
Shedding light on rare diseases: open data and model organisms
Why open data from model organisms is essential for rare disease research.
2023
perspectivesscience

Why open data from model organisms is essential for rare disease research.
2023
perspectivesscience

Jo McEntyre talks about data services, open data and a new era for research assessment.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesperspectives

Microbial communities play essential roles in ocean ecology and planetary health. A recent publication highlights priorities for understanding and protecting ocean microbiomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

Scientists identify previously unexplored gene segments to be added to human genome databases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology

EMBO Director Fiona Watt discusses preprints, data sharing, and evaluation in light of EMBL’s new Open Science policy
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
A cell is a busy place. In a permanent rush hour, molecules are transported along a dynamic motorway system made up of filaments called microtubules. Microtubules constantly grow and shrink and are rapidly assembled wherever a cargo needs to go, but during this transportation process they need to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology

Today, Janez Potočnik, European Commissioner for Science and Research, received a statement of support for the European Charter for Researchers and the Code of Conduct for the Recruitment of Researchers from EIROforum. “The EIROforum partners warmly welcome this valuable initiative by…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS2006
connectionslab-matters
Today the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) launches its new, faster and easier website with an exhaustive search engine at its centre. The web interface has been streamlined on the basis of user feedback from a recent extensive…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
lab-mattersscience-technology
The BioModels Database, hosted by the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) in Cambridge, UK, has entered a formal data-exchange agreement with the Database of Quantitative Chemical Signalling (DOQCS) of the National Centre for…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS2006
connectionslab-matters
Today the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) launches CiteXplore, a new freely accessible literature resource service. Biological researchers require two crucial sources of information: scientific literature published in peerreviewed…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
lab-mattersscience-technology

Muscle wasting can occur at all ages as the result of genetic defects, heart failure, spinal injury or cancer. A therapy to cure the loss of muscle mass and strength, which has a severe impact on patients’ lives, is desperately sought. Blocking a central signal molecule, researchers from the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Today, the German Minister for Education and Research, Annette Schavan, breaks ground for the new training and conference centre for the life sciences that will be built on the EMBL campus in Heidelberg. The German Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF), the Klaus Tschira…
LAB MATTERS2006
lab-matters
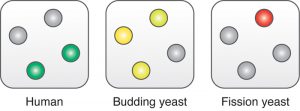
The life of a cell is all about growing and dividing at the right time. That is why the cell cycle is one of the most tightly regulated cellular processes. A control system with several layers adjusts when key components of the cell cycle machinery are produced, activated and degraded to make sure…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Today the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) and the Spanish Ministry for Education and Science (MEC) officially launch their new joint EMBL/CRG Research Unit in Systems Biology on the campus of the Barcelona Biomedical Research Park. The Spanish…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS2006
embl-announcementslab-matters

Blood cells have limited lifespans, which means that they must be continually replaced by calling up reserves and turning these into the blood cell types needed by the body. Claus Nerlov and his colleagues at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) unit in Monterotondo, Italy, in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
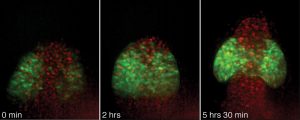
Eyes are among the earliest recognisable structures in an embryo; they start off as bulges on the sides of tube-shaped tissue that will eventually become the brain. Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg have now discovered that cells are programmed to make…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Cells in an embryo divide at an amazing rate to build a whole body, but this growth needs to be controlled. Otherwise the result may be defects in embryonic development or cancer in adults. Controlling growth requires that some cells divide while others die; their fates are determined by signals…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Today EMBL scientists, EMBL’s commercial affiliate, EMBL Enterprise Management Technology Transfer GmbH (EMBLEM) and EMBL’s venture vehicle, EMBL Ventures GmbH, announce the foundation of Elara Pharmaceuticals GmbH, a start-up company that will translate basic research findings into new…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
lab-mattersscience-technology
Depression, coordination and speech problems, muscle weakness and disability are just a few of the symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Researchers from the Mouse Biology Unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Italy and the Department of Neuropathology at the Faculty of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Scientists will be able to access a vast collection of biomedical research at the touch of a button thanks to a major new initiative that aims to promote the free transfer of ideas in a bid to speed up scientific discovery. Based on a model currently used in the United States, UK PubMed Central…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS2006
embl-announcementslab-matters
In the early days of X-ray crystallography obtaining a three-dimensional model of a protein required wire models, screws, bolts and years of tedious calculations by hand. Today macromolecular models are built by computers – thanks to sophisticated software and in particular a package called…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
lab-mattersscience-technology
Croatia has officially joined the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) as the organisation’s 19th Member State. The Croatian parliament ratified its membership after EMBL’s council had accepted the country’s application. “Joining EMBL is a very important step…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS2006
embl-announcementslab-matters
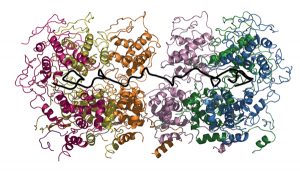
Ebola, measles and rabies are serious threats to public health in developing countries. Despite different symptoms all of the diseases are caused by the same class of viruses that unlike most other living beings carry their genetic information on a single RNA molecule instead of a double strand of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Tuberculosis remains one of the deadliest threats to public health. Every year two million people die of the disease, which is caused by the microorganism Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Roughly one third of the world’s population is infected and more and more bacterial strains have developed…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Today the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s (EMBL) European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), the Swiss Institute for Bioinformatics (SIB), the University of Cologne, Germany, and the European Patent Office launch FELICS (Free European Life-science Information and Computational Services).…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS2006
connectionslab-matters
EMBOSS, the European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite, has received a vital funding boost from the UK Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) that will guarantee its continued maintenance under an open source license for the next three years. This ends two years of…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS2006
connectionslab-matters
Today three research organisations announce the merging of their expertise to fight cardiovascular diseases, which are among the most common health problems and causes of death in the world. The Magdi Yacoub Institute (MYI) at the UK’s Harefield Heart Science Centre, Imperial College London,…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS2006
connectionslab-matters
Today the network of excellence for Biology and Pathology of the Malaria Parasite (BioMalPar), will bring together the world’s elite in the field of Malaria research at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg. At the second annual BioMalPar conference, organised jointly…
CONNECTIONS2006
connectionsevents
Science is moving more rapidly than ever; one groundbreaking discovery chases the next at an incredible speed. School teachers have trouble keeping up with the pace, and many pupils call science classes “boring”. Today, Europe’s major research organisations launch Science in…
LAB MATTERS2006
lab-matters
Recent research at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) reveals new insights into how cells achieve equality between the sexes. A new link discovered between the membrane surrounding the nucleus and the male X-chromosome in fruit flies may play a crucial role in determining how active…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
In 1870 the German scientist Ernst Haeckel mapped the evolutionary relationships of plants and animals in the first ‘tree of life’. Since then scientists have continuously redrawn and expanded the tree adding microorganisms and using modern molecular data, yet, many parts of the tree…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
A detailed structural picture of a molecule that plays a key role in activating the Epstein Barr Virus in human cells has now been obtained by researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the Institut de Virologie Moléculaire et Structurale (IVMS), associated with the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Today researchers in Germany announce they have finished the first complete analysis of the “molecular machines” in one of biology’s most important model organisms: S. cerevisiae (baker’s yeast). The study from the biotechnology company Cellzome, in collaboration with the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology

Imagine grabbing two snakes by the tail so that they can’t wriggle off in opposite directions. Scientists at the Hamburg Outstation of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and collaborators from King’s College in London have now discovered that something similar happens to a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology

On Friday, 13 January 2006, the new Carl-Ivar Brändén Building (CIBB) will be inaugurated on the Polygone Scientifique Campus in Grenoble, France. The CIBB will be operated as a collaboration between major international and national partners based in Grenoble and is a further step in the…
LAB MATTERS2006
lab-matters
No matching posts found