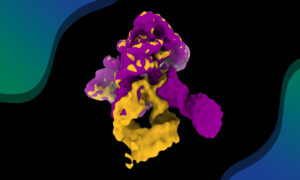
RNA in action: filming a ribozyme’s self-assembly
Researchers have visualised, in unprecedented detail, how a large RNA molecule assembles itself into a functional machine.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology
Showing results out of

Researchers have visualised, in unprecedented detail, how a large RNA molecule assembles itself into a functional machine.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology

An EMBL alumnus’ work with tRNA, along with support from EMBLEM, has led to a start-up, Umlaut.bio, that is positioned to aid drug development.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2025
people-perspectives

A recent symposium on ‘The complex life of RNA’ brought together scientists from across the world interested in exploring one of the most crucial molecules essential to life.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
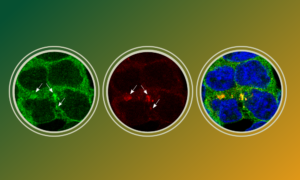
Scientists have discovered how the antiviral protein TRIM25 finds and binds viral RNA to activate an innate immune response.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
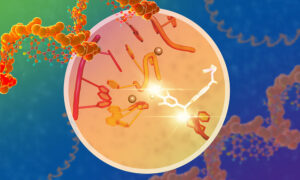
A new research paper published in Nature Communications lays the groundwork for the development of new drugs specific to genetic mutations or alterations responsible for the onset of tumours or genetic diseases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

EMBL Grenoble’s Kowalinski Group analysed the structure of an enzyme responsible for modifying tRNA molecules to fine-tune protein production. They discovered that to distinguish almost identical, yet different, tRNA molecules, the enzyme uses help from another enzyme – a type of cooperation…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

Simone Heber talks about studying RNA transport, organising the Bike Club at EMBL, and participating in the Ironman World Championship.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2024
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
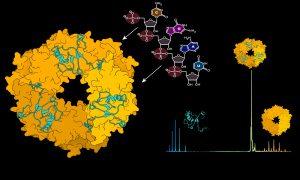
The Kosinski Group at EMBL Hamburg collaborated with other groups in Hamburg to reveal critical steps in Lassa virus ribonucleoparticle assembly and recruitment, and the crucial role played by RNA in in the Lassa virus life cycle.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

EMBL Hamburg, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Postnova Analytics GmbH, and BioNTech SE have developed a new method to quantitatively investigate sizes of nanoparticles containing mRNA. It may become an important part of regular characterisation of mRNA nanomedicines in the future.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

Pioneers of the mRNA nanomedicines technology receive 2023 Nobel Prize in Physiology or medicine. EMBL is pleased to have supported the development of the application of the mRNA nanomedicine technology through our long-standing collaboration with BioNTech, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

EMBL’s French site was highlighted in a short film presenting its expertise in structural biology research and services.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS2023
connectionslab-matters

EMBL researchers now understand the function of an elusive small DNA in bacteria and have developed a tool that can be used to better understand what might ‘switch on’ bacterial immune defences.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
EMBL research with Enolase 1 (ENO1) points to a possible new way to understand RNA’s leading role in how cells develop.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

EMBL Heidelberg’s Matthias Hentze receives the Biochemical Society’s Centenary Award for his discoveries in RNA biology.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS2022
embl-announcementslab-matters

Genomes are made up of thousands of individual pieces – genes – which are expressed at different levels. Researchers at EMBL have shed light on how the placement of a gene affects its expression, as well as that of its neighbours.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
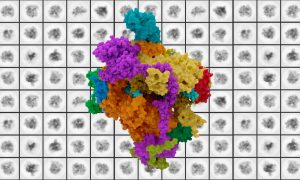
New structural biology research provides fundamental information critical to understanding enzyme mutations connected to rare diseases and cancers.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
RNA vaccines, such as the ones for COVID-19, represent a new approach in vaccine technology. Cy Jeffries, faculty staff scientist at EMBL Hamburg, explains the clever technology behind RNA vaccines, and how structural biology contributes to its development. EMBL Hamburg collaborated on several…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
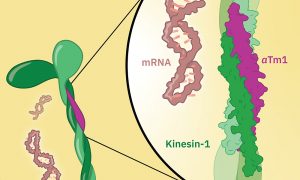
EMBL scientists generate a high-resolution crystal structure of the Kinesin-1/aTm1 transport complex in the fruit fly.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

New software enables scientists to visualise RNA secondary structures using the world’s largest RNA structure dataset.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
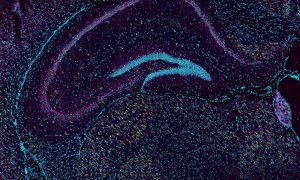
At EMBL, we have many dream teams – groups of individuals who support each other, innovate, and work together. One of those dream teams bridges two core facilities at EMBL Rome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
New EMBL research shows where & to what degree a component of cellular machinery known as RNA Pol III is mutated and becomes problematic.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
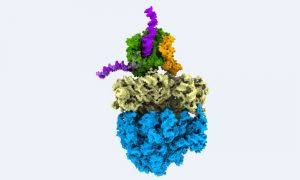
This colourful image shows biological information flow in action: It’s a supramolecular assembly of DNA, RNA and proteins, observed directly inside a bacterial cell while turning genetic information into protein.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

One of EMBL’s newest group leaders, Olivier Duss, will explore how RNA folds into functional structures and how it works with proteins to control a diverse range of activities in the cell.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
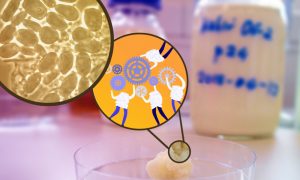
Researchers discovered the dominant species of bacteria in kefir grains cannot endure without other species that help the 'team' survive.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
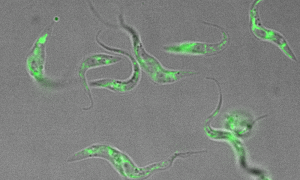
Members of the EMBL community are working to improve our understanding of the parasites that cause malaria and sleeping sickness
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Biotechnology company BioNTech and Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz conduct collaborative research with EMBL scientists at the beamline P12 in Hamburg
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

While global research on coronaviruses has shed light on the function of many SARS-CoV-2 proteins, the role of some crucial components remains unknown. Researchers at EMBL Grenoble will use a range of structural biology methods to try to solve some of the puzzles of the molecular mechanics of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
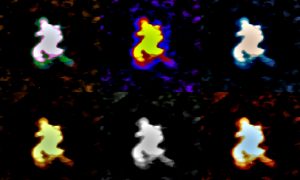
Researchers from EMBL Grenoble have developed a way to visualise large RNAs in 3D using biochemical and structural biology techniques.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
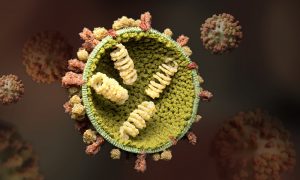
The infectious disease commonly known as flu is caused by the influenza virus. It spreads around the world in seasonal outbreaks, causing millions of infections and hundreds of thousands of deaths each year. Stephen Cusack, Head of EMBL Grenoble, has been studying different aspects of the influenza…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists working in the groups of Matthias Hentze and Wolfgang Huber have created RBPbase – a database of RNA-binding proteins – to assist the identification of proteins that interact with the SARS-CoV-2 RNA genome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
The largest and most comprehensive catalogue of cancer-specific RNA alterations reveals new insights into the cancer genome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

EMBL Director honoured by the international RNA Society
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS2020
embl-announcementsevents

MEG3 adopts a complex three-dimensional structure to fulfil its tumour suppressor function.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists identify RNA regulating protein behaviour in switch of normal roles
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
Researchers develop new method to analyse the entire protein-RNA network of the cell
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
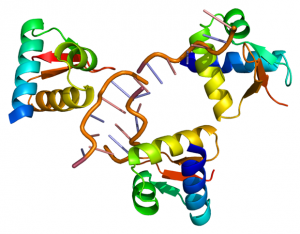
The Hentze Lab enhanced a RNA-interactome capture technique to pave the way towards medical progress
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

EMBL researchers develop method that simplifies the isolation of DNA- and RNA- protein complexes
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Elisa Izaurralde, EMBL alumna, has passed away
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2018
alumnipeople-perspectives

EMBL scientists unveil how 3D chromatin structure affects RNA splicing
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
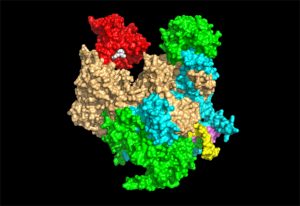
ERC grantee Stephen Cusack shares his vision for the next ten years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
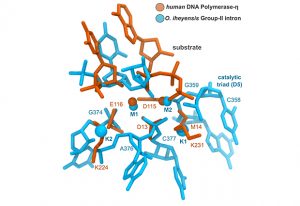
EMBL scientists superimpose structures of two-metal-ion enzymes and reveal new potential drug targets
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

New technique reveals uncharted docking sites in RNA-binding proteins
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
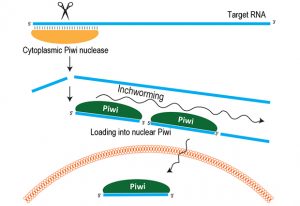
European team identify mechanism for producing piRNAs that silence jumping genes in germline cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

RNAcentral is the first unified resource for all types of non-coding RNA data.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
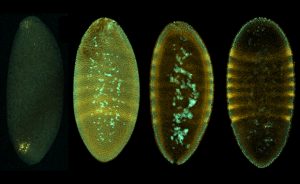
How fruit flies beat the cold, plus the value of precisely controlled experiments and detailed analysis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology

Focusing on basic research is crucial for the development of more advanced genetics techniques
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
The molecular machine that makes essential components of ribosomes – the cell’s protein factories – is like a Swiss-army knife, researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and the Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas in Madrid, Spain, have found.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
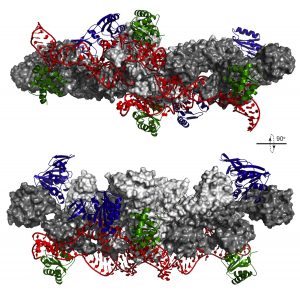
An important step in building ribosomes – the cell’s protein factories – is like a strictly choreographed dance, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have discovered. To build these factories, other ‘machines’ inside the cell have to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
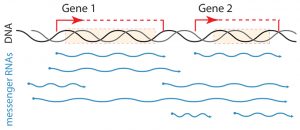
Like musicians in an orchestra who have the same musical score but start and finish playing at different intervals, cells with the same genes start and finish transcribing them at different points in the genome. For the first time, researchers at EMBL have described the striking diversity of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
Studies screening the genome of hundreds of thousands of individuals (known as Genome-wide association studies or GWAS) have linked more than 100 regions in the genome to the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
A research team of scientists from EMBL Grenoble and the IGBMC in Strasbourg, France, have, for the first time, described in molecular detail the architecture of the central scaffold of TFIID: the human protein complex essential for transcription from DNA to mRNA. The study, published today…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology

In one of the most famous faux pas of exploration, Columbus set sail for India and instead ‘discovered’ America. Similarly, when scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, set out to find enzymes – the proteins that carry out chemical…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
Influenza is and remains a disease to reckon with. Seasonal epidemics around the world kill several hundred thousand people every year. In the light of looming pandemics if bird flu strains develop the ability to infect humans easily, new drugs and vaccines are desperately sought. Researchers at…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
It does not take much to injure a muscle. Sometimes one sudden, inconsiderate movement does the job. Unfortunately, damaged muscles are not as efficient at repair as other tissues such as bone. Researchers of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s Mouse Biology Unit (EMBL), Italy, and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Cells in an embryo divide at an amazing rate to build a whole body, but this growth needs to be controlled. Otherwise the result may be defects in embryonic development or cancer in adults. Controlling growth requires that some cells divide while others die; their fates are determined by signals…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Mutations in genes are the basis of evolution, so we owe our existence to them. Most mutations are harmful, however, because they cause cells to build defective proteins. So cells have evolved quality control mechanisms that recognize and counteract genetic mistakes. Now scientists of the Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
The world’s three leading public repositories for DNA and RNA sequence information have reached 100 gigabases (100,000,000,000 bases; the ‘letters’ of the genetic code) of sequence. Thanks to their data exchange policy, which has paved the way for the global exchange of many types…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS2005
connectionslab-matters

A systematic search through human genes has begun at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany. Working within the MitoCheck consortium that includes 10 other institutes throughout Europe, the EMBL scientists will silence all human genes, one-by-one, to find those…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS2005
connectionslab-matters
No results found