBB) will be inaugurated on the Polygone Scientifique Campus in Grenoble, France. The CIBB will be operated as a collaboration between major international and national partners based in Grenoble and is a further step in the…
LAB MATTERS
21 December 2005
Researchers at the International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB) in India and a unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in France have made a key discovery about a molecule that helps the malaria parasite infect human cells. India is one of the countries…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
6 December 2005
In the December 6 issue of Nature Biotechnology, scientists from 14 different organizations around the world, including the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute, propose a new quality standard for biochemical models. MIRIAM [for Minimum information requested in the annotation of biochemical…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
lab-mattersscience-technology
24 November 2005
Species evolve at very different rates, and the evolutionary line that produced humans seems to be among the slowest. The result, according to a new study by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory [EMBL], is that our species has retained characteristics of a very ancient ancestor…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
16 November 2005
Today the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) opens a new highthroughput crystallization facility at its Outstation located on the campus of the German Synchrotron Radiation Facility (DESY) in Hamburg, Germany. The facility, made possible by major funds from the German Ministry for Science…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2005
embl-announcementslab-matters
15 November 2005
Most of what happens in cells is the work of machines that contain dozens of molecules, chiefly proteins. With the completion of human and other genomes, researchers now have a nearly complete ‘parts list’ of such machines; what’s lacking is the manual telling where all the pieces…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
13 November 2005
Scientists at the Universities of Heidelberg and Ulm and a unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Monterotondo, Italy, have discovered that a specific signal within brain cells may determine whether they live or die after a stroke. Their study, published online (November 13) by…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
31 October 2005
The Commission of the European Union has awarded EUR 9 million over five years for a new Network of Excellence that will make computational systems biology accessible to bench scientists throughout Europe and beyond. ENFIN, which stands for ‘Experimental Network for Functional…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
lab-mattersscience-technology
6 October 2005
Mutations in genes are the basis of evolution, so we owe our existence to them. Most mutations are harmful, however, because they cause cells to build defective proteins. So cells have evolved quality control mechanisms that recognize and counteract genetic mistakes. Now scientists of the Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
12 September 2005
The European Commission has selected the EBI to coordinate a project that will stimulate and explore synergies between bioinformatics (the science of storing, retrieving and analysing large amounts of biological information) and medical informatics (the science of processing, sharing and using…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2005
connectionslab-matters
4 September 2005
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg and the Institute of Biomedical Research of the Parc Científic de Barcelona (IRB-PCB) have now added key evidence to claims that some types of cancer originate with defects in stem cells. The study, reported this week in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
29 August 2005
The European Bioinformatics Institute and Flanders Interuniversity Institute for Biotechnology (VIB) – Ghent University have launched the PRoteomics IDEntifications database (PRIDE). PRIDE allows researchers who work in the field of proteomics – the large-scale study of proteins – to…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2005
connectionslab-matters
29 August 2005
The executive teams of five major molecular interaction databases announced today the signing of an agreement to share curation efforts and exchange completed records through a mechanism known as the International Molecular Exchange (IMEx) consortium. IMEx will provide a network of stable,…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2005
connectionslab-matters
25 August 2005
Achieving equality between the sexes can be a challenge even for single cells. Since evolution began removing bits of male DNA to create the ‘Y’ chromosome, males have had a single copy of certain key genes on the X chromosome, whereas females have two. Normally this would lead females…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
22 August 2005
The world’s three leading public repositories for DNA and RNA sequence information have reached 100 gigabases (100,000,000,000 bases; the ‘letters’ of the genetic code) of sequence. Thanks to their data exchange policy, which has paved the way for the global exchange of many types…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2005
connectionslab-matters
18 July 2005
The first rate research from the Molecular Medicine Partnership Unit (MMPU) is now set to continue for the long-term. The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the Medical Faculty of University of Heidelberg, who formed the joint venture in 2002, have announced their plans to initiate a…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2005
connectionslab-matters
13 July 2005
Microtubules need a helping hand to find chromosomes in dividing egg cells, scientists have discovered. Although it was generally accepted that microtubules act alone as the cellular ropes to pull chromosomes into place, a new study by researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL)…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
12 July 2005

A systematic search through human genes has begun at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany. Working within the MitoCheck consortium that includes 10 other institutes throughout Europe, the EMBL scientists will silence all human genes, one-by-one, to find those…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2005
connectionslab-matters
1 July 2005
EBI researchers have changed our view of 4 billion years of microbial evolution. Christos Ouzounis and colleagues have gained intriguing quantitative insights into how gene families are transferred, not only ‘vertically’ through passage from one organism to its progeny, but also…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
19 June 2005
Living organisms need to sense the amount of energy that is available to them and regulate the activity of their genes accordingly. Scientists have made the unexpected finding that a histone protein, which wraps DNA into tight bundles and regulates gene activity, can bind a small molecule produced…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
13 May 2005
The European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) has received a big boost from The Wellcome Trust, the Medical Research Council (MRC) and the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC), who have given funds to expand the EBI site in Hinxton, Cambridgeshire, UK. The new…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2005
embl-announcementslab-matters
1 May 2005
Dr. Iain Mattaj today took over the leadership of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory [EMBL], a prominent basic research and training institute with laboratories in France, Germany, Italy and the UK. “The pace of progress in the life sciences is remarkable. I see my job as ensuring that…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2005
embl-announcementslab-matters
21 April 2005
Instead of sequencing the genome of one organism, why not sequence a drop of sea water, a gram of farm soil or even a sunken whale skeleton? Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg and their US collaborators have done just that, and the result is a new…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
11 April 2005
Today sees the launch of BioModels, the world’s first database of annotated biological models. BioModels is the result of a collaboration led by the European Bioinformatics Institute (UK) and the SBML Team, an international group that develops opensource standards to describe biological…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
31 March 2005

A novel high-tech microscope will be brought to the marketplace, giving laboratories everywhere fascinating new insights into living organisms. EMBLEM Technology Transfer GmbH (EMBLEM), the commercial entity of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), announced today that it has signed a…
CONNECTIONS
28 February 2005
The International Society for Computational Biology has named two scientists from the European Bioinformatics Institute as the winners of its awards for 2005. Janet Thornton wins the Senior Scientist Accomplishment Award while the Overton Prize goes to Ewan Birney. Thomas Lengauer, the ISCB’s…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
3 February 2005
Most things that happen in the cell are the work of ‘molecular machines’ – complexes of proteins that carry out important cellular functions. Until now, scientists didn’t have a clear idea of when proteins form these machines – are these complexes pre-fabricated or put…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
1 February 2005
The Commission of the European Union has awarded 8.3 million Euro to a pan-European task force who will improve access to biological information for scientists throughout and beyond Europe. The EMBRACE Network of Excellence, which encompasses computational biologists from 17 institutes in 11…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
25 January 2005
One of the most basic yet least understood processes in our bodies is how cells crawl along tissues. This behavior is essential to the formation of an embryo and other processes, but it must be tightly controlled. A disturbance can lead to the spread of cancer cells or diseases like Spina…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
No results found
























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































![A new tool for single-cell genomics helps us better understand differences between T cell populations. [Illustration: Spencer Phillips, EMBL-EBI]](https://www.embl.org/news/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/TCell_news_EMBL-e1457443531496-300x205.jpg)











































































![Tara expeditions docks in London, September 2015, on its way to the UN Climate Change Conference in Paris. [PHOTO: Robert Slowley]](https://www.embl.org/news/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/1509-tara-london-ib-300x206.jpg)










































































































































































































































































































































