
Shedding light on rare diseases: open data and model organisms
Why open data from model organisms is essential for rare disease research.
2023
perspectivesscience

Why open data from model organisms is essential for rare disease research.
2023
perspectivesscience

Jo McEntyre talks about data services, open data and a new era for research assessment.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesperspectives

Microbial communities play essential roles in ocean ecology and planetary health. A recent publication highlights priorities for understanding and protecting ocean microbiomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

Scientists identify previously unexplored gene segments to be added to human genome databases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology

EMBO Director Fiona Watt discusses preprints, data sharing, and evaluation in light of EMBL’s new Open Science policy
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
Researchers at the International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB) in India and a unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in France have made a key discovery about a molecule that helps the malaria parasite infect human cells. India is one of the countries…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
In the December 6 issue of Nature Biotechnology, scientists from 14 different organizations around the world, including the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute, propose a new quality standard for biochemical models. MIRIAM [for Minimum information requested in the annotation of biochemical…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
lab-mattersscience-technology
Species evolve at very different rates, and the evolutionary line that produced humans seems to be among the slowest. The result, according to a new study by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory [EMBL], is that our species has retained characteristics of a very ancient ancestor…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
Today the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) opens a new highthroughput crystallization facility at its Outstation located on the campus of the German Synchrotron Radiation Facility (DESY) in Hamburg, Germany. The facility, made possible by major funds from the German Ministry for Science…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS2005
embl-announcementslab-matters
Most of what happens in cells is the work of machines that contain dozens of molecules, chiefly proteins. With the completion of human and other genomes, researchers now have a nearly complete ‘parts list’ of such machines; what’s lacking is the manual telling where all the pieces…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the Universities of Heidelberg and Ulm and a unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Monterotondo, Italy, have discovered that a specific signal within brain cells may determine whether they live or die after a stroke. Their study, published online (November 13) by…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
The Commission of the European Union has awarded EUR 9 million over five years for a new Network of Excellence that will make computational systems biology accessible to bench scientists throughout Europe and beyond. ENFIN, which stands for ‘Experimental Network for Functional…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
lab-mattersscience-technology
Mutations in genes are the basis of evolution, so we owe our existence to them. Most mutations are harmful, however, because they cause cells to build defective proteins. So cells have evolved quality control mechanisms that recognize and counteract genetic mistakes. Now scientists of the Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
The European Commission has selected the EBI to coordinate a project that will stimulate and explore synergies between bioinformatics (the science of storing, retrieving and analysing large amounts of biological information) and medical informatics (the science of processing, sharing and using…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS2005
connectionslab-matters
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg and the Institute of Biomedical Research of the Parc Científic de Barcelona (IRB-PCB) have now added key evidence to claims that some types of cancer originate with defects in stem cells. The study, reported this week in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
The European Bioinformatics Institute and Flanders Interuniversity Institute for Biotechnology (VIB) – Ghent University have launched the PRoteomics IDEntifications database (PRIDE). PRIDE allows researchers who work in the field of proteomics – the large-scale study of proteins – to…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS2005
connectionslab-matters
The executive teams of five major molecular interaction databases announced today the signing of an agreement to share curation efforts and exchange completed records through a mechanism known as the International Molecular Exchange (IMEx) consortium. IMEx will provide a network of stable,…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS2005
connectionslab-matters
Achieving equality between the sexes can be a challenge even for single cells. Since evolution began removing bits of male DNA to create the ‘Y’ chromosome, males have had a single copy of certain key genes on the X chromosome, whereas females have two. Normally this would lead females…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
The world’s three leading public repositories for DNA and RNA sequence information have reached 100 gigabases (100,000,000,000 bases; the ‘letters’ of the genetic code) of sequence. Thanks to their data exchange policy, which has paved the way for the global exchange of many types…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS2005
connectionslab-matters
The first rate research from the Molecular Medicine Partnership Unit (MMPU) is now set to continue for the long-term. The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the Medical Faculty of University of Heidelberg, who formed the joint venture in 2002, have announced their plans to initiate a…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS2005
connectionslab-matters
Microtubules need a helping hand to find chromosomes in dividing egg cells, scientists have discovered. Although it was generally accepted that microtubules act alone as the cellular ropes to pull chromosomes into place, a new study by researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL)…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology

A systematic search through human genes has begun at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany. Working within the MitoCheck consortium that includes 10 other institutes throughout Europe, the EMBL scientists will silence all human genes, one-by-one, to find those…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS2005
connectionslab-matters
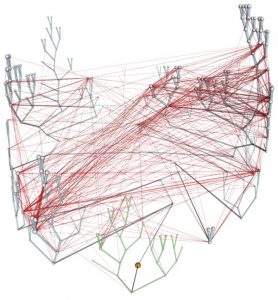
EBI researchers have changed our view of 4 billion years of microbial evolution. Christos Ouzounis and colleagues have gained intriguing quantitative insights into how gene families are transferred, not only ‘vertically’ through passage from one organism to its progeny, but also…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
Living organisms need to sense the amount of energy that is available to them and regulate the activity of their genes accordingly. Scientists have made the unexpected finding that a histone protein, which wraps DNA into tight bundles and regulates gene activity, can bind a small molecule produced…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
The European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) has received a big boost from The Wellcome Trust, the Medical Research Council (MRC) and the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC), who have given funds to expand the EBI site in Hinxton, Cambridgeshire, UK. The new…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS2005
embl-announcementslab-matters
Dr. Iain Mattaj today took over the leadership of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory [EMBL], a prominent basic research and training institute with laboratories in France, Germany, Italy and the UK. “The pace of progress in the life sciences is remarkable. I see my job as ensuring that…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS2005
embl-announcementslab-matters
Instead of sequencing the genome of one organism, why not sequence a drop of sea water, a gram of farm soil or even a sunken whale skeleton? Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg and their US collaborators have done just that, and the result is a new…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
Today sees the launch of BioModels, the world’s first database of annotated biological models. BioModels is the result of a collaboration led by the European Bioinformatics Institute (UK) and the SBML Team, an international group that develops opensource standards to describe biological…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology

A novel high-tech microscope will be brought to the marketplace, giving laboratories everywhere fascinating new insights into living organisms. EMBLEM Technology Transfer GmbH (EMBLEM), the commercial entity of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), announced today that it has signed a…
CONNECTIONS2005
connections
The International Society for Computational Biology has named two scientists from the European Bioinformatics Institute as the winners of its awards for 2005. Janet Thornton wins the Senior Scientist Accomplishment Award while the Overton Prize goes to Ewan Birney. Thomas Lengauer, the ISCB’s…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS2005
embl-announcements
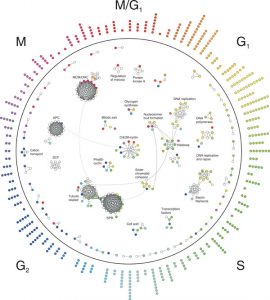
Most things that happen in the cell are the work of ‘molecular machines’ – complexes of proteins that carry out important cellular functions. Until now, scientists didn’t have a clear idea of when proteins form these machines – are these complexes pre-fabricated or put…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
The Commission of the European Union has awarded 8.3 million Euro to a pan-European task force who will improve access to biological information for scientists throughout and beyond Europe. The EMBRACE Network of Excellence, which encompasses computational biologists from 17 institutes in 11…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS2005
embl-announcements
One of the most basic yet least understood processes in our bodies is how cells crawl along tissues. This behavior is essential to the formation of an embryo and other processes, but it must be tightly controlled. A disturbance can lead to the spread of cancer cells or diseases like Spina…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
No matching posts found