
Leading EMBL’s six sites
As Peer Bork and Ewan Birney take up interim leadership of EMBL, the organisation announces additional changes in site leadership.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS2025
embl-announcements
Showing results out of

As Peer Bork and Ewan Birney take up interim leadership of EMBL, the organisation announces additional changes in site leadership.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS2025
embl-announcements
Blood stem cells from healthy people carry major chromosomal alterations, a study in Nature Genetics by researchers at the Max Delbrück Center and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) finds. The discovery suggests that we are all genetic mosaics, which may contribute to ageing-related…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
Former EMBL staff scientist founds a start-up – DenovAI – for broader, faster and cheaper antibody discovery using advanced machine learning and computational biophysics.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology
Using Oxford Nanopore long-read sequencing, EMBL scientists sequenced a primary childhood brain tumour known as a medulloblastoma, uncovering a novel complex mutation pattern.
2023
science
Researchers at EMBL Heidelberg found that inversions in the human genome are more common than previously thought, which impacts our understanding of certain genetic diseases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
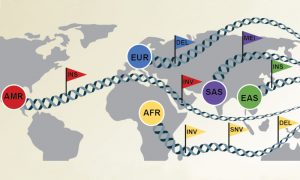
A collaboration including EMBL scientists has created the most diverse set of reference human genomes ever assembled.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Three changes in senior staff positions have been confirmed at EMBL today. Jessica Vamathevan becomes Head of Strategy, Jan Korbel becomes Head of Data Science for EMBL Heidelberg, and Nassos Typas becomes Senior Scientist.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
A national consortium including EMBL and the DKFZ is set to launch the German Human Genome–Phenome Archive, creating an invaluable bridge between fundamental biomedical research and applied healthcare.
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS2020
connectionslab-matters
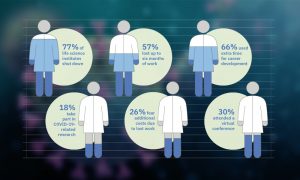
Jan Korbel and Oliver Stegle have performed a survey of fellow life scientists to learn how the current crisis, with partial or complete institutional shutdowns, is affecting their work.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
lab-mattersscience-technology

EMBL scientists will contribute to the new German COVID-19 OMICS Initiative to study the biological mechanisms contributing to coronavirus infections. EMBL group leaders Jan Korbel and Oliver Stegle, who is also affiliated with the DKFZ Heidelberg, will coordinate the set-up of IT infrastructures…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

The causes of 40 percent of all cases of certain medulloblastoma – dangerous brain tumours affecting children – are hereditary. These are the findings of a recent genetic analysis carried out by scientists from EMBL and numerous colleagues around the world.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

EMBL co-leads most comprehensive study of genetic causes of cancer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Scientists from EMBL present a tool for large-scale analysis of genomic data with cloud computing. Main advantages of the new tool, called Butler, are continuous system monitoring and its ability to self-heal in case of failure, allowing for 43% more efficient data processing than previous…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Using the data from the Pan-Cancer project EMBL scientists describe how our genetic background influences cancer development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Researchers have developed a cheaper and faster method to check for genetic differences in individual cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

Does rearranging chromosomes affect their function? EMBL scientists reveal uncoupling of 3D chromatin organisation and gene expression.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
Thorough characterisation of structural variants in human genomes
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

Cancer researchers have developed a computer model to predict the course of disease for prostate cancer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
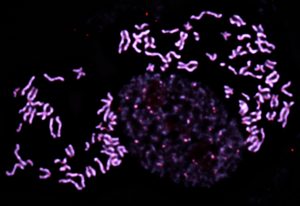
EMBL group leader Jan Korbel reflects on his scientific origins and current research
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
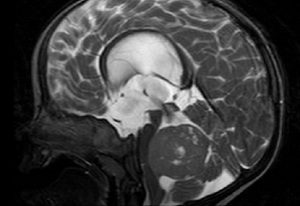
Researchers identify genes that can cause brain tumours in children and other cancers later in life
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists regularly receive prestigious awards – meet the latest honourees.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS2016
embl-announcementslab-matters

EMBL scientists regularly receive prestigious awards – meet the latest honourees.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS2015
embl-announcementslab-matters

Jan Korbel and colleagues publish commentary on risks and rewards of genome cloud computing.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Enabling neighbours: intact genes can cause cancer when placed near "enhancing" regions of DNA
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
A detailed analysis of data from 185 human genomes sequenced in the course of the 1000 Genomes Project, by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, in collaboration with researchers at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute in Cambridge, UK, as well as the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
The 1000 Genomes Project, a major international collaboration to build a detailed map of human genetic variation, has completed its pilot phase. The results are now published in the journal Nature and freely available through the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
Once the human genome was sequenced in 2001, the hunt was on for the genes that make each of us unique. But scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and Yale and Stanford Universities in the USA, have found that we differ from each other mainly because…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
No results found