11 March 2024

Science & Technology
New research from EMBL Heidelberg shows how cells in developing embryos undergo a major shift in the way they regulate gene expression as they mature and differentiate.
2024
sciencescience-technology
4 August 2022
Science & Technology
EMBL and UW researchers plus additional collaborators have constructed a complete map of fruit fly embryonic development using machine learning. This research is foundational to better understanding overall embryo development in other species, including humans.
2022
sciencescience-technology
4 March 2022
Science & Technology
A recent study by EMBL researchers proposes a new method to grow early embryos in the laboratory. With a 3D culture set-up, scientists can closely monitor the changes embryos undergo around the time of implantation.
2022
sciencescience-technology
25 February 2022
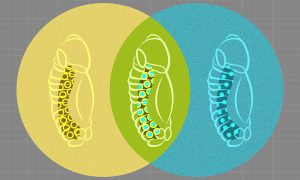
Science & Technology
Researchers from the Furlong group at EMBL have come up with a way to observe the development of fruit-fly embryos simultaneously at the genetic and cellular levels, generating a high-resolution and integrated view of how different cell lineages form.
2022
sciencescience-technology
6 September 2021
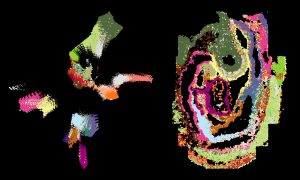
Science & Technology
Researchers have combined spatial gene expression information with single-cell genomics data to create a high-resolution atlas of mouse organogenesis.
2021
sciencescience-technology
30 March 2021

Lab MattersPeople & Perspectives
The new group leader at EMBL Rome will study how embryos can inherit non-genetic information from their parents that causes stable and heritable effects
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
27 January 2021

Lab MattersPeople & Perspectives
New group leader Nicoletta Petridou explains her fascination with the complexity of early embryo development, and how the interdisciplinary nature of EMBL will aid her research.
2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
15 July 2019

Science & Technology
Does rearranging chromosomes affect their function? EMBL scientists reveal uncoupling of 3D chromatin organisation and gene expression.
2019
sciencescience-technology
4 July 2010
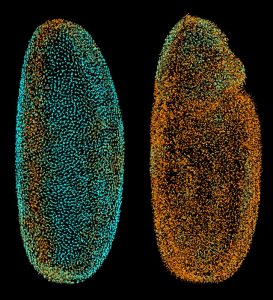
Science & Technology
The scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, who ‘fathered’ the Digital Embryo have now given it wings, creating the Fly Digital Embryo. In work published today in Nature Methods, they were able to capture fruit fly development on film, and were the…
2010
sciencescience-technology
No matching posts found