
Shedding light on rare diseases: open data and model organisms
Why open data from model organisms is essential for rare disease research.
2023
perspectivesscience

Why open data from model organisms is essential for rare disease research.
2023
perspectivesscience

Jo McEntyre talks about data services, open data and a new era for research assessment.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesperspectives

Microbial communities play essential roles in ocean ecology and planetary health. A recent publication highlights priorities for understanding and protecting ocean microbiomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

Scientists identify previously unexplored gene segments to be added to human genome databases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology

EMBO Director Fiona Watt discusses preprints, data sharing, and evaluation in light of EMBL’s new Open Science policy
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
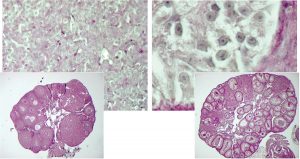
Is it a boy or a girl? Expecting parents may be accustomed to this question, but contrary to what they may think, the answer doesn’t depend solely on their child’s sex chromosomes. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany and the Medical Research…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
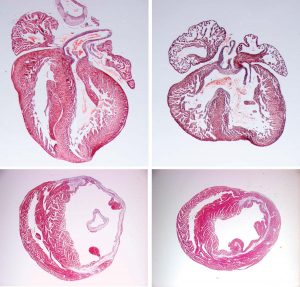
Almost a century after it was discovered in fruit flies with notches in their wings, the Notch signalling pathway may come to play an important role in the recovery from heart attacks. In a study published today in Circulation Research, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL)…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
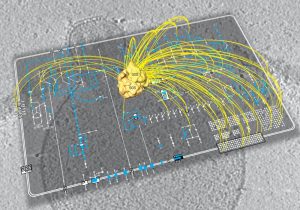
What are the bare essentials of life, the indispensable ingredients required to produce a cell that can survive on its own? Can we describe the molecular anatomy of a cell, and understand how an entire organism functions as a system? These are just some of the questions that scientists in a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Much as adrenaline coursing through our veins drives our body’s reactions to stress, the plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) is behind plants’ responses to stressful situations such as drought, but how it does so has been a mystery for years. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
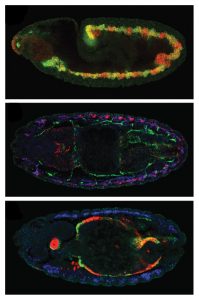
Embryonic development is like a well-organised building project, with the embryo’s DNA serving as the blueprint from which all construction details are derived. Cells carry out different functions according to a developmental plan, by expressing, i.e. turning on, different combinations of genes.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
For many years, the mosquitoes that transmit malaria to humans were seen as public enemies, and campaigns to eradicate the disease focused on eliminating the mosquitoes. But, as a study published today in Science shows, the mosquitoes can also be our allies in the fight against this common foe,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
In the quest for speed, olympic swimmers shave themselves or squeeze into high-tech super-suits. In the body, sperm are the only cells that swim and, as speed is crucial to fertility, have developed their own ways to become exceptionally streamlined. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
For scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Monterotondo, Italy, what seemed like a disappointing result turned out to be an important discovery. Their findings, published online this week in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), provide…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
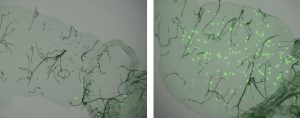
Stem cells have a unique ability: when they divide, they can either give rise to more stem cells, or to a variety of specialised cell types. In both mice and humans, a layer of cells at the base of the skin contains stem cells that can develop into the specialised cells in the layers above.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
BBSRC has awarded funding to the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), based at Hinxton near Cambridge, to permit a dramatic increase in the institute’s data storage and handling capacity. The funding is the first step in developing the existing…
LAB MATTERS2009
lab-matters
Our genome is constantly under attack from things like UV light and toxins, which can damage or even break DNA strands and ultimately lead to cancer and other diseases. Scientists have known for a long time that when DNA is damaged, a key enzyme sets off a cellular ‘alarm bell’ to alert the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Chronic inflammatory lung diseases like chronic bronchitis and emphysema are a major global health problem, and the fourth leading cause of death and disability in developed countries, with smoking accounting for 90% of the risk for developing them. Work by scientists at the European Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the University of Heidelberg, Germany, have come a step closer to understanding how cholesterol levels are regulated. In a study published today in the journal Cell Metabolism, the researchers identified 20 genes that are involved…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology

On June 26 2009 the joint international Unit for Virus and Host Cell Interactions (Unité Mixte Internationale) was formally established in Grenoble. The unit is run jointly by CNRS, the Grenoble outstation of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the Grenoble University Joseph…
LAB MATTERS2009
lab-matters
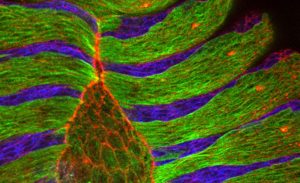
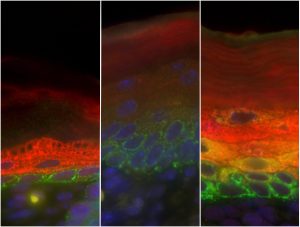
Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, came a step closer to understanding how cells close gaps not only during embryonic development but also during wound healing. Their study, published this week in the journal Cell, uncovers a fundamental…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
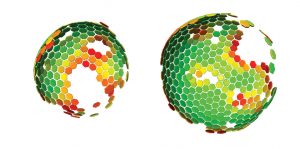
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the University Clinic Heidelberg, Germany, have produced a three-dimensional reconstruction of HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus), which shows the structure of the immature form of the virus at unprecedented detail. Immature HIV is…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology

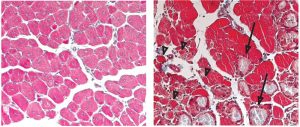
Mice are one of biology’s most important model organisms, because 98% of their genes and many of their traits and diseases are similar to ours. Researchers at the Mouse Biology Unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) take advantage of these similarities and use mice to study…
LAB MATTERS2009
lab-matters
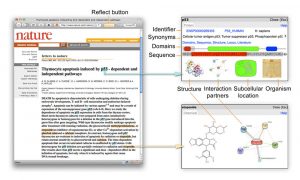
The life sciences are scaling up and produce huge amounts of data and new literature at an amazing pace. The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) now offers a new free service to help researchers, teachers and students keep up-to-date with scientific literature on the web, especially when…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
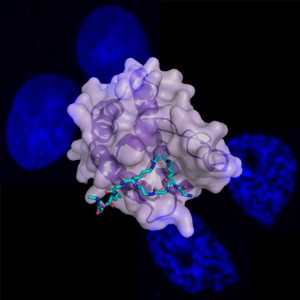
Proteins are the executive agents that carry out all processes in a cell. Their activity is controlled and modified with the help of small chemical tags that can be dynamically added to and removed from the protein. 25 years after its first discovery, researchers at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Most cellular processes are carried out by molecular machines that consist of many interacting proteins. These protein complexes lie at the heart of life science research, but they are notoriously hard to study. Their abundance is often too low to extract them directly from cells and generating…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Recycling is important not only on a global scale, but also at the cellular level, since key molecules tend to be available in limited numbers. This means a cell needs to have efficient recycling mechanisms. Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and Heidelberg University,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
It can be found in all life forms, and serves a multitude of purposes, from energy storage to stress response to bone calcification. This molecular jack-of-all trades is polyphosphate, a long chain of phosphate molecules. Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
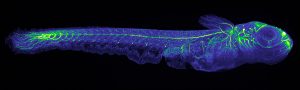
‘Useless fish with big eyes’. This is what Medaka, the name of the Japanese killifish in the pictures, means in Japan where it originally comes from. While its eyes are undeniably big, the fish has proven remarkably useful for scientists. It is a simple model organism, amenable to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
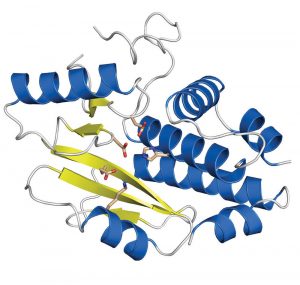
Influenza is and remains a disease to reckon with. Seasonal epidemics around the world kill several hundred thousand people every year. In the light of looming pandemics if bird flu strains develop the ability to infect humans easily, new drugs and vaccines are desperately sought. Researchers at…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Genes that contain instructions for making proteins make up less than 2% of the human genome. Yet, for unknown reasons, most of our genome is transcribed into RNA. The same is true for many other organisms that are easier to study than humans. Researchers in the groups of Lars Steinmetz at the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
No matching posts found