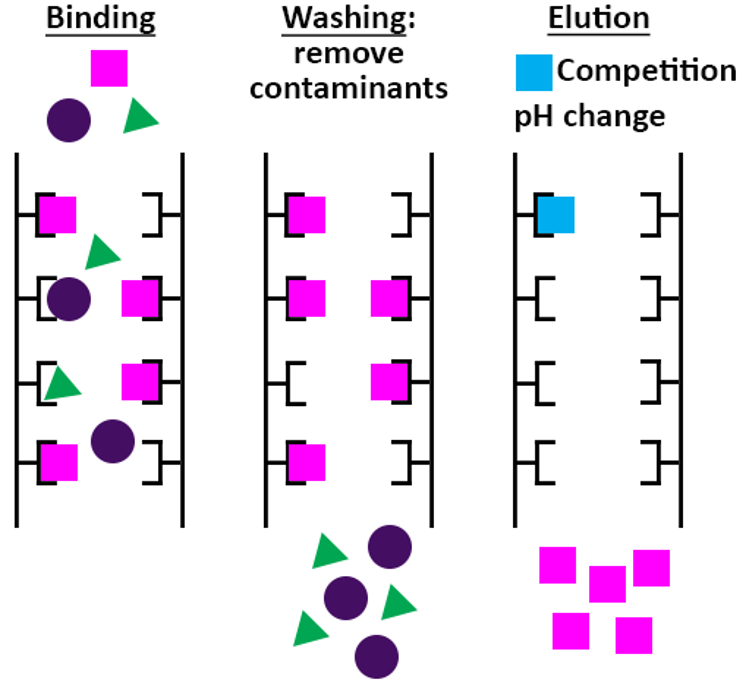
The goal of the affinity chromatography step is to separate your protein of interest from the majority of the host proteins. You start with loading the cleared cell lysate (or cell culture medium in case of secreted proteins) onto the affinity chromatography resin to allow binding of your tagged protein. Then a washing step is performed to remove weakly bound contaminants. Finally, the protein of interest is eluted from the affinity chromatography resin, usually either by adding a competitor for binding or a change in pH.
The affinity chromatography resin you will use depends on the type of the affinity tag you have chosen during the construct design. The table below gives a brief overview of some commonly used affinity tags and their corresponding affinity chromatography resin materials and elution methods.
| Affinity tag | Binding matrix | Elution |
|---|---|---|
| His6 (or His10) | Immobilised transition metal ions: Ni2+, Co2+ (Ni-NTA, Talon) | Imidazole (250 mM – 1M) Lower pH (~ pH 5) |
| StrepII, Twin-StrepII | Strep-Tactin (engineered streptavidin) | Desthiobiotin, biotin (2.5 – 5 mM) |
| Flag | Immobilised anti-Flag antibody | Synthetic Flag peptide Low pH (~ pH 2-3) |
| Glutathione-S-Transferase (GST) | Immobilised glutathione (GSH) | Reduced GSH (20-50 mM) |
| Maltose binding protein (MBP) | Amylose | Maltose (10 mM) |
| S-tag (S-peptide derived from RNAseA) | Immobilised S-protein (from RNAseA) | Low pH (~ pH 2-3) Synthetic S-peptide Tag cleavage |
| Calmodulin-binding peptide (CBP) | Immobilised calmodulin | EGTA (2 mM) |
| Cellulose-binding domain (CBD) | Immobilised cellulose | Ethylene glycol |
| Chitin-binding domain with self-splicing inteins | Immobilised chitin | Thiol reagent (DTT, MESNA, beta-mercaptoethanol) |
| HA-tag | Immobilised antibodies | Low pH (~ pH 2-3) Synthetic HA peptide |
| c-Myc tag | Immobilised antibodies | Low pH (~ pH 2-3) Synthetic c-Myc peptide |
References
Schmidt T.G.M., Batz L., Bonet L., Carl U., Holzapfel G., Kiem K., Matulewicz K., Niermeier D., Schuchardt I. and Stanar K. (2013) Development of the Twin-Strep-tag® and its application for purification of recombinant proteins from cell culture supernatants. Protein Expression and Purification 92:54-61
Wood D.W. (2014) New trends and affinity tag designs for recombinant protein purification. Current Opinion in Structural Biology 26:54-61