
Exploring diversity in cell division
Science & Technology New research by EMBL scientists shows how different modes of cell division used by animals and fungi might have evolved to support diverse life cycles.
2024
science-technology

Science & Technology New research by EMBL scientists shows how different modes of cell division used by animals and fungi might have evolved to support diverse life cycles.
2024
science-technology

Alumni, EMBL Announcements Two former EMBL scientists have been recognised for their outstanding contributions to research and leadership capabilities in the fields of evolutionary cell biology and molecular medicine.
2024
alumniembl-announcements
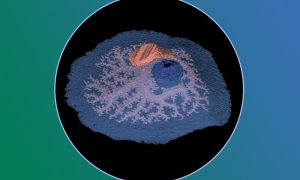
Science, Science & Technology Sponges lack muscles and neurons. Yet, they make coordinated movements. Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg have discovered that sponge movement is controlled by an ancient ‘relaxant-inflammatory’ response that is also present in vertebrate blood vessels. The findings shed light on sponge physiology…
2024
sciencescience-technology

Connections, Events Scientists from the MELIS department at UPF and EMBL Barcelona have organised a symposium to discuss the work of the visionary Catalan scientist Pere Alberch, who passed away 25 years ago.
2023
connectionsevents

Science EMBL researchers are stepping outside the lab and thinking outside the box to understand the basic principles that underlie the development and evolution of organismal characteristics.
2023
science

Alumni, EMBL Announcements Two former EMBL staff members have been recognised for their outstanding contributions to research in the fields of brain evolution and cancer.
2022
alumniembl-announcements

Science, Science & Technology What can sponges tell us about the evolution of the brain? Sponges have the genes involved in neuronal function in higher animals. But if sponges don’t have brains, what is the role of these? EMBL scientists imaged the sponge digestive chamber to find out.
2021
sciencescience-technology

Lab Matters, People & Perspectives Gautam Dey is fascinated by the evolutionary origins of the nucleus, and is looking forward to making the most of EMBL's infrastructure.
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
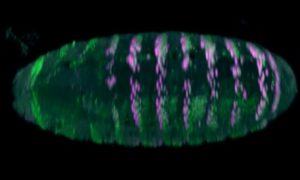
Science, Science & Technology Researchers from EMBL Heidelberg have established an automated pipeline to create mutations in genomic enhancers, letting them watch evolution unfold before their eyes.
2020
sciencescience-technology

Science, Science & Technology Exploring the diverse routes by which EMBL scientists are driving forward neurobiology
2019
sciencescience-technology
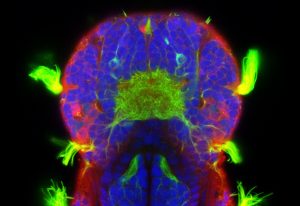
Science, Science & Technology EMBL researchers discover that four organs in a marine worm’s head can sense different chemicals
2018
sciencescience-technology

Lab Matters, People & Perspectives EMBL alumna, Èlia Benito-Gutiérrez, on how her research and career evolved after searching the seas
2018
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
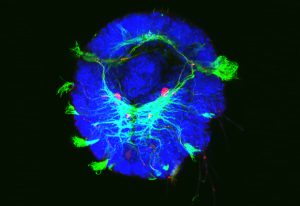
Science, Science & Technology EMBL scientists discover how a molecule’s role changes from simple metabolite to instructive signal
2018
sciencescience-technology

Science, Science & Technology How Darwin’s work revealed the intimate relationship between orchids and insects
2018
sciencescience-technology

People & Perspectives, Science Meet Justin Crocker, EMBL’s new group leader in gene regulation during evolution and development
2017
people-perspectivesscience
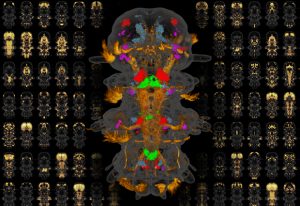
Science, Science & Technology EMBL researchers complete a molecular atlas showing gene expression in all cells in an entire animal
2017
sciencescience-technology
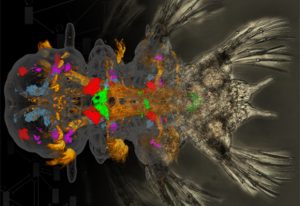
Science, Science & Technology ERC grantee Detlev Arendt shares his vision for the next ten years
2017
sciencescience-technology
Science, Science & Technology A rapid, versatile mechanism that modifies proteins is revealed to be crucial for the evolutionary process
2016
sciencescience-technology
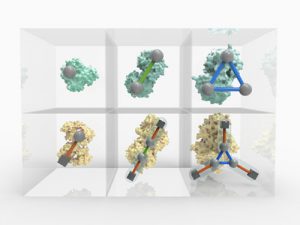
Science, Science & Technology Making it easier to visualise, understand and predict how proteins combine to drive biological processes.
2015
sciencescience-technology

Events, Lab Matters Two PhD students sink their teeth into the science and speculations of Jurassic Park.
2015
eventslab-matters

Science, Science & Technology From jumping genes to organ transplants, the non-human features that make us human.
2015
sciencescience-technology
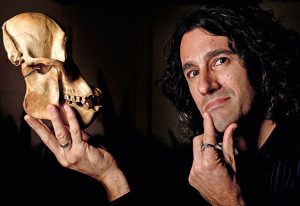
People & Perspectives, Science & Technology What really sets humans apart? Forming societies, teaching and compassion, says Agustin Fuentes.
2015
people-perspectivesscience-technology

Events, People & Perspectives Highlights from the 'What makes us human?' symposium at EMBL Heidelberg.
2015
eventspeople-perspectives
Science, Science & Technology From the role of diatoms to how life evolved - scientists' pressing questions about life in the sea.
2015
sciencescience-technology

Connections, Events Insights from organisers of upcoming EMBO|EMBL Aquatic Microeukaryotes symposium.
2015
connectionsevents

Events, Lab Matters A contagious cancer threatens the Tasmanian devil – extract from Science in School journal.
2015
eventslab-matters

Science Tara Oceans results reveal climate change insights, and a treasure trove of novel species and genes.
2015
science
Science New research shows that some proteins domains can function even with big parts missing.
2015
science
Science New single-cell genomics techniques bring ‘omics to evolution and development research.
2015
science

Lab Matters PhD student Silvia Rohr on studying eyes – and talking about it for a general audience.
2015
lab-matters

Science How do E.coli and similar bacteria grow safely? By using barrel-plugs as sensors.
2014
science

Science From anemones to starfish, sea creatures are helping understand development, evolution and more.
2014
science
Science How plankton gets jet lagged: the same hormone governs our sleep patterns and a daily marine migration.
2014
science
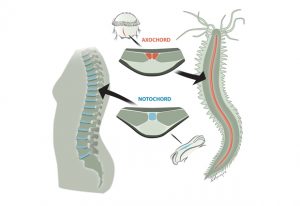
Science Evolutionary surprise: notochord likely evolved from muscle, earlier than assumed.
2014
science
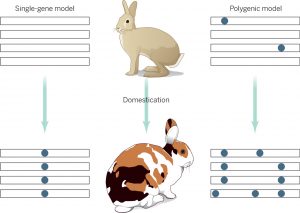
Science Bronwen Aken discusses what research into the rabbit genome reveals about animal domestication.
2014
science

Science Marmoset genome provides insights into chimerism: data available in Ensembl genome explorer
2014
science

Science Surprising finding: enhancers find their targets long before activation in Drosophila embryos
2014
science
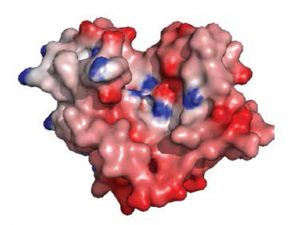
Science Surprising protein from a flu-like virus is 10 000th ESRF structure
2014
science
Science, Science & Technology In a nutshell: 1st map combining human genetic variation at different scales – from single letters to large chunks Based on genomes of 1092 healthy people from Europe, the Americas and East Asia Could help identify genetic causes of disease, rather than just links Data made freely available in…
2012
sciencescience-technology
Science, Science & Technology A team of geneticists and computational biologists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute and Cancer Research UK reveal how an ancient mechanism is involved in gene control and continues to drive genome…
2012
sciencescience-technology
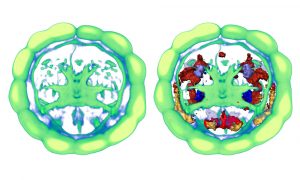
Science Our cerebral cortex, or pallium, is a big part of what makes us human: art, literature and science would not exist had this most fascinating part of our brain not emerged in some less intelligent ancestor in prehistoric times. But when did this occur and what were these ancestors? Unexpectedly,…
2010
science
Science The last ancestor we shared with worms, which roamed the seas around 600 million years ago, may already have had a sophisticated brain that released hormones into the blood and was connected to various sensory organs. The evidence comes not from a newly found fossil but from the study of microRNAs…
2010
science
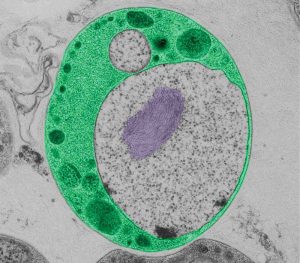
Science Although they are present almost everywhere, on land and sea, a group of related bacteria in the superphylum Planctomycetes-Verrucomicrobia-Chlamydiae, or PVC, have remained in relative obscurity ever since they were first described about a decade ago. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology…
2010
science

Science The best-selling novel The swarm captured the imagination of countless readers with the fascination of marine life. But it also showed how little we understand life in the depth of the ocean. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the Max Planck Institute (MPI)…
2008
science
Science Genetic recombination, the process by which sexually reproducing organisms shuffle their genetic material when producing germ cells, leads to offspring with a new genetic make-up and influences the course of evolution. In the current issue of Nature, researchers at the European Molecular…
2008
science
Science What makes a human different from a chimp? Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) have come one important step closer to answering such evolutionary questions correctly. In the current issue of Science they uncover…
2008
science
Science Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) in Hinxton, UK, have revealed new insights into how sex chromosomes are regulated. A chromatin modifying enzyme helps compensate for the fact that…
2008
science
Science UK-based researchers at the Medical Research Council Functional Genomics Unit in Oxford and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute in Cambridge have revealed the genetic makeup of the one of the world’s strangest mammals. They have analysed the DNA…
2008
science
Science Hormones control growth, metabolism, reproduction and many other important biological processes. In humans, and all other vertebrates, the chemical signals are produced by specialised brain centres such as the hypothalamus and secreted into the blood stream that distributes them around the body.…
2007
science

Science The rise of the central nervous system (CNS) in animal evolution has puzzled scientists for centuries. Vertebrates, insects and worms evolved from the same ancestor, but their CNSs are different and were thought to have evolved only after their lineages had split during evolution. Researchers from…
2007
science
Science Microorganisms make up more than a third of the Earth’s biomass. They are found in water, on land and even in our bodies, recycling nutrients, influencing the planet’s climate or causing diseases. Still, we know surprisingly little about the smallest beings that colonise Earth. A new…
2007
science
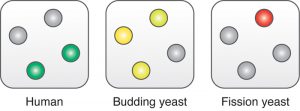
Science The life of a cell is all about growing and dividing at the right time. That is why the cell cycle is one of the most tightly regulated cellular processes. A control system with several layers adjusts when key components of the cell cycle machinery are produced, activated and degraded to make sure…
2006
science
Science Recent research at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) reveals new insights into how cells achieve equality between the sexes. A new link discovered between the membrane surrounding the nucleus and the male X-chromosome in fruit flies may play a crucial role in determining how active…
2006
science
Science In 1870 the German scientist Ernst Haeckel mapped the evolutionary relationships of plants and animals in the first ‘tree of life’. Since then scientists have continuously redrawn and expanded the tree adding microorganisms and using modern molecular data, yet, many parts of the tree…
2006
science
Science Species evolve at very different rates, and the evolutionary line that produced humans seems to be among the slowest. The result, according to a new study by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory [EMBL], is that our species has retained characteristics of a very ancient ancestor…
2005
science
Science Achieving equality between the sexes can be a challenge even for single cells. Since evolution began removing bits of male DNA to create the ‘Y’ chromosome, males have had a single copy of certain key genes on the X chromosome, whereas females have two. Normally this would lead females…
2005
science
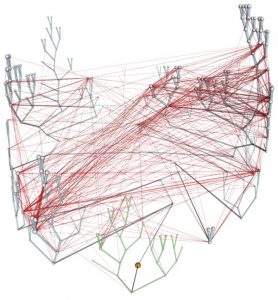
Science EBI researchers have changed our view of 4 billion years of microbial evolution. Christos Ouzounis and colleagues have gained intriguing quantitative insights into how gene families are transferred, not only ‘vertically’ through passage from one organism to its progeny, but also…
2005
science
No matching posts found
Looking for past print editions of EMBLetc.? Browse our archive, going back 20 years.
EMBLetc. archive