
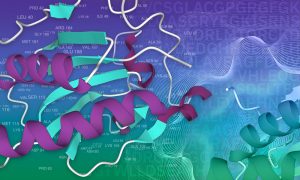
Cerelixis: precision phytostimulants for resilient agriculture
A new EMBL spin-off leverages new insights into plant biology for more efficient crop protection
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology
Showing results out of

A new EMBL spin-off leverages new insights into plant biology for more efficient crop protection
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology

Parkinson's disease, a neurodegenerative condition causing motor and non-motor symptoms like gut issues (often appearing decades early), is being investigated for its link to the gut microbiome. While previous studies have shown gut microbiome changes in Parkinson's patients, a clear consensus on…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
sciencescience-technology
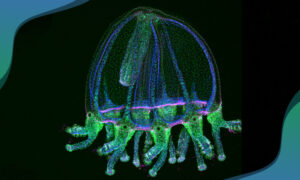
EMBL scientists are on a quest to investigate the underlying biological processes that enable regeneration in jellyfish, which could also help us understand how wounds heal.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology

SAVANA is a new tool designed for accurate detection of structural variations in clinical samples.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
research-highlightsscience-technology

Five key takeaways from an EMBL | EMBO symposium that explored the ‘wild frontiers’ of model organisms, from phytoplankton to sea anemones, waterstriders, roundworms, and more.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology
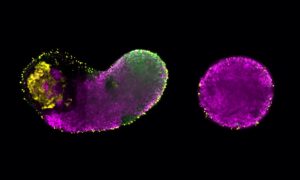
EMBL Barcelona and MPI-CBG Dresden researchers reveal how glycolysis drives early embryonic cell decisions.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology
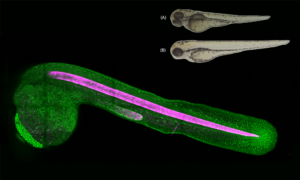
EMBL scientists investigate how zebrafish bodies change when grown at higher temperatures.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology

Supported by EMBL services, students Misha Hegde & Mia Maurer have identified a previously unknown bacteriophage that targets Rhizobium rhizogenes, a pathogen harming crops. Using cutting-edge imaging and DNA sequencing at EMBL Heidelberg, they are exploring its potential as a natural alternative…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology
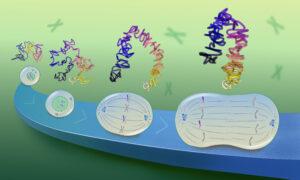
EMBL scientists have shown how overlapping loops of DNA stack upon each other in dividing cells to give rise to rod-shaped chromosomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology

Texas A&M University researchers work with experts from EMBL Imaging Centre to uncover how molecules navigate the nuclear pore complex.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology

EMBL Barcelona researchers developed a computational method that reconstructs embryonic development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology
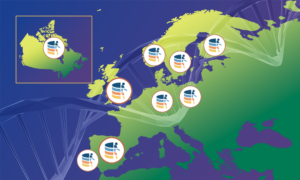
The Federated European Genome-phenome Archive (FEGA) has expanded its network and continues to evolve by embracing emerging technologies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation
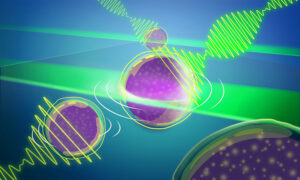
Another EMBL-engineered advance to Brillouin microscopy has significantly widened the aperture to provide quick 3D imaging in real time of light-sensitive samples.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology
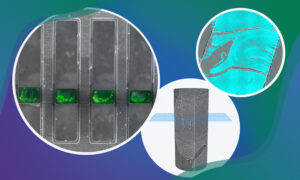
New funding from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (CZI) supports two multidisciplinary projects across EMBL’s units and sites to support the development of imaging technologies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology
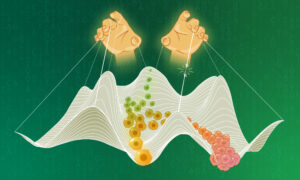
Scientists at EMBL and DKFZ have discovered how cells in the liver maintain their identity and avoid becoming tumour cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology

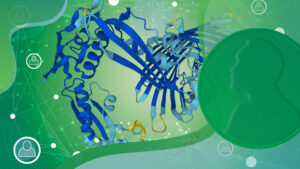
Researchers in the Galej Group at EMBL Grenoble have provided new insights into the structure of the minor spliceosome, an essential RNA-protein complex.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology
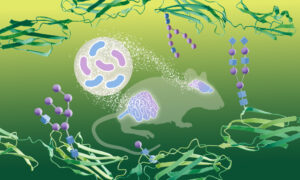
Scientists have discovered that gut bacteria can alter molecular signatures in the brain, using a brand new method to study how carbohydrates modify proteins.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology

Yerba mate is a popular caffeinated beverage. Scientists mapped its genome, revealing surprising facts about its biochemistry and the evolution of caffeine biosynthesis. The findings might pave the way for new varieties of yerba mate.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology

A new study from EMBL Barcelona researchers shows that metabolism is a selective modulator of developmental tempo, contributing to our evolutionary understanding.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology

Researchers from Mainz University and EMBL Hamburg have presented a new approach for assessing the form of disordered proteins by using anomalous X-ray scattering method for structural analysis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology

The Paleocore project, led by the French marine institute Ifremer and part of the TREC expedition, aims to study marine sediments to understand the impact of major historical events on ecosystems.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology
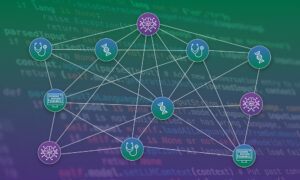
Introducing an open-source large language model (LLM) framework designed for custom biomedical research.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
research-highlightsscience-technology
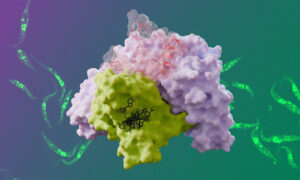
The Kowalinski group at EMBL Grenoble identified significant differences between the trypanosomal and human nuclear cap-binding complex, a key player in cellular RNA metabolism and a potential target for novel anti-parasitic drugs.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology

Study identifies a novel mechanism driving osteosarcoma and provides insights to help predict patient outcomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
research-highlightsscience-technology

The Arendt Group at EMBL Heidelberg focuses on mechanisms of evolution, studying Platynereis dumerilli – evolutionarily ancient marine worms found broadly along European coasts.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology
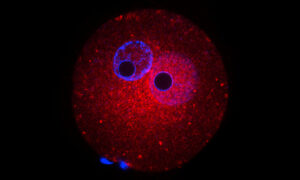
Researchers in the Boulard group at EMBL Rome demonstrated that the catalytic activity of the OGT enzyme is essential for embryonic development, and that when it’s reduced, embryo development is delayed – especially in males.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology
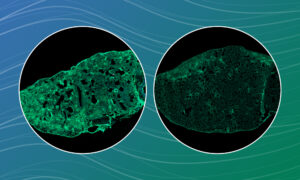
EMBL scientists discovered that dextromethorphan, an FDA-approved active ingredient in cough syrups, has potential to treat fibrotic lung disease by containing collagen and other pro-fibrotic molecules capable of forming scars inside the cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

The Prevedel group at EMBL Heidelberg developed a mobile microscope: miniature in scale, fast in sample imaging, and giant in resolution.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

Right from the early days of DNA sequencing, EMBL’s scientists have been instrumental in helping the world understand, decode, archive, and manipulate genomes at scale and across many branches of the evolutionary tree, a task they continue to excel at today.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
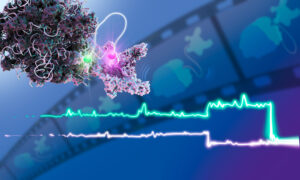
With a novel approach, EMBL scientists discovered important interactions between molecular machines, potentially offering new opportunities for drug development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
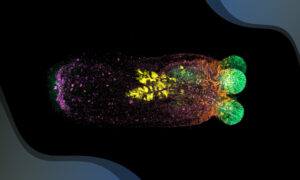
Scientists have shown how regenerating sea anemones restore their shape following a major injury, uncovering novel cellular and molecular mechanisms.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

The introduction of computational methods in biology opened up an entirely new world of insights and breakthroughs. Over the last several decades, EMBL has been at the forefront of discoveries and innovations that have not only propelled the field forward but also opened up access to bioinformatics…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

A recent symposium on ‘The complex life of RNA’ brought together scientists from across the world interested in exploring one of the most crucial molecules essential to life.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

The findings of the study provide insights into vaccines or treatments to protect people from severe malaria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
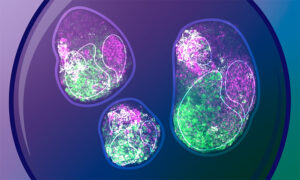
Researchers from the Trivedi Group at EMBL Barcelona unveil how cells can act autonomously during early development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
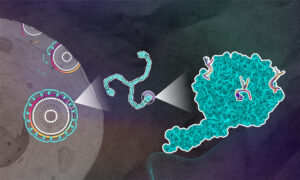
Scientists from EMBL Hamburg and CSSB have revealed key insights into the cellular process of clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
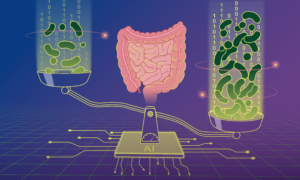
Scientists have developed a new machine-learning model to predict microbial load — the density of microbes in our guts — and used it to demonstrate how microbial load plays an important role in disease-microbiome associations.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

Nicolas Foos, a postdoctoral fellow at EMBL Grenoble, talks about the implementation of a new method for in situ serial crystallography developed during his ARISE fellowship.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

Employing a library of more than 1,000 chemicals, EMBL researchers and collaborators investigated how agrochemicals affect insect populations.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
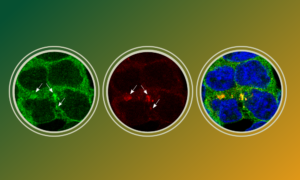
Scientists have discovered how the antiviral protein TRIM25 finds and binds viral RNA to activate an innate immune response.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

Imaging lets us observe biology in action – it makes visible the hidden processes of life. From its founding, EMBL has been a centre of breakthroughs and developments in bioimaging, and it continues to play a pioneering role in this field today.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
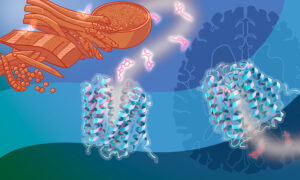
EMBL Hamburg scientists have gained molecular insights into how we absorb vitamin B1 – a mechanism with implications for disease and drug development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
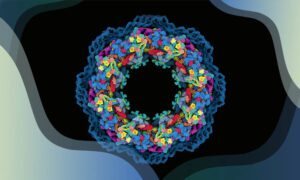
The function of biological molecules is intimately linked to their structure. In the 50 years since EMBL was established, its researchers and engineers have constantly provided leadership in structural biology research and services, resulting in many scientific breakthroughs and novel insights.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
Creators of AI system AlphaFold receive 2024 Nobel Prize for Chemistry.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
sciencescience-technology

The prize was awarded to John J. Hopfield, Princeton University, USA, and Geoffrey Hinton, University of Toronto, Canada, for their seminal contributions to the foundational methods that enabled the development of machine learning.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg and University of Virginia revealed a new cellular response to starvation: ribosomes attach to the mitochondrial outer membrane in a very unusual way, via their small subunit. The finding made in yeast might provide insights into how cancer cells survive the harsh…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

Addition of data from more diverse populations to the Polygenic Score (PGS) Catalog and a new software tool for PGS calculation could help produce more equitable disease risk predictions.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation
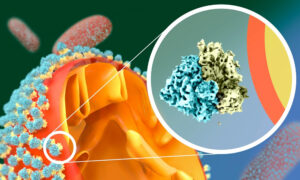
EMBL Heidelberg researchers compared the effect of drugs on isolated bacteria versus those growing in communities. This is the first study showing that bacteria are more resilient when in community due to cross-protection strategies. This could help researchers design more efficient therapies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
Researchers have identified key cellular control sites that regulate gene expression and prevent the activation of ancient viral sequences in the genome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

EMBL-EBI data resources help advance biodiversity and climate change research by enabling scientists to study species interactions, evolutionary processes, ecosystem health, and more.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation

An AI-enhanced advanced microscopy approach offers promise in better understanding glioblastomas, one of the deadliest brain cancers.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
EMBL scientists applied molecular engineering to build photoacoustic probes to label and visualise neurons deep within brain tissue.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
EMBL Heidelberg researchers discovered how a protein switches between repelling and gluing chromosomes during cell division. This helps the mother cell to divide the genome equally into two daughter cells and cluster chromosomes inside the daughter nuclei, ensuring a successful cell division.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
A new publication from the Cusack group sheds light on how a key avian influenza virus enzyme can mutate to allow the virus to replicate in mammals.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
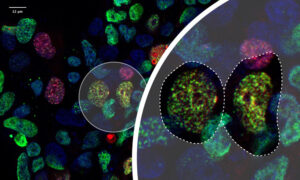
EMBL Grenoble researchers have come up with a new way to identify the targets of a crucial protein-modifying enzyme involved in diverse cellular processes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

Using machine learning to analyse the genetic factors behind early clinical trial termination, researchers find a link between genetic evidence and trial outcome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
research-highlightsscience-technology
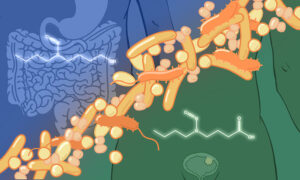
Study shows that gut bacteria can metabolise carcinogens and cause them to accumulate in distant organs, leading to tumour development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

The dynamic world of proteomics is shaping the future of personalised medicine, but some obstacles stand in the way
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
perspectivesscience-technology
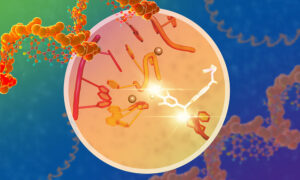
A new research paper published in Nature Communications lays the groundwork for the development of new drugs specific to genetic mutations or alterations responsible for the onset of tumours or genetic diseases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
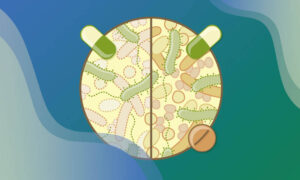
EMBL researchers and their partners have been studying microbial functions and interactions for the benefit of human and planetary health for the last two decades.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

EMBL Grenoble’s Kowalinski Group analysed the structure of an enzyme responsible for modifying tRNA molecules to fine-tune protein production. They discovered that to distinguish almost identical, yet different, tRNA molecules, the enzyme uses help from another enzyme – a type of cooperation…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
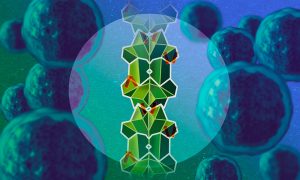
EMBL Hamburg scientists and collaborators discovered a new molecular mechanism in which an unstructured protein disables one of the main cancer-promoting proteins by gluing them into an elongated stack. Data from human patient samples support the role of this mechanism in prostate cancer…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
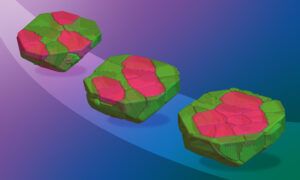
A theoretical model involving tiny Minecraft-like cubes can help us understand dynamic biological processes, such as cell sorting in embryos.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

EMBL-EBI data resource helps scientists upcycle animal by-products.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
perspectivesscience-technology
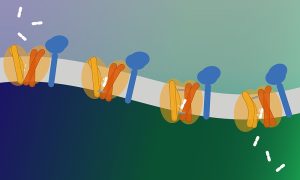
The group of Christian Löw at EMBL Hamburg and CSSB, and collaborators from the Christian-Albrechts-University Kiel and CNRS & Université Paris Cité worked together to reveal the structure and function of a previously unknown lysosome transporter, MFSD1.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
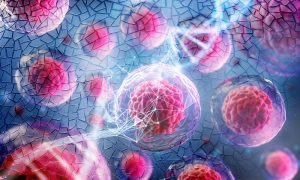
Blood stem cells from healthy people carry major chromosomal alterations, a study in Nature Genetics by researchers at the Max Delbrück Center and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) finds. The discovery suggests that we are all genetic mosaics, which may contribute to ageing-related…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
Large-scale study uses data from Danish health registries to predict individual risks of developing cancer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
research-highlightsscience-technology

New research by EMBL scientists shows how different modes of cell division used by animals and fungi might have evolved to support diverse life cycles.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

A study from the Hackett group at EMBL Rome led to the development of an epigenetic editing system that allows to precisely program chromatin modifications at any specific position in the genome, to understand their causal role in transcription regulation.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
Scientists from EMBL Rome and EMBL Heidelberg found that disrupting the gut microbiome of male mice increases the risk of disease in their offspring. Their findings suggest that a father’s pre-conception environment can have lifelong effects on offspring.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

Experts in quantum computing and genomics to develop new methods and algorithms to process biological data.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
announcementsscience-technology

SpatialData is a tool developed by EMBL scientists in cooperation with multiple research institutions to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies in a spatial environment, providing holistic insights into health and disease. Researchers can now freely access and use SpatialData…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

A recent EMBO | EMBL conference provided a forum for researchers to share how AI is making a difference in biology and bioinformatics.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

New study from the Galej group provides deeper structural insight into the assembly of a critical molecular machine, that removes non-coding information from genes during their expression.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
New study uncovers the potential of immunotherapy in preventing breast cancer and creates the openly available Human Breast Cell Atlas.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
research-highlightssciencescience-technology

New research from EMBL Heidelberg shows how cells in developing embryos undergo a major shift in the way they regulate gene expression as they mature and differentiate.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
sciencescience-technology
Plasmodium falciparum, a malaria parasite, uses gene conversion to produce genetic diversity in two surface protein genes targeted by the human immune system.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
announcementssciencescience-technology

An international team of researchers aim to combine social determinants of health with genomics, immune profiling, and exposomics data to tackle cancer inequities at an unprecedented scale.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
announcementssciencescience-technology
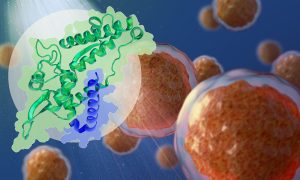
A new study from the Bhogaraju Group at EMBL Grenoble reveals how the cancer-promoting MAGE family of proteins bind to their targets, aiding the development of anti-cancer drugs that target these proteins.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
sciencescience-technology

The Traversing European Coastlines (TREC) expedition prepares to begin its next phase of sampling, with stops in Spain, Greece, Italy, and beyond.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
sciencescience-technology
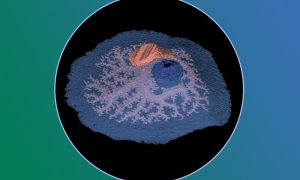
Sponges lack muscles and neurons. Yet, they make coordinated movements. Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg have discovered that sponge movement is controlled by an ancient ‘relaxant-inflammatory’ response that is also present in vertebrate blood vessels. The findings shed light on sponge physiology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
sciencescience-technology

Approximately 300 scientists met up at EMBL Heidelberg to unravel the centuries-old puzzle of cancer through the modern lens of genomics.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
eventsscience-technology
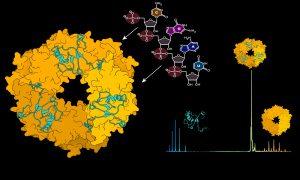
The Kosinski Group at EMBL Hamburg collaborated with other groups in Hamburg to reveal critical steps in Lassa virus ribonucleoparticle assembly and recruitment, and the crucial role played by RNA in in the Lassa virus life cycle.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology
Researchers reveal that healthy lung development hinges on immune-epithelial crosstalk, with implications for respiratory diseases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
research-highlightsscience-technology
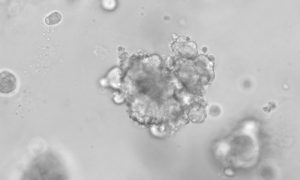
A new organoid model mimics the behaviour of neuroendocrine tumours (NETs), providing a novel and invaluable tool to study the disease in the lab.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

EMBL Hamburg, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Postnova Analytics GmbH, and BioNTech SE have developed a new method to quantitatively investigate sizes of nanoparticles containing mRNA. It may become an important part of regular characterisation of mRNA nanomedicines in the future.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology
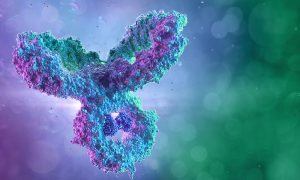
Former EMBL staff scientist founds a start-up – DenovAI – for broader, faster and cheaper antibody discovery using advanced machine learning and computational biophysics.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

The new initiative brings together genomic data from various biodiversity projects to aid conservation and biodiversity efforts.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
announcementssciencescience-technology

An interdisciplinary collaboration between Hamburg scientists has yielded new insights into the structure and function of a heat-resistant enzyme from an exotic microbe. In this interview, EMBL Hamburg’s Matthias Wilmanns and TUHH’s Garo Antranikian discuss how their collaboration developed and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

A new study from the Asari group at EMBL Rome shows a different retinal function in awake mice compared to isolated retinal samples. These new insights could help to develop prosthetic devices that can act as a retina in the future.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology
A recent EMBO | EMBL symposium brought together leading developers of imaging methods with cutting-edge applications that illustrate how imaging can answer biological questions.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
eventsscience-technology
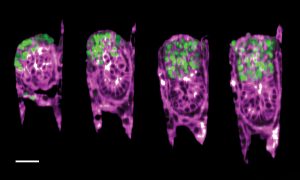
EMBL researchers have created an engineered uterus that allows a closer look at a mouse embryo’s development and its interactions with the uterine environment.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
picture-of-the-weeksciencescience-technology
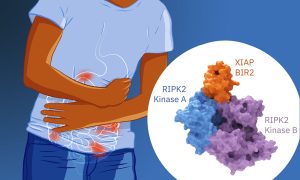
Researchers from the Cusack group at EMBL Grenoble provide structural insights on the XIAP/RIPK2 complex, a promising drug target to fight inflammatory bowel diseases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

Here are six takeaways from a recent EMBO/EMBL symposium that brought together scientists to discuss the state of research involving the human microbiome and its connection to health and disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
eventsscience-technology
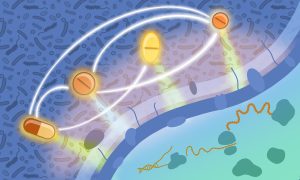
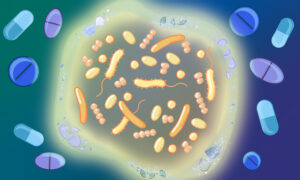
In an extensive investigation, EMBL researchers have tested over 10,000 drug combinations against some of the leading pathogenic bacteria carrying antimicrobial resistance and causing mortality.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

A two-week practical course introduced participants to the intricacies of studying the dynamic interplay between organisms and their changing environment and how it impacts development and evolution.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
lab-mattersscience-technology
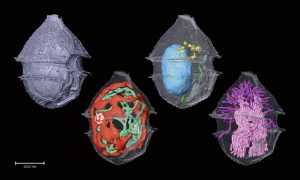
A new method developed by EMBL scientists can help us identify and investigate plankton species in field samples with greater speed, accuracy, and resolution than ever possible before.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

Pioneers of the mRNA nanomedicines technology receive 2023 Nobel Prize in Physiology or medicine. EMBL is pleased to have supported the development of the application of the mRNA nanomedicine technology through our long-standing collaboration with BioNTech, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology
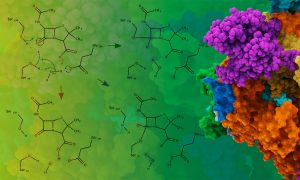
Enzymes constitute a large fraction of genomes – 20% in humans – which makes them a very important part of life. Despite decades of studies and a rich literature dedicated to understanding the reaction mechanisms of enzymes, the rules of enzyme catalysis are still not fully clear. A new…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation

Ensembl Variant Effect Predictor integrates Google DeepMind’s new AlphaMissense Database for better predictions of genetic variant pathogenicity.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation
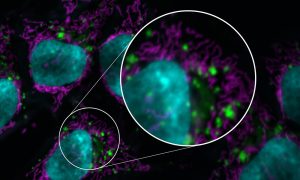
A working group of researchers from the QUAREP-LiMi initiative has developed global guidelines to improve the quality of microscopy data and images published in scientific publications.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

EMBL Grenoble and University of Geneva researchers shed light on the molecular activation of the MAP kinase p38α, the final ‘switch’ triggering the inflammatory response.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology
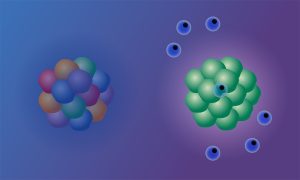
New research improves understanding of the molecular mechanisms behind why some cancers respond to immunotherapy and others don't.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
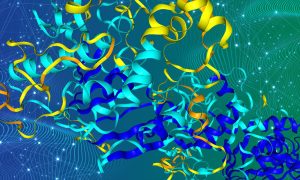
Researchers use the AlphaFold database and Foldseek Cluster algorithm to analyse millions of predicted protein structures and offer new insights into protein evolution.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
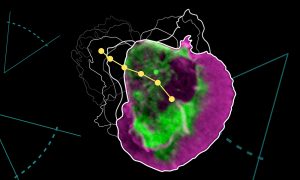
EMBL researchers have identified a novel mechanism that allows cells to sense obstacles in their path and avoid them while navigating complex environments.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

As part of the EMBL-led Traversing European Ecosystems (TREC) expedition, scientists are studying plankton to understand biodiversity, health, and our planet’s future.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
lab-mattersscience-technology
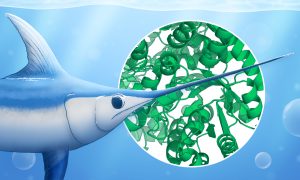
Learn how scientists use bio-SAXS, an experimental X-ray technique, to study the shape and dynamics of proteins and other biomolecules. SAXS can be even used to analyse the structure of mineral particles in the swordfish sword bone, which can help scientists better understand bone ageing.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology
For a fruit fly embryo to develop correctly, key factors need to get to the right place at the right time – a journey that starts in the developing egg, as seen in this image from the Ephrussi Group at EMBL Heidelberg
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
picture-of-the-weeksciencescience-technology

Elena Conti will discuss how cells control the life and death of mRNA molecules at the next annual Kafatos Lecture on 20 October in Munich.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
alumniscience-technology
SComatic enables researchers to link genotype to phenotype using only single-cell profiling data
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
research-highlightssciencescience-technology

EMBL’s newly deployed Advanced Mobile Laboratory (AML) is bringing cutting-edge technologies to the European coast to help researchers study ‘life in context’.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
lab-mattersscience-technology

The first EMBO Practical Course on imaging-based spatial-omics was organised at EMBL Rome to explore the latest techniques to visualise RNA transcripts and proteins in their native tissues.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
lab-mattersscience-technology
EMBL researchers have made new strides into understanding and reversing genetic defects that underlie familial heart disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology
Research from the Eustermann group at EMBL Heidelberg reveals how the packaging of DNA into hexasomes impacts the function of enzymes involved in gene regulation.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

EMBL researchers use a new cell sorting technology to gain new insights into cellular function in health and disease, as well as for other innovative applications.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology
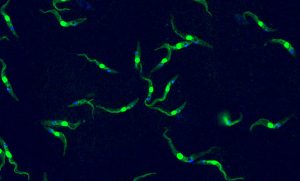
This single-celled organism the size of a dust particle is capable of causing deadly tropical diseases in both humans and livestock –Trypanosoma brucei, in an image by Luciano Dolce from EMBL.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
lab-matterspicture-of-the-weekscience-technology
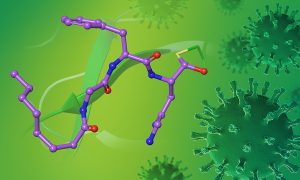
A collaboration between EMBL Grenoble and EBRIS scientists led to the characterisation of a new compound with promising activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

Enabling researchers worldwide to share and analyse pathogen data generated across the world
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation

A third of all known proteins are either completely or partially unstructured. EMBL scientists contributed to a new set of guidelines – Minimum Information About a Disorder Experiment (MIADE) – that will help researchers share data on unstructured proteins in a more useful way and will enable…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

HoloFood, the first consistent collection of multiomic data about chicken and salmon gut microbiomes, set to enable the development of better animal feeds.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation
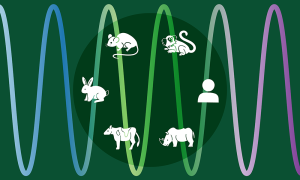
Researchers from the Ebisuya Group at EMBL Barcelona have used an unprecedented stem cell zoo to compare six different mammalian species and their developmental time.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

A recent EMBL conference brought together scientists from various disciplines to conjoin scientific pursuits studying ‘life in context’.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
eventsscience-technology

EMBL-EBI data resources are being used to deliver thousands of genetic diagnostics to patients every month.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
perspectivessciencescience-technology

A new tool for the interpretation of missense variation in humans – ProtVar – will help enable drug discovery.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation
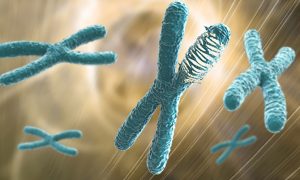
Understanding chromothripsis offers insights into how cancer develops.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
research-highlightsscience-technology

The human pangenome – one of the most complete collections of genome sequences released so far – captures rich human diversity.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
announcementssciencescience-technology

EMBL Hamburg scientists have contributed to the development of the Spitrobot, a ground-breaking experimental setup that will simplify creating molecular movies. The Spitrobot automates the sample preparation for time-resolved crystallography, which is used to create 3D snapshots of protein…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

Dey Group holds second annual ‘labbatical’ to step outside daily research tasks with the help of single-celled model organisms.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
lab-mattersscience-technology

EMBL-EBI is making a key contribution to a historic effort to understand the function of every human gene
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
announcementslab-mattersscience-technology

WormBase ParaSite release 18 adds largest number of new genomes and annotations since launch, as well as full integration with AlphaFold.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
science-technologyupdates-from-data-resources

EMBL-EBI researchers have developed a new tool capable of performing state-of-the-art phylogenetic inference on larger datasets than previously thought possible.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
research-highlightssciencescience-technology

Upcoming EMBO/EMBL symposium provides a forum to explore how organisms function together, and how they react or adapt to changes at different molecular levels.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
eventsscience-technology

Home to some of Europe’s most cutting-edge tools in molecular biology, EMBL has long shared its expertise and access to these tools through an extensive repertoire of courses, conferences, seminars, and other training. And now included in this mix is a job shadowing programme at EMBL Imaging…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
lab-mattersscience-technology
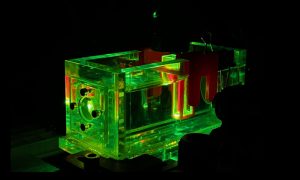
A new microscope built by EMBL researchers, based on Brillouin scattering principles, allows scientists to observe the dynamics of mechanical properties inside developing embryos in real time.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
lab-matterssciencescience-technology

Physicists, engineers and robotics experts work together in EMBL Hamburg’s Instrumentation Team to design instruments that support structural biology research. The team has finished a transfer robot that facilitates automated handling of protein crystals with care and precision. This will help…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
lab-mattersscience-technology
Researchers in the Prevedel Group use photoacoustic spectroscopy setup to test and optimise probes before their usage in mouse neuroscience.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
lab-matterspicture-of-the-weekscience-technology

EMBL is one of the partners of this project that aims to accelerate drug discovery and development, bringing in expertise from EMBL Grenoble and EMBL-EBI.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
lab-mattersscience-technology

EMBL Hamburg’s Sample Preparation and Characterisation (SPC) Facility offers scientists access to almost all available biophysics technologies. The facility’s staff provides advice and support with experiments and data analysis. The facility is conveniently located just next to the EMBL…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
lab-mattersscience-technology
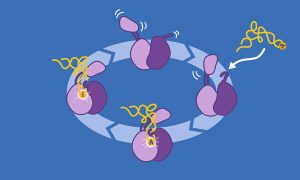
EMBL Grenoble scientists provide new insights into the function of an essential RNA editing enzyme.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

Open Targets is using artificial intelligence and machine learning to identify and prioritise drug targets.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation

Tasmanian flatworms add to an EMBL researcher’s collection as she studies principles that control animal body size.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
lab-matterspicture-of-the-weekscience-technology
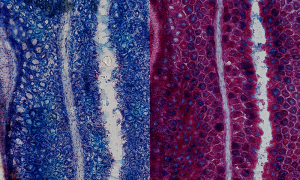
Mucus present in the mouse colon can be visualised using Alcian blue staining, as imaged here by EMBL predoctoral fellow Linda Decker.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
lab-matterspicture-of-the-weekscience-technology

We look back through some of the 2022 highlights from the Darwin Tree of Life project.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
perspectivessciencescience-technology
EMBL Grenoble researchers have investigated the interaction between THC and some proteins it might bind to. In a recent study, they showed in vitro that THC inhibits an important human enzyme called autotaxin.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology
EMBL Heidelberg researchers and their collaborators reveal how the nuclear pore complex, one of the biggest molecular machines in eukaryotic cells, is assembled one protein at a time.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology
A new method developed by EMBL-EBI researchers helps to streamline nanopore sequencing in real-time.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
research-highlightssciencescience-technology

Zebrafish embryos during gastrulation, a very early stage of development, to study the effect of temperature on vertebrate embryo development.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
lab-matterspicture-of-the-weekscience-technology

To identify which drugs disrupt bacterial envelope integrity, the Typas group uses a molecule called chlorophenyl red-β-D-galactopyranoside.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
lab-matterspicture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Recent studies supported by EMBL Grenoble’s expertise in structural biology research and scientific services have identified Altiratinib as a potential drug to stop toxoplasmosis infection and opened up treatment options against malaria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

A recent EMBO|EMBL symposium provided a forum for discussing recent research on a range of issues for organisms as they cope with changing environments.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
eventsscience-technology

Researchers and engineers have integrated a CrystalDirect harvester into the fully automated beamline MASSIF-1, a unique combination of structural biology technologies that is now open to external academic users.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
lab-mattersscience-technology

The recent construction of the new ID29 beamline in Grenoble is pioneering a new way of doing experiments in time-resolved crystallography and opening up technology transfer possibilities
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
lab-mattersscience-technology

The final pilot project in Iceland marked the countdown to the ‘Traversing European Coastlines’ (TREC) expedition to study coastal ecosystems and their response to changes in the environment.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
lab-mattersscience-technology
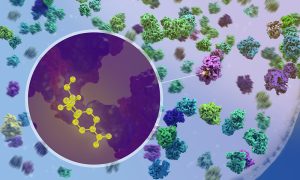
New research by EMBL scientists shows at atomic detail how antibiotics affect the process of protein production inside bacteria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

Researchers have come up with a way to test the efficacy of hundreds of anticancer drug combinations – simultaneously, rapidly, and accurately.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

EMBL joined a kick-off event focusing on the developments related to the upgrade of the PETRA III synchrotron storage ring to PETRA IV at the DESY campus, where EMBL Hamburg is located. PETRA IV could open new possibilities at EMBL Hamburg, contributing to the goals of the EMBL Programme…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
lab-mattersscience-technology
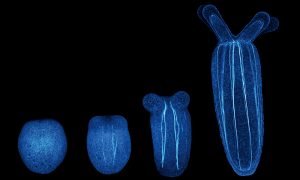
The latest research from EMBL’s Ikmi group employs interdisciplinary approaches to show how sea anemone ‘exercise’ changes their developing size and shape, uncovering an intimate relationship between behaviour and body development
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

EMBL researchers used data from over 300 human faecal microbiota transplants to gain an ecological understanding of what happens when two gut microbiomes clash.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

A new grant will provide a way for fundamental metabolomic research to realise its commercial potential and promise in aiding drug development and precision medicine.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
lab-mattersscience-technology
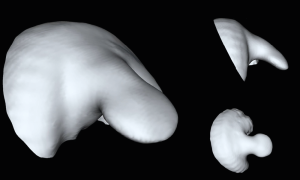
EMBL researchers use a “fearless” computer reconstruction and a two-centuries-old mathematical approach to study limb bud growth.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
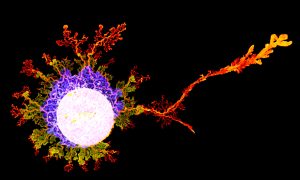
Physarum polycephalum, a single, giant cell containing tens of thousands of nuclei is large enough to be photographed with a phone.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
A new method for the robust analysis of copy number variation and used UK Biobank data to identify links between genome and disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
International consortium analyses the genetic sequences and antibiotic susceptibility of 10,000 global Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
How do gene expression patterns result in the generation of different cell types? Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg used the zebrafish notochord to find out.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
EMBL and UW researchers plus additional collaborators have constructed a complete map of fruit fly embryonic development using machine learning. This research is foundational to better understanding overall embryo development in other species, including humans.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
Machine learning has helped researchers uncover new insights into how bacteria infect host cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology

AlphaFold database offers a look at 3D protein universe.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation

EMBL researchers now understand the function of an elusive small DNA in bacteria and have developed a tool that can be used to better understand what might ‘switch on’ bacterial immune defences.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

The GEEF facility at EMBL Rome supports scientists worldwide with scientific expertise and state-of-the-art gene editing technologies.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
lab-mattersscience-technology

Microbial communities play essential roles in ocean ecology and planetary health. A recent publication highlights priorities for understanding and protecting ocean microbiomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

Scientists identify previously unexplored gene segments to be added to human genome databases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
EMBL research with Enolase 1 (ENO1) points to a possible new way to understand RNA’s leading role in how cells develop.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
Scientists have solved several mysteries around the structure and function of a true molecular giant: the human nuclear pore complex. They created the most complete model of the complex thanks to combining the program AlphaFold2 with cryo-electron tomography, integrative modelling, molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
Researchers have discovered the mechanism by which a family of DNA motor proteins packages loosely arranged strands of DNA into compact individual chromosomes during cell division.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
Researchers discover how DNA mutations change blood cell production and how this relates to ageing and cancer development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
Researchers in the Ensembl team are making the most of machine learning methods to speed up genome annotation pipelines
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation

How text mining collaborations benefit our research, data resources, and the wider scientific community.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation
Researchers at EMBL Heidelberg found that inversions in the human genome are more common than previously thought, which impacts our understanding of certain genetic diseases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
EMBL researchers revise the old problem of sintering droplets to understand the mechanical properties of tissues.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
Virginie Uhlmann shares her tips for using deep learning for bioimage analysis in the life sciences.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
perspectivessciencescience-technology
Scientists at EMBL Barcelona have created for the first time a 3D in vitro model that recapitulates the periodic formation of human somites – structures that give rise to the spinal column.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

Recent studies from the Hackett group at EMBL Rome have revealed new insights on the mechanism regulating transmission of non-genetic information during embryonic development, and inspired a scientific illustration
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

Researchers from the MANE collaboration bring you the most comprehensive human genome annotation dataset to date.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology

Researchers lay out a set of principles for open genomic data sharing or pathogens
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
perspectivesscience-technology

Condensates are membraneless organelles that control specific functions within a cell. Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg have shown how the physical state of condensates can influence biological function.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

Zamin Iqbal and his team are working with researchers all over the globe to help put a stop to Tuberculosis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
perspectivessciencescience-technology

Our researchers highlight their contributions to the Darwin Tree of Life project and how new genome annotations helps to further biodiversity research
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
announcementssciencescience-technology

The African BioGenome Project aims to safeguard biodiversity and build bioinformatics capacity across Africa
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
perspectivessciencescience-technology
EMBL’s imaging technology helps researchers gain insights in the fungus’ journey from the lung to the brain.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
A molecular signature of 27 microorganisms in stool defines the high-risk population for the most common pancreatic cancer and could be used for early detection of the disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
Deep learning models can improve protein annotations and has helped expand the Pfam database.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
perspectivessciencescience-technology

Genomes are made up of thousands of individual pieces – genes – which are expressed at different levels. Researchers at EMBL have shed light on how the placement of a gene affects its expression, as well as that of its neighbours.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
A recent study by EMBL researchers proposes a new method to grow early embryos in the laboratory. With a 3D culture set-up, scientists can closely monitor the changes embryos undergo around the time of implantation.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
Researchers from the Furlong group at EMBL have come up with a way to observe the development of fruit-fly embryos simultaneously at the genetic and cellular levels, generating a high-resolution and integrated view of how different cell lineages form.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

Scientists urge the adoption of a sensible international policy for digital sequence information.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
announcementssciencescience-technology
Experiences at EMBL Rome led former group leader to establish his start-up in Italy, developing a new generation of gene therapies.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
alumnilab-mattersscience-technologytechnology-and-innovation

DeepMind visits EMBL Heidelberg to discuss current and future implications of Artificial Intelligence for life science research.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

EMBL Hamburg’s Grzegorz Chojnowski from the Wilmanns Group developed software called findMySequence, which identifies proteins’ amino-acid sequences based on electron cryo-microscopy and X-ray crystallography data. It’s useful for identifying unknown proteins in samples from natural sources.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
An exploration of where in the world genomics methods are applied and where the data are used.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
perspectivessciencescience-technology
EMBL researchers, in collaboration with BD Biosciences, have demonstrated a new technology that allows rapid image-based sorting of cells. The new technology represents a major upgrade to flow cytometry and has applications in diverse life science fields.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

On track to reach an ambitious goal of 3,000 genomes sequenced by the end of 2022, what’s next for the Earth Biogenome Project?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
announcementssciencescience-technology

The Galej group at EMBL Grenoble has recently obtained high resolution snapshots of a crucial step in RNA splicing involving the U2 snRNP complex, a crucial component of the human spliceosome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
Researchers have identified hundreds of new bacterial species and viruses in the human skin microbiome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
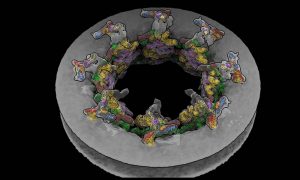
EMBL Hamburg’s Kosinski Group, the Beck Laboratory at the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics, and colleagues at EMBL Heidelberg recorded the nuclear pore complex contracting in living cells. They visualised the movement with an unprecedented level of detail with help of new software called…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
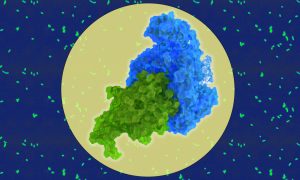
Using cryo-EM and structural biology techniques, EMBL researchers have shown how two proteins of Legionella pneumophila interact. This finding sheds light on a mechanism critical to the infection process and could lead to the development of new drugs to treat pneumonia.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

A look back at some of the 2021 highlights from the Darwin Tree of Life partner institutes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

The systematic application of AI in life sciences as in the AlphaFold algorithm for predicting protein structures has been named '2021 Breakthrough of the Year' by Science magazine.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Bork Group at EMBL Heidelberg analysed a new global gene database to study how genes emerge and spread across various habitats on our planet. In the future, the group will expand the database and use it for studying microbial gene evolution and dispersal at a finer-grained scale.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
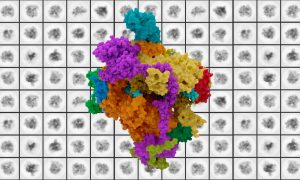
New structural biology research provides fundamental information critical to understanding enzyme mutations connected to rare diseases and cancers.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
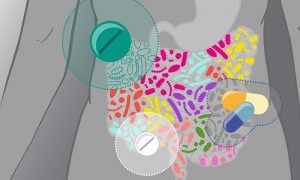
Researchers studying a massive cohort of European patients have found that commonly prescribed drugs for cardiometabolic disorders can have long-term effects on the gut microbiome. Such effects can complicate the understanding of how disease affects the microbiome and must be taken into…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
RNA vaccines, such as the ones for COVID-19, represent a new approach in vaccine technology. Cy Jeffries, faculty staff scientist at EMBL Hamburg, explains the clever technology behind RNA vaccines, and how structural biology contributes to its development. EMBL Hamburg collaborated on several…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
EMBL structural biology is part of an international collaboration addressing zoonotic disease caused by Lassa virus.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

How genomics, open data, and multidisciplinary science can improve food security.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

An alumnus reflects on the reptile database he started in 1996 while at EMBL. The database helps understand biodiversity issues.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
alumniscience-technology

A new model could serve as a platform to investigate critical placenta barrier phenomena, including defence against bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
lab-mattersscience-technology

EMBL alum Lara Urban has developed mobile DNA approaches to monitor impacts upon biodiversity in remote areas of New Zealand and elsewhere.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
alumniscience-technology

Correlative microscopy service enables PhD student from Switzerland to study structure and location of proteins cells use to communicate.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
lab-mattersscience-technology

The GA4GH Data Use Ontology (DUO) supports a data authorisation and access framework to streamline consent to use biomedical data
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Independent impact review finds EMBL experimental services are ‘critical’ for research and endorses EMBL as a world-class service provider for academia and industry.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
lab-mattersscience-technology
A vast, curated collection of bacterial genomes is now organised, searchable and open to the community.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Each year, EMBL Hamburg’s Svergun Group offers practical EMBO courses and lecture courses on biological small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). The courses provide young scientists an opportunity to gain hands-on experience by measuring their own samples, and by exploring different aspects of SAXS…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
lab-mattersscience-technology

What can sponges tell us about the evolution of the brain? Sponges have the genes involved in neuronal function in higher animals. But if sponges don’t have brains, what is the role of these? EMBL scientists imaged the sponge digestive chamber to find out.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
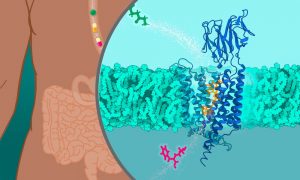
Scientists at EMBL Hamburg determined the molecular structure of Peptide Transporters 1 and 2. The findings will enable developing drugs that more efficiently pass from the gut to target tissues.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Independent study reveals that EMBL-EBI open data resources are critical for the life sciences.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
lab-mattersscience-technology

The Darwin Tree of Life project is an unprecedented initiative sequencing 70,000 species
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

International project uses biomolecular data to improve animal feed and make meat production more sustainable
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
Using metagenomic data to find novel enzymes for plastic degradation and beyond
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

EMBL Hamburg’s Sample Preparation and Characterisation (SPC) Facility has released eSPC, an online platform for analysing data from biophysical experiments. The platform enables the scientific community to analyse data from different experiments without the need to travel.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
A technology around since the ‘60s, flow cytometry has increasing applications. New leadership at EMBL’s flow cytometry facilities is looking to ease use, expand training, and encourage more collaboration.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
lab-mattersscience-technology

The BY-COVID project aims to make infectious disease data, including COVID-19, openly available to everyone.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Profiling M. tuberculosis strains from 27 countries to reveal causes of drug resistance.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
Researchers develop a new high-throughput approach to assess the functional significance of protein phosphosites.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
The Graham and Crump groups at the University of Cambridge and the Svergun Group at EMBL Hamburg have discovered a mechanism by which the herpes simplex virus takes control of the molecular machinery of human cells. Their work reveals how a dedicated viral protein hijacks key host proteins, forcing…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Largest in-depth analysis of genomic data tracks the spread of SARS-CoV-2 lineages in England.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
Researchers from EMBL’s Typas group and collaborators have analysed the effects of 144 antibiotics on the wellbeing of gut microbes. The study improves our understanding of antibiotics’ side effects and suggests a new approach to mitigating the adverse effects of antibiotics therapy on gut…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

If researchers can identify specifically when good cells go bad, they can potentially understand disease better.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

EMBL will host a conference to look at the state of the pandemic, lessons learned, and ways to improve pandemic preparedness. Here’s a sneak peek into what promises to be another interesting and informative EMBL conference.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
eventsscience-technology
Structural biology provides insights into the diverse functions of fibrous protein in humans, amphibians, and bacteria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists and colleagues have developed an interactive atlas of the entire marine worm Platynereis dumerilii in its larval stage. The PlatyBrowser resource combines high-resolution gene expression data with volume electron microscopy images.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Scientists in EMBL’s Prevedel Group have developed a pioneering microscopy technique that allows researchers to observe cells hidden within opaque tissues, such as live neurons embedded deep in the brain.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
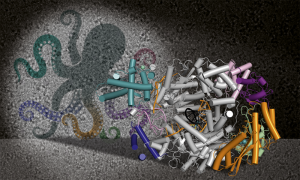
Some of the most amazing creatures live in the deep blue sea. The Mesoscopic Imaging Facility (MIF) at EMBL Barcelona was recently involved in studying one unique feature of the octopus: the ephemeral structures on the surface of their skin called Kölliker’s organs.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

MOrgAna is an open source, user-friendly, modular software that is able to analyse organoids with machine learning.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
EMBL scientists have found evidence of an unexpected role for retinal cells in pre-processing visual information; their results provide potential opportunity for future prosthetic visual aids.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
research-highlightssciencescience-technology

A research collaboration used machine learning to map tumour molecular make-up, potentially paving way to more customised cancer treatment.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
Packaged for simple installation and free use, the novel method DECODE enables researchers to reduce imaging times and increase localisation density in single-molecule localisation microscopy (SMLM).
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
A new collaborative study led by EMBL group leaders Kiran Patil, Nassos Typas, and Peer Bork has found that common medications accumulate in human gut bacteria. This process reduces drug effectiveness and affects the metabolism of common gut microbes, thereby altering the gut microbiome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

In the Mesoscopic Imaging Facility (MIF) at EMBL Barcelona, researchers study the details of biological systems in the context of organs, body parts, or entire organisms. This image shows OPTiSPIM1, one of the custom light-sheet microscope setups available at the facility.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
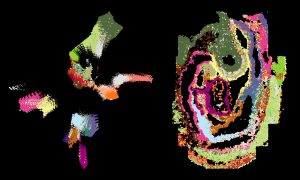
Researchers have combined spatial gene expression information with single-cell genomics data to create a high-resolution atlas of mouse organogenesis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Giulia Zanetti from the Institute of Structural and Molecular Biology (ISMB) in London explains how the collaboration with the Cryo-Electron Microscopy Service Platform enabled her group to reveal the structure of protein transport complexes.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
lab-mattersscience-technology

MASSIF-1, run jointly by EMBL Grenoble and the ESRF, is a beamline for macromolecular crystallography. It is used by the research community to study the 3D structure of proteins, which is important for drug development.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
lab-mattersscience-technology

A community of scientists is looking at the estimated three billion heart muscle cells in a human heart to better understand heart disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
alumniscience-technology
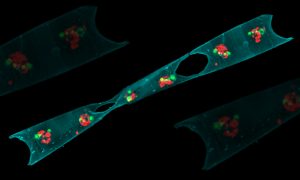
Analysis of more than 2 million images has boosted understanding of ocean microbes, shedding light on the distribution of nitrogen-fixers at a global level
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
A collaboration led by EMBL Hamburg’s Svergun Group used small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) at the European XFEL to obtain data on samples containing coronavirus spike proteins and antibodies that bind them.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
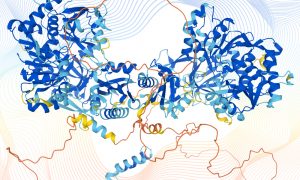
Partners use AlphaFold, the AI system recognised last year as a solution to the protein structure prediction problem, to release more than 350,000 protein structure predictions including the entire human proteome to the scientific community.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
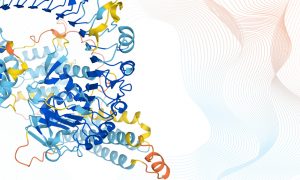
DeepMind and EMBL-EBI to make millions of protein structure predictions freely available to the scientific community.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
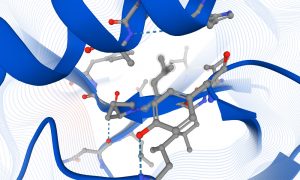
A discussion of the applications that AlphaFold DB may enable and the possible impact of the resource on science and society.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
Researchers establish a framework for identifying new drugs capable of exploiting a cell’s own machinery.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
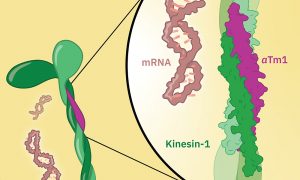
EMBL scientists generate a high-resolution crystal structure of the Kinesin-1/aTm1 transport complex in the fruit fly.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

EMBL’s Melissa Graewert and colleagues are taking a structural biologist’s approach to better understanding nanoplastic particles.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
Research in the Typas group uncovers new details of the strategies Salmonella uses to survive in infected cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
As evocative as a constellation of planets, these egg cells within a mouse ovary are at different stages of maturity.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weeksciencescience-technology
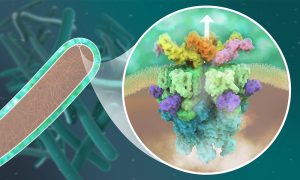
EMBL Hamburg’s Wilmanns and Kosinski groups have determined the detailed structure of a bacterial protein complex critical for tuberculosis infection.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
EMBL PhD student Anniek Stokkermans captured this side view of a Nematostella vectensis larva during this transition, using instrumentation in the Advanced Light Microscopy Facility at EMBL Heidelberg.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Researchers investigate how external factors can influence the persistence of microbe species in the human gut
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

As perfect as a summer night sky, these nuclear pores help calibrate a customised super-resolution microscope in EMBL’s Ries group.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

New software enables scientists to visualise RNA secondary structures using the world’s largest RNA structure dataset.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
At EMBL, we have many dream teams – groups of individuals who support each other, innovate, and work together. One of those dream teams bridges two core facilities at EMBL Rome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Under the innovative Planetary Biology research theme, EMBL scientists aim to understand life in the context of its environment.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
Captured by EMBL postdoc Arina Rybina, these ‘nuclear twins’ are two daughter nuclei straight after division of a HeLa cell.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

The largest in-depth analysis of genomic surveillance data mapping out the dynamics of 62 lineages of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
The Bernabeu Group aims to increase our knowledge of cerebral malaria, using in vitro engineered networks of human blood vessels and brain cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

EMBL scientists support research on malaria by providing freely available data resources and using innovative experimental approaches. Our Course and Conference Office facilitates the exchange of knowledge in the field by hosting the annual BioMalPar conference.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
The EMBL Picture of the Week features a series of Jurkat T cells during different stages of the activation process.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Researchers at EMBL Hamburg reveal how peg-like proteins clasp and reshape the cell membrane
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

A workshop run by EMBL Hamburg explored opportunities for structural biology at the future, upgraded PETRA IV synchrotron.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
eventsscience-technology

EMBL scientists have combined artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms with two cutting-edge microscopy techniques.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

EMBL Hamburg’s integrated structural biology facility has contributed to the success of a large-scale SARS-CoV-2 study
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Researchers reveal the best technology for assembling reference genomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
EMBL scientists, together with collaborators from Heidelberg University, have provided further evidence of the gut’s role in COVID-19.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
A page from a biologist’s colouring book? EMBL’s new interior wall design? Not quite – a bunch of liver cells, grown in the lab so that scientists can learn about fatty liver disease, or steatosis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Researchers identify differences in immune response in asymptomatic COVID-19 cases compared to those with severe symptoms
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
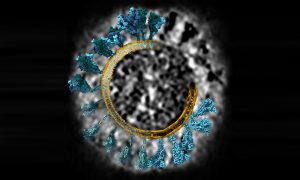
What does coronavirus’s spike protein look like in 3D? EMBL scientists and colleagues used cryo-electron tomography and molecular dynamics simulations to find out.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Researchers have used a metagenomics approach to piece together the genomes of yeasts found in wild lichens.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Florent Cipriani, who recently retired as Head of the Instrumentation Team after a long career at EMBL Grenoble, is one of the pioneers of instrumentation development in this field.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
lab-mattersscience-technology

Researchers use large-scale human genetic studies to identify drug targets important for managing COVID-19 in its early stages
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
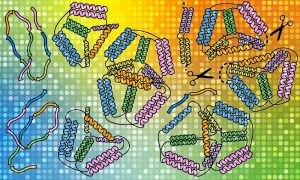
Using EMBL Hamburg’s world-class structural biology infrastructure, researchers advance the folding of protein ‘origami’ designed in the lab.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Researchers have used human medical and genetic data from UK Biobank to investigate the genetics of age-related diseases
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
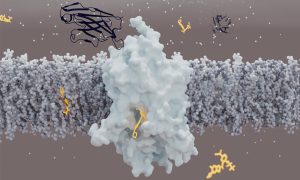
Scientists have determined the structure of Glycine Transporter 1. The finding could open new avenues for developing therapeutics for psychiatric disorders
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
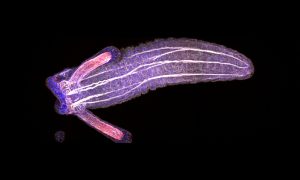
This image of a young Nematostella vectensis polyp shows two of the characteristic tentacles as well as the gaping mouth of the animal.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Scientists at EMBL Hamburg use droplets of protein solution to grow protein crystals. By exposing the crystals to X-rays, they are able to determine the protein’s molecular structure.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

EMBL alumnus Kai Simons did early work with Semliki Forest virus membranes, which is now central to a COVID-19 vaccine.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
alumniscience-technology
Scientists in the Stegle group and colleagues have studied induced pluripotent stem cells from around 1,000 donors to identify correlations between individual genetic variants and altered gene expression. They linked more than 4,000 of the genetic variants responsible for altered expression…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
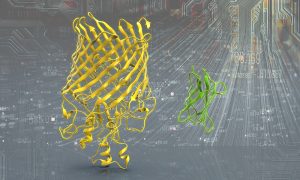
Thousands of new protein structure models, prected using deep learning, now available to explore
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
A new method has the potential to boost international research efforts to find drugs that eradicate cancer at its source.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
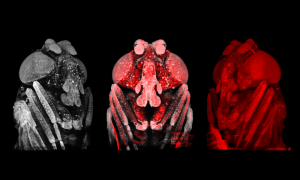
Like caterpillars turning into beautiful butterflies, fruit fly larvae have to go through metamorphosis to finish their development. However, despite the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster being one of the best studied model organisms in biology, comparatively little attention has been given to this…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
A collaboration including EMBL scientists has created the most diverse set of reference human genomes ever assembled.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
Liang Xue used cryo-electron tomography to capture this detailed image of a Mycoplasma pneumoniae cell.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Scientists identify more than 140 000 virus species in the human gut; more than half have never been seen before
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Researchers from EMBL and Heidelberg University Hospital combine high-resolution imaging to observe the infection process in cell nuclei, opening the door for new therapeutics.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
A team of EMBL scientists and colleagues have analysed how the novel coronavirus affects proteins in human cells. They identified several human proteins as potential drug targets to prevent viral replication.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
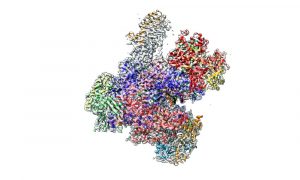
This week's Picture of the Week, which could also be a masterpiece of modern art, shows the enzyme RNA polymerase III, an assembly of 17 individual proteins combined into this complex structure.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Researchers at EMBL Heidelberg have identified sequences in human proteins that might be used by SARS-CoV-2 to infect cells. They have discovered that the virus might hijack certain cellular processes, and they discuss potentially relevant drugs for treating COVID-19.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

The regular structures of crystals are a source of inspiration and fascination to us humans. While the crystals in this picture were not grown in nature, but instead by Petra Drncova from EMBL Grenoble, they share the same attributes as those found in nature.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
New EMBL research shows where & to what degree a component of cellular machinery known as RNA Pol III is mutated and becomes problematic.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
A new paper from the Galej group at EMBL Grenoble describes the structure of key parts of the Integrator complex, involved in gene expression.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

A new lineage of coronavirus was first identified in the UK, but why is it spreading much more rapidly within the population?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
This colourful image shows biological information flow in action: It’s a supramolecular assembly of DNA, RNA and proteins, observed directly inside a bacterial cell while turning genetic information into protein.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Engineers at EMBL Hamburg installed specially designed mirrors to reflect and focus X-ray beams onto tiny crystals made of proteins or other biological molecules.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

A note on the coronavirus variant B.1.1.7, which has first been described in the U.K. and has spread to 57 countries. The note summarises epidemiological information about the spread of B.1.1.7 in the U.K. collated and in part conducted by researchers from EMBL-EBI.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Freshwater sports can cause waterborne infections, but real-time DNA sequencing could help.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
It’s almost a year since the coronavirus outbreak was declared a pandemic, affecting all our lives. While the virus continues its grip on the world, scientists are understanding it better and better, increasing our knowledge about it and opening up new ways to fight it.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
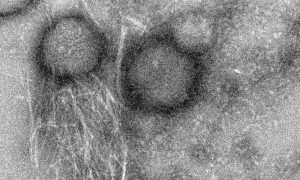
Researchers at the Technion – Israel Institute of Technology and EMBL Hamburg, in collaboration with scientists in Israel and Spain, have discovered remarkable molecular properties of an antimicrobial peptide from the skin of the Australian toadlet. The discovery could inspire the development of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Structural biologists want to study proteins at the atomic level. The device shown in this Picture of the Week is essential for this.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
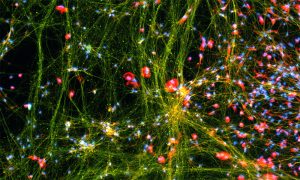
Fluorescent dyes light up a cellular community of neurons and brain immune cells (microglia), which were derived from stem cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
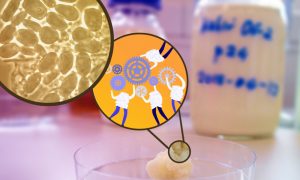
Researchers discovered the dominant species of bacteria in kefir grains cannot endure without other species that help the 'team' survive.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Despite restrictions, 2020 has been a busy year for the Darwin Tree of Life Project. We take a look at some of this year’s achievements and highlights.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
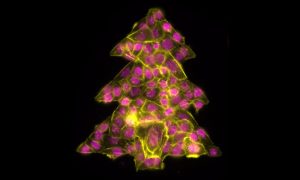
It is that time of year to get into the holiday spirit, prepare for some time at home and relax after a strange and stressful year. Even the cells in our Picture of the Week are getting into the holiday spirit, forming this colourful Christmas tree.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

The story of a life-long friendship and a professional partnership that sowed the seeds for a ground-breaking vaccine technology.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
alumniscience-technology
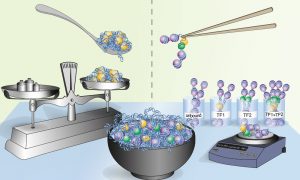
Gene activation requires the cooperative activity of multiple transcription factors. Until now, the mechanism used by these factors to coordinate their actions has been poorly understood. EMBL’s Krebs group presents a DNA footprinting method that makes it possible to determine whether…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
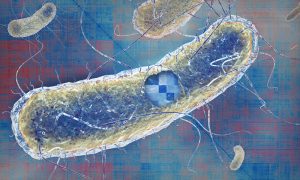
A new paper from EMBL’s Savitski team and Typas group describes their work on E. coli and how it brings a greater understanding of the way genes function and interact.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

While cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) was first envisioned in 1968, the advances the Mahamid group are bringing to this 3D method for studying molecules directly inside cells are new, and are likely to greatly expand its use.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

How artificial intelligence can help us solve the mysteries of the protein universe
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
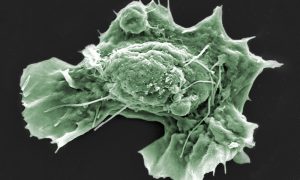
Scientists in the Diz-Muñoz group at EMBL Heidelberg are working to build understanding of the role that mechanical properties play in affecting cell behaviour – a young and rapidly developing field of study. They have developed and successfully used a highly specialised technique to manipulate…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
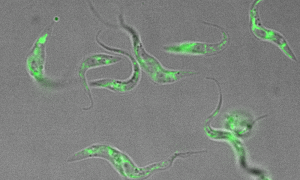
Members of the EMBL community are working to improve our understanding of the parasites that cause malaria and sleeping sickness
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Biotechnology company BioNTech and Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz conduct collaborative research with EMBL scientists at the beamline P12 in Hamburg
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Bioinformaticians at EMBL-EBI and beyond are adapting computational tools to investigate coronavirus genomes and proteins.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
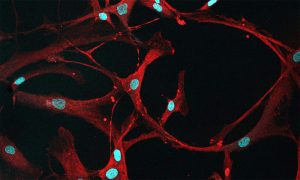
Studying cancers means also knowing what healthy cells look like. In this case, mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) from healthy bone marrow are a bit ‘loopy’.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
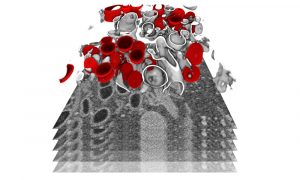
Researchers have studied SARS-CoV-2 replication in cells and obtained detailed insights into the alterations induced in infected cells. This information is essential to guide the development of urgently needed therapeutic strategies for suppressing viral replication and induced pathology.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
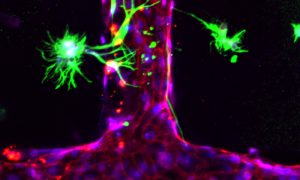
To help understand cerebral malaria the Bernabeu group has created in vitro engineered networks of human blood vessels.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
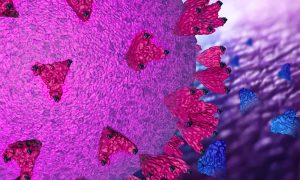
By screening hundreds of sybodies (synthetic mini-antibodies), scientists have identified one that might stop SARS-CoV-2 from infecting human cells. This work, which holds promise for treating COVID-19, was conducted by EMBL Hamburg and collaborators from the Centre for Structural Systems Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

On autumn days without Heidelberg’s characteristic fog, the woods present themself in beautiful colours. You may even capture a rainbow.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Researchers in the Gross group at EMBL Rome have investigated the mechanism behind defensive behaviour in mice. They have identified a specific area of the brain that encodes both spatial and threat cues to drive location-specific defensive responses.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
The nucleus of this cell fluoresces in bright green thanks to GFP-labelled nucleoporin proteins. EMBL scientists use engineered nucleoporins as 3D reference standards to improve super-resolution microscopy.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Why should researchers make artificial intelligence more transparent and how can they do it?
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
lab-mattersscience-technology

Open access data benefits millions of scientists around the world and is essential for a rapid response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Scientists from the Beltrao Group at EMBL-EBI and collaborators identified drug targets common to SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV-1, and MERS-CoV, three pathogenic coronaviruses. They also found potential drugs that could be repurposed as COVID-19 treatments, and against emerging coronavirus strains in the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Researchers from EMBL Heidelberg have established an automated pipeline to create mutations in genomic enhancers, letting them watch evolution unfold before their eyes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
A group of scientists led by EMBL Hamburg’s Christian Löw provide insights into the molecular structure of proteins involved in the gliding movements through which the parasites causing malaria and toxoplasmosis invade human cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
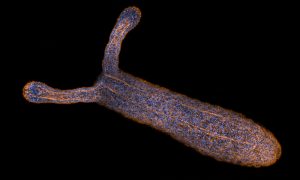
Sea anemones are amazing creatures. Despite their plant-like appearance and their tendency to remain fixed in one spot, they are actually animals.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Research facilities play a crucial role in the advancement of science by supporting scientists with specialised expertise and state-of-the-art equipment. The Microscopy Facility at EMBL Rome exemplifies this role by making a wide variety of light microscopy technologies available to its researchers…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
lab-mattersscience-technology
The genome editing tool CRISPR–Cas9 – which plays a critical role in EMBL’s research – was recognised by the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
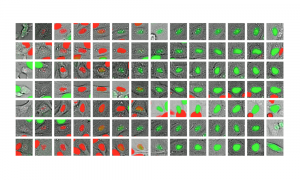
Members of an EMBL-led research group with collaborators in Estonia and Russia have built and trained a deep learning model to better understand how cells grow and divide.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
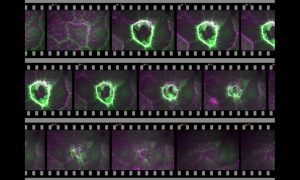
We’ve all had wounds at certain times in our lives. But they heal due to the self-repairing mechanisms in the body.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

To study the effect of commonly used drugs on bacterial envelopes, EMBL scientists applied a biochemical assay using a colour reaction. The deeper the red, the stronger the disruptive effect of the drug.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

EMBL’s 21st Science and Society Conference will address scientific and societal responses to mass extinctions. Ahead of his keynote speech, renowned palaeontologist Mike Benton explains how looking into the deep past can give us vital insights into the future of life on Earth.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
eventsscience-technology

How does your crystal garden grow? EMBL's Electron Microscopy Core Facility was able to capture this garden of blooming crystals as they studied mosquito reproductive cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
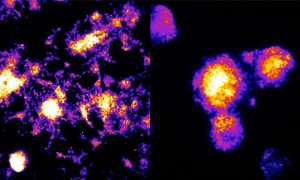
The internal clock that governs the development of embryos ticks slower for humans than for mice. Differences in the speed of biochemical reactions underlie the differences between species in the tempo of development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
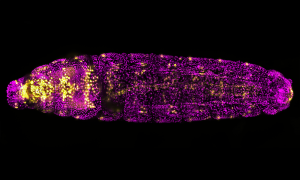
Not just another pretty fruit fly. This magenta and golden drosophila larva is lit up with a fluorescent molecule to help researchers study heart formation.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
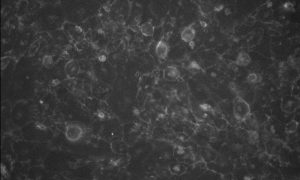
Researchers have found the cause of dilated cardiomyopathy – a leading cause of heart failure – and identified a potential treatment for it: a drug already used to treat acne.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
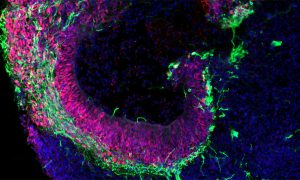
A decadal roadmap points the way to cell-based medicine for Europe
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
lab-mattersscience-technology
While this may seem like a nebula made up of interstellar clouds of dust and ionised gases, this image isn’t of a galaxy beyond the Milky Way.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
The Gerstung Group at EMBL-EBI and collaborators have developed a statistical model that analyses genomic data to predict whether a patient has a high or low risk of developing oesophageal cancer.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
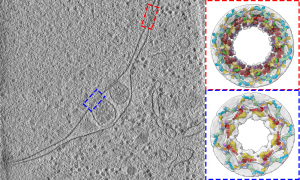
Scientists from the Beck group have studied the 3D structure of nuclear pores in budding yeast. They show how the architecture of the nuclear pore complex differs inside cells compared to its form observed in vitro studies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
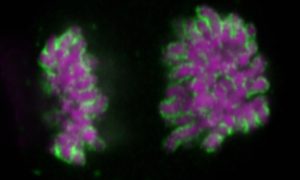
Researchers have uncovered how cells remove unwanted components from the nucleus following mitosis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
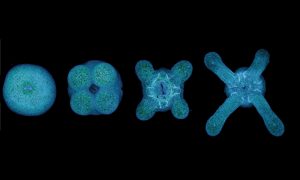
An international group of researchers, led by scientists from EMBL Heidelberg, have discovered that the number of tentacle arms a sea anemone grows depends on the amount of food it eats.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
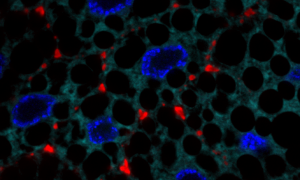
Those heart-shaped cells aren't just for show. They help tell the story of two proteins working together
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
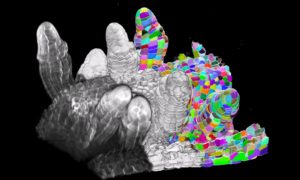
Starting with computer code and moving on to a more user-friendly graphical interface called PlantSeg, the Kreshuk Group at EMBL and collaborators built a simple open-access method to provide the most accurate and versatile analysis of plant tissue development to date.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

More than 500 people have registered for an EMBL conference, "The impact of the COVID-19 crisis on women in science: Challenges and solutions." Scheduled for 9 September, the conference is free and open to all. Pre-registration is still available and required to attend.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
eventsscience-technology
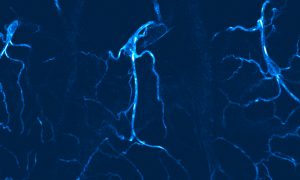
Beautiful flashes of blue colour help light the way for researchers to study cells in fruit fly larva that provide oxygen to tissues.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
An international team of scientists involving Ewan Birney's group has investigated the function of a complex mesh of muscle fibres that line the inner surface of the heart.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Discoveries at EMBL will help researchers to interpret one of the most common types of experiments in genomics and medical studies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
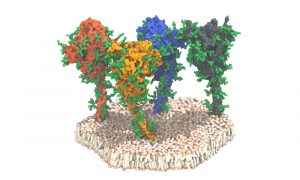
Researchers studied the spike protein on the surface of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. With its spikes, the virus binds to human cells and infects them. The study gave surprising insights into the spike protein, including an unexpected freedom of movement and a protective coat to hide it from antibodies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Despite their ghostly appearance, these are very real cell nuclei infected with Influenza A virus – the only influenza virus known to cause pandemics.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
This image is a composite of lateral pentascolopidial organs, a wing imaginal disc pouch, and an epithelial wound in a Drosophila larva. The organs are arranged here like eyelashes. Cells surrounding an epidermal wound appear as the iris and pupil of this artistic eye.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Researchers from all life science disciplines – from fundamental biological research to medical applications – generate immense datasets. Analysing these datasets and gaining new knowledge from them is a growing challenge for scientists. The fields of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
lab-mattersscience-technology

A global team of researchers including the Flicek Team at EMBL-EBI has partnered up with the Māori tribe Ngātiwai to sequence the genome of the tuatara, a rare reptile endemic to New Zealand.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
This group of cells represents an interesting example of organ formation where cells simultaneously move and change their shapes in a highly coordinated manner.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

The human genome harbours about 19 000 protein-coding genes, many of which still have no known function. As scientists unveil the secrets of our DNA, they come across novel genes that they need to refer to using a unique name. The Human Genome Organisation’s Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) at…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
A new approach that allows researchers to see molecular machinery at work inside cells has offered a deeper understanding of how bacteria produce proteins and a unique glimpse into how they respond to antibiotics.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Europe PMC has begun indexing full-text COVID-19 preprints along with the associated data. The project aims to accelerate research to fight the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
EMBL scientists and collaborators help reveal the process by which enormous quantities of DNA are folded into cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
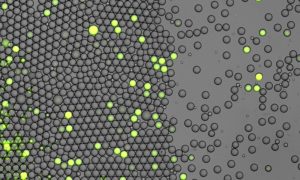
Bacterial cells are embedded in microfluidic droplets in oil. The fluorescence indicates the presence of the targeted DNA strain with the help of a characteristic DNA sequence.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Researchers have developed an artificial intelligence algorithm that uses computer vision to analyse tissue samples from cancer patients. The algorithm can distinguish between healthy and cancerous tissues, and can also identify patterns DNA and RNA changes in tumours.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

The image shows one of the four rows of roof lights above the atrium, which is the main public space of the Imaging Centre.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
EMBL scientists have created a new, realistic 3D testbed that could help achieve the goal of stopping cancers before they start by studying cancer cells as they first form.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
An international team of scientists has collated all known bacterial genomes from the human gut microbiome into a single large database. Their work will allow researchers to explore the links between bacterial genes and proteins, and their effects on human health.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
The image shows a larva of Platynereis dumerilii, a marine worm. The image here was produced by Constantin Pape, a visiting predoctoral fellow in the Kreshuk group at EMBL Heidelberg.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
The virtual EMBL Conference ‘SARS-CoV-2: Towards a New Era in Infection Research’ explored the importance of fundamental research, collaboration, and data science in containing the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, and discussed opportunities to improve our response to pandemics in the future.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
eventsscience-technology
Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg have investigated stem cells and how they differentiate to become neurons. Their approach included an assessment of the complex interplay of molecules during the differentiation process and generated fundamental new insights into the role of a protein called Sox2 in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
A study conducted by the Hackett group at EMBL Rome has identified key factors controlling the complex system of gene regulation during early embryo development, shedding new light on the mechanisms behind these events and on their evolutionary implications. Their findings are published in Nature…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

To study how SARS-CoV-2 infects cells, the Gene Editing and Embryology Facility (GEEF) at EMBL Rome will generate mice that express a human version of a protein called ACE2. The mouse line will be shared with preclinical research collaborators carrying out vaccine and antibody trials, and with the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
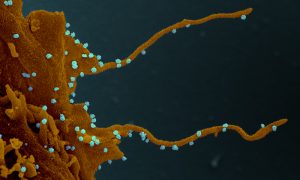
Researchers evaluate how the new coronavirus rewires human proteins for its own replication, and identify several antiviral drugs ready for clinical trials
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Today we celebrate the 20th anniversary of the first draft of the entire human genome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists develop a new molecular tool to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice. This tool is able to cause targeted epigenetic modifications of specific genes in specific cell populations. They will use it in mice to target airway cells that express the ACE2 protein – the receptor that…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

DNA damage caused by chemical mutagens is not repaired immediately and can create more genetic diversity in tumours.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Jan Korbel and Oliver Stegle have performed a survey of fellow life scientists to learn how the current crisis, with partial or complete institutional shutdowns, is affecting their work.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
lab-mattersscience-technology

While global research on coronaviruses has shed light on the function of many SARS-CoV-2 proteins, the role of some crucial components remains unknown. Researchers at EMBL Grenoble will use a range of structural biology methods to try to solve some of the puzzles of the molecular mechanics of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Scientists at EMBL and Heidelberg University Hospital are studying how the novel coronavirus behaves in the gut to try to better understand its epidemiology and prevent its spread. To do this, they are combining advanced imaging and sequencing technologies to study coronavirus in human intestinal…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

In this composite image, visual artist Mona Kakanj assembled three different biological structures in fly larvae into a flower. The original images were taken as part of a research project by Parisa Kakanj in Maria Leptin’s group.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Scientists discovered that antihypertensive agent alters the tissue characteristics of colon cancer metastases. This "stiffness" of metastases has an effect on the therapeutic success.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Scientists at EMBL Rome unveil the mechanism behind the most studied epigenetic modification.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
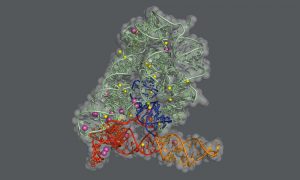
Researchers in the Marcia group at EMBL Grenoble and the De Vivo lab at the Italian Institute of Technology in Genoa have obtained some of the most detailed ever snapshots of the splicing process in systems known as group II self-splicing introns. The new insights will help scientists to develop…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

EMBL researchers are studying COVID-19-related molecules by exposing them to high-brilliance X-ray beams. The Svergun group at EMBL Hamburg is using biological small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) as part of a global effort by scientists to elucidate the structural organisation of SARS-CoV-2…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
This image shows mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), their cell skeletons (green) and nuclei (blue) under a confocal microscope, photographed by Julia Hansen in the lab of Matthieu Boulard at EMBL Rome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Scientists including members of EMBL’s Typas group have investigated how immune cells called macrophages respond to infection by the intracellular pathogen Salmonella enterica. They discovered that Salmonella causes newly produced cathepsins to accumulate in the nuclei of infected cells to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
This image is a 3D-rendering of the automatic segmentation of a HeLa cell, made by Julian Hennies from the Schwab team at EMBL Heidelberg.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg have developed a new method, called Targeted Perturb-seq (TAP-seq), which increases the scale and precision of functional genomics CRISPR–Cas9 screens by orders of magnitude. Their method overcomes limitations in previous applications of single-cell RNA sequencing,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Researchers from EMBL Grenoble have developed a way to visualise large RNAs in 3D using biochemical and structural biology techniques.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists have performed a large-scale analysis of over 4700 SARS-CoV-2 genome sequences. They found that many of the most interesting changes in the SARS-CoV-2 genome that have been reported so far are likely to be technical artefacts, rather than biological mutations.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
In the Leptin Group, Eva Hasel investigates the innate immune system in Japanese rice fish.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Scientists hope that a legacy of the novel coronavirus in recovered COVID-19 patients – antibodies in their blood – could lead to drugs to treat others. The Merten group at EMBL Heidelberg has pivoted its microfluidics platform to support the search for neutralising antibodies that could…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Researchers in EMBL’s Zaugg group have studied the causes of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), a rare disease that causes high blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs. The study, carried out in collaboration with Stanford University School of Medicine, compared lung cells of patients…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
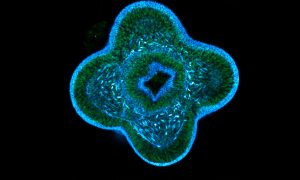
The image shown here, taken by Anniek Stokkermans from EMBL’s Ikmi Group, shows a larva of Nematostella vectensis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Researchers from the Sharpe group at EMBL Barcelona have published a method to track the developmental history of a cell using the gene editing tool CRISPR–Cas9, but without the need to create transgenic organisms.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists will contribute to the new German COVID-19 OMICS Initiative to study the biological mechanisms contributing to coronavirus infections. EMBL group leaders Jan Korbel and Oliver Stegle, who is also affiliated with the DKFZ Heidelberg, will coordinate the set-up of IT infrastructures…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
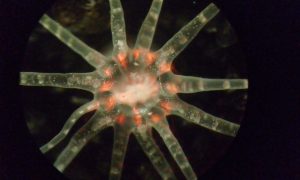
This image of the starlet sea anemone was taken by Petrus Steenbergen using a stereoscope.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

The Sample Preparation and Characterisation Facility (SPC) at EMBL Hamburg reopens to support scientists working on Covid-19 research. The SPC Facility is one of the best equipped facilities in Europe is therefore in high demand from external users. Re-opening the facility also allows experts at…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

DNA mutations are caused by a combination of DNA damage and repair, shows study by EMBL-EBI and collaborators.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
The image shown here, taken by Daniel Rios-Barrera from the Leptin Group shows the cells of the early wing tissue of the fly during larval development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

By re-opening the High-Throughput Crystallisation (HTX) lab at EMBL Grenoble, EMBL is supporting structural biology projects to respond to the health threats posed by coronaviruses.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

The Marquez Team has restarted operations at the High-Throughput Crystallisation (HTX) lab at EMBL Grenoble. The team has developed a fully automated protein-to-structure pipeline, which can be operated remotely and provides virtual access to the facilities.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

EMBL electron microscopy specialists collaborate with researchers from Heidelberg University Hospital to understand the changes occurring in cell structures upon SARS-CoV-2 infection.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
The infectious disease commonly known as flu is caused by the influenza virus. It spreads around the world in seasonal outbreaks, causing millions of infections and hundreds of thousands of deaths each year. Stephen Cusack, Head of EMBL Grenoble, has been studying different aspects of the influenza…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
In human cells, the genetic material is packaged into 23 different DNA molecules, the chromosomes. Each chromosome is present in two copies, one inherited from the paternal sperm, and the other from the maternal egg. During most of the cell’s life, chromosomes take the shape of long,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Scientists at EMBL Hamburg and Karolinska Institutet Stockholm aim to find synthetic antibodies – known as nanobodies – that bind a surface protein of the novel SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. Nanobodies could prevent the virus from entering human cells and causing COVID-19.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists working in the groups of Matthias Hentze and Wolfgang Huber have created RBPbase – a database of RNA-binding proteins – to assist the identification of proteins that interact with the SARS-CoV-2 RNA genome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

In March 2020, planes were grounded, streets went quiet, and our lives changed forever. But while the world came to a halt, many scientists were ramping up their efforts to understand the new virus.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
This Picture of the Week shows a stained cryosection of a retina – the light-sensitive part of the eye – of an ancient fish, the lamprey.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Researchers from EMBL Heidelberg have created a complete description of early embryo development, accounting for every single cell in the embryo.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

The new collaborative space will help scientists, public health and healthcare professionals around the world to fight the coronavirus pandemic.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg are contributing their expertise in a community effort to develop large-scale testing methods for coronavirus. Their goal is to increase the capacity and speed of testing, which is crucial for containing the pandemic.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

EMBL researchers are studying how drugs that have shown good results against COVID-19 work in living cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

The Protein Expression and Purification Core Facility at EMBL Heidelberg will produce proteins for several coronavirus-related research projects, to assist the development of new strategies to fight the virus.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
What may look like a branch of a tree with the first flower buds emerging after winter are, in fact, tracheal cells of a fruit fly larva and their nuclei.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
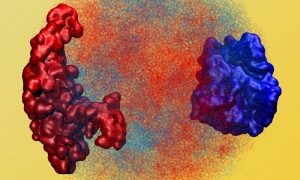
EMBL researchers in the Heard group at EMBL Heidelberg explore the interaction between DNA organisation and gene expression in the early embryo
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

EMBL is all about exciting science, through which we aim to achieve a fundamental understanding of biological processes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
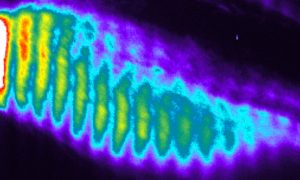
EMBL scientists examine the molecular causes of a rare hereditary disease of the spine and ribs
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

The causes of 40 percent of all cases of certain medulloblastoma – dangerous brain tumours affecting children – are hereditary. These are the findings of a recent genetic analysis carried out by scientists from EMBL and numerous colleagues around the world.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Paola Bertucci, from the Arendt Group at EMBL Heidelberg, studies the evolution of Platynereis dumerilii – a species of annelid polychaete worm.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

EMBL-EBI set to launch European COVID-19 Data Platform to help store, share, and analyse research data linked to the COVID-19 pandemic.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
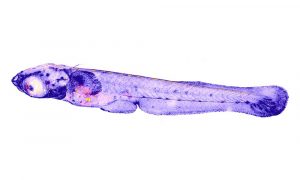
The medaka shown in this Picture of the Week was captured by Eva Hasel, a postdoc in the Leptin group at EMBL Heidelberg.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
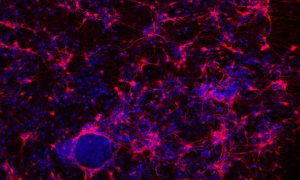
EMBL researchers investigate the role of a histone protein in regulating gene expression
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
EMBL researchers combine multiple datasets to develop expandable atlas of an entire animal
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
In the Trivedi Group at EMBL Barcelona, Krisztina Arató and Jia Le Lim study the early development of zebrafish embryos.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
In this image, Julian Hennies from the Schwab Team has reconstructed the 3D structure of a human cell's organelles.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
This image shows the tracheal system of a live fruit fly larva. Daniel Rios from the Leptin Group and Dimitri Kromm from the Hufnagel Group used this advanced microscope to investigate the dynamics of tracheal cells during development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
This technique provides a simple but effective way to study the functions of organs in living animals
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Scientists provide important new insights into the molecular basis of X-inactivation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

EMBL co-leads most comprehensive study of genetic causes of cancer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Cloud computing offers unprecedented opportunities for global-scale research collaborations. It also presents a unique set of challenges in terms of data protection and the ethics of data sharing.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
The largest and most comprehensive catalogue of cancer-specific RNA alterations reveals new insights into the cancer genome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Researchers at EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) and the Francis Crick Institute have analysed the whole genomes of over 2600 tumours from 38 different cancer types to determine the chronology of genomic changes during cancer development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Scientists from EMBL present a tool for large-scale analysis of genomic data with cloud computing. Main advantages of the new tool, called Butler, are continuous system monitoring and its ability to self-heal in case of failure, allowing for 43% more efficient data processing than previous…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Using the dataset from the Pan-Cancer project, scientists has developed methods to group, classify, and describe large rearrangements of the genome that are a key driver of cancer.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Analysis of whole cancer genomes gives key insights into the role of the non-coding genome in cancer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Researchers at Harvard Medical School and EMBL-EBI have carried out the largest analysis across cancer types of the newly discovered mutational phenomenon chromothripsis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Using the data from the Pan-Cancer project EMBL scientists describe how our genetic background influences cancer development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
New resource that categorises genes essential for supporting life could be used to identify rare disease mutations
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Morgan Oatley and her colleagues in Christophe Lancrin’s group investigated how haematopoietic stem cells emerge from the endothelium in developing mouse embryos.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Muzamil Majid Khan, a postdoc in the Pepperkok team at EMBL Heidelberg, studied the piece of tissue visible in this image.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
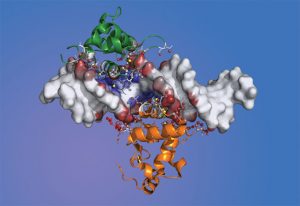
EMBL researchers have developed a method to observe interactions between transcription factors
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

The new EMBL spinoff company Araxa Biosciences GmbH aims to set new standards for the development of antibody-based therapeutics and diagnostics
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
lab-mattersscience-technology

Dame Janet Thornton presents the 2019 EMBL Insight Lecture: Ageing and disease – what is the link?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
eventsscience-technology
The image shown here is a 3D-rendering created by Julian Hennies from the Schwab team.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
EMBL scientists identify drug targets in blood and organs
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

This image has been composed from thousands of individual super-resolution microscopy images. It was created by Markus Mund in the Ries Group.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
What might also be an artistic representation of a scattered bowl of Skittles is actually a 3D reconstruction of a high-pressure frozen HeLa cell.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women. It is so deadly because tumours often return after successful cancer treatment. This recurrence is caused by individual dormant cancer cells remaining inside the breast. These cells can develop into active cancer cells…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
What looks like a photo-series of an explosive eruption are actually uptaking proteins, captured by Markus Mund from the Ries Group at EMBL Heidelberg. The images were made in an attempt to learn how the different proteins that take up molecules into the cells via endocytosis – the cellular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Researchers have developed a cheaper and faster method to check for genetic differences in individual cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
Researchers have developed new methods to reveal the 3D-organisation of bone marrow at a single cell level
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
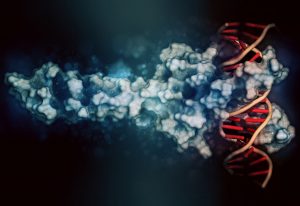
The software diffTF quantifies activity of transcription factors and predicts their mode of action
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
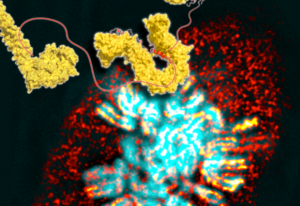
DNA is present in each cell of our body. If all the DNA from one human cell was removed and aligned in a single strand, it would in theory add up to a total length of about two metres. In order to fit into the nucleus of a cell, DNA has to be compressed by […]
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Resource has implications for disease research
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
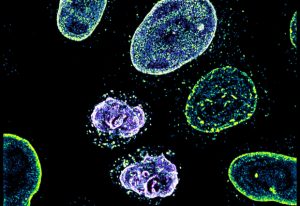
This picture of the week, taken by Arina Rybina in the Ellenberg group at EMBL Heidelberg, shows a high-resolution 3D microscopy image of living human cells: HeLa cells. In this fascinating fluorescing microspace, two newly formed daughter nuclei are captured to study the assembly of nuclear pore…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
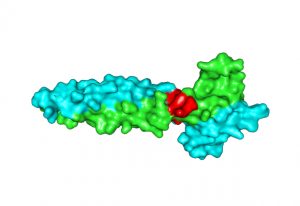
A new paper describes a unique mechanism of partner selectivity in transcription factors.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
This beautiful mosaic of mostly hexagonal cells is the outer skin layer of a zebrafish larva as seen under a microscope. Each skin cell exhibits a unique pattern of actin ridges. Actin is a family of globular multifunctional proteins found in almost all eukaryotic cells. Actin forms microfilaments,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Exploring the diverse routes by which EMBL scientists are driving forward neurobiology
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
The hormone insulin helps to remove sugar from the blood after a meal. This is important, as in the long term high blood sugar levels damage our bodies. Diabetes of type 1 or type 2 is a direct consequence of a failure to produce sufficient insulin or to release it from the cells in which […]
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Shedding light on the mechanisms that control the fate of embryonic cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
The brain is the most complex organ in the human body. Yet despite it being the organ that makes us conscious beings – and despite the fact that researchers have been studying it for generations – it’s still a constant source of surprise. To help lift the veil on some of its mystery, Lina…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
A new technique in cryo-EM
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
EMBL researchers have published two new studies involving the nuclear pore complex
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
Traditionally, we talk about having five senses: sight, hearing, taste, smell and touch. In reality, our bodies are capable of much more. Sitting right under our skin are a variety of sensory neurons, which are specialised in detecting light touch, pain, temperature, itch or the body’s position.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

New possibilities for gene therapies
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

The three bluish blobs shown in the top right corner of this image may not resemble the sphere of noodles that is the human brain, but they are still essential – at least for the fruit fly. This Picture of the Week shows the brain lobes of Drosophila. It’s an insect so tiny and so […]
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
EMBL’s Genomics Core Facility supports students participating in the annual iGEM competition.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
Is it a fungus or a strange plant? Actually it’s the larval form of Platynereis – a group of marine ringed worms. Scientists have been using them in their studies for the past 70 years, and they are among the preferred lab organisms. They are easy to keep in the lab, and under temperature and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Funding awarded to EMBL-EBI for tuberculosis monitoring tool
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
Despite missing the characteristic stripes one would expect from a zebra – or a zebrafish – the fractals in this Picture of the Week show a zebrafish; or at least some cells in a zebrafish embryo, a few hours after fertilisation. Zebrafish are not only popular aquarium fish, they are also an…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Model organisms are species that are studied extensively to understand particular biological phenomena and processes, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. The small marine ringed worm Platynereis dumerilii gained…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Fruit flies have something that we don’t have: they produce a protein called dumpy. This protein is the largest created by insects, and is comparable in size to the largest human protein – titin. While titin is vital for our muscle function, dumpy connects the soft cells of the insect’s…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Researchers from Hamburg simplify time-resolved X-ray crystallography
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
Immunotherapy: the role of B cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
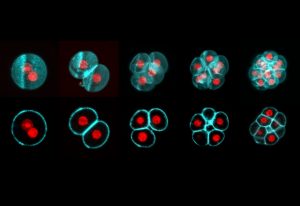
All mammalian life starts with the fusion of egg and sperm, resulting in the creation of a single cell called a zygote. This develops into an embryo through a series of cell divisions, in which the number of cells doubles at each step. Todays’ Picture of the Week was taken by Manuel Eguren of the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

This gorgeous image of a stained adult marine worm was created by former EMBL postdoc Hernando Martinez using structured microscopy. The worm itself was captured during plankton extraction off the coast of Sweden. There are over 10 000 species of these swimming worms, and they have adapted to every…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

MEG3 adopts a complex three-dimensional structure to fulfil its tumour suppressor function.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
Today’s picture of the week is not only a colourful one, it is also a snapshot of the vast number of shapes that the cells inside an animal body can adopt. How this variety comes about is investigated in the Leptin group at EMBL Heidelberg. To understand the shapes of the cells in fruit fly…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Understanding how ageing works at a molecular level
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
Low blood pressure (hypotension) or high blood pressure (hypertension) are risk factors for many diseases and affect more than 20% of the global population. How blood pressure is regulated is part of the research done in the Heppenstall group at EMBL Rome. In today’s Picture of the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
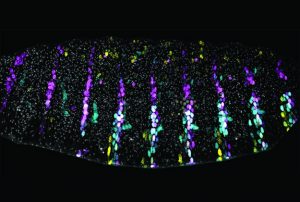
Enhancers in Drosophila embryos gather together to preserve phenotypes under stressful conditions
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
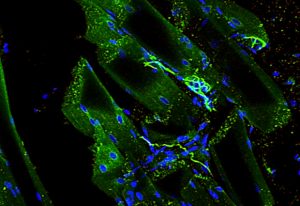
Every single moment of our life we use our muscles – most of the time without even thinking about it. Some muscles, like our heart, we cannot even control at all. How our brain communicates with our muscles is still not fully understood. The communication between our brain and our skeletal…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
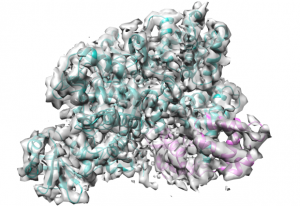
SidJ enforces a unique modification on human proteins and helps legionella grow.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists collaborate to develop new protocol for screening membrane protein stability
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
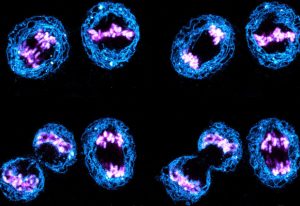
This colourful picture, taken by EMBL postdoc Arina Rybina using a confocal fluorescence microscope, shows human cells in the process of cell division. Eventually, each mother cell brings into existence two identical daughter cells. To visualise the process by light microscopy, different cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Does rearranging chromosomes affect their function? EMBL scientists reveal uncoupling of 3D chromatin organisation and gene expression.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
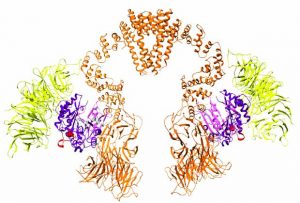
Using cryo-EM, scientists have determined the structure of a large protein complex called Elongator.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

How computer processing of human language is harnessed by EMBL scientists
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
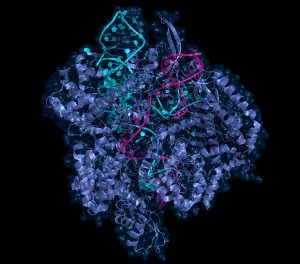
What CRISPR may bring for the future of biology, and how it is used at EMBL
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
New insights into mechanisms behind embryonic development
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

The BioImage Archive - EMBL-EBI's first dedicated imaging data resource
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
What looks like a pair of scary alien eyes is actually the final stage in the duplication of a cell. Cell duplication is preceded by a process called mitosis, in which the replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Mitosis is the prerequisite for a cell to divide into two identical…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

The increasing importance of code in the biological sciences
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

Using genomics to help endangered species
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
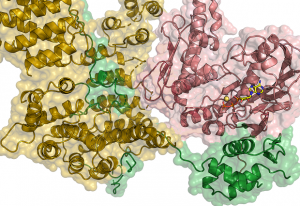
The mystery of how condensin maintains the integrity of the genome during cell division.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
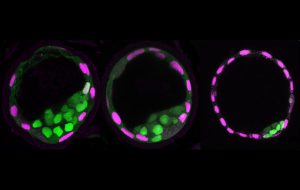
Uncovering new role of fluid pressure in controlling embryo size and cell fate
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
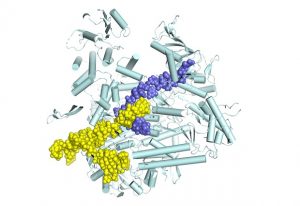
Snapshots of the flu virus replication machine in action
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
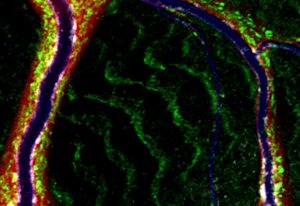
This image – resembling a network of rivers and canals – actually shows the tracheal tip cell of a fruit fly. Fruit flies are heavily used in research and they are a common model organism in developmental biology. Researchers at EMBL use the larvae of fruit flies to study tracheal cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
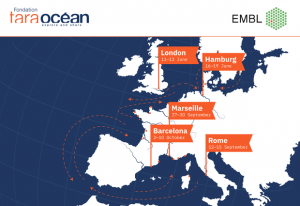
Tara Ocean Foundation launches the exploration of 10 European rivers
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
Scientists develop software tools for automated acquisition of electron microscopy data
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

EMBL is a world-leading organisation for life science research. Its scientists work in diverse research fields spanning the whole of molecular biology. While the molecules the researchers are working on are often microscopic and impossible to see with the naked eye, one research topic clearly…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

A newly developed 3D microscope visualises fast biological processes better than ever.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

Results from the Tara Oceans expedition reveal the Arctic Ocean as a cradle of viral biodiversity
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists have discovered that the proteome is substantially affected by both sex and diet
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
Thorough characterisation of structural variants in human genomes
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
Large CRISPR screen prioritises hundreds of promising genes for personalised cancer treatment
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

Colorectal cancer characterised by consistent changes in gut bacteria across continents, cultures and diets
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
EMBL scientists create membraneless organelle to build proteins in living cell
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

Scientists develop technology to measure how ATP concentration affects protein solubility in cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

New group leader at EMBL Grenoble is investigating the cellular role of melanoma antigens
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
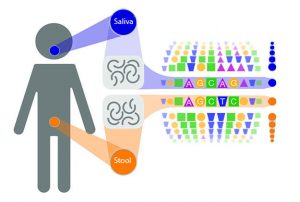
Many microbes traverse the oral-gut barrier
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

How organs form in a mouse embryo
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
Suicide system in tuberculosis bacteria might hold key to treatment
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists identify RNA regulating protein behaviour in switch of normal roles
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
Researchers identify novel gut bacteria species and call for more data from beyond Europe and North America
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

A new database of bacteria in the human microbiome is the most comprehensive to date.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
New search engine allows researchers to identify antibiotic resistance genes or mutations in real time
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
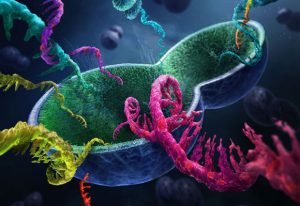
Scientists develop high-throughput yeast single-cell RNA sequencing method
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
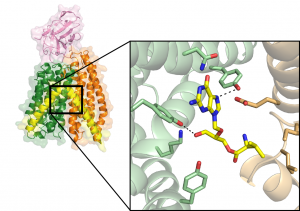
Scientists develop structural model that could help in the development of drugs with increased absorption rates
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

Federated data sharing will now be possible on an unprecedented scale
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

Scientists build self-organising features into robot swarms to study shape formation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
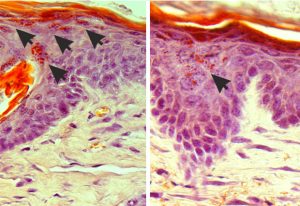
EMBL researchers have found a way to stop itch with light in mice
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Cancer researchers have developed a computer model to predict the course of disease for prostate cancer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Researchers develop new method to analyse the entire protein-RNA network of the cell
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

EMBL-EBI industry case study: Biocatalysts
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
What does it take to create a vaccine or improve cancer therapies?
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
lab-mattersscience-technology

New algorithm will enhance understanding of relationship between genotype and environmental factors
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Scientists uncover effects of mutation that can cause autism and intellectual disability
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

How EMBL scientists are using machine learning to advance biology
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
lab-mattersscience-technology
The De Renzis group investigated invagination, the first step of organ development in embryos.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Translating 2D hospital scans into 3D prints is informing patients and aiding surgeons
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
alumniscience-technology

Genomes of 66,000 UK species to be sequenced in global effort to sequence all known eukaryotic species
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
EMBL scientists investigate the structure of a key protein involved in blood clotting
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
The Hentze Lab enhanced a RNA-interactome capture technique to pave the way towards medical progress
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Speeding up time-resolved X-ray crystallography with EMBL beamline P14
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
EMBL researchers discover that four organs in a marine worm’s head can sense different chemicals
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
New study reveals how to make therapeutic insulins more effective than they currently are
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
ERC grantees Wolfgang Huber and Oliver Stegle share their vision for the next 10 years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
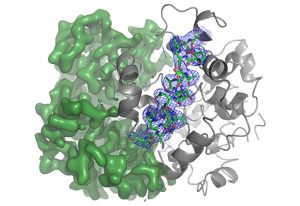
Researchers at EMBL Hamburg have released the next generation of their ARP/wARP software
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
lab-mattersscience-technology
How embryonic stem cells develop into the germ line
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
EMBL scientists gain mechanistic insights into how cellular signalling controls gene regulation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Researchers from EMBL and Heidelberg University unveil the molecular mechanisms of ageing
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Meet the organisers of EMBO’s first course on molecular geobiology
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
eventsscience-technology
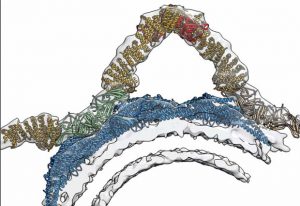
Retromer’s 3D structure improves understanding of cellular sorting and packaging
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

X-ray experiments show that scaffolding protein PDZK1 has a L-shaped conformation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Real-time tracking of proteins during mitosis is now possible using a 4D computer model
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Complex metabolomics analyses in the cloud
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
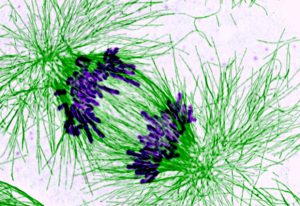
EMBL scientists discover how a component of the cohesin ring binds DNA
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Large-scale systematic analysis explores how inherited genome affects drug response of cancer cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
First global survey of soil genomics reveals a war between fungi and bacteria
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
EMBL researchers visualise the proteins needed to capture molecules and bring them into a cell
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
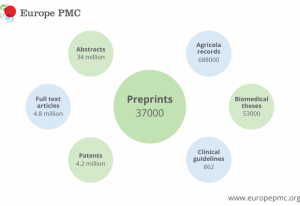
Europe PMC adds preprints to its search
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Mammalian life begins differently than we thought
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Scientists show how bacteria and other microorganisms are passed on from mother to child
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Acute myloid leukaemia risk could be detected years before diagnosis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists investigate how bacteria melt to study their reaction to drugs
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Combining antibiotics with each other, non-antibiotic drugs or food additives can alter their effectiveness
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
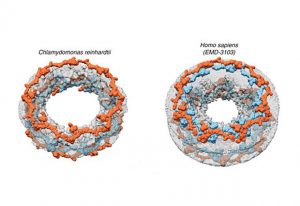
EMBL scientists reveal NPC architecture of algae
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
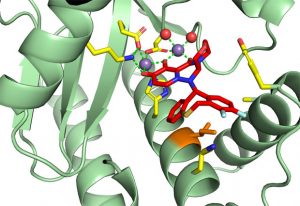
EMBL scientists investigate how influenza virus responds to new drug treatment
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

EMBL researchers develop method that simplifies the isolation of DNA- and RNA- protein complexes
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Combinations of cancer drugs can be quickly and cheaply tested using a novel microfluidic device
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
EMBL scientists extend Turing’s theory to help understand how biological patterns are created
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
New computational method uses multi-omics analysis for personalised medicine
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
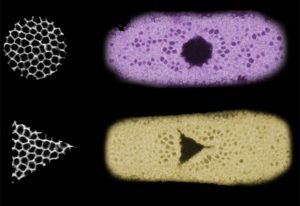
EMBL researchers guide the shape of cells and tissues with optogenetics
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Of mice and gorillas: using mouse data for conservation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
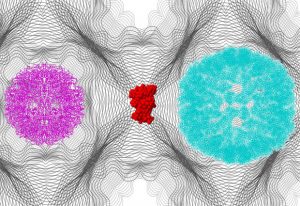
Scientists at EMBL Hamburg determine shapes of intermediate states in dynamic biological systems
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
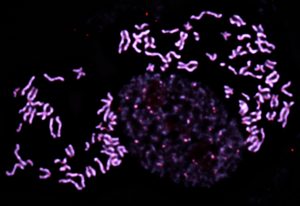
EMBL group leader Jan Korbel reflects on his scientific origins and current research
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Researchers identify genes that can cause brain tumours in children and other cancers later in life
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

New platform transforms CRISPR gene editor into precision tool
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

What worms can tell us about cancer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
EMBL scientists uncover large solubility and thermal stability changes of proteins during the cell cycle
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Discover how EMBL scientists are using GPU computing to push biology forward
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at EMBL Rome develop new method that uses light to manage neuropathic pain in mice
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Open-source software allows standard microscopes to accurately image 3D structures
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
EMBL scientists count and locate chromosomal proteins during cell duplication
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Launch of the first free global online catalogue of PDX models
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
For the first time, EMBL Rome researchers have captured microglia nibbling on brain synapses on film.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
What does a cell's location tell us?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
EMBL scientists discover how blood vessel cells become blood stem cells during embryonic development
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
One in four drugs with human targets inhibit the growth of bacteria in the human gut, and may promote antibiotic resistance, EMBL researchers report in Nature
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists show how to grow a wide range of gut bacteria in the lab
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists unravel the molecular basis of a major antibiotic resistance transfer mechanism
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at EMBL and Cellzome develop technology to monitor the effects of drug treatments on protein degradation and synthesis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
EMBL scientists show how chromatin usage in individual cells reveals developmental trajectories
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Thanos Halazonetis discusses the EMBO/EMBL Symposium: DNA Replication: From Basic Biology to Disease
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
eventsscience-technology
EMBL scientists discover how two guidance cues work together when neurons project axons across the midline
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

New EMBL spinoff company Velabs Therapeutics aims to speed up discovery of therapeutic antibodies
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
lab-mattersscience-technology
Is depression in your genes?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Join us in our new editorial theme as we ask how everything began
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
New technique offers insight into early cell life
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Access to state-of-the-art microscopes and outstanding expertise
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Researchers from Delft University and EMBL crack the mystery of condensin’s neat DNA loop extrusion
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists show that the rhythm between Wnt and Notch waves enables patterning in embryos.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
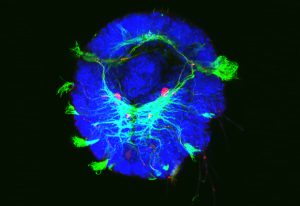
EMBL scientists discover how a molecule’s role changes from simple metabolite to instructive signal
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
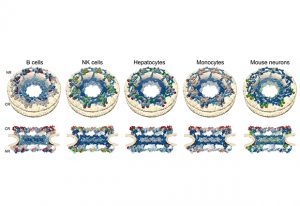
EMBL scientists create a turnover catalogue of almost 10.000 proteins from primary cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Network of genes linked to development of diabetes
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

How Darwin’s work revealed the intimate relationship between orchids and insects
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
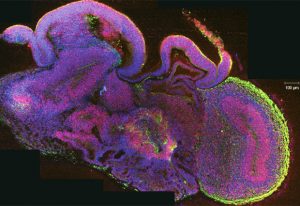
What opportunities can organoids bring to further the understanding of the human brain?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
eventsscience-technology
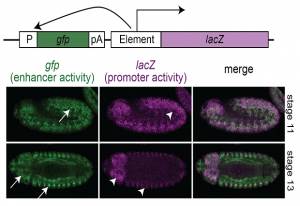
EMBL scientists show that some promoters can act as enhancers and vice versa
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
EMBL instrumentation teams adapting tech to run biological experiments on the synchrotron after its upgrade
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
lab-mattersscience-technology

Nick Goldman of EMBL-EBI issued a challenge in 2015. In 2018, a winner emerged just in time.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
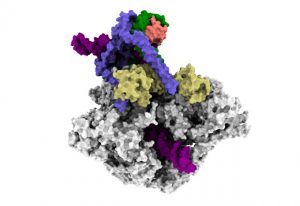
EMBL researchers uncover how a key enzyme that helps cells make new proteins starts its work
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
EMBL researchers solve a decades-long debate on a key process for brain and embryo-development
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists unveil how 3D chromatin structure affects RNA splicing
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

Molecule mapping method raises interest in forensics, agriculture and microbiome studies
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

What are the strangest genomes in EMBL-EBI's Ensembl?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
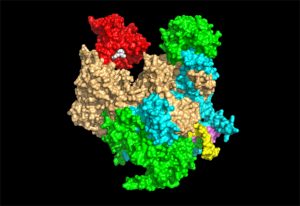
ERC grantee Stephen Cusack shares his vision for the next ten years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
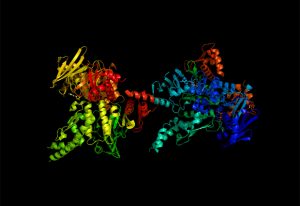
New research reveals that two different mechanisms are responsible for chromosome folding
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
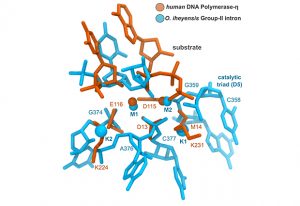
EMBL scientists superimpose structures of two-metal-ion enzymes and reveal new potential drug targets
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

New research shows how pores form in the membrane that surrounds a cell’s nucleus
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

High resolution 3D protein structures in a giffy with PDBe
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

New BioModels infrastructure supports significantly more model formats and offers improved search
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
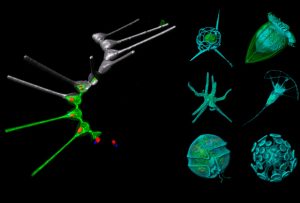
New method for 3D imaging microorganisms lends insight into the creatures that inhabit our oceans
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
Insights into the reproduction of Plasmodium parasites in mosquitoes reveal rapid and broad activity
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
EMBL researchers create highest resolution 3D model of important structure within Ebola virus
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

Inside the Centre for Structural Systems Biology
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
A summary of recent research highlights from EMBL
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

As a new cryo-EM facility is inaugurated, EMBL’s Michael Hons describes his role in the project
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

How open data is changing our pursuit of discovery
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

A talent for organisation has taken EMBL’s Steffi Kandels-Lewis across the globe
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

Five things researchers have learned from bizarre fruit flies
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

Find out how curiosity is driving some of the work we do here at EMBL
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

Meet Ig Nobel emcee Marc Abrahams, an EMBL Science and Society speaker in December
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
eventsscience-technology
EMBL researchers and collaborators unravel how chromosomes form
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

How microbes can create niches for each other
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
New study by Paola Kuri and Maria Leptin shows how inflammation happens in zebrafish in real time
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

EMBL researchers separated facts from fiction at a Friends of EMBL Science Movie Night
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVESSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesscience-technology
How patient-derived computational models can help researchers understand cancer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
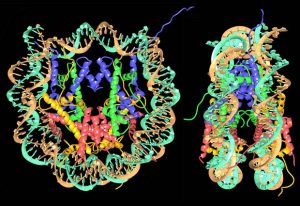
Tim Richmond looks back on the work that revealed the high-resolution structure of the nucleosome
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
eventsscience-technology
Science and Society event answers controversial questions about gut microbes
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
eventsscience-technology

IMPC explains how much the sex of animals is misdirecting research results
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

EMBL-EBI and IMPC characterised over 3000 mouse genes, revealing new gene associations with disease
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

Exploring the potential of user experience for life sciences through industry workshops
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
eventsscience-technology
The Image Data Resource - prototype of the first open repository linking imaging and molecular data
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
EMBL’s Cornelius Gross wants to understand fear responses and the brain circuitry that governs them
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
EMBL researchers complete a molecular atlas showing gene expression in all cells in an entire animal
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
Two EMBL researchers are exploring new ways to filter out noise and get to the data they need
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

EMBL-EBI, the Broad and UCSC Genomics Institute to build Data Coordination Platform with CZI support
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
lab-mattersscience-technology

EMBL’s Hiroki Asari investigates how our internal state can change the way our eyes work
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

An EMBL collaboration devises a new method that could speed up vaccine development for HIV
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
Hallmarks of residual breat cancer cells suggest new approaches for preventing relapse
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
Introducing one of the largest collections of high-quality human induced pluripotent stem cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
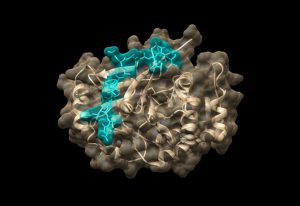
ERC grantee Maja Köhn shares her vision for the next ten years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
EMBL researchers develop an optical method for measuring the release of insulin from single cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
EMBL scientists detect important function of genetic sequence our ancestors assimilated from a virus
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
EMBL-EBI researchers identify mouse epigenetic clock that could help scientists understand ageing
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
EMBL scientists add crucial knowledge to understanding of the bacterium that causes tuberculosis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
Study by EMBL and DKFZ researchers means origins of myeloid leukaemias may need rethinking
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

Researchers use single-cell sequencing to understand how cells age
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
ERC grantee Edward Lemke shares his vision for the next ten years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
ERC grantee Detlev Arendt shares his vision for the next ten years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
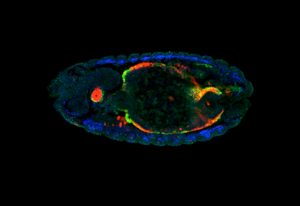
ERC grantee Eileen Furlong shares her vision for the next ten years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
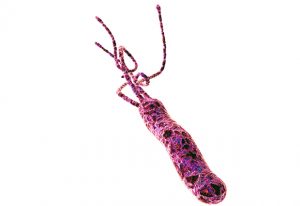
Keeping bacterial chromosomes tangled could lead to new approaches to treatment
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

Reconstructing T-cell development in high resolution
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
EMBL researchers develop a computer model to explore the movement of nuclei in a multinuclear cell
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
Differentiated and undifferentiated cells get energy in different ways, sensor made at EMBL shows
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

Beamline BM14 in Grenoble shuts down, continues collaboration with India
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
lab-mattersscience-technology
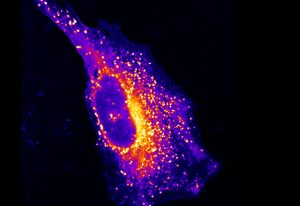
A new technique developed at EMBL reveals the way fats interact with other molecules in cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists discovered that common mutations can change the shape of gene promoters
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

Healing and anxiety are influenced by the genetics of one’s social partners
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

New mechanism revealed
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
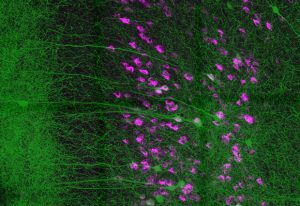
EMBL scientists find out how the prefrontal cortex puts a break on instinctive behaviours
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
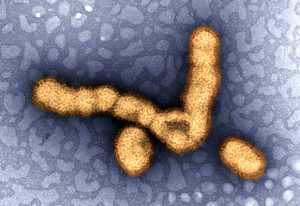
Understanding how the flu virus steals host RNA offers hope of new drugs
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
Inducible mechanism found by EMBL scientists links receptor degradation and replenishment
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

Ewan Birney's nine "Structures of Christmas" celebrate 20 years of PDBe
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
lab-mattersscience-technology
EMBL scientists use new techniques to describe the architecture of conical HIV capsids
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
Research on the effect of nerve cell stiffness on sensitivity to touch could lead to new painkillers
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

Paul Nurse’s failed experiment inspired a career that would uncover key mechanisms of cell division
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
New method combines signalling pathway data resources to improve systems biology research
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

How Christian Löw’s failed experiment led to an unexpected scientific journey
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

How a team of scientists and artists at EMBL transformed microscopy data into stunning 3D images
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
lab-mattersscience-technology
Exploring what it would take to regrow a lost limb, and what we might learn along the way
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
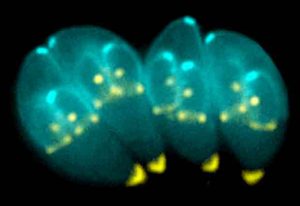
Parasite’s method of rewiring our immune response leads to novel tool for drug tests
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

EMBL study finds that rearranging how DNA packs the nucleus can activate cancer genes
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
lab-mattersscience-technology
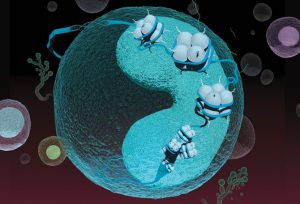
BLUEPRINT: EMBL-EBI and the push to decipher the blood epigenome
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
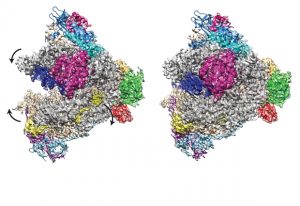
Cryo EM reconstruction of RNA Polymerase I reveals details of how molecule binds and transcribes DNA
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

Open source bioinformatics method for finding metabolites makes experiments comparable across labs
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
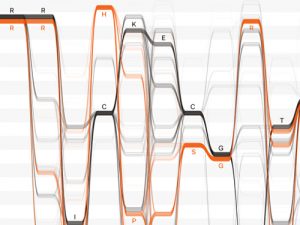
Where design meets bioinformatics, new scientific perspectives abound.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
What happens when plant's leaf-placing feedback loop isn't quite right
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
New platform useful for studies of protein binding, human tissue and more
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
A rapid, versatile mechanism that modifies proteins is revealed to be crucial for the evolutionary process
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists investigate how leaves grow flat to efficiently capture sunlight
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
IMPC study identifies 410 genes essential to life in the mouse, providing a window on human disease
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

CORBEL Open Call launches October 2016, for access to 15 facilities and 8 research infrastructures
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
lab-mattersscience-technology
Side-effects of leukaemia drug explained, reveal possibility of repurposing to treat other diseases
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
Puzzle of nuclear pore formation in growing nuclei solved
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
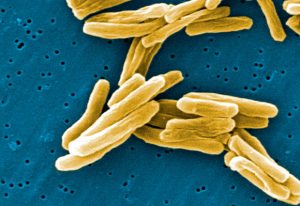
EMBL researchers help to design a lead compound active against four different pathogens
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

A new repository helps identify emerging trends in data-driven science.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
lab-mattersscience-technology

Collaborating to take crystallography into a new time dimension
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
3D printing, gaming, virtual reality and lenticular posters bring new perspectives to research
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

Emmanuelle Charpentier sheds light on how CRISPR–Cas9 went from side project to global revolution
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
'The PDB plays a crucial role in structural biology research and development'
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

Team leader investigates how the gut microbiome could relate to human diseases
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

Storage of pre-made nuclear pores allows for rapid cell division in fruit fly embryos
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
Detailed structure paves the way for more effective cancer therapies
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
Strength of contraction determines whether cells become embryo or placenta
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
Molecular messengers synthesised to help study how cells respond to outside stimuli
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

New technique reveals uncharted docking sites in RNA-binding proteins
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
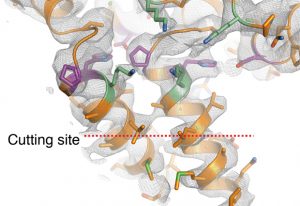
Study provides insights into workings of new HIV drugs and how virus becomes resistant
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

Core Technologies in Life Sciences (CTLS) association will be key resource for facility professionals
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
“Like getting hold of a microscope for the first time”
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

Collaborations shorten distance between EMBL Heidelberg, Germany, and CEITEC in Brno, Czech Republic
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

Studying at EMBL in Grenoble helps Japanese postdoc see her native country through different eyes
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
How cells eliminate protein deposits that can lead to neurodegenerative disorders
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

Establishing a programme of research, development and user services for time-resolved crystallography
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

What's a microbiome? How on Earth do they work?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

New method enables scientists to use light to direct where cancer cells go
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

From shared interests at a conference to a surprising discovery
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
Unexpected results: structure of DAPK enzyme reveals dual-purpose loop
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

A perfect match: behaviourist Takefumi Kikusui visits the Gross group to explore animal attraction
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
Largest-ever study of breast cancer genomes reveals new genes and mutations
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
Stool transplants: finding the right match important, EMBL study shows
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

How EMBL scientists are discovering and understanding the waves and rhythms inside us
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

Florent Cipriani talks about his passion for developing beamline instrumentation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

EMBL PhD project puts development in a new light
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
CrystalDirect, developed at EMBL, automates crystal preparation for X-ray analysis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
First detailed structural description of all the rings of nuclear pores
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
Information on structure of molecule used for genome engineering yields increased efficiency
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
Subtle genetic differences destine cells to placenta or animal, very early in embryo development
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
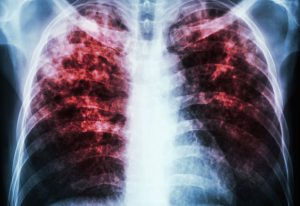
How an EMBL team is making and sharing tools to explore tuberculosis protein structures
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

Commentary in Nature Methods introduces the EMPIAR resource and gives glimpse of future developments
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
1st real-time video of starfish egg cell eliminating crucial structures, to ensure embryo viability
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
New technique uses X-rays to find landmarks when combining fluorescence and electron microscopy
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
Neural mechanisms in mouse brains indicate that we actively forget as we learn
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
![A new tool for single-cell genomics helps us better understand differences between T cell populations. [Illustration: Spencer Phillips, EMBL-EBI]](https://www.embl.org/news/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/TCell_news_EMBL-e1457443531496-300x205.jpg)
TraCeR: new method for studying T cells opens up opportunities to explore immune responses
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
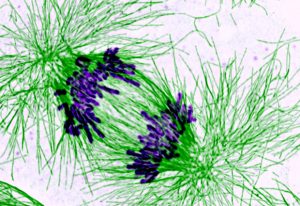
Structural insights into how cohesin keeps DNA together during the cell cycle
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
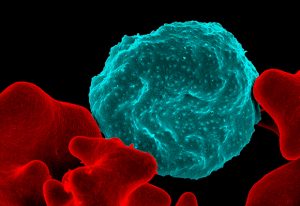
First detailed atlas of start points for genes expression in malaria-causing parasite
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

“It’s a bit like drawing a picture of an intricate object just by looking at its shadow on the wall."
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
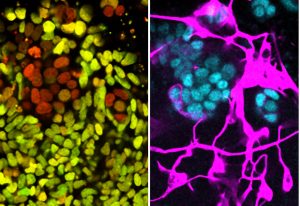
How stem cells resist change
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
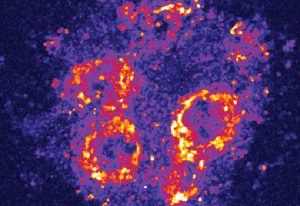
What do cells in an embryo have in common with schools of fish, swarms of fireflies, and applauding audiences?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
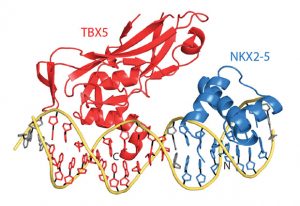
How transcription factors interact to create a heart
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

Plankton network linked to ocean's biological carbon pump revealed
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

Protein screens developed at EMBL Hamburg now commercially available
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
Hamburg collaborators analyse protein crystals inside the cells that made them.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
Further insights into how viral enzymes degrade the cell walls of Clostridia bacteria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
New method is first to enable parallel profiling of the transcriptome and epigenome of a single cell.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology

From initial development to a start-up company: Selective Plane Illumination Microscopy (SPIM) at EMBL.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
New microscope can record the first days of a mouse embryo’s life
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
Making it easier to visualise, understand and predict how proteins combine to drive biological processes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
Commonly used diabetes drug metformin impacts gut bacteria more than disease itself
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
CryoEM solves 3D atomic structure of largest and most elusive RNA polymerase.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

From jumping genes to organ transplants, the non-human features that make us human.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
What really sets humans apart? Forming societies, teaching and compassion, says Agustin Fuentes.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVESSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
people-perspectivesscience-technology
Using lasers to shed light on how tissues get into shape
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
Embryology, genomics and bioinformatics combine to identify factors regulating mammalian pluripotency.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Fibres that pull membrane to form a vesicle exert a force that’s 2500 times a yeast cell’s own weight
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
Findings help demonstrate the evolutionary basis for allergy.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
Enzyme Portal makes it easier to explore all enzyme-related data in EMBL-EBI’s public resources.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Evaluation of MinION™ sequencer finds performance and reliability consistently good.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Study of mouse embryonic stem cells reveals new genes involved in the stem-cell regulatory network.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
A microscopy technique is poised to shine new light on biological questions: as sheets of light can scan everything from developing embryos to single cells or functioning brains, a technique called light-sheet microscopy is gaining traction. It enables scientists to observe living cells in three…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
lab-mattersscience-technology
Spaghetti-like proteins are surprisingly effective 'keys'
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

1000 Genomes Project pushed technologies and knowledge forward to understand what is 'normal' human genetic variation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
From the role of diatoms to how life evolved - scientists' pressing questions about life in the sea.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Missing a gene may not be a big deal – a conclusion from global catalogue of genetic changes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

A nuclear pore riddle: how can you use the same number of pieces to form two rings that fit inside each other?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

MASSIF-1 processes its 10,000th crystal, less than one year after the beamline became operational.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Multifaceted approach reveals how brain and liver age, helps explain why ageing brain loses plasticity.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Introducing the Small Angle Scattering Biological Data Bank, developed at EMBL Hamburg.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
lab-mattersscience-technology

New computational method to study biological signalling networks in healthy and cancer cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Theodore Alexandrov is using mathematics to analyse the countless molecules produced by our cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Behind the scenes of start-up Miroculus, developing a non-invasive test for early-stage disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
alumniscience-technology

A journalist who spent six weeks aboard Tara reflects on the expedition’s extraordinary outcomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
EMBL scientists map ‘switches’ for distant control of gene expression.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
Collaboration between scientists reveals collaboration between lipids.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Crowd sourcing initiative to predict effects of toxic compounds: results of 2013 DREAM Challenge.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
Multidisciplinary research provides clues to new treatments for deadly form of leukaemia in children
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
How T-cells are trained on what not to kill
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
Iron regulatory proteins play important role in combatting infection, protecting against Salmonella.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
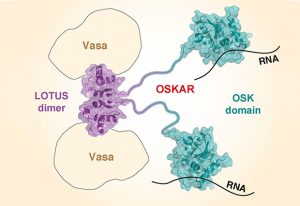
3D structure of Oskar protein gives first molecular insight into how it functions.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
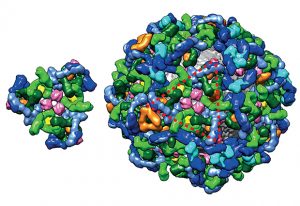
3D imaging unravels COPI coat of cells' transport vesicles.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Jan Korbel and colleagues publish commentary on risks and rewards of genome cloud computing.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
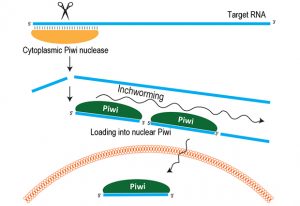
European team identify mechanism for producing piRNAs that silence jumping genes in germline cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Academic community clouds take cancer research towards a brighter future.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
lab-mattersscience-technology
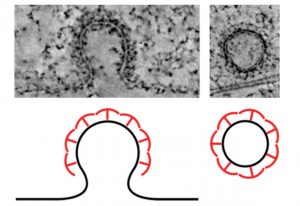
Behaviour of clathrin proteins, crucial for endocytosis, is clarified using new imaging techniques.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

A puzzling peculiarity resolved by Hamburg’s Sample Preparation and Characterisation facility.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Researchers at EMBL-EBI speed up complex GWAS analyses with new method and algorithm.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
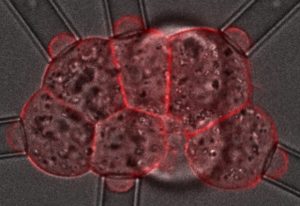
Cells 'dance' as they draw together during early embryo development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
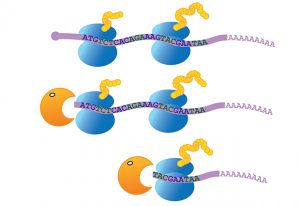
Decaying RNA molecules tell a story that could add more chapters to the study of ribosomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Tara Oceans results reveal climate change insights, and a treasure trove of novel species and genes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
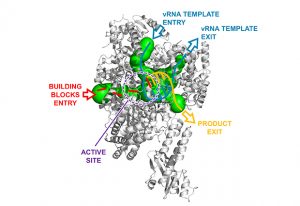
Detailed structural study shows distantly related viruses share a common machinery for replication.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
EMBL scientists demonstrate that spatial constraints are a key factor in determining nucleus size.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
New research shows that some proteins domains can function even with big parts missing.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
Not all embryonic macrophages are the same, and only some are destined to become microglia.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
Unveiling the shape of... the 'molecular bin man' – cryoEM helps reveals p62 polymer in 3D.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Stanford University biophysicist KC Huang on his collaboration with the Typas group in Heidelberg.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Cooperate or compete? Microbes show us that getting along is the better choice for communities.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Radiocarbon studies are helping researchers shine light on how neurons stay stable yet adaptable.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
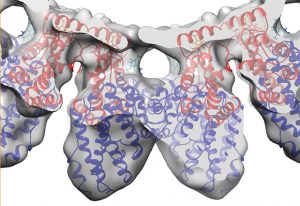
Ground-breaking microscopy technique gives unprecedented insight into endocytosis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
New single-cell genomics techniques bring ‘omics to evolution and development research.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
Coin toss inspires CorMap: a new statistical test that sidesteps need for error estimation.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
Go Team Genome! New method reveals genetic teamwork in drosophila genome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
New fully automated technique enables scientists to chart complex protein networks in living cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
Combining three different kinds of microscopy to determine how molecules move during endocytosis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
How strong does a spindle need to be? Videos put cell’s chromosome-separating machinery to the test
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
Hamburg-led tuberculosis study demonstrates the power of collaboration.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

EMBL Insight Lecture – Why do we do what we do? – now available to view online.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
eventsscience-technology

Tried and tested do's and don'ts of crowdsource writing.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
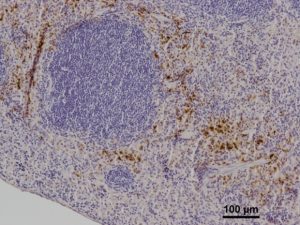
New way mice starve pathogens raises alternative approach to treatments for anaemia of chronic disease
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
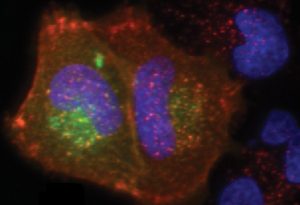
New microscopy-based method goes beyond gene sequencing, pinpointing the cause of disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

How repurposing non-coding elements in the genome gave rise to the great ‘mammalian radiation’.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

New Bar-ChIP method makes it easier to search for epigenetic marks in many samples at once
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
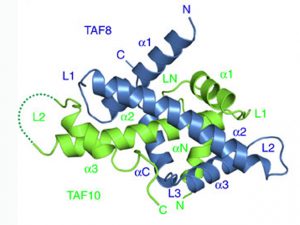
First experimental proof that a key cellular machine forms by uniting pre-assembled modules.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
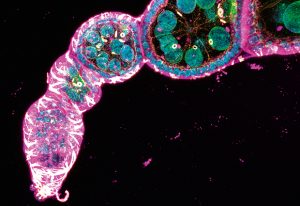
A brief history of microscopes, from van Leeuwenhoek to Betzig, Hell and Moerner.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

As EMBL Hamburg celebrates 40 years, we explore the past, present and future of crystallography.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

From using light to control brain activity to illuminating fruit fly development and mice’s sense of touch
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

New statistical method for RNA-seq analysis creates order out of seeming chaos.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

New group leader Marco Marcia aims to broaden horizons while mapping molecules.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
Research led by Teichmann group identifies fundamental mechanism for controlling protein function.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

How do E.coli and similar bacteria grow safely? By using barrel-plugs as sensors.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Compound that can restore the function of poorly working mitochondria, with therapeutic potential.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
Unprecedented detail in images of mouse neurons thanks to new SNAP-tagging microscopy technique.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Genome-based insights into evolution of malaria-carrying Anopheles mosquitoes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

In two months, 2.3 million diffraction images collected on new, fully automated ESRF/EMBL beamline.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Largest collection of helminth genomic data ever assembled, in new open-access WormBase ParaSite.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Life Science Nord event reveals how pharmaceutical companies use synchrotrons for their research.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
eventsscience-technology

First complete picture of flu virus polymerase. A story of two decades of blood, sweat and sneezes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Appetite to ZzZzZzZ… bite-sized highlights from this year’s Science and Society conference.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
eventsscience-technology

Course attendees go hunting (protein) aliens in a quest for optimal SAXS data.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
eventsscience-technology

EMPIAR lets researchers take a closer look at the images used to build 3D molecular structures.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Open Day in Grenoble celebrates crystallography for the Fête de la Science.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
eventsscience-technology
Unprecedented detail on HIV structure continues virus’ string of surprises.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

How to make good quality samples for good quality structural biology experiments.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
eventsscience-technology

New, open repository helps researchers share computational models of disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Kidney cancer linked to exposure to aristolochic acid, an ingredient in some herbal remedies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Like sports teams, cells can huddle to communicate in secret and organise group behaviour
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
Growth factor IGF-1 boosts natural defence against type-1 diabetes and multiple sclerosis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

European Variation Archive makes it easier to explore detailed information about genetic variation.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
How Nobel-winning work by alumnus Stefan Hell shapes and inspires current EMBL scientists' research.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

From anemones to starfish, sea creatures are helping understand development, evolution and more.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
Flow cytometry: finding needles in haystacks
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Experts from multiple fields come together to understand how the instructions in genes are read
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
eventsscience-technology
How plankton gets jet lagged: the same hormone governs our sleep patterns and a daily marine migration.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

EMBL-EBI hosts successful first EMBO Practical Course in Genotype to Phenotype Mapping.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
eventsscience-technology
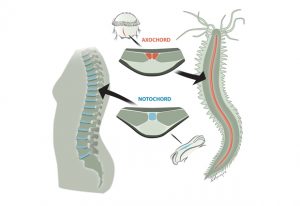
Evolutionary surprise: notochord likely evolved from muscle, earlier than assumed.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
Researchers produce pristine stem cells, which can be precisely changed into clinically relevant cell types.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Gibbon genome gives insights into evolution of this singing, swinging, tree-dwelling ape.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

RNAcentral is the first unified resource for all types of non-coding RNA data.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
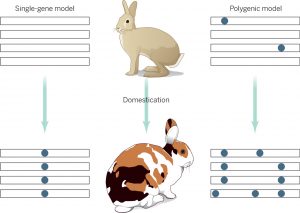
Bronwen Aken discusses what research into the rabbit genome reveals about animal domestication.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
Vasa protein preserves pieces of 'enemy' DNA to help protect the genes of future generations.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
How a single molecule can attract and repel growing brain connections
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Ensembl has incorporated a vast amount of knowledge into a fully annotated reference human genome
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
A rare form of an iron overload disorder kills pancreatic function, Heidelberg scientists find
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
How fruit flies beat the cold, plus the value of precisely controlled experiments and detailed analysis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
Edward Lemke edits special issue of ChemBioChem on boom of technology for genetic code expansion
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
Molecular switch enables viruses to destroy C.diff bacteria – potential alternative to antibiotics
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Marmoset genome provides insights into chimerism: data available in Ensembl genome explorer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
Cell biologists "underestimate the complexity" of protein interactions, says Toby Gibson.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Embed chemists in biology departments, asking their own biological questions, says Carsten Schultz
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Surprising finding: enhancers find their targets long before activation in Drosophila embryos
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
Surprising protein from a flu-like virus is 10 000th ESRF structure
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Focusing on basic research is crucial for the development of more advanced genetics techniques
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
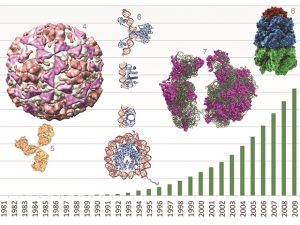
New ways of handling and distributing data at PDBe to tackle ever larger and more complex proteins
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
Scientists determine the structure of auxin response factors: daisy-chains that regulate gene expression
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Enabling neighbours: intact genes can cause cancer when placed near "enhancing" regions of DNA
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Data from first ever worldwide Ocean Sampling Day will be shared via EMBL-EBI resources this autumn.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
Reference sheep genome, published by International Sheep Genomics Consortium, available in Ensembl
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
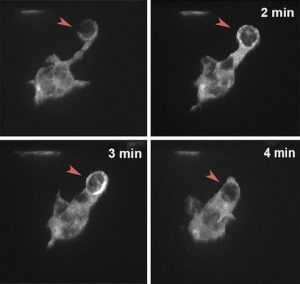
A kaleidoscope of molecules is needed to clean up dead brain cells, and failure can have disastrous consequences
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
How a DNA stretch influences face formation and contributes to common congenital malformations
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
High-resolution structure reveals crucial interactions for HIV maturation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
DNA-coralling protein complex in an unexpected bind
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
Genome Campus researchers discover that some immune cells turn themselves off by producing a steroid.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
The balance behind membrane changes that turn one cell into 6000 as a fruit fly embryo develops
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
Tsetse fly genome sequenced; scientists hope to find new ways to control sleeping sickness.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
In many people with autism and other neurodevelopmental disorders, different parts of the brain don’t talk to each other very well. Scientists have now identified, for the first time, a way in which this decreased functional connectivity can come about. In a study published online today…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
What do bullies and sex have in common? Based on work by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Monterotondo, Italy, it seems that the same part of the brain reacts to both. In a study published today in Nature Neuroscience, the researchers found that – at least in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
The molecular machine that makes essential components of ribosomes – the cell’s protein factories – is like a Swiss-army knife, researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and the Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas in Madrid, Spain, have found.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
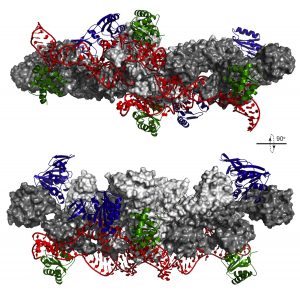
An important step in building ribosomes – the cell’s protein factories – is like a strictly choreographed dance, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have discovered. To build these factories, other ‘machines’ inside the cell have to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
Migrating cells, it seems, cover their tracks not for fear of being followed, but to keep moving forward. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have now shown that cells in a zebrafish embryo determine which direction they move in by effectively…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg and Regensburg University, both in Germany, and the University of Lisboa, in Portugal, have discovered a promising potential drug target for cystic fibrosis. Their work, published online today in Cell, also uncovers a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
Like a fireman who becomes an arsonist, a protein that prevents cells becoming cancerous can also cause tumours, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Grenoble, France, have discovered. The finding, published today in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, stems…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
How our body processes cholesterol has a well-known impact on our health, but it turns out that another ‘fat molecule’ – or lipid – may be at the heart of some diseases which were thought to involve cholesterol. A group of proteins linked to conditions such as metabolic syndrome and some…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
The process cells use to ‘swallow’ up nutrients, hormones and other signals from their environment – called endocytosis – can play a crucial role in shaping the cells themselves, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have found. The study,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
It’s a parent’s nightmare: opening a Lego set and being faced with 500 pieces, but no instructions on how to assemble them into the majestic castle shown on the box. Thanks to a new approach by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
Although we know the tool’s general purpose, it can sometimes be difficult to tell if a specific pair of precision tweezers belongs to a surgeon or a master jeweller. It is now easier to solve similar conundrums about a type of protein that allows cells to react to their environment, thanks to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
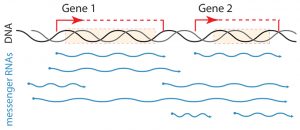
Like musicians in an orchestra who have the same musical score but start and finish playing at different intervals, cells with the same genes start and finish transcribing them at different points in the genome. For the first time, researchers at EMBL have described the striking diversity of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
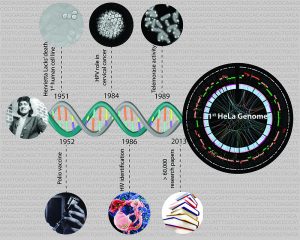
HeLa cells are the world’s most commonly used human cell lines, and have served as a standard for understanding many fundamental biological processes. In a study published today in G3: Genes, Genomes and Genetics online, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
During embryo development, genes are dynamically, and very precisely, switched on and off to confer different properties to different cells and build a well-proportioned and healthy animal. Fgf8 is one of the key genes in this process, controlling in particular the growth of the limbs and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
Studies screening the genome of hundreds of thousands of individuals (known as Genome-wide association studies or GWAS) have linked more than 100 regions in the genome to the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
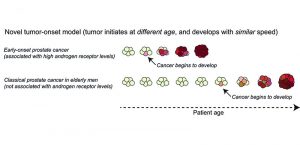
While prostate cancer is the most common cancer in elderly Western men it also, but more rarely, strikes patients aged between 35 and 50. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, in collaboration with several other research teams in Germany*, have…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
Mature cells can be reprogrammed to pluripotency and thus regain the ability to divide and differentiate into specialized cell types. Although these so-called induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) represent a milestone in stem cell research, many of the biochemical processes that underlie…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) and the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology in the UK have discovered how our genome keeps the effects of mutations in check. The discovery, published in the journal Cell, will help in the study of diseases such as cancer and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
Researchers at the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) have created a way to store data in the form of DNA – a material that lasts for tens of thousands of years. The new method, published today in the journal Nature, makes it possible to store at least 100 million hours of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
This may look like yet another video of a dividing cell, but there’s a catch. You are looking at chromosomes (red) being pulled apart by the mitotic spindle (green), but it’s not a cell, because there’s no cell membrane. Like a child sucking an egg out of its shell, Ivo Telley from the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
A research team of scientists from EMBL Grenoble and the IGBMC in Strasbourg, France, have, for the first time, described in molecular detail the architecture of the central scaffold of TFIID: the human protein complex essential for transcription from DNA to mRNA. The study, published today…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
Gene expression wave in the lower part of the future vertebrae column of a mammalian embryo. As the wave goes forward, new pre-vertebrae are formed and the future vertebrae column elongates. (Image and video credit: Nature) In a nutshell: The size of pre-vertebrae in a mammalian embryo is…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
In a nutshell : The gut metagenome is the collection of all the genomes of all the microbes in the human intestinal tract : it is specific to each human, like a second genetic signature At least in healthy humans, this personal metagenome is stable over time The gut metagenome is…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
In a nutshell: 1st map combining human genetic variation at different scales – from single letters to large chunks Based on genomes of 1092 healthy people from Europe, the Americas and East Asia Could help identify genetic causes of disease, rather than just links Data made freely available in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
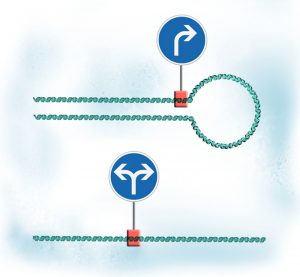
In a nutshell: Looping and unlooping DNA adjusts readout from gene and spread of regulation throughout the genome When a gene forms a loop, its output increases, as the transcription machinery that reads it is trapped into moving only along that gene When the gene loop is undone, transcription…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
In a nutshell: New method allows precise analysis of proteins released by cells over time (distinguishes them from proteins in the cells’ culture serum) Advantages: cells don’t have to be starved: avoids bias and allows more cell types to be studied; can follow fast reactions like immune…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
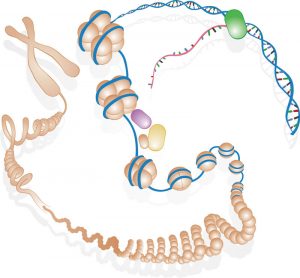
Today, an international team of researchers reveal that much of what has been called ‘junk DNA’ in the human genome is actually a massive control panel with millions of switches regulating the activity of our genes. Without these switches, genes would not work – and mutations in these regions…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Grenoble, France, have determined the detailed 3-dimensional structure of part of the flu virus’ RNA polymerase, an enzyme that is crucial for influenza virus replication. This important finding is published today in PLoS…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology

What do you get when you dissect 10 000 fruit-fly larvae? A team of researchers led by the EMBL- European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) in the UK and the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics (MPI) in Germany has discovered a way in which cells can adjust the activity of many…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
A traffic policeman standing at a busy intersection directing the flow of vehicles may be a rare sight these days, but a similar scene appears to still frequently play out in our cells. A protein called Lem4 directs a crucial step of cell division by preventing the progress of one molecule while…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
Savira pharmaceuticals GmbH, a spin-off of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) based in Vienna, Austria, has signed a collaboration and license agreement with Roche, thus further strengthening the links between fundamental research and major pharmaceutical development companies. This…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
As a retrovirus matures, the two parts of its shell protein (red and blue or yellow and blue) dramatically rearrange themselves, twisting and moving away from each other. (Credit: EMBL/T.Bharat) Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have for the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
“This video shows a fruit fly embryo from when it was about two-and-a-half hours old until it walked away from the microscope as a larva, 20 hours later,” says Lars Hufnagel, from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany. “It shows all the hallmarks of fruit fly…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have conducted the first comprehensive census of human cells’ export workers. In a study published online today in Nature Cell Biology, they found an unexpected variety of genes involved in transporting…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology

In one of the most famous faux pas of exploration, Columbus set sail for India and instead ‘discovered’ America. Similarly, when scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, set out to find enzymes – the proteins that carry out chemical…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
These spheres may look almost identical, but subtle differences between them revealed a molecular version of the robots from Transformers. Each sphere is a vesicle, a pod that cells use to transport materials between different compartments. The images, produced by Marco Faini from John…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
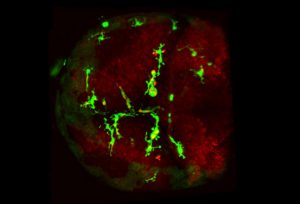
Like emergency workers rushing to a disaster scene, cells called microglia speed to places where the brain has been injured, to contain the damage by ‘eating up’ any cellular debris and dead or dying neurons. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology

Just as banks store away only the most valuable possessions in the most secure safes, cells prioritise which genes they guard most closely, researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) have found. The study, published online today…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology

As spring arrives, flowers seem to bloom everywhere – even under the microscopes at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany. But the ‘flowers’ in this picture actually help an animal, not a plant, to pass on its genes. The image, which has been false-coloured…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Like any law-abiding train passenger, a molecule called oskar RNA carries a stamped ticket detailing its destination and form of transport, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have found. They show that for this molecule, moving in the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
Today a consortium of leading IT providers and three of Europe’s biggest research centres (CERN, EMBL and ESA) announced a partnership to launch a European cloud computing platform. ‘Helix Nebula ‐ the Science Cloud’, will support the massive IT requirements of European…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
The bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae, which causes atypical pneumonia, is helping scientists uncover how cells make the most of limited resources. By measuring all the proteins this bacterium produces, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
Breakthroughs in biomedical science are a step closer today, with the launch of a new distributed research infrastructure for the science of structural biology: Instruct. The launch of Instruct will give academic and commercial scientists across Europe access to a full portfolio of integrated…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
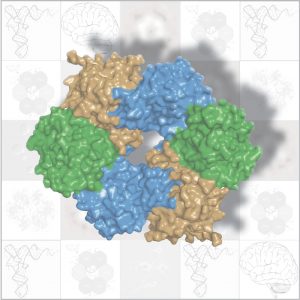
In fairy tales, magic rings endow their owners with special abilities: the ring makes the wearer invisible, fulfils his wishes, or otherwise helps the hero on the path to his destiny. Similarly, a ring-like structure found in a protein complex called ‘Elongator’ has led researchers at the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
Myomesin stretching to 2.5 times its length. Credit: EMBL/Wilmanns. In this video, a protein called myomesin does its impression of Mr. Fantastic, the leader of the Fantastic Four of comic book fame, who performed incredible feats by stretching his body. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
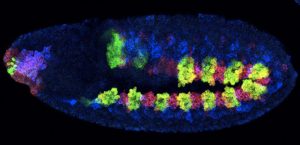
If you wanted to draw your family tree, you could start by searching for people who share your surname. Cells, of course, don’t have surnames, but scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have found that genetic switches called enhancers, and the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
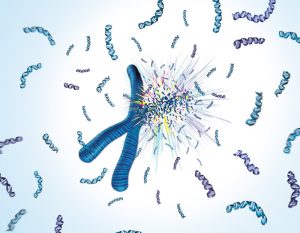
An inherited mutation in a gene known as the guardian of the genome is likely the link between exploding chromosomes and some particularly aggressive types of cancer, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), the German Cancer Research Centre (DKFZ) and the University…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
A team of geneticists and computational biologists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute and Cancer Research UK reveal how an ancient mechanism is involved in gene control and continues to drive genome…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
As an embryo develops, different genes are turned on in different cells, to form muscles, neurons and other bodily parts. Inside each cell’s nucleus, genetic sequences known as enhancers act like remote controls, switching genes on and off. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
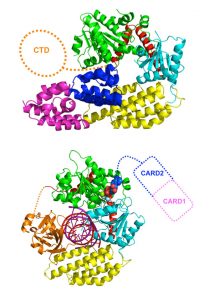
When a thief breaks into a bank vault, sensors are activated and the alarm is raised. Cells have their own early-warning system for intruders, and scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Grenoble, France, have discovered how a particular protein sounds that alarm when it…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
When an egg cell is being formed, the cellular machinery which separates chromosomes is extremely imprecise at fishing them out of the cell’s interior, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have discovered. The unexpected degree of trial-and-error…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology

Researchers can now watch molecules move in living cells, literally millisecond by millisecond, thanks to a new microscope developed by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany. Published online today in Nature Biotechnology, the new technique provides…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
Gardeners know that some trees require regular pruning: some of their branches have to be cut so that others can grow stronger. The same is true of the developing brain: cells called microglia prune the connections between neurons, shaping how the brain is wired, scientists at the European…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
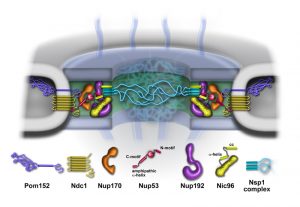
A fungus that lives at extremely high temperatures could help understand structures within our own cells. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and Heidelberg University, both in Heidelberg, Germany, were the first to sequence and analyse the genome of a heat-loving fungus,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
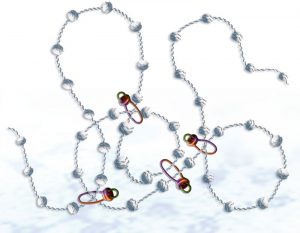
As any rock-climber knows, trailing a long length of rope behind you is not easy. A dangling length of rope is unwieldy and hard to manoeuvre, and can get tangled up or stuck on an outcropping. Cells face the same problem when dragging chromosomes apart during cell division. The chromosomes are…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
In the future, when you walk into a doctor’s surgery or hospital, you could be asked not just about your allergies and blood group, but also about your gut type. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and collaborators in the international MetaHIT…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have developed a new method for studying gene regulation, by employing a jumping gene as an informant. Published online today in Nature Genetics, the new method is called GROMIT. It enables researchers to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have developed a new method which enables researchers to label any protein of their choice with any of a wide variety of previously available compounds, in living cells, by introducing a single reactive…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the German Cancer Research Centre (DKFZ), both in Heidelberg, Germany, have developed a new method that uncovers the combined effects of genes. Published online today in Nature Methods, it helps understand how different genes can…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
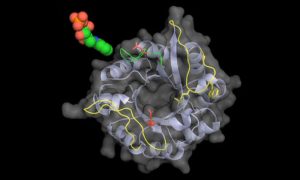
In a paper published online today in PNAS, scientists from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Hamburg, Germany, reveal new insights into the workings of enzymes from a group of bacteria including Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium that causes tuberculosis. The new findings…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
In our not-so-distant evolutionary past, stress often meant imminent danger, and the risk of blood loss, so part of our body’s stress response is to stock-pile blood-clotting factors. Scientists in the Molecular Medicine Partnership Unit (MMPU), a collaboration between the European Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
A detailed analysis of data from 185 human genomes sequenced in the course of the 1000 Genomes Project, by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, in collaboration with researchers at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute in Cambridge, UK, as well as the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
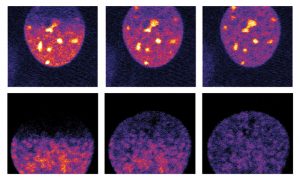
The sight of a researcher sitting at a microscope for hours, painstakingly searching for the right cells, may soon be a thing of the past, thanks to new software created by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany. Presented today in Nature Methods, the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
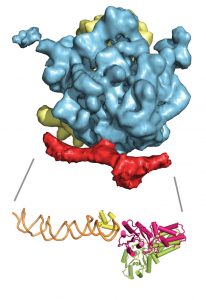
Like an overprotective parent on the first day of school, a targeting factor sometimes needs a little push to let go of its cargo. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Grenoble, France, have visualised one such hand-over. They were the first to determine the structure…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
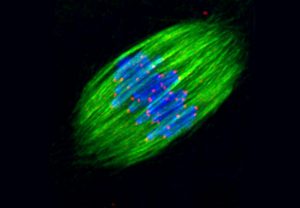
From microscopy to computer tomography (CT) scans, imaging plays an important role in biological and biomedical research, but obtaining high-quality images often requires advanced technology and expertise, and can be costly. Euro-BioImaging, a project which launches its preparatory phase today,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
The cells in the different parts of this video are always the same (grey), but, like actors using make-up to highlight different facial features, they have fluorescent labels that mark different cellular components in different colours: blue shows the nucleus, yellow shows tubulin (a component of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
The 1000 Genomes Project, a major international collaboration to build a detailed map of human genetic variation, has completed its pilot phase. The results are now published in the journal Nature and freely available through the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
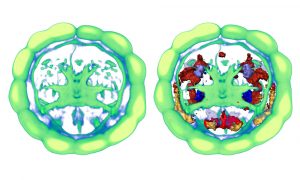
Our cerebral cortex, or pallium, is a big part of what makes us human: art, literature and science would not exist had this most fascinating part of our brain not emerged in some less intelligent ancestor in prehistoric times. But when did this occur and what were these ancestors? Unexpectedly,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
Fear can make you run, it can make you fight, and it can glue you to the spot. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Monterotondo, Italy and GlaxoSmithKline in Verona, Italy, have identified not only the part of the brain but the specific type of neurons that determine…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
During cell division, microtubules emanating from each of the spindle poles meet and overlap in the spindle’s midzone. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have uncovered the molecular mechanism that determines the extent of this overlap. In a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
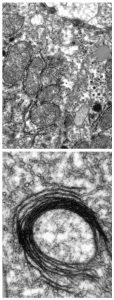
Most organisms need iron to survive, but too much iron is toxic, and can cause fatal organ failure. The same is true inside cells, where iron balance must also be maintained. In a study published today in Cell Metabolism, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
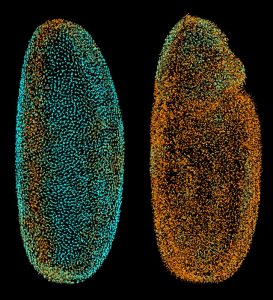
The scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, who ‘fathered’ the Digital Embryo have now given it wings, creating the Fly Digital Embryo. In work published today in Nature Methods, they were able to capture fruit fly development on film, and were the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
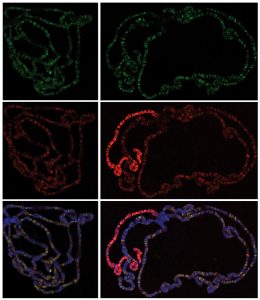
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and the Max-Planck Institute of Immunobiology Freiburg have identified a novel protein complex that regulates around 4000 genes in the fruit fly Drosophila and likely plays an important role in mammals, too.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
Red blood cells, the delivery men that take oxygen to cells all around the body, have short lives. To keep enough of them in circulation, the human body produces around 2 million of these cells every second – even more in response to challenges like severe blood loss. In a study published today…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
During embryonic development, proteins called Polycomb group complexes turn genes off when and where their activity must not be present, preventing specialised tissues and organs from forming in the wrong places. They also play an important role in processes like stem cell differentiation and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
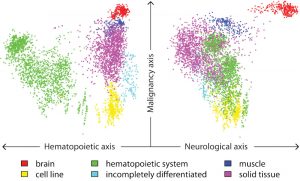
Just like members of an orchestra are active at different times although playing the same piece of music, every cell in our body contains the same genetic sequence but expresses this differently to give rise to cells and tissues with specialised properties. By integrating gene expression data from…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
Name a human gene, and you’ll find a movie online showing you what happens to cells when it is switched off. This is the resource that researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and their collaborators in the Mitocheck consortium are making freely…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
Once the human genome was sequenced in 2001, the hunt was on for the genes that make each of us unique. But scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and Yale and Stanford Universities in the USA, have found that we differ from each other mainly because…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
The thousands of bacteria, fungi and other microbes that live in our gut are essential contributors to our good health. They break down toxins, manufacture some vitamins and essential amino acids, and form a barrier against invaders. A study published today in Nature shows that, at 3.3 million,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
The last ancestor we shared with worms, which roamed the seas around 600 million years ago, may already have had a sophisticated brain that released hormones into the blood and was connected to various sensory organs. The evidence comes not from a newly found fossil but from the study of microRNAs…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
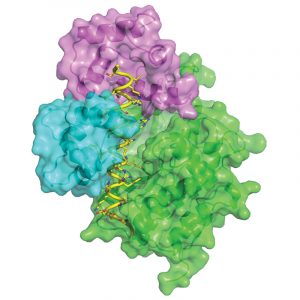
Cells rely on a range of signalling systems to communicate with each other and to control their own internal workings. Scientists from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Hamburg, Germany, have now found a way to hack into a vital communications system, raising the possibility of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
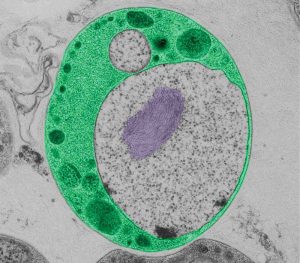
Although they are present almost everywhere, on land and sea, a group of related bacteria in the superphylum Planctomycetes-Verrucomicrobia-Chlamydiae, or PVC, have remained in relative obscurity ever since they were first described about a decade ago. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
ChEMBLdb, a vast online database of information on the properties and activities of drugs and drug-like small molecules and their targets, launches today with information on over half a million compounds. The data lie at the heart of translating information from the human genome into successful new…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
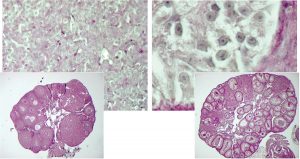
Is it a boy or a girl? Expecting parents may be accustomed to this question, but contrary to what they may think, the answer doesn’t depend solely on their child’s sex chromosomes. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany and the Medical Research…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
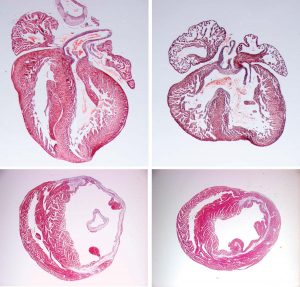
Almost a century after it was discovered in fruit flies with notches in their wings, the Notch signalling pathway may come to play an important role in the recovery from heart attacks. In a study published today in Circulation Research, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL)…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
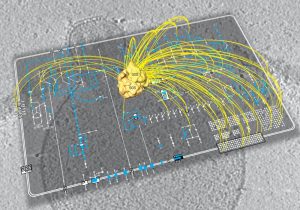
What are the bare essentials of life, the indispensable ingredients required to produce a cell that can survive on its own? Can we describe the molecular anatomy of a cell, and understand how an entire organism functions as a system? These are just some of the questions that scientists in a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Much as adrenaline coursing through our veins drives our body’s reactions to stress, the plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) is behind plants’ responses to stressful situations such as drought, but how it does so has been a mystery for years. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
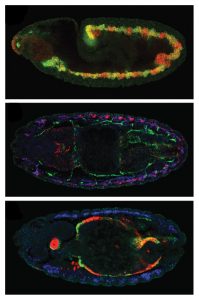
Embryonic development is like a well-organised building project, with the embryo’s DNA serving as the blueprint from which all construction details are derived. Cells carry out different functions according to a developmental plan, by expressing, i.e. turning on, different combinations of genes.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
For many years, the mosquitoes that transmit malaria to humans were seen as public enemies, and campaigns to eradicate the disease focused on eliminating the mosquitoes. But, as a study published today in Science shows, the mosquitoes can also be our allies in the fight against this common foe,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
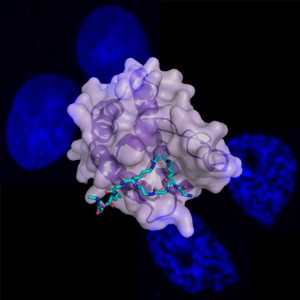
In the quest for speed, olympic swimmers shave themselves or squeeze into high-tech super-suits. In the body, sperm are the only cells that swim and, as speed is crucial to fertility, have developed their own ways to become exceptionally streamlined. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
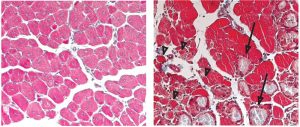
For scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Monterotondo, Italy, what seemed like a disappointing result turned out to be an important discovery. Their findings, published online this week in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), provide…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
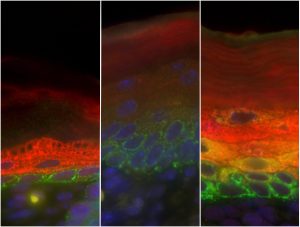
Stem cells have a unique ability: when they divide, they can either give rise to more stem cells, or to a variety of specialised cell types. In both mice and humans, a layer of cells at the base of the skin contains stem cells that can develop into the specialised cells in the layers above.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Our genome is constantly under attack from things like UV light and toxins, which can damage or even break DNA strands and ultimately lead to cancer and other diseases. Scientists have known for a long time that when DNA is damaged, a key enzyme sets off a cellular ‘alarm bell’ to alert the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Chronic inflammatory lung diseases like chronic bronchitis and emphysema are a major global health problem, and the fourth leading cause of death and disability in developed countries, with smoking accounting for 90% of the risk for developing them. Work by scientists at the European Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the University of Heidelberg, Germany, have come a step closer to understanding how cholesterol levels are regulated. In a study published today in the journal Cell Metabolism, the researchers identified 20 genes that are involved…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
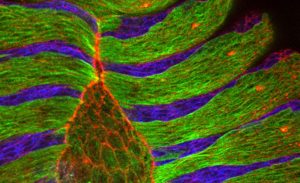
Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, came a step closer to understanding how cells close gaps not only during embryonic development but also during wound healing. Their study, published this week in the journal Cell, uncovers a fundamental…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the University Clinic Heidelberg, Germany, have produced a three-dimensional reconstruction of HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus), which shows the structure of the immature form of the virus at unprecedented detail. Immature HIV is…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
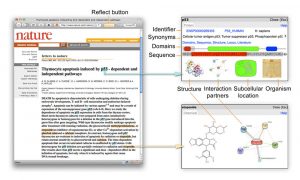
The life sciences are scaling up and produce huge amounts of data and new literature at an amazing pace. The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) now offers a new free service to help researchers, teachers and students keep up-to-date with scientific literature on the web, especially when…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Proteins are the executive agents that carry out all processes in a cell. Their activity is controlled and modified with the help of small chemical tags that can be dynamically added to and removed from the protein. 25 years after its first discovery, researchers at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Most cellular processes are carried out by molecular machines that consist of many interacting proteins. These protein complexes lie at the heart of life science research, but they are notoriously hard to study. Their abundance is often too low to extract them directly from cells and generating…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Recycling is important not only on a global scale, but also at the cellular level, since key molecules tend to be available in limited numbers. This means a cell needs to have efficient recycling mechanisms. Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and Heidelberg University,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
It can be found in all life forms, and serves a multitude of purposes, from energy storage to stress response to bone calcification. This molecular jack-of-all trades is polyphosphate, a long chain of phosphate molecules. Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
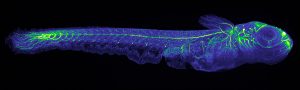
‘Useless fish with big eyes’. This is what Medaka, the name of the Japanese killifish in the pictures, means in Japan where it originally comes from. While its eyes are undeniably big, the fish has proven remarkably useful for scientists. It is a simple model organism, amenable to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
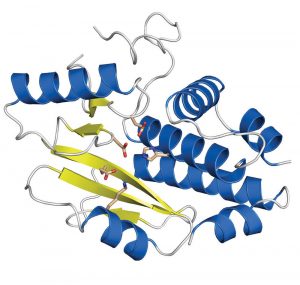
Influenza is and remains a disease to reckon with. Seasonal epidemics around the world kill several hundred thousand people every year. In the light of looming pandemics if bird flu strains develop the ability to infect humans easily, new drugs and vaccines are desperately sought. Researchers at…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Genes that contain instructions for making proteins make up less than 2% of the human genome. Yet, for unknown reasons, most of our genome is transcribed into RNA. The same is true for many other organisms that are easier to study than humans. Researchers in the groups of Lars Steinmetz at the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Cell division is one of the most fundamental processes of life. It explains how one cell can give rise to an organism of several million cells, it determines the shape of different life forms and it underpins our body’s capacity to heal when injured. Often we only notice how important cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology

The best-selling novel The swarm captured the imagination of countless readers with the fascination of marine life. But it also showed how little we understand life in the depth of the ocean. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the Max Planck Institute (MPI)…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
What at the first sight could be pictures of planets or other cosmic structures are actually microscope images of balls (cysts) of human kidney cells. They were taken by Emmanuel Reynaud, in the group of Ernst Stelzer at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), with a widefield microscope.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) have generated a digital zebrafish embryo – the first complete developmental blueprint of a vertebrate. With a newly developed microscope scientists could for the first time track all cells for the first 24 hours in the life of a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
Mouse mothers-to-be have a remarkable way to protect their unborn pups. Because the smell of a strange male’s urine can cause miscarriage and reactivate the ovulatory cycle, pregnant mice prevent the action of such olfactory stimuli by blocking their smell. Researchers from the European…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) discovered a new way to make use of drugs’ unwanted side effects. They developed a computational method that compares how similar the side effects of different drugs are and predicts how likely the drugs act on the same target…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
Genetic recombination, the process by which sexually reproducing organisms shuffle their genetic material when producing germ cells, leads to offspring with a new genetic make-up and influences the course of evolution. In the current issue of Nature, researchers at the European Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) is a condition that unexpectedly and unexplainably takes the lives of seemingly healthy babies aged between a month and a year. Now researchers of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory in Monterotondo, Italy, have developed a mouse model of the so-called crib…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
What makes a human different from a chimp? Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) have come one important step closer to answering such evolutionary questions correctly. In the current issue of Science they uncover…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) in Hinxton, UK, have revealed new insights into how sex chromosomes are regulated. A chromatin modifying enzyme helps compensate for the fact that…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
UK-based researchers at the Medical Research Council Functional Genomics Unit in Oxford and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute in Cambridge have revealed the genetic makeup of the one of the world’s strangest mammals. They have analysed the DNA…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
Influenza is currently a grave concern for governments and health organisations around the world. Now one of the tactics used by influenza virus to take over the machinery of infected cells has been laid bare by structural biologists at the EMBL, the joint Unit of Virus Host-Cell Interaction of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
Leukaemia – cancer of blood or bone marrow – is caused by mutations that allow defective blood cells to accumulate and displace healthy blood. To devise effective therapies it is crucial to know which mutations cause leukaemia and which cell type gives rise to leukaemic cells. Researchers from…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
Epigenetic regulation – modifications to the structure of chromatin that influence which genes are expressed in a cell – is a key player in embryonic development and cancer formation. Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg now gained new insight…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
Much less widely known than the dangerous consequences of iron deficiencies is the fact that too much iron can also cause problems. The exact origin of the genetic iron overload disorder hereditary hemochromatosis [HH] has remained elusive. In a joint effort, researchers from the European Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) have discovered that proteins that regulate the body’s iron household play a vital role in making sure enough nutrients and water are absorbed in the intestine. Mice lacking these proteins suffer from weight loss and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
It does not take much to injure a muscle. Sometimes one sudden, inconsiderate movement does the job. Unfortunately, damaged muscles are not as efficient at repair as other tissues such as bone. Researchers of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s Mouse Biology Unit (EMBL), Italy, and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Seeing proteins in their natural environment and interactions inside cells has been a longstanding goal. Using an advanced microscopy technique called cryo-electron tomography, researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) have visualised proteins responsible for cell-cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Cells in our body come in various shapes and sizes. Each cell is shaped in such a way as to optimise it for a specific function. When things go wrong and a cell does not adopt its dedicated shape, its function can be impaired and the cell can cause problems in the body. Researchers at […]
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
New insights into the cellular signal chain through which pheromones stimulate mating in yeast have been gained by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory [EMBL]. Similar signal chains are found in humans, where they are involved in many important processes such as the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Many neuronal disorders, including epilepsy, schizophrenia and lissencephaly ─ a form of mental retardation ─ result from abnormal migration of nerve cells during the development of the brain. Researchers from the Mouse Biology Unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Italy,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Scientists from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) have developed a new method to prepare and image biological samples in three dimensions with laser light-sheet based fluorescence microscopy. The technological advance, which is published in the current online issue of Nature…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Which genes are passed on from mother to child is decided very early on during the maturation of the egg cell in the ovary. In a cell division process that is unique to egg cells, half of the chromosomes are eliminated from the egg before it is fertilised. Using a powerful microscope, researchers…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
The UniProt Consortium, which includes the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), has added a new database repository for metagenomic and environmental data to its family of protein sequence databases. Metagenomics is the large-scale genomic…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
To protect us from disease our immune system employs macrophages, cells that roam our body in search of disease-causing bacteria. With the help of long tentacle-like protrusions, macrophages can catch suspicious particles, pull them towards their cell bodies, internalise and destroy them. Using a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the University of Michigan have discovered a gene that protects us against a serious kidney disease. In the current online issue of Nature Genetics they report that mutations in the gene cause nephronopthisis (NPHP) in humans and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Hormones control growth, metabolism, reproduction and many other important biological processes. In humans, and all other vertebrates, the chemical signals are produced by specialised brain centres such as the hypothalamus and secreted into the blood stream that distributes them around the body.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
A new mechanism to attack hard-to-treat fungal infections has been revealed by scientists from the biotech company Anacor Pharmaceuticals Inc., California, and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory [EMBL] outstation in Grenoble, France. In the current issue of Science they describe…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the Samuel Lunenfeld Research Institute of Mount Sinai Hospital (Canada), the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (Germany), and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (USA) have created a new computational method called NetworKIN. This method uses biological networks to better…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
The ENCyclopedia Of DNA Elements (ENCODE), an international research consortium organised by the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), today published the results of its exhaustive, four-year effort to build a “parts list” of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
A human cell contains an enormous 1.8 metres of DNA partitioned into 46 chromosomes. These have to be copied and distributed equally into two daughter cells at every division. Condensation, the shortening of chromosomes, allows the cell to handle such huge amounts of genetic material during cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Why does the same diet make some of us gain more weight than others? The answer could be a molecule called Bsx, as scientists from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), the German Institute for Nutrition (DIFE), Potsdam, and the University of Cincinnati report in the current issue of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
People who suffer from anxiety tend to interpret ambiguous situations, situations that could potentially be dangerous but not necessarily so, as threatening. Researchers from the Mouse Biology Unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Italy have now uncovered the neural basis for…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Over 30% of our genes are under the control of small molecules called microRNAs. They prevent specific genes from being turned into protein and regulate many crucial processes like cell division and development, but how they do so has remained unclear. Now researchers from the European Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
When a cell divides, normally the result is two identical daughter cells. In some cases however, cell division leads to two cells with different properties. This is called asymmetric cell division and plays an important role in embryonic development and the self-renewal of stem cells. Researchers…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology

The rise of the central nervous system (CNS) in animal evolution has puzzled scientists for centuries. Vertebrates, insects and worms evolved from the same ancestor, but their CNSs are different and were thought to have evolved only after their lineages had split during evolution. Researchers from…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative Colitis, severely impair the lives of more than four million people worldwide. The development of effective therapies against these diseases requires an understanding of their underlying molecular mechanisms. Researchers from…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Like our body every cell has a skeleton that provides it with a shape, confers rigidity and protects its fragile inner workings. The cytoskeleton is built of long protein filaments that assemble into networks whose overall architecture and fine detail can only be revealed with high resolution…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology

The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) has developed a new computational tool that makes images obtained with cutting-edge microscopes even sharper. The technological advance and its applications are published in this week’s online issue of the journal Nature Methods. Since the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
In 1918, 50 million people died during a worldwide influenza pandemic caused by mutation of a bird-specific strain of the influenza virus. Recently H5N1, another highly infectious avian strain has caused outbreaks of bird flu around the world. There is great concern that this virus might also…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Liver cancer is one of the deadliest cancers worldwide; every year sees more than 400,000 new cases, and most of the victims die in less than one year. Despite extensive research, the underlying molecular mechanisms of the disease are poorly understood. A new study by researchers from the Mouse…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
We all know that iron deficiencies are dangerous, but also too much iron is bad for our health. Our body stores excess iron in various tissues, where it can lead to organ failure and even death if not treated before irreversible damage has occurred. Researchers from the Innsbruck Medical…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Microorganisms make up more than a third of the Earth’s biomass. They are found in water, on land and even in our bodies, recycling nutrients, influencing the planet’s climate or causing diseases. Still, we know surprisingly little about the smallest beings that colonise Earth. A new…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Phone numbers, the way to work, granny’s birthday – our brain with its finite number of nerve cells can store incredible amounts of information. At the bottom of memory lies a complex network of molecules. To understand how this network brings about one of the most remarkable capacities of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
A cell is a busy place. In a permanent rush hour, molecules are transported along a dynamic motorway system made up of filaments called microtubules. Microtubules constantly grow and shrink and are rapidly assembled wherever a cargo needs to go, but during this transportation process they need to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Today the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) launches its new, faster and easier website with an exhaustive search engine at its centre. The web interface has been streamlined on the basis of user feedback from a recent extensive…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
lab-mattersscience-technology
Today the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) launches CiteXplore, a new freely accessible literature resource service. Biological researchers require two crucial sources of information: scientific literature published in peerreviewed…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
lab-mattersscience-technology

Muscle wasting can occur at all ages as the result of genetic defects, heart failure, spinal injury or cancer. A therapy to cure the loss of muscle mass and strength, which has a severe impact on patients’ lives, is desperately sought. Blocking a central signal molecule, researchers from the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
The life of a cell is all about growing and dividing at the right time. That is why the cell cycle is one of the most tightly regulated cellular processes. A control system with several layers adjusts when key components of the cell cycle machinery are produced, activated and degraded to make sure…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology

Blood cells have limited lifespans, which means that they must be continually replaced by calling up reserves and turning these into the blood cell types needed by the body. Claus Nerlov and his colleagues at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) unit in Monterotondo, Italy, in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Eyes are among the earliest recognisable structures in an embryo; they start off as bulges on the sides of tube-shaped tissue that will eventually become the brain. Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg have now discovered that cells are programmed to make…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Cells in an embryo divide at an amazing rate to build a whole body, but this growth needs to be controlled. Otherwise the result may be defects in embryonic development or cancer in adults. Controlling growth requires that some cells divide while others die; their fates are determined by signals…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Today EMBL scientists, EMBL’s commercial affiliate, EMBL Enterprise Management Technology Transfer GmbH (EMBLEM) and EMBL’s venture vehicle, EMBL Ventures GmbH, announce the foundation of Elara Pharmaceuticals GmbH, a start-up company that will translate basic research findings into new…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
lab-mattersscience-technology
Depression, coordination and speech problems, muscle weakness and disability are just a few of the symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Researchers from the Mouse Biology Unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Italy and the Department of Neuropathology at the Faculty of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
In the early days of X-ray crystallography obtaining a three-dimensional model of a protein required wire models, screws, bolts and years of tedious calculations by hand. Today macromolecular models are built by computers – thanks to sophisticated software and in particular a package called…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
lab-mattersscience-technology
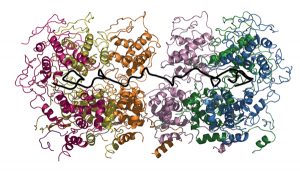
Ebola, measles and rabies are serious threats to public health in developing countries. Despite different symptoms all of the diseases are caused by the same class of viruses that unlike most other living beings carry their genetic information on a single RNA molecule instead of a double strand of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Tuberculosis remains one of the deadliest threats to public health. Every year two million people die of the disease, which is caused by the microorganism Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Roughly one third of the world’s population is infected and more and more bacterial strains have developed…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Recent research at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) reveals new insights into how cells achieve equality between the sexes. A new link discovered between the membrane surrounding the nucleus and the male X-chromosome in fruit flies may play a crucial role in determining how active…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
In 1870 the German scientist Ernst Haeckel mapped the evolutionary relationships of plants and animals in the first ‘tree of life’. Since then scientists have continuously redrawn and expanded the tree adding microorganisms and using modern molecular data, yet, many parts of the tree…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
A detailed structural picture of a molecule that plays a key role in activating the Epstein Barr Virus in human cells has now been obtained by researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the Institut de Virologie Moléculaire et Structurale (IVMS), associated with the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Today researchers in Germany announce they have finished the first complete analysis of the “molecular machines” in one of biology’s most important model organisms: S. cerevisiae (baker’s yeast). The study from the biotechnology company Cellzome, in collaboration with the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology

Imagine grabbing two snakes by the tail so that they can’t wriggle off in opposite directions. Scientists at the Hamburg Outstation of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and collaborators from King’s College in London have now discovered that something similar happens to a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Researchers at the International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB) in India and a unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in France have made a key discovery about a molecule that helps the malaria parasite infect human cells. India is one of the countries…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
In the December 6 issue of Nature Biotechnology, scientists from 14 different organizations around the world, including the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute, propose a new quality standard for biochemical models. MIRIAM [for Minimum information requested in the annotation of biochemical…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
lab-mattersscience-technology
Species evolve at very different rates, and the evolutionary line that produced humans seems to be among the slowest. The result, according to a new study by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory [EMBL], is that our species has retained characteristics of a very ancient ancestor…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
Most of what happens in cells is the work of machines that contain dozens of molecules, chiefly proteins. With the completion of human and other genomes, researchers now have a nearly complete ‘parts list’ of such machines; what’s lacking is the manual telling where all the pieces…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the Universities of Heidelberg and Ulm and a unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Monterotondo, Italy, have discovered that a specific signal within brain cells may determine whether they live or die after a stroke. Their study, published online (November 13) by…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
The Commission of the European Union has awarded EUR 9 million over five years for a new Network of Excellence that will make computational systems biology accessible to bench scientists throughout Europe and beyond. ENFIN, which stands for ‘Experimental Network for Functional…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
lab-mattersscience-technology
Mutations in genes are the basis of evolution, so we owe our existence to them. Most mutations are harmful, however, because they cause cells to build defective proteins. So cells have evolved quality control mechanisms that recognize and counteract genetic mistakes. Now scientists of the Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg and the Institute of Biomedical Research of the Parc Científic de Barcelona (IRB-PCB) have now added key evidence to claims that some types of cancer originate with defects in stem cells. The study, reported this week in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
Achieving equality between the sexes can be a challenge even for single cells. Since evolution began removing bits of male DNA to create the ‘Y’ chromosome, males have had a single copy of certain key genes on the X chromosome, whereas females have two. Normally this would lead females…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
Microtubules need a helping hand to find chromosomes in dividing egg cells, scientists have discovered. Although it was generally accepted that microtubules act alone as the cellular ropes to pull chromosomes into place, a new study by researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL)…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
EBI researchers have changed our view of 4 billion years of microbial evolution. Christos Ouzounis and colleagues have gained intriguing quantitative insights into how gene families are transferred, not only ‘vertically’ through passage from one organism to its progeny, but also…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
Living organisms need to sense the amount of energy that is available to them and regulate the activity of their genes accordingly. Scientists have made the unexpected finding that a histone protein, which wraps DNA into tight bundles and regulates gene activity, can bind a small molecule produced…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
Instead of sequencing the genome of one organism, why not sequence a drop of sea water, a gram of farm soil or even a sunken whale skeleton? Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg and their US collaborators have done just that, and the result is a new…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
Today sees the launch of BioModels, the world’s first database of annotated biological models. BioModels is the result of a collaboration led by the European Bioinformatics Institute (UK) and the SBML Team, an international group that develops opensource standards to describe biological…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
Most things that happen in the cell are the work of ‘molecular machines’ – complexes of proteins that carry out important cellular functions. Until now, scientists didn’t have a clear idea of when proteins form these machines – are these complexes pre-fabricated or put…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
One of the most basic yet least understood processes in our bodies is how cells crawl along tissues. This behavior is essential to the formation of an embryo and other processes, but it must be tightly controlled. A disturbance can lead to the spread of cancer cells or diseases like Spina…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
No results found