21 August 2024
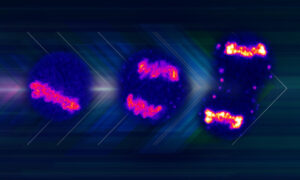
EMBL Heidelberg researchers discovered how a protein switches between repelling and gluing chromosomes during cell division. This helps the mother cell to divide the genome equally into two daughter cells and cluster chromosomes inside the daughter nuclei, ensuring a successful cell division.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
22 May 2024

New research by EMBL scientists shows how different modes of cell division used by animals and fungi might have evolved to support diverse life cycles.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
23 November 2023

Alba Diz-Muñoz and Arnaud Krebs from EMBL Heidelberg have received grants to work on projects that aim, respectively, to understand the cellular mechanics that control cell division and investigate the regulatory networks that govern transcription factor function.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
2 July 2019
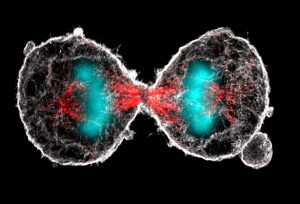
What looks like a pair of scary alien eyes is actually the final stage in the duplication of a cell. Cell duplication is preceded by a process called mitosis, in which the replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Mitosis is the prerequisite for a cell to divide into two identical…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
10 September 2018
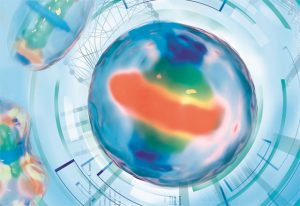
Real-time tracking of proteins during mitosis is now possible using a 4D computer model
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
12 July 2018
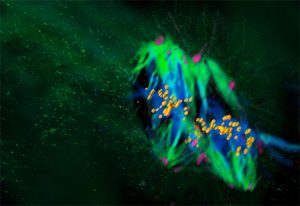
Mammalian life begins differently than we thought
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
26 April 2018
EMBL scientists uncover large solubility and thermal stability changes of proteins during the cell cycle
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
5 July 2012
A traffic policeman standing at a busy intersection directing the flow of vehicles may be a rare sight these days, but a similar scene appears to still frequently play out in our cells. A protein called Lem4 directs a crucial step of cell division by preventing the progress of one molecule while…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
1 April 2010
Name a human gene, and you’ll find a movie online showing you what happens to cells when it is switched off. This is the resource that researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and their collaborators in the Mitocheck consortium are making freely…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
10 June 2007
A human cell contains an enormous 1.8 metres of DNA partitioned into 46 chromosomes. These have to be copied and distributed equally into two daughter cells at every division. Condensation, the shortening of chromosomes, allows the cell to handle such huge amounts of genetic material during cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology







