13 November 2024
Science & Technology
Scientists have developed a new machine-learning model to predict microbial load — the density of microbes in our guts — and used it to demonstrate how microbial load plays an important role in disease-microbiome associations.
24 September 2024
Science & Technology
EMBL Heidelberg researchers compared the effect of drugs on isolated bacteria versus those growing in communities. This is the first study showing that bacteria are more resilient when in community due to cross-protection strategies. This could help researchers design more efficient therapies.
31 July 2024
Science & Technology
Study shows that gut bacteria can metabolise carcinogens and cause them to accumulate in distant organs, leading to tumour development.
27 June 2024
Science & Technology
EMBL researchers and their partners have been studying microbial functions and interactions for the benefit of human and planetary health for the last two decades.
1 May 2024
Science & Technology
Scientists from EMBL Rome and EMBL Heidelberg found that disrupting the gut microbiome of male mice increases the risk of disease in their offspring. Their findings suggest that a father’s pre-conception environment can have lifelong effects on offspring.
8 March 2024

The MGnify data resource for microbiome data has launched the latest MGnify Genomes catalogue comprising 112,951 genomes derived from mouse gut datasets, represented by 2,847 species-level cluster representative genomes. This catalogue was generated as part of our work with the MRC funded…
2024
updates-from-data-resources
26 October 2023

EMBL Announcements
Jan Kosinski, Julia Mahamid, and Georg Zeller have received grants to enable ambitious projects aimed at mapping the cellular protein synthesis machinery in context and understanding complex host-microbiome interactions, respectively.
2023
embl-announcementsscience
20 October 2023

Science & Technology
Here are six takeaways from a recent EMBO/EMBL symposium that brought together scientists to discuss the state of research involving the human microbiome and its connection to health and disease.
2023
eventsscience-technology
5 September 2023

EMBL AnnouncementsLab Matters
Jordi van Gestel and Maria Zimmermann-Kogadeeva each receive 1.5 million EUR funding for research projects on microbial predators and the gut microbiome respectively
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
14 August 2023

People & Perspectives
EMBL-EBI Senior Scientist Rob Finn explains why data coordination and sharing are fundamental for a sustainable blue economy.
2023
people-perspectivesperspectivesscience
27 June 2023

Science & Technology
HoloFood, the first consistent collection of multiomic data about chicken and salmon gut microbiomes, set to enable the development of better animal feeds.
2023
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation
19 April 2023

People & Perspectives
As a postdoc Alex Almeida used bioinformatics to push the boundaries of what we know about the gut microbiome. Here, Almeida explains how his time at EMBL-EBI generated new research avenues, and how the skills and connections from his postdoc prepared him for leading his own research group at the…
2023
people-perspectivesperspectives
8 March 2023

EMBL AnnouncementsLab Matters
EMBL is leading the TREC project: the first pan-European and cross-disciplinary effort to examine life in its natural context.
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
6 February 2023

Funding awarded for developing tools to harness marine microbiome data for biotechnological applications and ecosystem services.
2023
announcementsscience
11 January 2023

Lab MattersPeople & Perspectives
Rob Finn, one of the co-chairs of the Microbial Ecosystems theme, discusses his work, the challenges of multidisciplinary research, and how the theme is already helping to promote the exchange of scientific ideas.
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
11 October 2022

Lab MattersScience & Technology
The final pilot project in Iceland marked the countdown to the ‘Traversing European Coastlines’ (TREC) expedition to study coastal ecosystems and their response to changes in the environment.
2022
lab-mattersscience-technology
15 September 2022

Science & Technology
EMBL researchers used data from over 300 human faecal microbiota transplants to gain an ecological understanding of what happens when two gut microbiomes clash.
2022
sciencescience-technology
14 July 2022

Science & Technology
Microbial communities play essential roles in ocean ecology and planetary health. A recent publication highlights priorities for understanding and protecting ocean microbiomes.
2022
sciencescience-technology
9 March 2022
Science & Technology
A molecular signature of 27 microorganisms in stool defines the high-risk population for the most common pancreatic cancer and could be used for early detection of the disease.
2022
sciencescience-technology
4 January 2022
Science & Technology
Researchers have identified hundreds of new bacterial species and viruses in the human skin microbiome.
2022
sciencescience-technology
20 December 2021

ConnectionsLab Matters
The agreement focuses on reinforcing the collaboration between scientists to strengthen our understanding of the organism in its environment.
2021
connectionslab-matters
15 December 2021

Science & Technology
Bork Group at EMBL Heidelberg analysed a new global gene database to study how genes emerge and spread across various habitats on our planet. In the future, the group will expand the database and use it for studying microbial gene evolution and dispersal at a finer-grained scale.
2021
sciencescience-technology
8 December 2021
Science & Technology
Researchers studying a massive cohort of European patients have found that commonly prescribed drugs for cardiometabolic disorders can have long-term effects on the gut microbiome. Such effects can complicate the understanding of how disease affects the microbiome and must be taken into…
2021
sciencescience-technology
25 November 2021

Lab MattersPeople & Perspectives
Maria Zimmermann-Kogadeeva is one of EMBL’s newest group leaders and a computational biologist whose research group applies computational modelling to better understand the metabolism of gut bacteria and their potential to have far-reaching impacts on other organs.
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
26 October 2021

Science & Technology
International project uses biomolecular data to improve animal feed and make meat production more sustainable
2021
sciencescience-technology
26 October 2021
Science & Technology
Using metagenomic data to find novel enzymes for plastic degradation and beyond
2021
sciencescience-technology
13 October 2021
Science & Technology
Researchers from EMBL’s Typas group and collaborators have analysed the effects of 144 antibiotics on the wellbeing of gut microbes. The study improves our understanding of antibiotics’ side effects and suggests a new approach to mitigating the adverse effects of antibiotics therapy on gut…
2021
sciencescience-technology
29 September 2021

Lab MattersPeople & Perspectives
In the lab, Diënty Hazenbrink works with microbes that live in our guts. In her free time, she enjoys wildlife photography. A shared set of skills facilitates both activities.
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
22 September 2021

ConnectionsLab Matters
EMBL and Helmholtz Association have signed a memorandum of understanding. The expanded collaboration of both institutions will focus on research related to health.
2021
connectionslab-matters
8 September 2021
Science & Technology
A new collaborative study led by EMBL group leaders Kiran Patil, Nassos Typas, and Peer Bork has found that common medications accumulate in human gut bacteria. This process reduces drug effectiveness and affects the metabolism of common gut microbes, thereby altering the gut microbiome.
2021
sciencescience-technology
16 June 2021

Science & Technology
Researchers investigate how external factors can influence the persistence of microbe species in the human gut
2021
sciencescience-technology
20 May 2021

EMBL AnnouncementsLab Matters
The Gesellschaft für Biochemie und Molekularbiologie has awarded a FEBS Anniversary Prize to Michael Zimmermann for his gut microbiome research.
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
19 January 2021

Science & Technology
Freshwater sports can cause waterborne infections, but real-time DNA sequencing could help.
2021
sciencescience-technology
4 January 2021
Science & Technology
Researchers discovered the dominant species of bacteria in kefir grains cannot endure without other species that help the 'team' survive.
2021
sciencescience-technology
23 November 2020
Connections
Microbiomes, plastics, and connectivity – AtlantECO aims to understand the fabric of the Atlantic Ocean.
28 July 2020
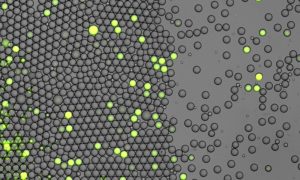
Science & Technology
Bacterial cells are embedded in microfluidic droplets in oil. The fluorescence indicates the presence of the targeted DNA strain with the help of a characteristic DNA sequence.
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
20 July 2020
Science & Technology
An international team of scientists has collated all known bacterial genomes from the human gut microbiome into a single large database. Their work will allow researchers to explore the links between bacterial genes and proteins, and their effects on human health.
2020
sciencescience-technology
13 July 2020

Lab Matters
The European Learning Laboratory for the Life Sciences (ELLS), EMBL’s education facility, invites secondary school science teachers to participate in a virtual training course this autumn entitled ‘Introducing your microbiome’.
8 November 2019

People & Perspectives
On microbiomes, public engagement and not being boring
2019
eventspeople-perspectives
22 July 2019

People & Perspectives
Michael Zimmermann's group will investigate how gut microbes affect the body’s response to drugs.
2019
people-perspectivesscience
1 April 2019

Science & Technology
Colorectal cancer characterised by consistent changes in gut bacteria across continents, cultures and diets
2019
sciencescience-technology
26 February 2019
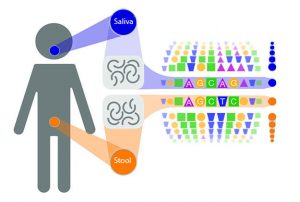
Science & Technology
Many microbes traverse the oral-gut barrier
2019
sciencescience-technology
11 February 2019
Science & Technology
Researchers identify novel gut bacteria species and call for more data from beyond Europe and North America
2019
sciencescience-technology
4 February 2019

Science & Technology
A new database of bacteria in the human microbiome is the most comprehensive to date.
2019
sciencescience-technology
22 November 2018

Lab Matters
Nina Kathe, Winner of the EU Contest for Young Scientists visits EMBL
1 August 2018
Science & Technology
First global survey of soil genomics reveals a war between fungi and bacteria
2018
sciencescience-technology
19 April 2018

People & Perspectives
Dog and human gut microbiomes have more similar genes and responses to diet than previously thought
2018
people-perspectivesscience
19 March 2018
Science & Technology
One in four drugs with human targets inhibit the growth of bacteria in the human gut, and may promote antibiotic resistance, EMBL researchers report in Nature
2018
sciencescience-technology
19 March 2018

Science & Technology
EMBL scientists show how to grow a wide range of gut bacteria in the lab
2018
sciencescience-technology
27 June 2017
Science & Technology
Science and Society event answers controversial questions about gut microbes
2017
eventsscience-technology
26 August 2016

Science & Technology
Team leader investigates how the gut microbiome could relate to human diseases
2016
sciencescience-technology
22 May 2016

Science & Technology
What's a microbiome? How on Earth do they work?
2016
sciencescience-technology
28 April 2016
Science & Technology
Stool transplants: finding the right match important, EMBL study shows
2016
sciencescience-technology
24 August 2015

People & Perspectives
Alumnus Luis Bejarano asked Spanish students to stick out their tongues to analyse their microbiome.
2015
alumnipeople-perspectives
5 May 2015

Science & Technology
Cooperate or compete? Microbes show us that getting along is the better choice for communities.
2015
sciencescience-technology
20 April 2011
Science & Technology
In the future, when you walk into a doctor’s surgery or hospital, you could be asked not just about your allergies and blood group, but also about your gut type. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and collaborators in the international MetaHIT…
2011
sciencescience-technology
4 March 2010
Science & Technology
The thousands of bacteria, fungi and other microbes that live in our gut are essential contributors to our good health. They break down toxins, manufacture some vitamins and essential amino acids, and form a barrier against invaders. A study published today in Nature shows that, at 3.3 million,…
2010
sciencescience-technology
16 October 2008
Lab Matters
Today at a meeting organised by the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, scientists from around the globe announced the formation of the International Human Microbiome Consortium (IHMC), an effort that will enable researchers to characterise the relationship of the…
14 March 2007
Science & Technology
Inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative Colitis, severely impair the lives of more than four million people worldwide. The development of effective therapies against these diseases requires an understanding of their underlying molecular mechanisms. Researchers from…
2007
sciencescience-technology
2 February 2007
Science & Technology
Microorganisms make up more than a third of the Earth’s biomass. They are found in water, on land and even in our bodies, recycling nutrients, influencing the planet’s climate or causing diseases. Still, we know surprisingly little about the smallest beings that colonise Earth. A new…
2007
sciencescience-technology
No matching posts found