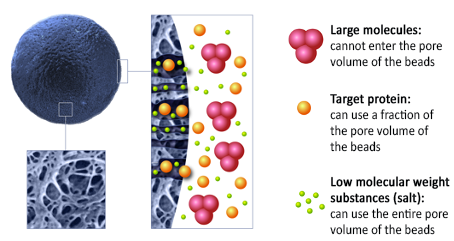
The aim of size exclusion chromatography (SEC) is to separate proteins based on their differences in size and shape. A porous matrix is used for protein separation. The large molecules (i.e. aggregates) cannot enter the pores of the beads and will therefore elute first from the column. The volume at which these aggregates elute is called the void volume. If your protein of interest elutes in the void volume, it’s most likely aggregated and not suitable for downstream experiments, which means you will need to optimize either the construct design or the expression/purification conditions and parameters. Molecules of intermediate size (i.e. most properly folded target proteins) will be able to use a fraction of the pore volume of the beads and elute at an intermediate volume. Very low molecular weight substances such as salt can use the entire pore volume of the beads and will elute totally at the end.
By calibrating the size exclusion chromatography column with a mixture of proteins of known molecular weight, you can correlate the elution volume with the corresponding molecular weight. This calibration curve can then be used to estimate the molecular weight at which your protein of interest elutes, allowing you to assess the oligomerization state of your protein. Please note that as SEC also depends on the shape of the proteins and not only on the size, this estimate is only correct for globular proteins. Generally, SEC coupled to multi-angle light scattering is the most optimal technique if you want to determine the absolute molar mass.
To draw up the calibration curve of a size exclusion chromatography column, the Kav is plotted versus the logarithm of the molecular weight. The Kav can be calculated as follows:
Kav = (Ve – Vo)/(Vt – Vo) with Ve the specific elution volume, Vo the void volume and Vt the total volume of the column.
The different SEC columns we use at EMBL PEPCF are the following:
- Superdex 75 Increase 10/300 GL: analytical SEC column
- Superdex 200 Increase 10/300 GL: analytical SEC column
- Superose 6 Increase 10/300 GL: analytical SEC column
- HiLoad Superdex 75 PG: preparative SEC column
- HiLoad Superdex 200 PG: preparative SEC column
The Superdex 75 columns offer good protein separation in the 3 – 70 kDa range, while the Superdex 200 columns can be used in the 10 – 600 kDa range. The Superose 6 columns offer a broad fractionation in the range from 5 – 5000 kDa. Sephadex G-25 columns can be used for desalting or buffer exchange.
References
Burgess R.R. (2018) A brief practical review of size exclusion chromatography: Rules of thumb, limitations, and troubleshooting. Protein Expression and Purification 150:81-85