Read the latest Issue
The cell that isn’t
New technique captures division of membrane-less cells
In a nutshell:
– New technique allows scientists to study cell division without cell membrane
– Advantages: can physically constrain and manipulate; can access nuclei normally buried deep in opaque embryo; combinable with wide-ranging fruit fly genetics techniques
– Revealed that, surprisingly, confined space not enough to restrict spindle size
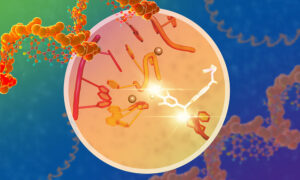
This may look like yet another video of a dividing cell, but there’s a catch. You are looking at chromosomes (red) being pulled apart by the mitotic spindle (green), but it’s not a cell, because there’s no cell membrane. Like a child sucking an egg out of its shell, Ivo Telley from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, removed these cellular ‘innards’ from a fruit fly embryo, at a stage when it is essentially a sac full of membrane-less ‘cells’ that divide and divide without building physical barriers to separate themselves from each other.
“It’s the first time we can study ongoing cell division without the cell membrane, and that means we can physically manipulate things,” says Telley, “so we can uncover the physical forces involved, and see what are the constraints.”
The new technique is described in detail today in Nature Protocols, and has already led Telley and colleagues to a surprising discovery. They found that, although successive divisions fill the embryo with more and more material, leaving less and less space for each spindle, and spindles become smaller as the embryo develops, simply squeezing the ‘cell’ into tighter quarters doesn’t make it produce a smaller spindle.
Combined with the genetic manipulation approaches commonly used in fruit fly studies, the scientists believe their new technique will help to unravel this and other mysteries of how a cell becomes two.
The work, which started in Thomas Surrey’s lab at EMBL, was carried out by Telley and Imre Gáspár in Anne Ephrussi’s lab at EMBL. Surrey is now at Cancer Research UK.
The video is also available on the EMBL YouTube channel.