The AlphaFold Protein Structure Database, a result of a collaborative effort between Google DeepMind and EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), has released an exciting update to its web pages, providing users with an enhanced experience. This update marks a significant step in facilitating the use of AlphaFold structure data.
By working hand in hand with researchers and incorporating their insights, the AlphaFold Database user interfaces and data access tools have been substantially improved. The AlphaFold Database team aims to:
- make use of protein structures more intuitive, inclusive and impactful for scientists worldwide
- enable the use of protein structures in fundamental and translational research
- empower scientists worldwide in the use of protein structures by developing intuitive and efficient tools
The latest upgrades come following comprehensive user research incorporating valuable insights gained from interviews, feedback emails, and other forms of communication.
For more information about the updated AlphaFold Protein Structure Database, visit the website.
Improved results filtering in the AlphaFold Database
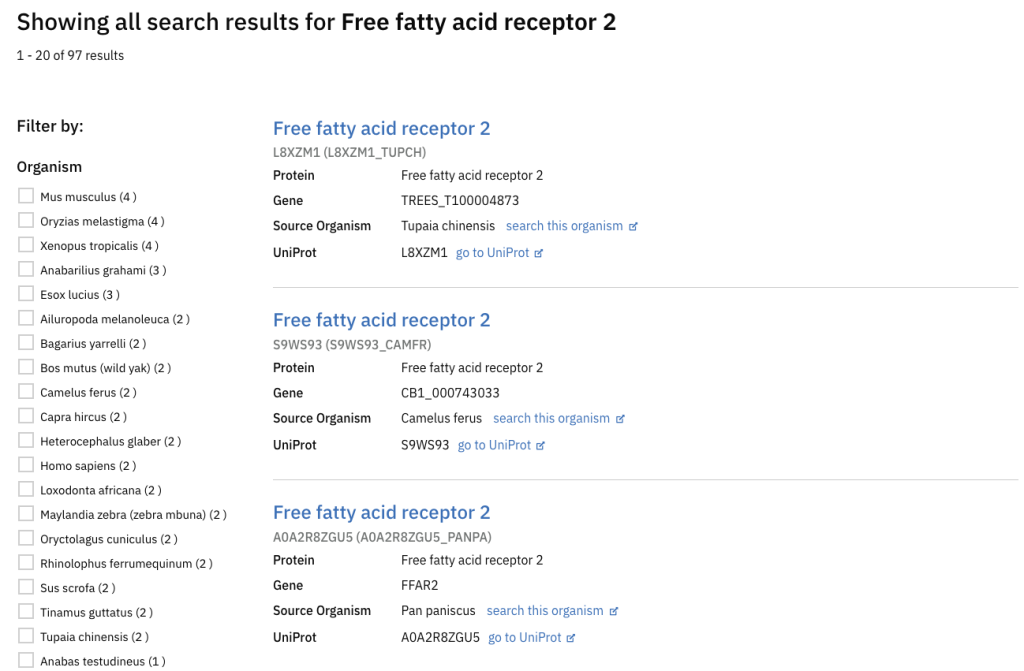
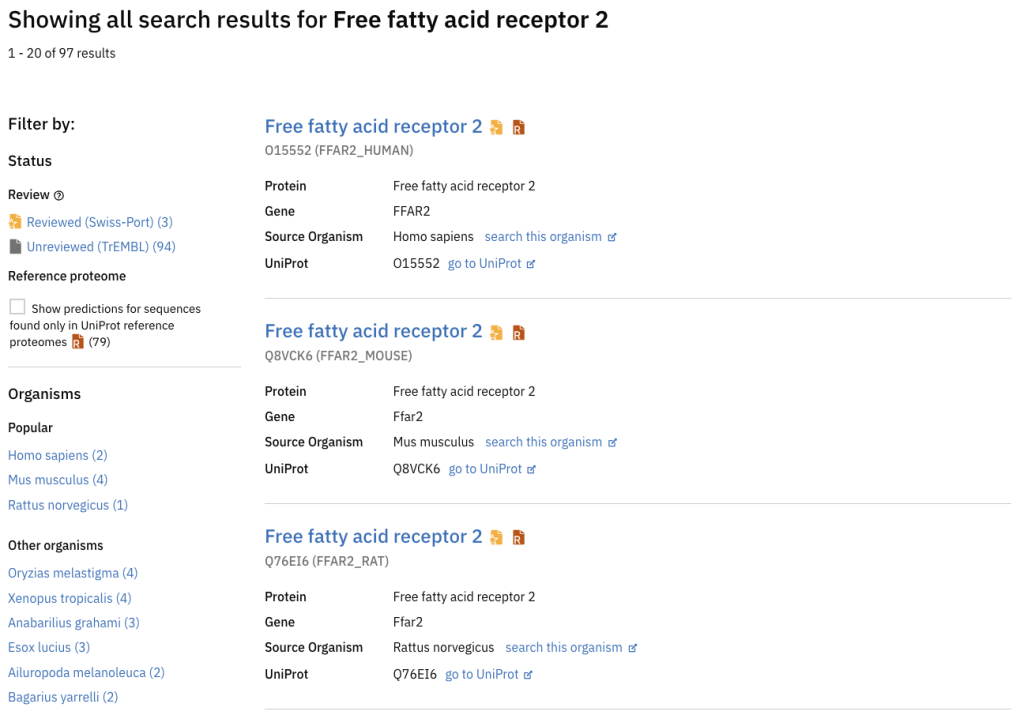
The updated AlphaFold Database introduces an improved search filter system offering users enhanced functionality, such as applying filters to distinguish between reviewed and unreviewed sequences. This information gives users a more comprehensive understanding of whether a predicted structure is derived from a manually annotated and reviewed entry (Swiss-Prot) or a computer-annotated sequence (TrEMBL) from the UniProt database.
A new filter, titled “is in reference proteome”, allows users to narrow their view to predictions within reference proteomes. A filter group for popular organisms has been introduced to enhance the user experience, streamlining the selection for frequently sought-after species or model organisms. Popular species include but are not limited to humans, mice, and Drosophila.
In addition to the added functionality, the overall appearance and usability of the search filters have undergone significant upgrades, ensuring a more user-friendly and intuitive experience for researchers.
Before:
After:
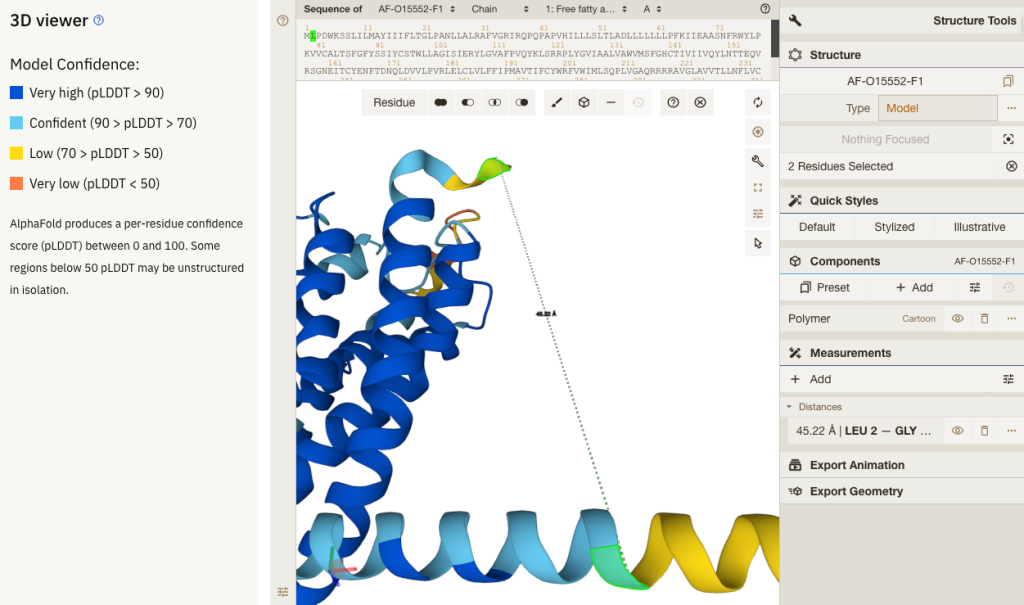
Enhanced customisation for the interactive 3D viewer
A standout feature of this update is the enhancement of the Mol* 3D viewer, which has undergone significant improvements based on user feedback. Users can select atoms, residues, and chains, facilitating focused analysis and exploration. For example, users can perform essential tasks like measuring distances between residue pairs to investigate and analyse protein structures.
Improved predicted aligned error interactivity
The predicted aligned error (PAE) data is an independent confidence metric generated by the AlphaFold algorithm. It informs users about the confidence in the relative orientation of residue pairs. It is frequently used to decide whether the relative orientation of two domains is confidently predicted. The team has improved the interaction between the PAE viewer and the 3D molecular graphics viewer, Mol*, so selecting regions on the off-diagonal part of the PAE heatmap highlights the corresponding regions in the 3D view. This improvement will make the PAE data more accessible, which is vital to correctly interpreting the overall conformation of the predicted structure.
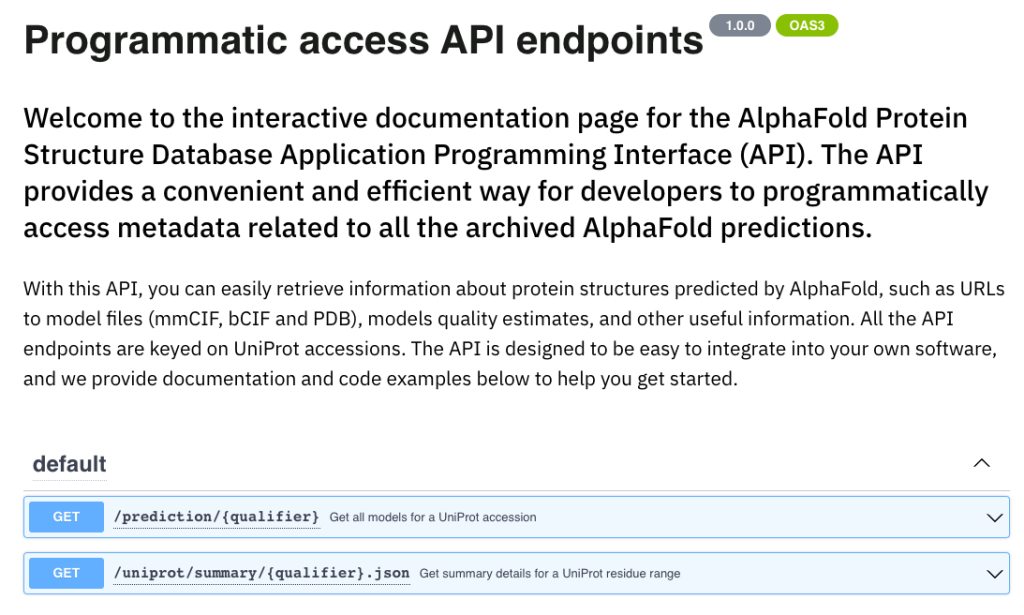
Interactive API documentation
Moreover, the team has introduced an interactive documentation page dedicated to the public API endpoints. This addition offers detailed information on the currently supported API endpoints, keyed on UniProt accessions. Users can now effortlessly retrieve high-throughput data with ease and convenience.