
Shedding light on rare diseases: open data and model organisms
Why open data from model organisms is essential for rare disease research.
2023
perspectivesscience

Why open data from model organisms is essential for rare disease research.
2023
perspectivesscience

Jo McEntyre talks about data services, open data and a new era for research assessment.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesperspectives

Microbial communities play essential roles in ocean ecology and planetary health. A recent publication highlights priorities for understanding and protecting ocean microbiomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

Scientists identify previously unexplored gene segments to be added to human genome databases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology

EMBO Director Fiona Watt discusses preprints, data sharing, and evaluation in light of EMBL’s new Open Science policy
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
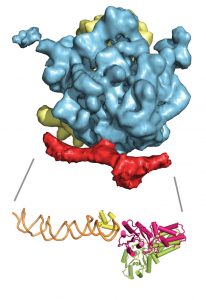
Like an overprotective parent on the first day of school, a targeting factor sometimes needs a little push to let go of its cargo. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Grenoble, France, have visualised one such hand-over. They were the first to determine the structure…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
From microscopy to computer tomography (CT) scans, imaging plays an important role in biological and biomedical research, but obtaining high-quality images often requires advanced technology and expertise, and can be costly. Euro-BioImaging, a project which launches its preparatory phase today,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
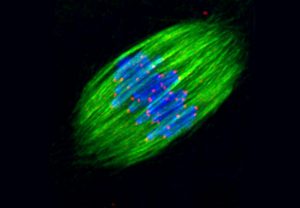
The cells in the different parts of this video are always the same (grey), but, like actors using make-up to highlight different facial features, they have fluorescent labels that mark different cellular components in different colours: blue shows the nucleus, yellow shows tubulin (a component of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology

At the Autumn 2010Council meeting of the EIROforum, a partnership of seven European intergovernmental research organisations with large research infrastructures, the Directors General unanimously accepted the European X-Ray Free-Electron Laser Facility (European XFEL), based in Hamburg, Germany, to…
LAB MATTERS2010
lab-matters
The 1000 Genomes Project, a major international collaboration to build a detailed map of human genetic variation, has completed its pilot phase. The results are now published in the journal Nature and freely available through the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
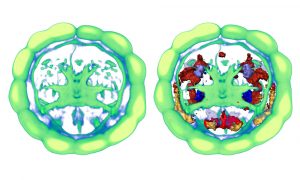
Our cerebral cortex, or pallium, is a big part of what makes us human: art, literature and science would not exist had this most fascinating part of our brain not emerged in some less intelligent ancestor in prehistoric times. But when did this occur and what were these ancestors? Unexpectedly,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
Fear can make you run, it can make you fight, and it can glue you to the spot. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Monterotondo, Italy and GlaxoSmithKline in Verona, Italy, have identified not only the part of the brain but the specific type of neurons that determine…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
During cell division, microtubules emanating from each of the spindle poles meet and overlap in the spindle’s midzone. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have uncovered the molecular mechanism that determines the extent of this overlap. In a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
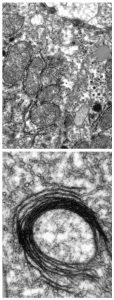
Most organisms need iron to survive, but too much iron is toxic, and can cause fatal organ failure. The same is true inside cells, where iron balance must also be maintained. In a study published today in Cell Metabolism, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
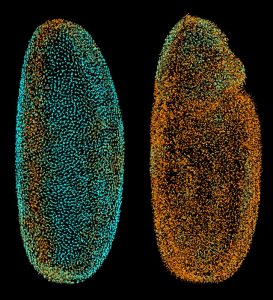
The scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, who ‘fathered’ the Digital Embryo have now given it wings, creating the Fly Digital Embryo. In work published today in Nature Methods, they were able to capture fruit fly development on film, and were the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
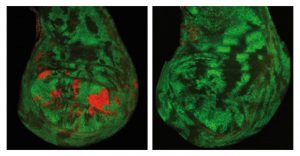
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and the Max-Planck Institute of Immunobiology Freiburg have identified a novel protein complex that regulates around 4000 genes in the fruit fly Drosophila and likely plays an important role in mammals, too.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
Red blood cells, the delivery men that take oxygen to cells all around the body, have short lives. To keep enough of them in circulation, the human body produces around 2 million of these cells every second – even more in response to challenges like severe blood loss. In a study published today…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
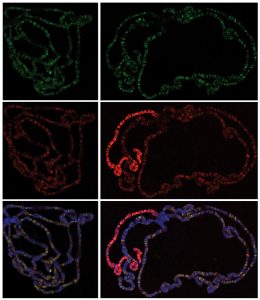
During embryonic development, proteins called Polycomb group complexes turn genes off when and where their activity must not be present, preventing specialised tissues and organs from forming in the wrong places. They also play an important role in processes like stem cell differentiation and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
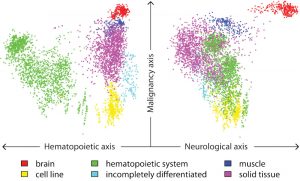
Just like members of an orchestra are active at different times although playing the same piece of music, every cell in our body contains the same genetic sequence but expresses this differently to give rise to cells and tissues with specialised properties. By integrating gene expression data from…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
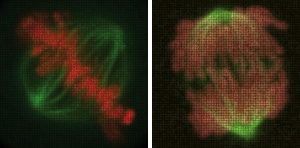
Name a human gene, and you’ll find a movie online showing you what happens to cells when it is switched off. This is the resource that researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and their collaborators in the Mitocheck consortium are making freely…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
Once the human genome was sequenced in 2001, the hunt was on for the genes that make each of us unique. But scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and Yale and Stanford Universities in the USA, have found that we differ from each other mainly because…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology

Today, the Nordic EMBL Partnership for Molecular Medicine officially inaugurates the Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland (FIMM) in Helsinki. Together with the Centre for Molecular Medicine Norway (NCMM, University of Oslo) and the Laboratory for Molecular Infection Medicine Sweden (MIMS, Umeå…
LAB MATTERS2010
lab-matters

Today, the German Minister for Education and Research, Annette Schavan, officially opens the new training and conference centre for the life sciences on the campus of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg. “This new centre in Heidelberg will form a central European…
LAB MATTERS2010
lab-matters
The thousands of bacteria, fungi and other microbes that live in our gut are essential contributors to our good health. They break down toxins, manufacture some vitamins and essential amino acids, and form a barrier against invaders. A study published today in Nature shows that, at 3.3 million,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
The last ancestor we shared with worms, which roamed the seas around 600 million years ago, may already have had a sophisticated brain that released hormones into the blood and was connected to various sensory organs. The evidence comes not from a newly found fossil but from the study of microRNAs…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
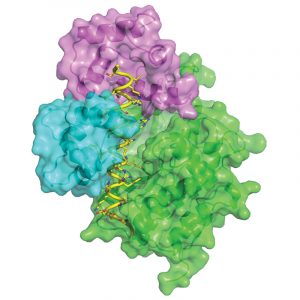
Cells rely on a range of signalling systems to communicate with each other and to control their own internal workings. Scientists from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Hamburg, Germany, have now found a way to hack into a vital communications system, raising the possibility of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
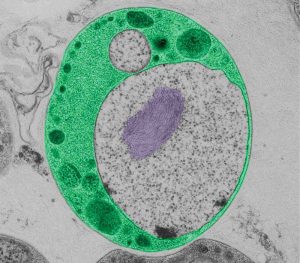
Although they are present almost everywhere, on land and sea, a group of related bacteria in the superphylum Planctomycetes-Verrucomicrobia-Chlamydiae, or PVC, have remained in relative obscurity ever since they were first described about a decade ago. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
ChEMBLdb, a vast online database of information on the properties and activities of drugs and drug-like small molecules and their targets, launches today with information on over half a million compounds. The data lie at the heart of translating information from the human genome into successful new…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
No matching posts found