5 November 2025
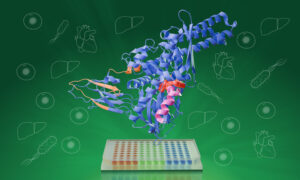
EMBL scientists improve a protein analysis technique, significantly expanding its use and making it 100 times faster – a development that could accelerate drug discovery and fundamental biological research.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
16 October 2025

From student helper to EMBL-EBI Director, Rolf Apweiler has shaped the journey of EMBL and bioinformatics for over four decades.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivesperspectives
28 April 2025

InterPro 105.0 is now live. This AI-driven update makes it easier than ever to explore the protein universe.
2025
updates-from-data-resources
13 December 2024

EMBL announced the winners of its Unfold Your World protein art project, an initiative intended to engage young people, interweaving science with art.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
9 October 2024
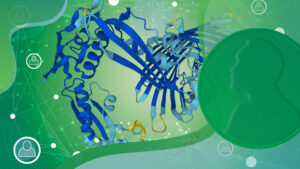
Creators of AI system AlphaFold receive 2024 Nobel Prize for Chemistry.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
sciencescience-technology
21 August 2024
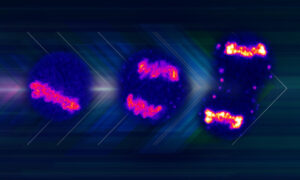
EMBL Heidelberg researchers discovered how a protein switches between repelling and gluing chromosomes during cell division. This helps the mother cell to divide the genome equally into two daughter cells and cluster chromosomes inside the daughter nuclei, ensuring a successful cell division.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
19 April 2024
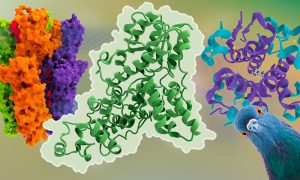
New project will help inform and educate young people about the important roles proteins play in nature, health, and disease, as part of EMBL’s 50th anniversary celebrations.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
10 April 2024
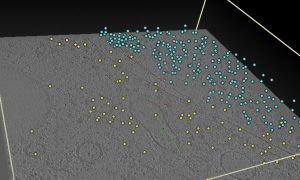
Data obtained through cryogenic sample electron tomography (cryo-ET) are openly available in the new Electron Microscopy Public Image Archive (EMPIAR) cryo-ET tomography browser.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2024
announcementsembl-announcements
15 November 2023

Promiscuity is critical for nourishment. How? This question lies at the focus of research by the Löw Group at EMBL Hamburg. Using structural biology methods, they explore how specialised molecules located in the cell membrane allow cells absorb nutrients from their environment.
EMBLetc
14 November 2023

InterPro version 97.0 and InterProScan 5.64-97.0 are now available. InterPro now features hundreds of new methods integrated from partner databases, and InterProScan draws on over 40000 entries.
2023
updates-from-data-resources
13 July 2023

We are excited to announce the latest releases of IntAct and Complex Portal. IntAct 244 highlights Complex Portal 244 highlights
2023
updates-from-data-resources
2 June 2023

A new tool for the interpretation of missense variation in humans – ProtVar – will help enable drug discovery.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation
17 March 2023

EMBL-EBI's metagenomics data resource increases in size and supports groundbreaking AI tools for protein structure prediction.
2023
updates-from-data-resources
7 March 2023

InterPro now features hundreds of new methods integrated from partner databases, and InterProScan draws on over 38,000 entries. InterPro version 93.0 InterPro 93.0 integrates 300 new methods from the CDD (261), PANTHER (12), PROSITE profiles (17), SMART (9), TIGRFAMs (1) databases, and covers 81.7%…
2023
updates-from-data-resources
4 January 2023

InterPro version 92.0 and InterProScan 5.60-92.0 are now available. InterPro now features hundreds of new methods integrated from partner databases, and InterProScan draws on over 38000 entries.
2023
updates-from-data-resources
20 October 2022

We are pleased to announce the release of InterPro 91.0 and InterProScan 5.59-91.0
2022
updates-from-data-resources
13 October 2022
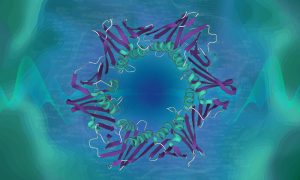
Over 40 million protein annotations have been added to the UniProt database using a Google Research natural language processing model.
2022
technology-and-innovation
9 August 2022

InterPro version 90.0 and InterProScan 5.57-90.0 are now available. InterPro now features hundreds of new methods integrated from partner databases, and InterProScan draws on over 40000 entries
2022
updates-from-data-resources
4 March 2022
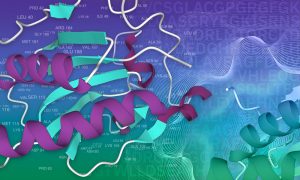
Deep learning models can improve protein annotations and has helped expand the Pfam database.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
perspectivessciencescience-technology
3 November 2021
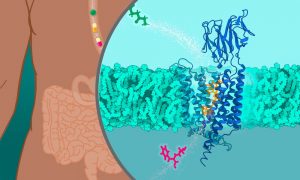
Scientists at EMBL Hamburg determined the molecular structure of Peptide Transporters 1 and 2. The findings will enable developing drugs that more efficiently pass from the gut to target tissues.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
15 October 2021
The Graham and Crump groups at the University of Cambridge and the Svergun Group at EMBL Hamburg have discovered a mechanism by which the herpes simplex virus takes control of the molecular machinery of human cells. Their work reveals how a dedicated viral protein hijacks key host proteins, forcing…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
6 October 2021
Structural biology provides insights into the diverse functions of fibrous protein in humans, amphibians, and bacteria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
30 August 2021

Giulia Zanetti from the Institute of Structural and Molecular Biology (ISMB) in London explains how the collaboration with the Cryo-Electron Microscopy Service Platform enabled her group to reveal the structure of protein transport complexes.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
lab-mattersscience-technology
22 July 2021
A discussion of the applications that AlphaFold DB may enable and the possible impact of the resource on science and society.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
13 July 2021

EMBL alumni Ilaria Piazza and Ken Holmes have been recognised for their outstanding contributions, and will receive their awards as part of the celebrations for EMBL World Alumni Day.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
alumnipeople-perspectives
3 March 2021
Thousands of new protein structure models, prected using deep learning, now available to explore
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
9 February 2021

Researchers at EMBL Heidelberg have identified sequences in human proteins that might be used by SARS-CoV-2 to infect cells. They have discovered that the virus might hijack certain cellular processes, and they discuss potentially relevant drugs for treating COVID-19.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
2 February 2021
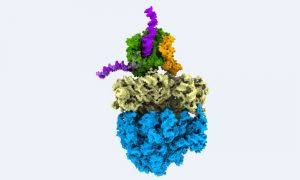
This colourful image shows biological information flow in action: It’s a supramolecular assembly of DNA, RNA and proteins, observed directly inside a bacterial cell while turning genetic information into protein.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
12 January 2021

Structural biologists want to study proteins at the atomic level. The device shown in this Picture of the Week is essential for this.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
23 December 2020

Schoolchildren create exquisite protein-inspired artworks
LAB MATTERS
4 December 2020

How artificial intelligence can help us solve the mysteries of the protein universe
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
2 September 2020
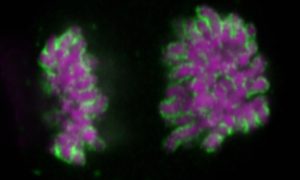
Researchers have uncovered how cells remove unwanted components from the nucleus following mitosis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
18 August 2020
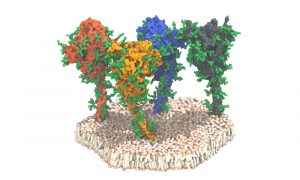
Researchers studied the spike protein on the surface of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. With its spikes, the virus binds to human cells and infects them. The study gave surprising insights into the spike protein, including an unexpected freedom of movement and a protective coat to hide it from antibodies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
26 May 2020
In the Leptin Group, Eva Hasel investigates the innate immune system in Japanese rice fish.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
4 February 2020
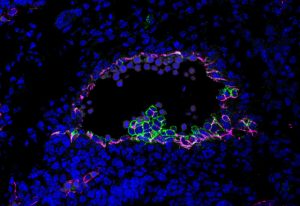
Morgan Oatley and her colleagues in Christophe Lancrin’s group investigated how haematopoietic stem cells emerge from the endothelium in developing mouse embryos.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
22 January 2020

The new EMBL spinoff company Araxa Biosciences GmbH aims to set new standards for the development of antibody-based therapeutics and diagnostics
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
lab-mattersscience-technology
20 January 2020
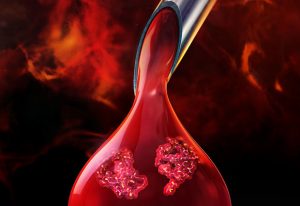
EMBL scientists identify drug targets in blood and organs
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
14 January 2020

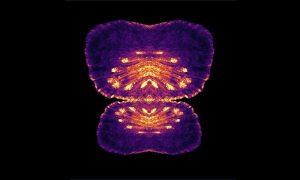
This image has been composed from thousands of individual super-resolution microscopy images. It was created by Markus Mund in the Ries Group.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
24 December 2019
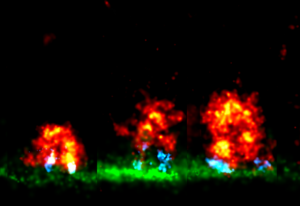
What looks like a photo-series of an explosive eruption are actually uptaking proteins, captured by Markus Mund from the Ries Group at EMBL Heidelberg. The images were made in an attempt to learn how the different proteins that take up molecules into the cells via endocytosis – the cellular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
25 September 2019

Fruit flies have something that we don’t have: they produce a protein called dumpy. This protein is the largest created by insects, and is comparable in size to the largest human protein – titin. While titin is vital for our muscle function, dumpy connects the soft cells of the insect’s…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
6 August 2019

Schoolchildren get creative with 3D protein structures
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsscience
14 February 2019

EMBL scientists identify RNA regulating protein behaviour in switch of normal roles
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
7 November 2018
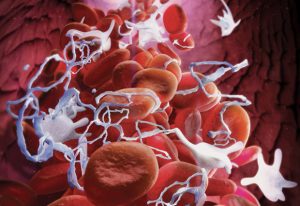
EMBL scientists investigate the structure of a key protein involved in blood clotting
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
2 November 2018
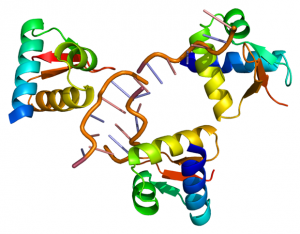
The Hentze Lab enhanced a RNA-interactome capture technique to pave the way towards medical progress
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
26 July 2018
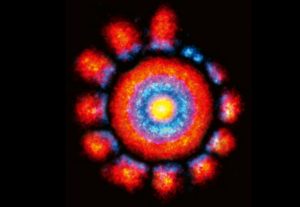
EMBL researchers visualise the proteins needed to capture molecules and bring them into a cell
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
25 June 2018

EMBL researchers develop method that simplifies the isolation of DNA- and RNA- protein complexes
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
26 April 2018
EMBL scientists uncover large solubility and thermal stability changes of proteins during the cell cycle
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
15 March 2018
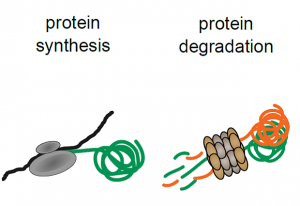
Scientists at EMBL and Cellzome develop technology to monitor the effects of drug treatments on protein degradation and synthesis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
11 August 2013
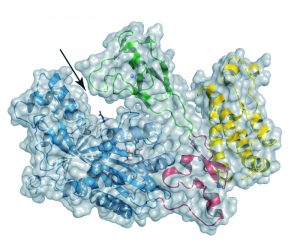
Like a fireman who becomes an arsonist, a protein that prevents cells becoming cancerous can also cause tumours, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Grenoble, France, have discovered. The finding, published today in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, stems…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
31 January 2013
Scientists at the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) and the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology in the UK have discovered how our genome keeps the effects of mutations in check. The discovery, published in the journal Cell, will help in the study of diseases such as cancer and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
23 September 2012
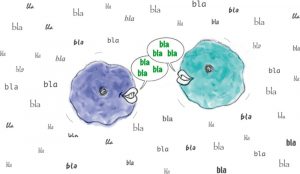
In a nutshell: New method allows precise analysis of proteins released by cells over time (distinguishes them from proteins in the cells’ culture serum) Advantages: cells don’t have to be starved: avoids bias and allows more cell types to be studied; can follow fast reactions like immune…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
2 August 2012
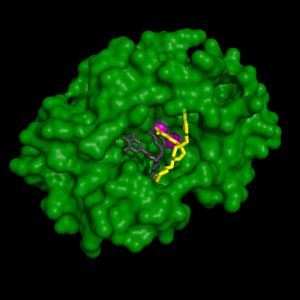
Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Grenoble, France, have determined the detailed 3-dimensional structure of part of the flu virus’ RNA polymerase, an enzyme that is crucial for influenza virus replication. This important finding is published today in PLoS…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
3 June 2012
As a retrovirus matures, the two parts of its shell protein (red and blue or yellow and blue) dramatically rearrange themselves, twisting and moving away from each other. (Credit: EMBL/T.Bharat) Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have for the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
24 May 2012
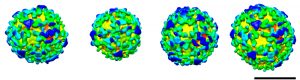
These spheres may look almost identical, but subtle differences between them revealed a molecular version of the robots from Transformers. Each sphere is a vesicle, a pod that cells use to transport materials between different compartments. The images, produced by Marco Faini from John…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
19 February 2012
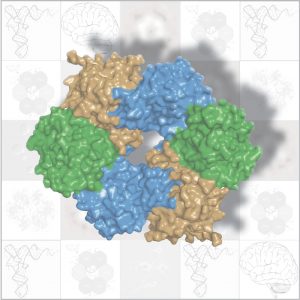
In fairy tales, magic rings endow their owners with special abilities: the ring makes the wearer invisible, fulfils his wishes, or otherwise helps the hero on the path to his destiny. Similarly, a ring-like structure found in a protein complex called ‘Elongator’ has led researchers at the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
14 February 2012
Myomesin stretching to 2.5 times its length. Credit: EMBL/Wilmanns. In this video, a protein called myomesin does its impression of Mr. Fantastic, the leader of the Fantastic Four of comic book fame, who performed incredible feats by stretching his body. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
4 May 2008
Influenza is currently a grave concern for governments and health organisations around the world. Now one of the tactics used by influenza virus to take over the machinery of infected cells has been laid bare by structural biologists at the EMBL, the joint Unit of Virus Host-Cell Interaction of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
25 February 2007
In 1918, 50 million people died during a worldwide influenza pandemic caused by mutation of a bird-specific strain of the influenza virus. Recently H5N1, another highly infectious avian strain has caused outbreaks of bird flu around the world. There is great concern that this virus might also…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
11 January 2006

Imagine grabbing two snakes by the tail so that they can’t wriggle off in opposite directions. Scientists at the Hamburg Outstation of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and collaborators from King’s College in London have now discovered that something similar happens to a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
21 December 2005
Researchers at the International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB) in India and a unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in France have made a key discovery about a molecule that helps the malaria parasite infect human cells. India is one of the countries…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
15 November 2005
Most of what happens in cells is the work of machines that contain dozens of molecules, chiefly proteins. With the completion of human and other genomes, researchers now have a nearly complete ‘parts list’ of such machines; what’s lacking is the manual telling where all the pieces…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
25 August 2005
Achieving equality between the sexes can be a challenge even for single cells. Since evolution began removing bits of male DNA to create the ‘Y’ chromosome, males have had a single copy of certain key genes on the X chromosome, whereas females have two. Normally this would lead females…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
3 February 2005
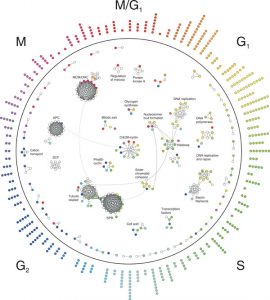
Most things that happen in the cell are the work of ‘molecular machines’ – complexes of proteins that carry out important cellular functions. Until now, scientists didn’t have a clear idea of when proteins form these machines – are these complexes pre-fabricated or put…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
No results found

















































