10 October 2025
EMBL scientists have developed a more sensitive single-cell sequencing tool that links genomic variants and RNA in the same cell, helping to better uncover links to complex diseases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
5 September 2025

An EMBL alumnus’ work with tRNA, along with support from EMBLEM, has led to a start-up, Umlaut.bio, that is positioned to aid drug development.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
24 July 2023
EMBL researchers have made new strides into understanding and reversing genetic defects that underlie familial heart disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
14 July 2023

EMBL researchers use a new cell sorting technology to gain new insights into cellular function in health and disease, as well as for other innovative applications.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
4 March 2022

Genomes are made up of thousands of individual pieces – genes – which are expressed at different levels. Researchers at EMBL have shed light on how the placement of a gene affects its expression, as well as that of its neighbours.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
21 January 2022
EMBL researchers, in collaboration with BD Biosciences, have demonstrated a new technology that allows rapid image-based sorting of cells. The new technology represents a major upgrade to flow cytometry and has applications in diverse life science fields.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
27 April 2021
EMBL scientists, together with collaborators from Heidelberg University, have provided further evidence of the gut’s role in COVID-19.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
2 March 2021
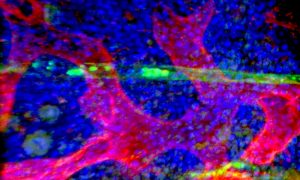
A new method has the potential to boost international research efforts to find drugs that eradicate cancer at its source.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
1 March 2021

Applications are now open for the Life Science Alliance’s Bridging Excellence Fellowships, enabling postdocs to carry out collaborative projects at EMBL and Stanford University.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
8 September 2020
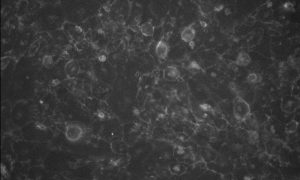
Researchers have found the cause of dilated cardiomyopathy – a leading cause of heart failure – and identified a potential treatment for it: a drug already used to treat acne.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
16 June 2020

Scientists at EMBL and Heidelberg University Hospital are studying how the novel coronavirus behaves in the gut to try to better understand its epidemiology and prevent its spread. To do this, they are combining advanced imaging and sequencing technologies to study coronavirus in human intestinal…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
27 September 2012
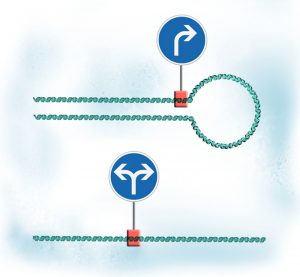
In a nutshell: Looping and unlooping DNA adjusts readout from gene and spread of regulation throughout the genome When a gene forms a loop, its output increases, as the transcription machinery that reads it is trapped into moving only along that gene When the gene loop is undone, transcription…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
1 October 2009
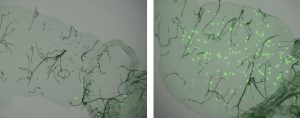
For many years, the mosquitoes that transmit malaria to humans were seen as public enemies, and campaigns to eradicate the disease focused on eliminating the mosquitoes. But, as a study published today in Science shows, the mosquitoes can also be our allies in the fight against this common foe,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
25 January 2009
Genes that contain instructions for making proteins make up less than 2% of the human genome. Yet, for unknown reasons, most of our genome is transcribed into RNA. The same is true for many other organisms that are easier to study than humans. Researchers in the groups of Lars Steinmetz at the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
No results found












