1 December 2025
Researchers release a comprehensive viral genome database covering diverse ecosystems to advance understanding of viral evolution and ecosystem functions.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
8 October 2024

EMBL-EBI’s microbiome data resource MGnify produces a valuable trove of protein sequence data through its ongoing analysis of microbiome derived data. Two new MGnify Proteins web resources make this dataset easily accessible and searchable, both for large queries across the entire database…
2024
updates-from-data-resources
7 June 2024

EMBL-EBI data resource helps scientists upcycle animal by-products.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
perspectivesscience-technology
8 March 2024

The MGnify data resource for microbiome data has launched the latest MGnify Genomes catalogue comprising 112,951 genomes derived from mouse gut datasets, represented by 2,847 species-level cluster representative genomes. This catalogue was generated as part of our work with the MRC funded…
2024
updates-from-data-resources
14 August 2023

EMBL-EBI Senior Scientist Rob Finn explains why data coordination and sharing are fundamental for a sustainable blue economy.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
people-perspectivesperspectivesscience
19 April 2023

As a postdoc Alex Almeida used bioinformatics to push the boundaries of what we know about the gut microbiome. Here, Almeida explains how his time at EMBL-EBI generated new research avenues, and how the skills and connections from his postdoc prepared him for leading his own research group at the…
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
people-perspectivesperspectives
17 March 2023

EMBL-EBI's metagenomics data resource increases in size and supports groundbreaking AI tools for protein structure prediction.
2023
updates-from-data-resources
11 January 2023

Rob Finn, one of the co-chairs of the Microbial Ecosystems theme, discusses his work, the challenges of multidisciplinary research, and how the theme is already helping to promote the exchange of scientific ideas.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
11 October 2022
EMBL-EBI’s MGnify data resource helps researchers find enzymes for novel applications.
2022
announcementsscience
15 September 2022

EMBL researchers used data from over 300 human faecal microbiota transplants to gain an ecological understanding of what happens when two gut microbiomes clash.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
4 January 2022
Researchers have identified hundreds of new bacterial species and viruses in the human skin microbiome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
15 December 2021

Bork Group at EMBL Heidelberg analysed a new global gene database to study how genes emerge and spread across various habitats on our planet. In the future, the group will expand the database and use it for studying microbial gene evolution and dispersal at a finer-grained scale.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
8 December 2021
Researchers studying a massive cohort of European patients have found that commonly prescribed drugs for cardiometabolic disorders can have long-term effects on the gut microbiome. Such effects can complicate the understanding of how disease affects the microbiome and must be taken into…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
26 October 2021
Using metagenomic data to find novel enzymes for plastic degradation and beyond
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
16 June 2021

Researchers investigate how external factors can influence the persistence of microbe species in the human gut
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
16 April 2021

Researchers have used a metagenomics approach to piece together the genomes of yeasts found in wild lichens.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
18 February 2021
Scientists identify more than 140 000 virus species in the human gut; more than half have never been seen before
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
19 January 2021

Freshwater sports can cause waterborne infections, but real-time DNA sequencing could help.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
23 November 2020
Microbiomes, plastics, and connectivity – AtlantECO aims to understand the fabric of the Atlantic Ocean.
CONNECTIONS
20 July 2020
An international team of scientists has collated all known bacterial genomes from the human gut microbiome into a single large database. Their work will allow researchers to explore the links between bacterial genes and proteins, and their effects on human health.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
26 February 2019
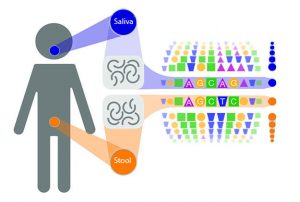
Many microbes traverse the oral-gut barrier
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
27 September 2018

Meet the organisers of EMBO’s first course on molecular geobiology
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
eventsscience-technology
1 August 2018
First global survey of soil genomics reveals a war between fungi and bacteria
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
22 May 2016

What's a microbiome? How on Earth do they work?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
21 June 2014

Data from first ever worldwide Ocean Sampling Day will be shared via EMBL-EBI resources this autumn.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
4 March 2010
The thousands of bacteria, fungi and other microbes that live in our gut are essential contributors to our good health. They break down toxins, manufacture some vitamins and essential amino acids, and form a barrier against invaders. A study published today in Nature shows that, at 3.3 million,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
16 October 2008
Today at a meeting organised by the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, scientists from around the globe announced the formation of the International Human Microbiome Consortium (IHMC), an effort that will enable researchers to characterise the relationship of the…
LAB MATTERS
30 July 2007
The UniProt Consortium, which includes the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), has added a new database repository for metagenomic and environmental data to its family of protein sequence databases. Metagenomics is the large-scale genomic…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
2 February 2007
Microorganisms make up more than a third of the Earth’s biomass. They are found in water, on land and even in our bodies, recycling nutrients, influencing the planet’s climate or causing diseases. Still, we know surprisingly little about the smallest beings that colonise Earth. A new…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
No results found























