
Shedding light on rare diseases: open data and model organisms
Perspectives, Science Why open data from model organisms is essential for rare disease research.
2023
perspectivesscience

Perspectives, Science Why open data from model organisms is essential for rare disease research.
2023
perspectivesscience

Lab Matters, People & Perspectives, Perspectives Jo McEntyre talks about data services, open data and a new era for research assessment.
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesperspectives

Science, Science & Technology Microbial communities play essential roles in ocean ecology and planetary health. A recent publication highlights priorities for understanding and protecting ocean microbiomes.
2022
sciencescience-technology

Research highlights, Science, Science & Technology Scientists identify previously unexplored gene segments to be added to human genome databases.
2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology

Lab Matters, People & Perspectives EMBO Director Fiona Watt discusses preprints, data sharing, and evaluation in light of EMBL’s new Open Science policy
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
Science It does not take much to injure a muscle. Sometimes one sudden, inconsiderate movement does the job. Unfortunately, damaged muscles are not as efficient at repair as other tissues such as bone. Researchers of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s Mouse Biology Unit (EMBL), Italy, and…
2007
science
Lab Matters ArrayExpress, the publicly available database of transcriptomics data at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), has doubled in size in 2007, reaching the 100,000-hybridisation milestone. The database now holds snapshots of gene expression…
2007
lab-matters
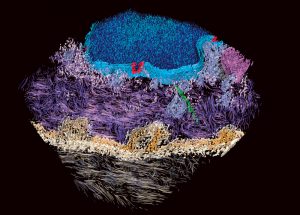
Science Seeing proteins in their natural environment and interactions inside cells has been a longstanding goal. Using an advanced microscopy technique called cryo-electron tomography, researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) have visualised proteins responsible for cell-cell…
2007
science
Science Cells in our body come in various shapes and sizes. Each cell is shaped in such a way as to optimise it for a specific function. When things go wrong and a cell does not adopt its dedicated shape, its function can be impaired and the cell can cause problems in the body. Researchers at […]
2007
science

Lab Matters Today, the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) announces Luxembourg as the new member of its international community. Accepted by EMBL’s council and ratified by the parliament of Luxembourg, the Grand-Duchy has officially joined the institute as the 20th member state. “EMBL is…
2007
lab-matters
Lab Matters The European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) officially opens its new East Wing today with a reception for prominent guests. The East Wing will be jointly opened by Ian Pearson, Minister of State for Science and Innovation, UK, and Robert-Jan Smits,…
2007
lab-matters
Science New insights into the cellular signal chain through which pheromones stimulate mating in yeast have been gained by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory [EMBL]. Similar signal chains are found in humans, where they are involved in many important processes such as the…
2007
science
Lab Matters Today the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), the University of Helsinki, Finland, the University of Oslo, Norway, and Umeå University, Sweden, officially launch their new Nordic EMBL Partnership for Molecular Medicine. The agreement will encourage scientific exchange and collaborations…
2007
lab-matters
Science Many neuronal disorders, including epilepsy, schizophrenia and lissencephaly ─ a form of mental retardation ─ result from abnormal migration of nerve cells during the development of the brain. Researchers from the Mouse Biology Unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Italy,…
2007
science
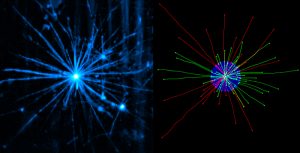
Science Scientists from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) have developed a new method to prepare and image biological samples in three dimensions with laser light-sheet based fluorescence microscopy. The technological advance, which is published in the current online issue of Nature…
2007
science
Lab Matters Three papers published by EMBL scientists and their collaborators will make it much easier to share and compare information from large-scale proteomics data. The papers are published in Nature Biotechnology on 8 and 26 August. As the quantity of available biological information and the use of…
2007
lab-matters
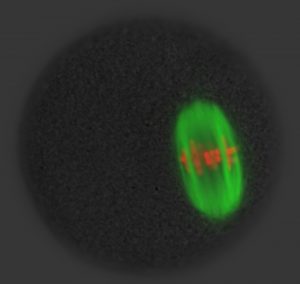
Science Which genes are passed on from mother to child is decided very early on during the maturation of the egg cell in the ovary. In a cell division process that is unique to egg cells, half of the chromosomes are eliminated from the egg before it is fertilised. Using a powerful microscope, researchers…
2007
science
Science The UniProt Consortium, which includes the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), has added a new database repository for metagenomic and environmental data to its family of protein sequence databases. Metagenomics is the large-scale genomic…
2007
science
Lab Matters Today, delegates representing the 19 member states of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) offered Australia associate membership in EMBL’s international community. The membership is planned to start officially in January 2008 and will initially last for seven years. “EMBL…
2007
lab-matters
Science To protect us from disease our immune system employs macrophages, cells that roam our body in search of disease-causing bacteria. With the help of long tentacle-like protrusions, macrophages can catch suspicious particles, pull them towards their cell bodies, internalise and destroy them. Using a…
2007
science
Science Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the University of Michigan have discovered a gene that protects us against a serious kidney disease. In the current online issue of Nature Genetics they report that mutations in the gene cause nephronopthisis (NPHP) in humans and…
2007
science
Science Hormones control growth, metabolism, reproduction and many other important biological processes. In humans, and all other vertebrates, the chemical signals are produced by specialised brain centres such as the hypothalamus and secreted into the blood stream that distributes them around the body.…
2007
science
Science A new mechanism to attack hard-to-treat fungal infections has been revealed by scientists from the biotech company Anacor Pharmaceuticals Inc., California, and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory [EMBL] outstation in Grenoble, France. In the current issue of Science they describe…
2007
science
Science Scientists at the Samuel Lunenfeld Research Institute of Mount Sinai Hospital (Canada), the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (Germany), and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (USA) have created a new computational method called NetworKIN. This method uses biological networks to better…
2007
science
Science The ENCyclopedia Of DNA Elements (ENCODE), an international research consortium organised by the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), today published the results of its exhaustive, four-year effort to build a “parts list” of…
2007
science
Science A human cell contains an enormous 1.8 metres of DNA partitioned into 46 chromosomes. These have to be copied and distributed equally into two daughter cells at every division. Condensation, the shortening of chromosomes, allows the cell to handle such huge amounts of genetic material during cell…
2007
science
Science Why does the same diet make some of us gain more weight than others? The answer could be a molecule called Bsx, as scientists from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), the German Institute for Nutrition (DIFE), Potsdam, and the University of Cincinnati report in the current issue of…
2007
science
Science People who suffer from anxiety tend to interpret ambiguous situations, situations that could potentially be dangerous but not necessarily so, as threatening. Researchers from the Mouse Biology Unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Italy have now uncovered the neural basis for…
2007
science
Lab Matters It was the world’s earliest public database of DNA and RNA sequences and remains Europe’s primary nucleotide sequence resource. The database is maintained by EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute in Hinxton (UK) in collaboration with its US and Japanese counterparts GenBank and…
2007
lab-matters
Science Over 30% of our genes are under the control of small molecules called microRNAs. They prevent specific genes from being turned into protein and regulate many crucial processes like cell division and development, but how they do so has remained unclear. Now researchers from the European Molecular…
2007
science
Science When a cell divides, normally the result is two identical daughter cells. In some cases however, cell division leads to two cells with different properties. This is called asymmetric cell division and plays an important role in embryonic development and the self-renewal of stem cells. Researchers…
2007
science

Science The rise of the central nervous system (CNS) in animal evolution has puzzled scientists for centuries. Vertebrates, insects and worms evolved from the same ancestor, but their CNSs are different and were thought to have evolved only after their lineages had split during evolution. Researchers from…
2007
science
Science Inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative Colitis, severely impair the lives of more than four million people worldwide. The development of effective therapies against these diseases requires an understanding of their underlying molecular mechanisms. Researchers from…
2007
science
Science Like our body every cell has a skeleton that provides it with a shape, confers rigidity and protects its fragile inner workings. The cytoskeleton is built of long protein filaments that assemble into networks whose overall architecture and fine detail can only be revealed with high resolution…
2007
science

Science The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) has developed a new computational tool that makes images obtained with cutting-edge microscopes even sharper. The technological advance and its applications are published in this week’s online issue of the journal Nature Methods. Since the…
2007
science
Science In 1918, 50 million people died during a worldwide influenza pandemic caused by mutation of a bird-specific strain of the influenza virus. Recently H5N1, another highly infectious avian strain has caused outbreaks of bird flu around the world. There is great concern that this virus might also…
2007
science
Science Liver cancer is one of the deadliest cancers worldwide; every year sees more than 400,000 new cases, and most of the victims die in less than one year. Despite extensive research, the underlying molecular mechanisms of the disease are poorly understood. A new study by researchers from the Mouse…
2007
science
Science We all know that iron deficiencies are dangerous, but also too much iron is bad for our health. Our body stores excess iron in various tissues, where it can lead to organ failure and even death if not treated before irreversible damage has occurred. Researchers from the Innsbruck Medical…
2007
science
Science Microorganisms make up more than a third of the Earth’s biomass. They are found in water, on land and even in our bodies, recycling nutrients, influencing the planet’s climate or causing diseases. Still, we know surprisingly little about the smallest beings that colonise Earth. A new…
2007
science

Lab Matters The German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF) has awarded 8.8 Million Euro to the Hamburg Outstation of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) for the construction of an Integrated Research Facility for Structural Biology at the new PETRA-III storage ring of the German…
2007
lab-matters
Lab Matters The European Commission has awarded 3.7 Million Euro under the European Union Framework 6 Programme over the next four years to a new Marie Curie Research Training Network, coordinated by Dr. Andreas Ladurner at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL). The long molecules of DNA that carry…
2007
lab-matters
Lab Matters From today scientists will be able to access a vast collection of biomedical research and to submit their own published results for inclusion in a new online resource. Based on a model currently used by the US National Institute of Health, UK PubMed Central (UKPMC) will provide free access to a…
2007
lab-matters
Science Phone numbers, the way to work, granny’s birthday – our brain with its finite number of nerve cells can store incredible amounts of information. At the bottom of memory lies a complex network of molecules. To understand how this network brings about one of the most remarkable capacities of…
2007
science
No matching posts found
Looking for past print editions of EMBLetc.? Browse our archive, going back 20 years.
EMBLetc. archive