
Rainer Pepperkok
Director of Scientific Core Facilities and Services
EditExpanding and integrating experimental and data services
In response to the Programme’s scientific themes and new technology developments, EMBL will strengthen and expand its experimental and data services, both individually and through the integration of new complementary services.
EMBL’s scientific services encompass over 40 bioinformatics and data resources and 20 experimental services in structural biology, imaging, genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, in vivo gene editing, and chemical biology. Using a combination of scientific and technical expertise, these services provide researchers with the highest quality results and enable fundamental research essential to helping solve global societal challenges.
As part of the new Programme, EMBL will develop new technologies and increase access to the latest infrastructure and data resources for life science researchers. In turn, this will enable life science researchers to tackle complex questions to understand the mechanisms of life in the context of different environments.
“All of EMBL’s scientific services are dynamic, meaning our user communities’ needs drive the way and speed in which they evolve. Throughout the next Programme, EMBL will strengthen and expand its services, both individually and by integrating new complementary services.”

Director of Scientific Core Facilities and Services
Edit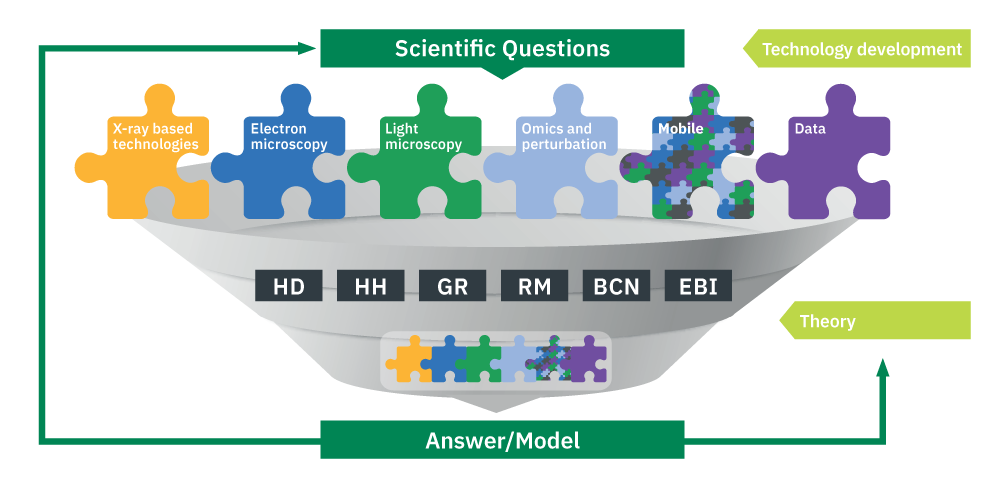
Jan Ellenberg
Head of CBB/ Head of EIC, EMBL Heidelberg
José Márquez
Head of Crystallisation Facility, EMBL Grenoble
Andrew McCarthy
Team Leader, EMBL Grenoble
Johanna McEntyre
Interim Director, EMBL-EBI
Rainer Pepperkok
Director of Scientific Core Facilities and Scientific Services, EMBL Heidelberg
Thomas R. Schneider
Joint Head of Research Infrastructures, Group Leader and Senior Scientist, EMBL Hamburg
EMBL aims to launch a new mobile laboratory service which will offer cutting-edge technology, such as advanced imaging, complex molecular profiling, and advanced data management, integration, and analysis. These mobile services will offer technologies for sampling and measurement, and will support time-series observational and other projects by scientific partners. Technologies will be set up in dedicated sampling vehicles and standardised containers to serve and support teams sampling ocean, coastal, and terrestrial regions and allow field experimentation. This service will help to establish shared, standardised local experimental platforms, coupled with global data storage, handling, analysis, and modelling workflows. As well as research and services, the mobile labs will also train and engage with scientists, students, and the public.

Director of Scientific Core Facilities and Services
Edit
Team Leader and Head of Electron Microscopy Core Facility
Edit
EMBL’s structural biology services offer a range of approaches and infrastructure to support the external research community. For example, current and planned fourth-generation synchrotron beams will offer substantial increases in beam brilliance, intensity, and coherence. Additionally, EMBL will offer time-resolved beamline measurements of dynamic processes inside macromolecules as well as X-ray holographic nanotomography for mapping atomic-level detail in large biological samples.

Interim Head of EMBL Hamburg
Edit
Head of Crystallisation Facility
Edit
The EMBL Imaging Centre is a hub of the most advanced microscopy technologies available to the international scientific user community. These technologies include electron and light microscopy technologies covering all scales, from the highest resolution cryo-EM to the latest intravital light microscopy technologies. The EMBL Imaging Centre will introduce the latest pre-commercial imaging technologies to groundbreaking life science applications.

Head of CBB/ Head of EIC
EditKnown worldwide for its commitment to expanding data access, EMBL-EBI will continue to store and make openly available world-wide biological data. With partners from around the world, EMBL will increase data sharing, reuse, and coordination of bioinformatics resources and tools across molecular biology, particularly for bioimaging, genomic medicine, and multi-omics data resources. EMBL will also help develop biology-specific data portals, enabling scientists to drill down to the scale and level of complexity needed for their research.

Interim Director, EMBL-EBI
Edit
EMBL’s core facilities ensure users gain access to infrastructure, expertise, and quality assurance. EMBL’s core facilities will continue to grow their multi-omics services, combining new techniques with world-class imaging technologies. Additionally, robotics will push forward microbial ecosystem research via new services, such as a culturomics core facility.

Head of Molecular Systems Biology
Edit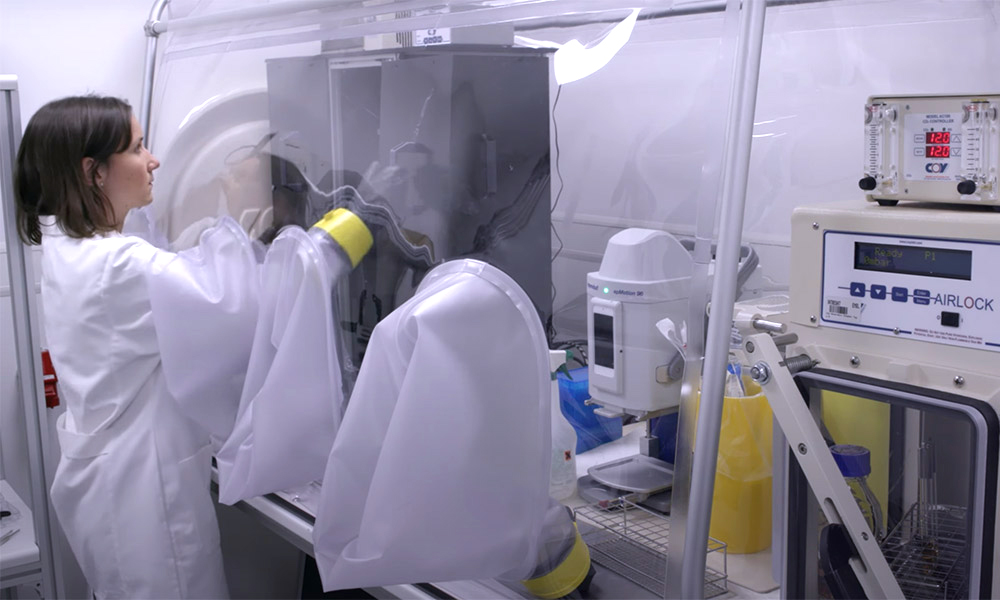
Advancing molecular biology research to study life in context.
Unravelling genetic and environmental influences in biomes and ecosystems to understand biological processes and improve planetary health.
Learn more about the technologies referred to in the EMBL Programme (pdf).
EMBL provides life science researchers in Europe and beyond with access to the very latest in scientific technologies, infrastructure, and data resources.
The EMBL IC provides open access for researchers to cutting-edge imaging technologies integrating methods in the field of electron and light microscopy.
EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) develops and maintains numerous community databases, tools, and software that are freely available to all.
EMBL’s vision is to advance understanding of ecosystems at the molecular level and study life in context. The result will be fundamental research that expands what we know about life on earth and provides the means to address major global challenges.
This new Programme will expand EMBL’s scope to study the molecular basis of life in the context of changing environments, transforming our understanding of life on earth and informing potential solutions for some of society’s biggest challenges, such as irreversible loss of biodiversity, antimicrobial resistance, pollution, climate change, food security, and emergent pathogens.
