
All heart
Science & Technology A community of scientists is looking at the estimated three billion heart muscle cells in a human heart to better understand heart disease.
2021
alumniscience-technology

Science & Technology A community of scientists is looking at the estimated three billion heart muscle cells in a human heart to better understand heart disease.
2021
alumniscience-technology

Lab MattersPeople & Perspectives EMBL group leaders Julia Mahamid, Anna Kreshuk & Jonas Ries awarded Chan Zuckerberg Initiative grant to advance what we see inside cells.
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
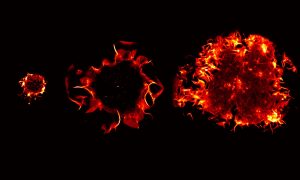
Science & Technology The EMBL Picture of the Week features a series of Jurkat T cells during different stages of the activation process.
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
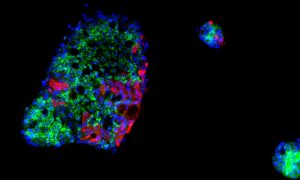
Science & Technology EMBL scientists, together with collaborators from Heidelberg University, have provided further evidence of the gut’s role in COVID-19.
2021
sciencescience-technology
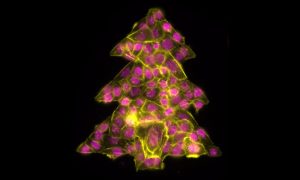
Science & Technology It is that time of year to get into the holiday spirit, prepare for some time at home and relax after a strange and stressful year. Even the cells in our Picture of the Week are getting into the holiday spirit, forming this colourful Christmas tree.
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Science & Technology While cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) was first envisioned in 1968, the advances the Mahamid group are bringing to this 3D method for studying molecules directly inside cells are new, and are likely to greatly expand its use.
2020
sciencescience-technology
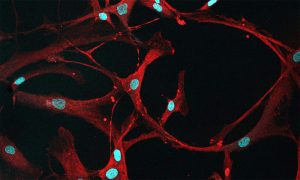
Science & Technology Studying cancers means also knowing what healthy cells look like. In this case, mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) from healthy bone marrow are a bit ‘loopy’.
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
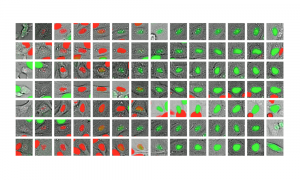
Science & Technology Members of an EMBL-led research group with collaborators in Estonia and Russia have built and trained a deep learning model to better understand how cells grow and divide.
2020
sciencescience-technology
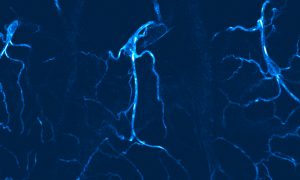
Science & Technology Beautiful flashes of blue colour help light the way for researchers to study cells in fruit fly larva that provide oxygen to tissues.
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
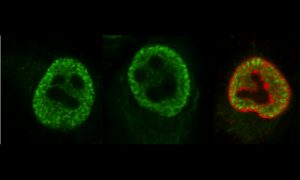
Science & Technology Despite their ghostly appearance, these are very real cell nuclei infected with Influenza A virus – the only influenza virus known to cause pandemics.
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
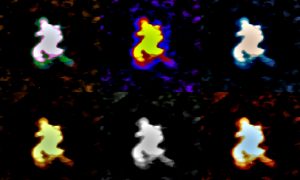
Science & Technology Researchers from EMBL Grenoble have developed a way to visualise large RNAs in 3D using biochemical and structural biology techniques.
2020
sciencescience-technology
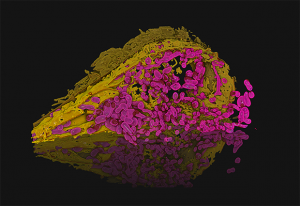
Science & Technology In this image, Julian Hennies from the Schwab Team has reconstructed the 3D structure of a human cell's organelles.
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
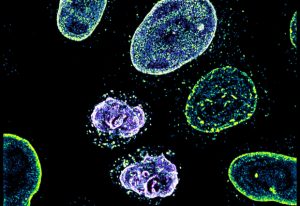
Science & Technology This picture of the week, taken by Arina Rybina in the Ellenberg group at EMBL Heidelberg, shows a high-resolution 3D microscopy image of living human cells: HeLa cells. In this fascinating fluorescing microspace, two newly formed daughter nuclei are captured to study the assembly of nuclear pore…
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
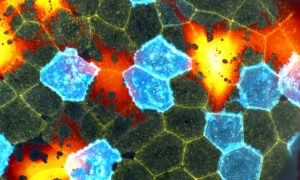
Science & Technology This beautiful mosaic of mostly hexagonal cells is the outer skin layer of a zebrafish larva as seen under a microscope. Each skin cell exhibits a unique pattern of actin ridges. Actin is a family of globular multifunctional proteins found in almost all eukaryotic cells. Actin forms microfilaments,…
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
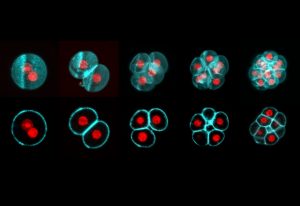
Science & Technology All mammalian life starts with the fusion of egg and sperm, resulting in the creation of a single cell called a zygote. This develops into an embryo through a series of cell divisions, in which the number of cells doubles at each step. Todays’ Picture of the Week was taken by Manuel Eguren of the…
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
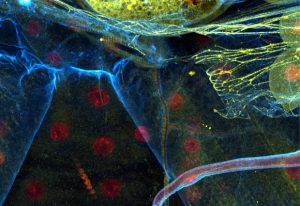
Science & Technology Today’s picture of the week is not only a colourful one, it is also a snapshot of the vast number of shapes that the cells inside an animal body can adopt. How this variety comes about is investigated in the Leptin group at EMBL Heidelberg. To understand the shapes of the cells in fruit fly…
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
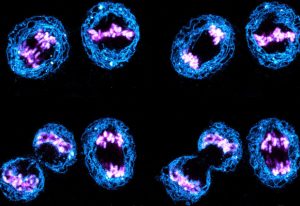
Science & Technology This colourful picture, taken by EMBL postdoc Arina Rybina using a confocal fluorescence microscope, shows human cells in the process of cell division. Eventually, each mother cell brings into existence two identical daughter cells. To visualise the process by light microscopy, different cell…
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have combined the power of two kinds of microscope to produce a 3-dimensional movie of how cells ‘swallow’ nutrients and other molecules by engulfing them. The study, published today in Cell, is the…
2012
sciencetechnology-and-innovation
Science & Technology Is it a boy or a girl? Expecting parents may be accustomed to this question, but contrary to what they may think, the answer doesn’t depend solely on their child’s sex chromosomes. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany and the Medical Research…
2009
sciencescience-technology
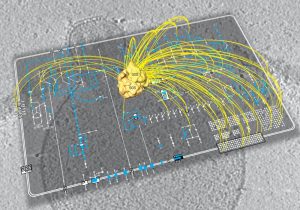
Science & Technology What are the bare essentials of life, the indispensable ingredients required to produce a cell that can survive on its own? Can we describe the molecular anatomy of a cell, and understand how an entire organism functions as a system? These are just some of the questions that scientists in a…
2009
sciencescience-technology
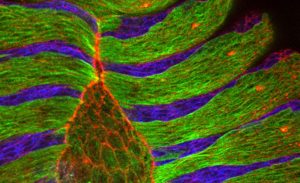
Science & Technology Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, came a step closer to understanding how cells close gaps not only during embryonic development but also during wound healing. Their study, published this week in the journal Cell, uncovers a fundamental…
2009
sciencescience-technology
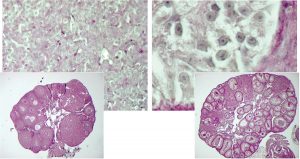
Science & Technology What at the first sight could be pictures of planets or other cosmic structures are actually microscope images of balls (cysts) of human kidney cells. They were taken by Emmanuel Reynaud, in the group of Ernst Stelzer at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), with a widefield microscope.…
2008
sciencescience-technology
Science & Technology A cell is a busy place. In a permanent rush hour, molecules are transported along a dynamic motorway system made up of filaments called microtubules. Microtubules constantly grow and shrink and are rapidly assembled wherever a cargo needs to go, but during this transportation process they need to…
2006
sciencescience-technology

Science & Technology Blood cells have limited lifespans, which means that they must be continually replaced by calling up reserves and turning these into the blood cell types needed by the body. Claus Nerlov and his colleagues at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) unit in Monterotondo, Italy, in…
2006
sciencescience-technology
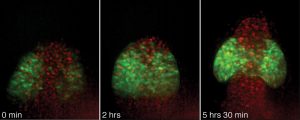
Science & Technology Eyes are among the earliest recognisable structures in an embryo; they start off as bulges on the sides of tube-shaped tissue that will eventually become the brain. Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg have now discovered that cells are programmed to make…
2006
sciencescience-technology
Science & Technology Achieving equality between the sexes can be a challenge even for single cells. Since evolution began removing bits of male DNA to create the ‘Y’ chromosome, males have had a single copy of certain key genes on the X chromosome, whereas females have two. Normally this would lead females…
2005
sciencescience-technology
Science & Technology One of the most basic yet least understood processes in our bodies is how cells crawl along tissues. This behavior is essential to the formation of an embryo and other processes, but it must be tightly controlled. A disturbance can lead to the spread of cancer cells or diseases like Spina…
2005
sciencescience-technology
No matching posts found
Looking for past print editions of EMBLetc.? Browse our archive, going back 20 years.
EMBLetc. archive